Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Athanazio D. Cystadenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatecystadenoma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign epithelial tumor composed of variably sized cysts lined by bland cuboidal cells
Essential features
- Distinguished from mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the seminal vesicle by the absence of stromal hypercellularity
- Should be distinguished from prostatic stromal tumor of uncertain malignant potential entrapping glands
- Factors that favor seminal vesicle cystadenoma:
- Cystic tumor centered in the seminal vesicle
- No expression of prostatic differentiation markers
- Factors that favor seminal vesicle cystadenoma:
Terminology
- Some authors consider it as the expression of lowest grade (benign) of mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the seminal vesicle (Adv Anat Pathol 2015;22:113)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8440/0 - cystadenoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2F34 & XH5RJ2 - benign neoplasm of male genital organs & cystadenoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare (< 30 described cases)
- Wide age distribution (23 - 66 years old)
Sites
- Centered within seminal vesicles
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Obstructive urinary symptoms
- Some patients present with an asymptomatic mass or the masses are incidentally detected in imaging studies
Diagnosis
- Cystic or solid and cystic masses detected in imaging studies
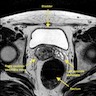
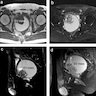
Radiology description
- Cystic or solid and cystic masses centered within the seminal vesicles
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign neoplasm; local resection is considered curative
Case reports
- 31 year old man with an 8.8 cm cystic pelvic mass (Asian J Androl 2013;15:697)
- 48 year old man with a 3.5 cm mass in the right seminal vesicle (J Endourol Case Rep 2015;1:62)
- 49 year old man with a 12.0 cm solid and cystic pelvic mass (Pan Afr Med J 2017;28:149)
- 59 year old man with a 9.8 cm oval cyst between bladder and rectum (Chin Med J (Engl) 2018;131:2897)
- 71 year old man with a 5.5 cm oval cyst between bladder and rectum (Asian J Androl 2017;19:384)
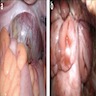
Treatment
- Surgical resection
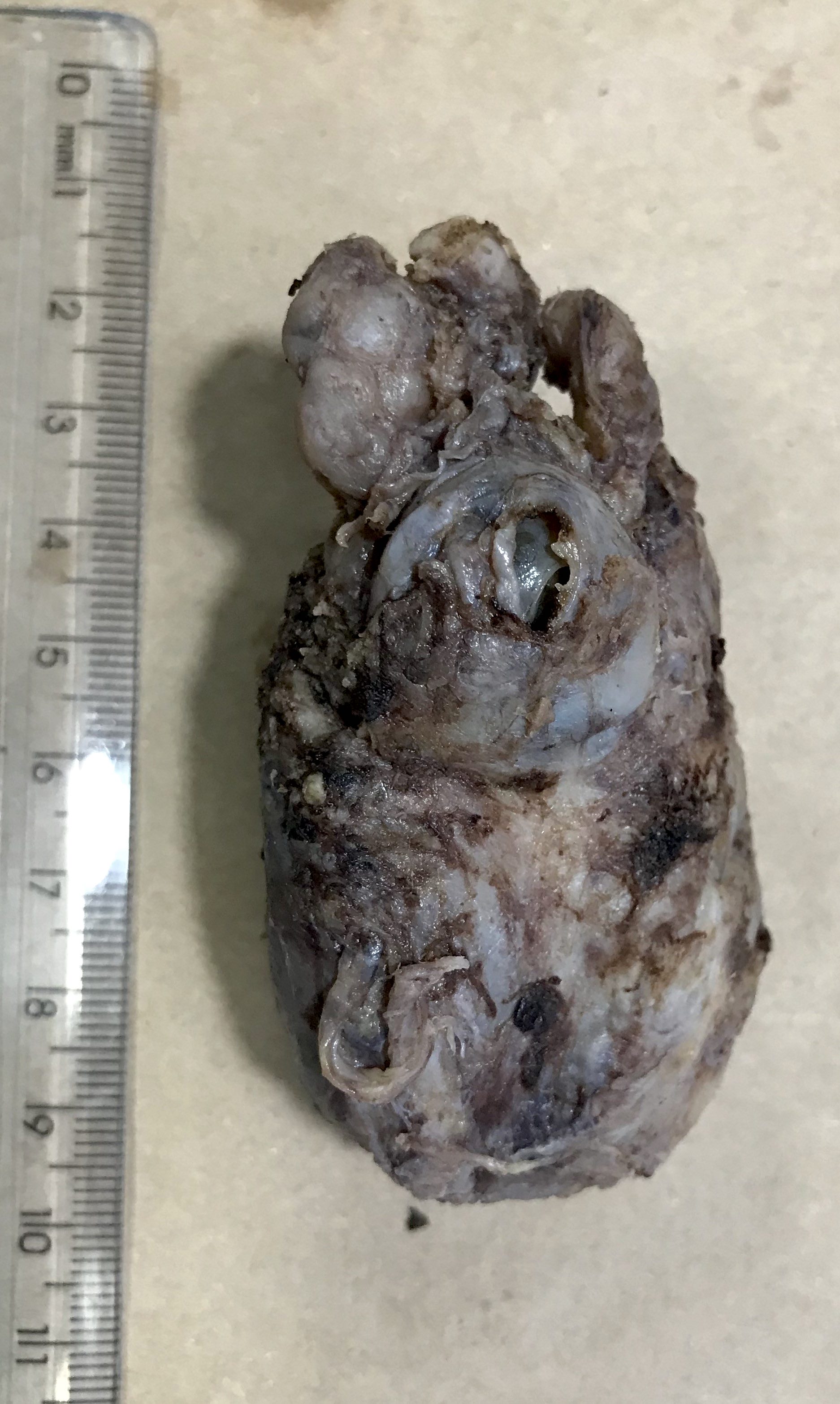
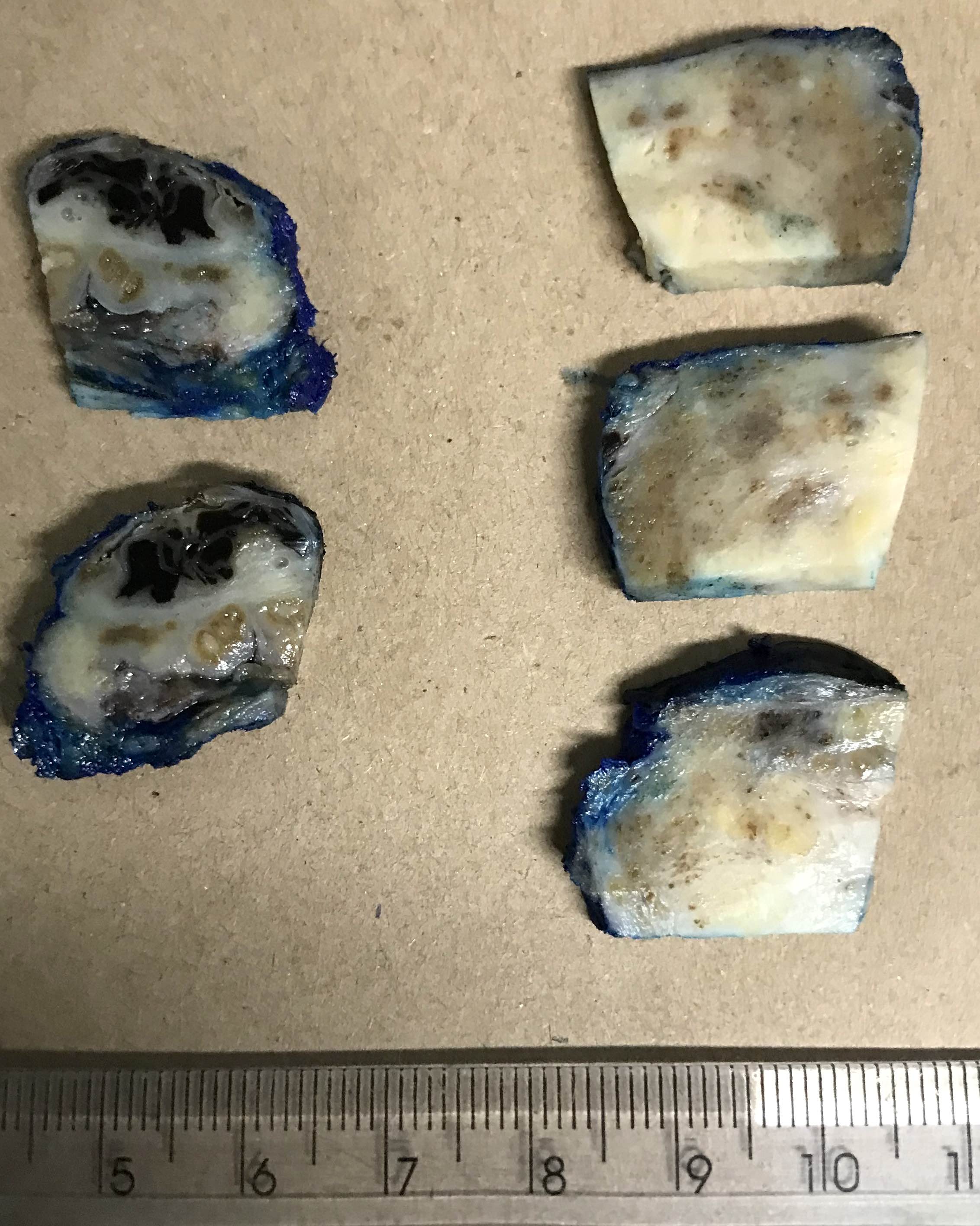
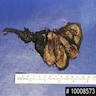
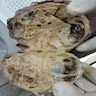
Gross description
- Cystic mass centered in the seminal vesicle with variable solid components
Gross images
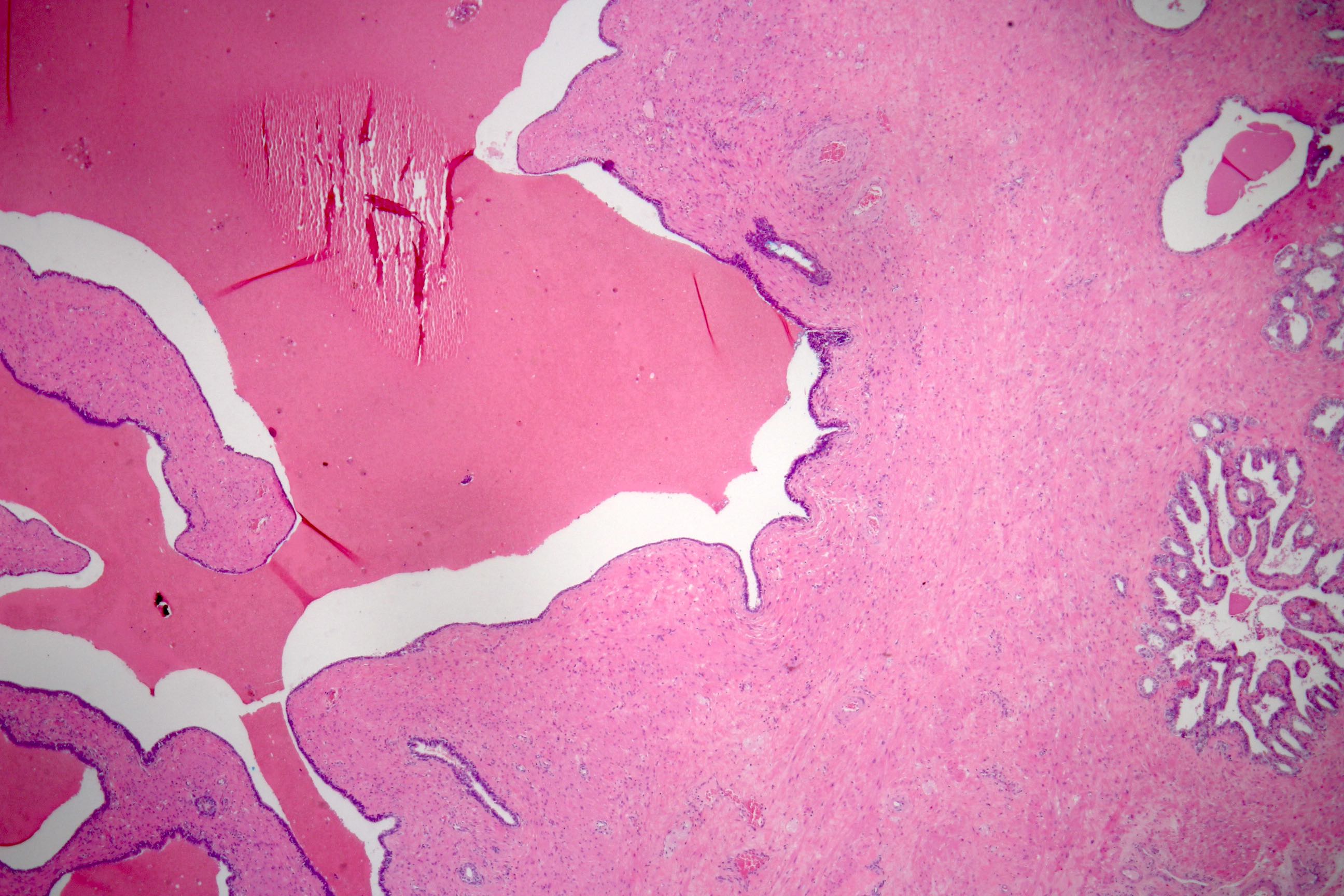
Microscopic (histologic) description
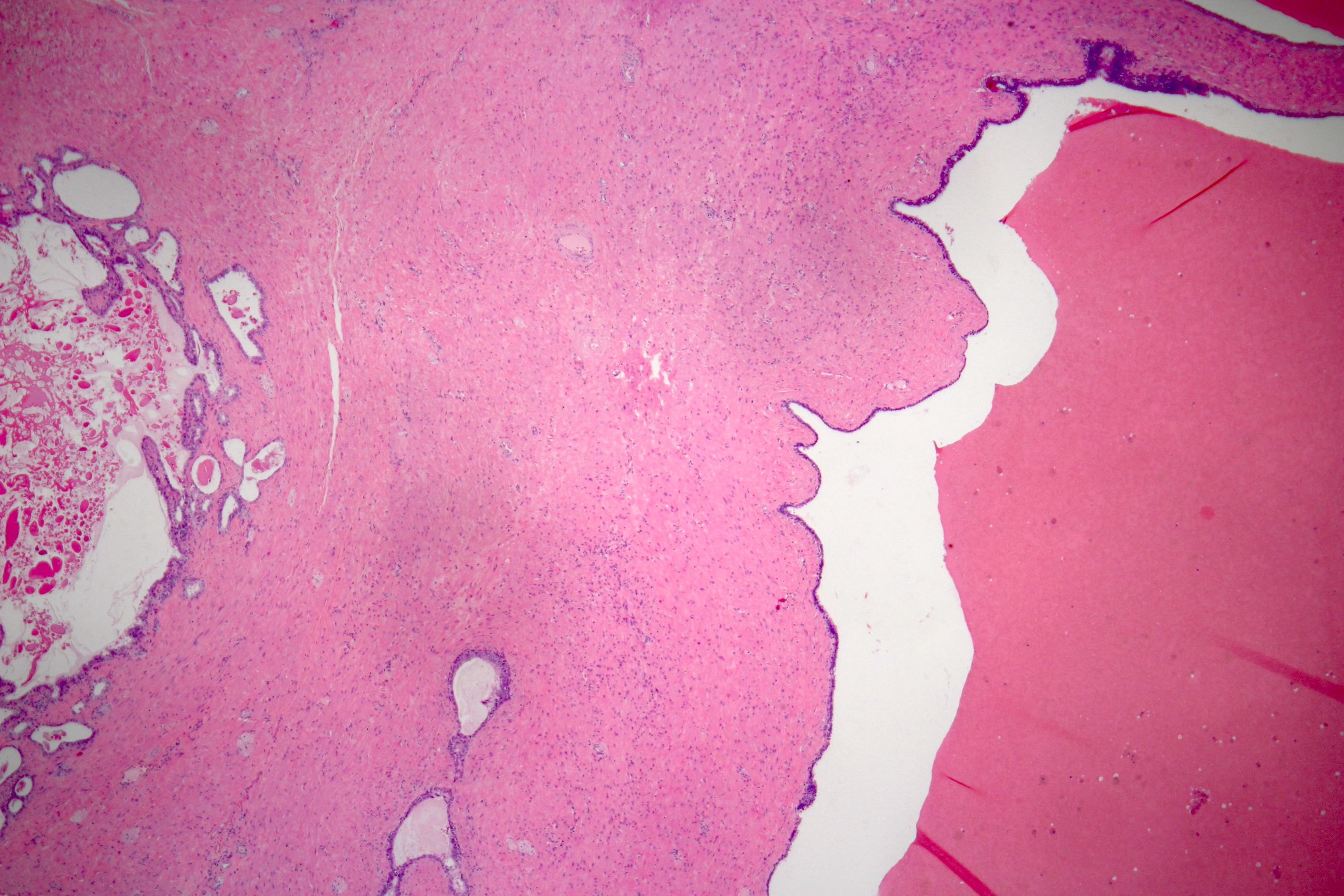
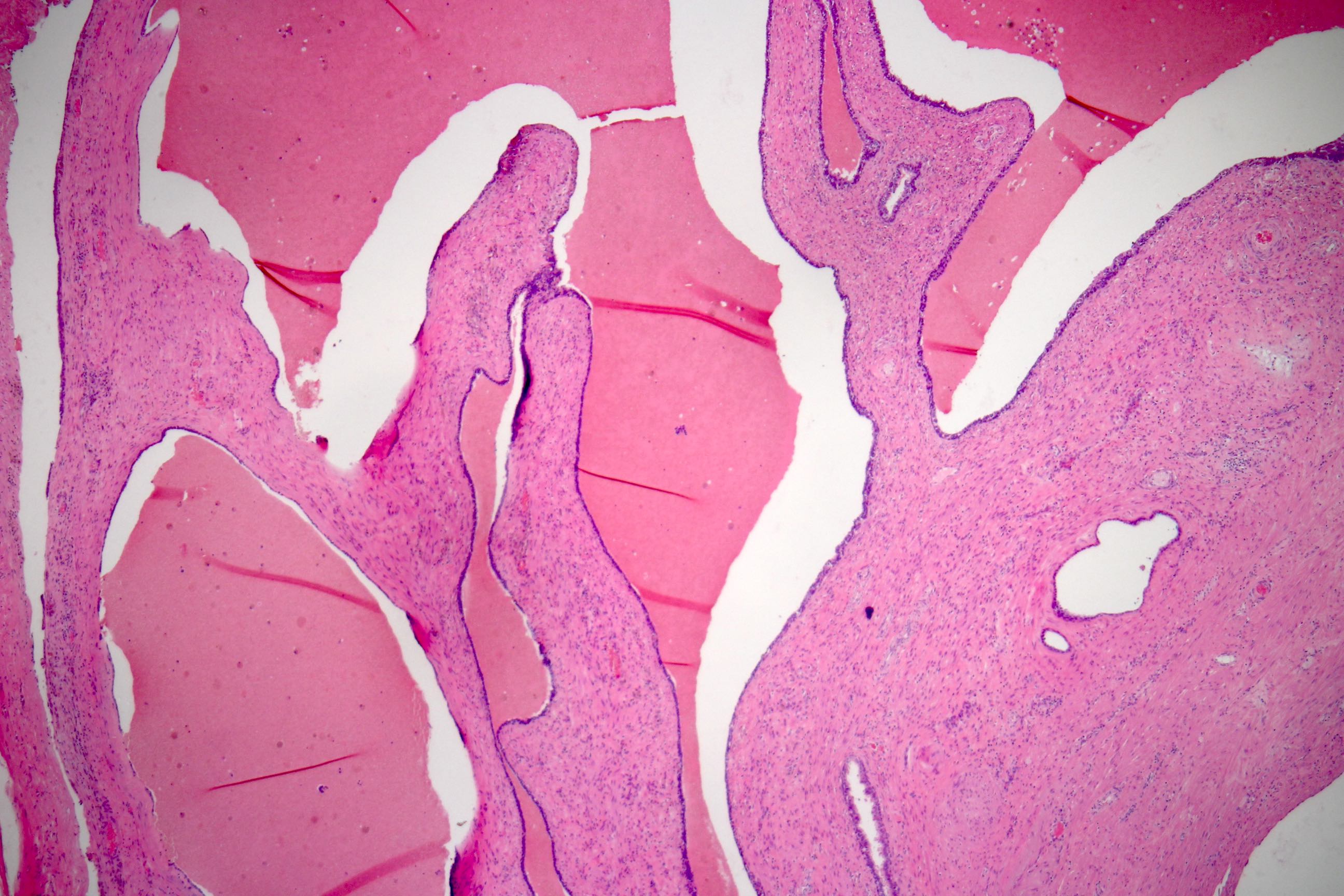
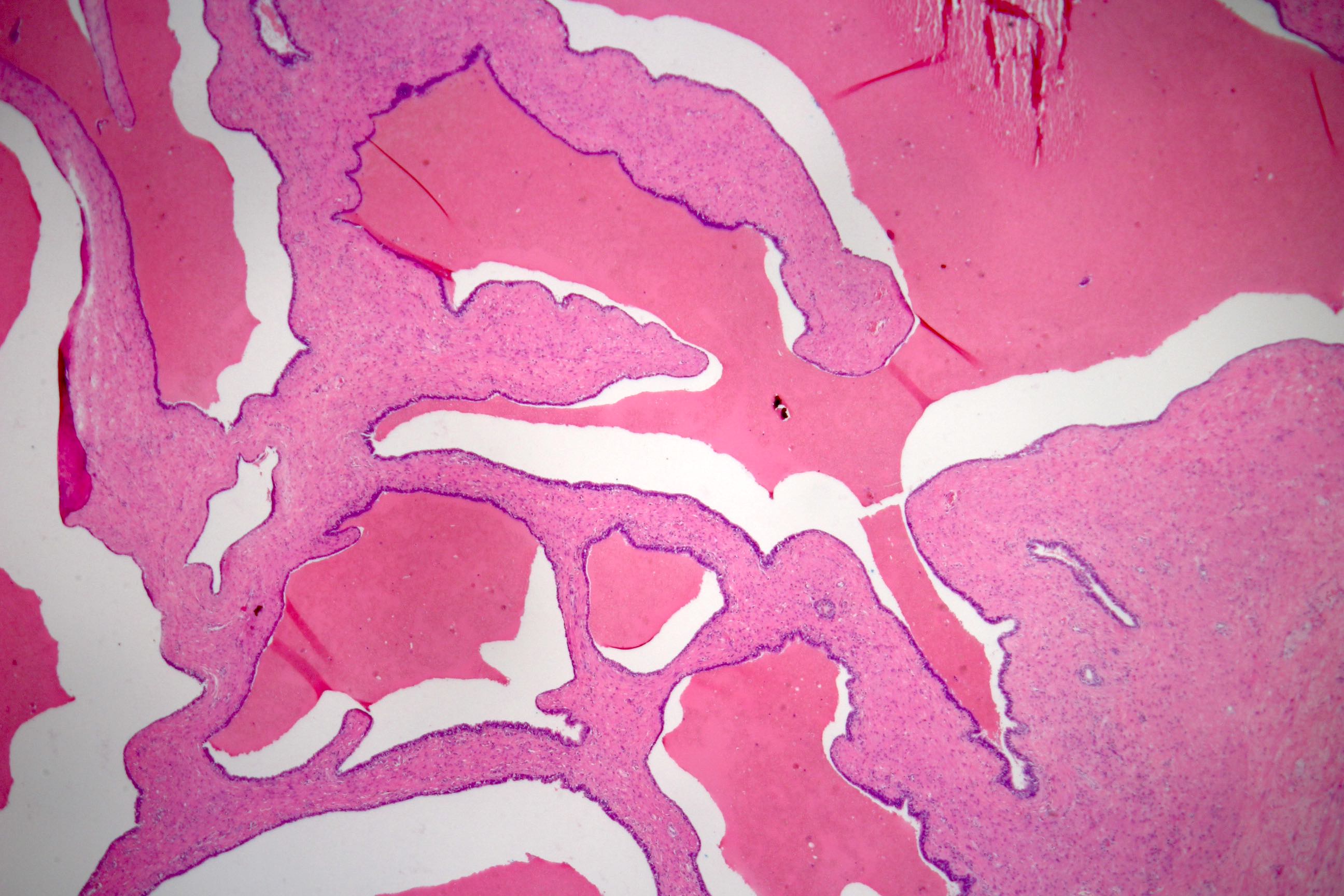
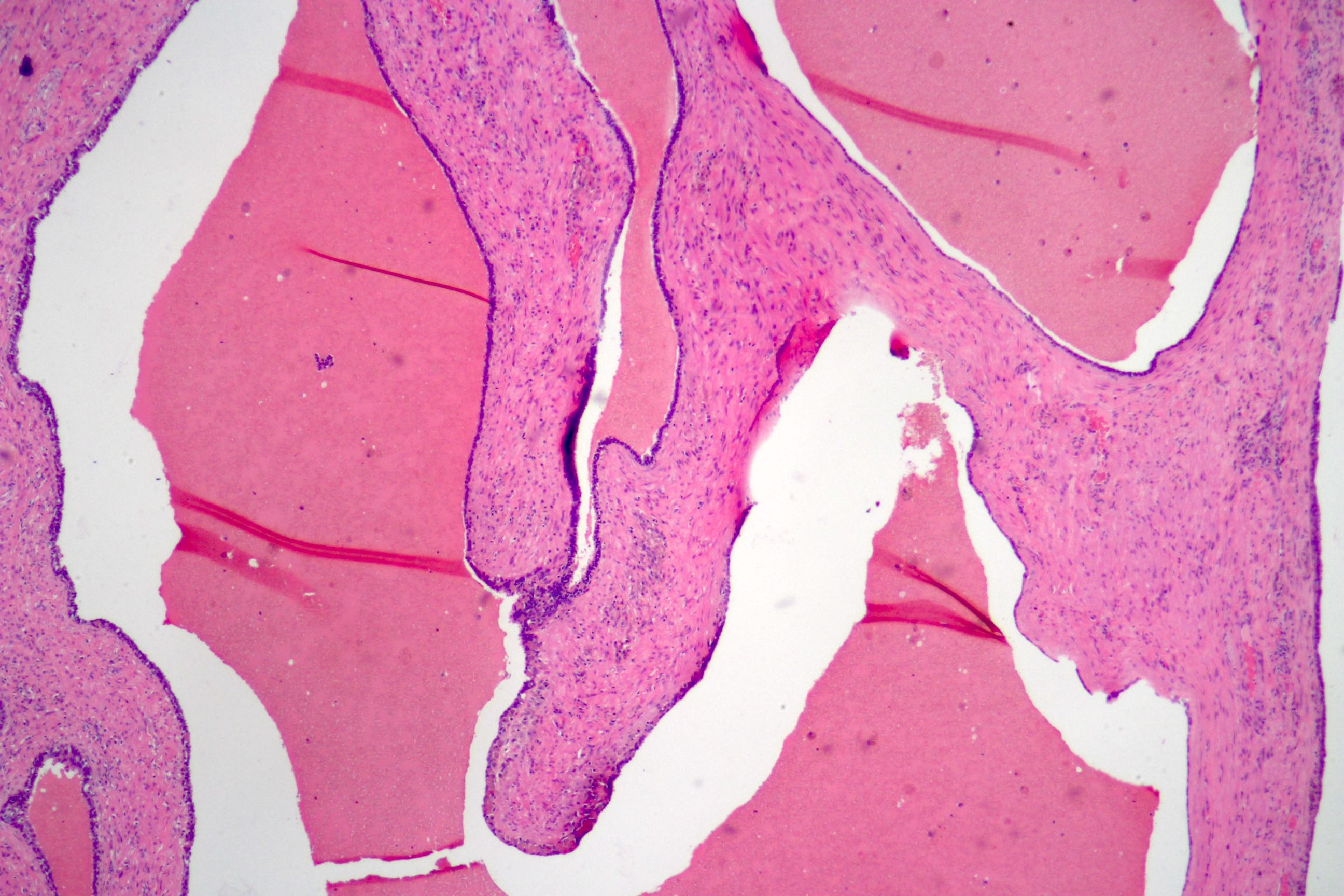
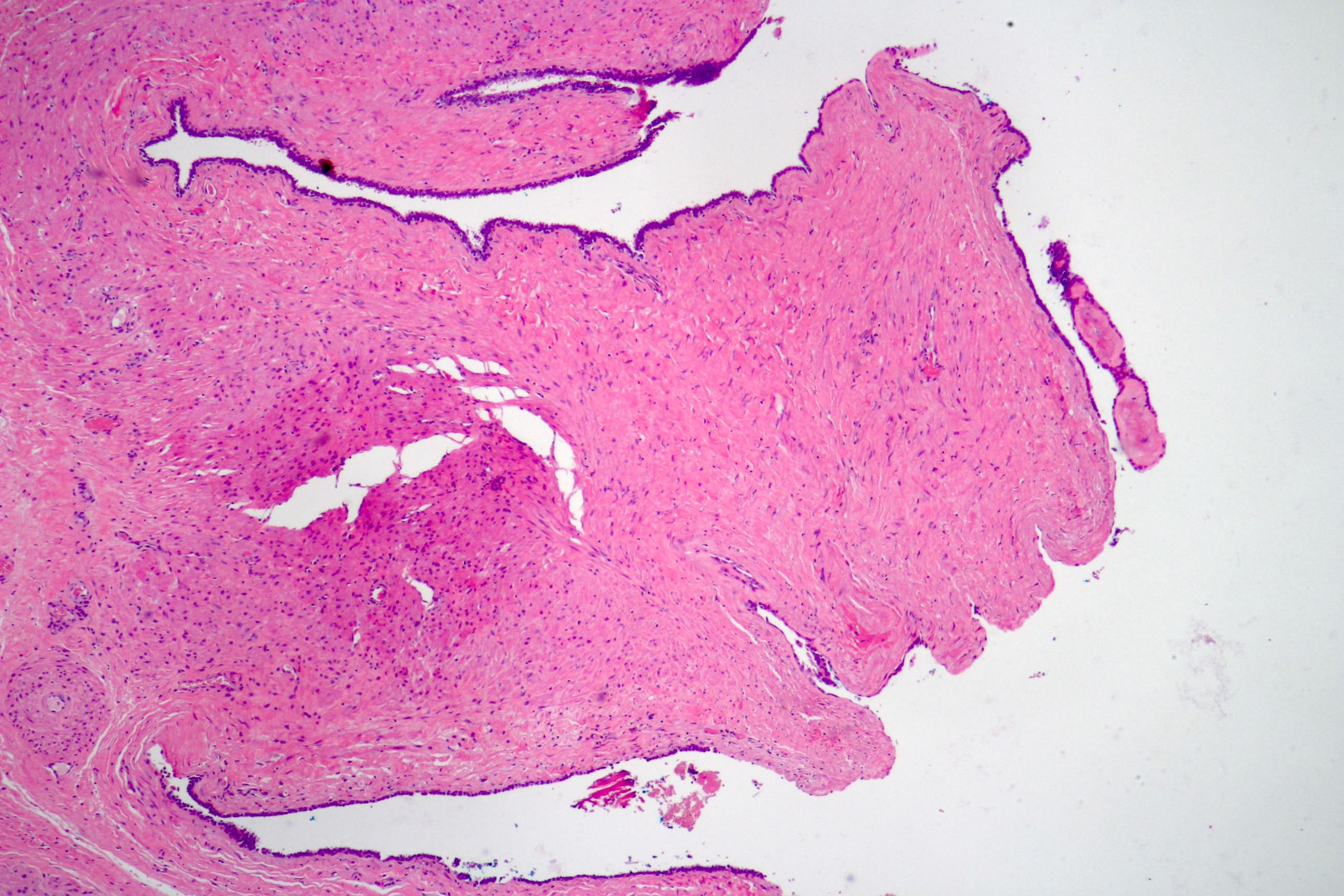
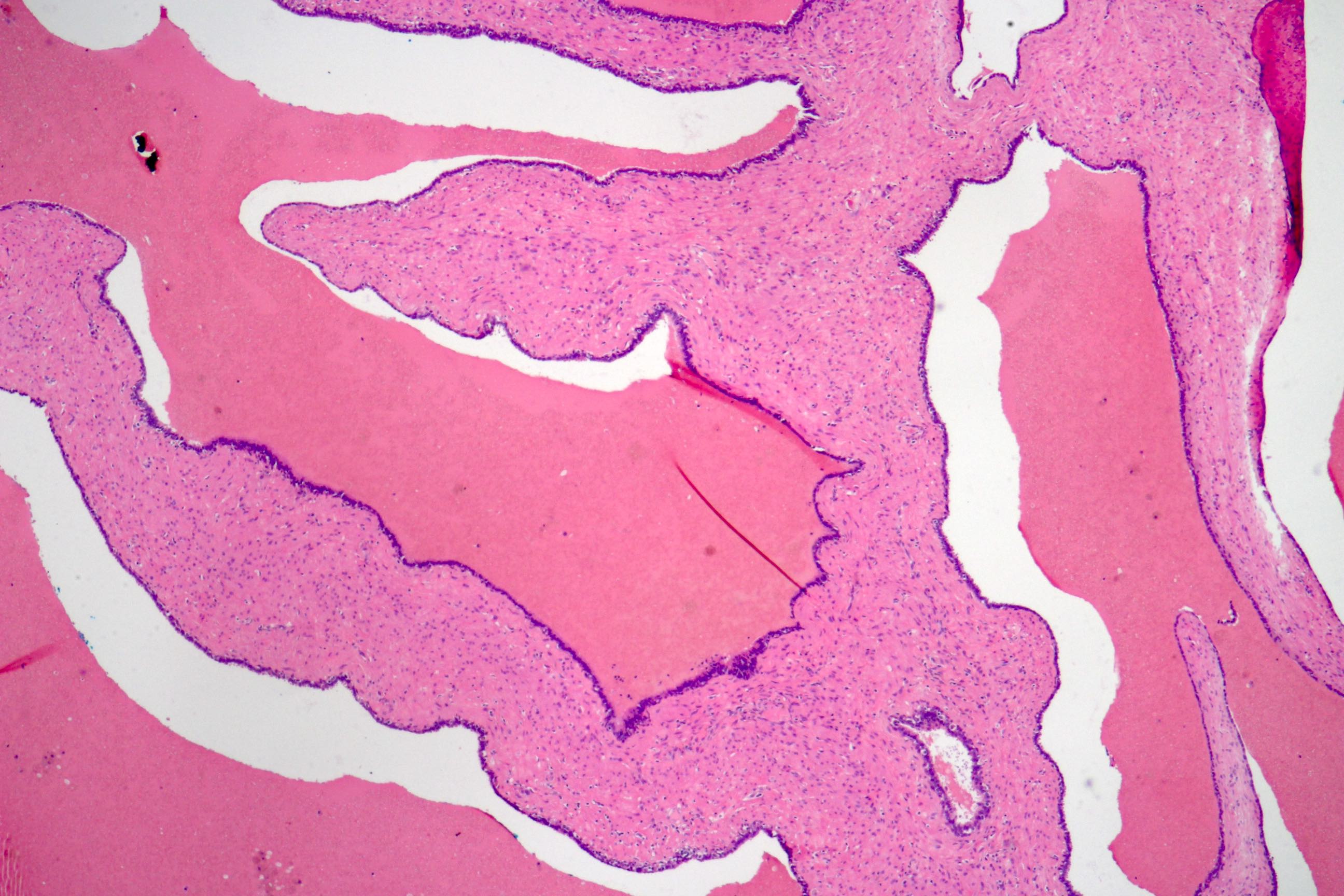
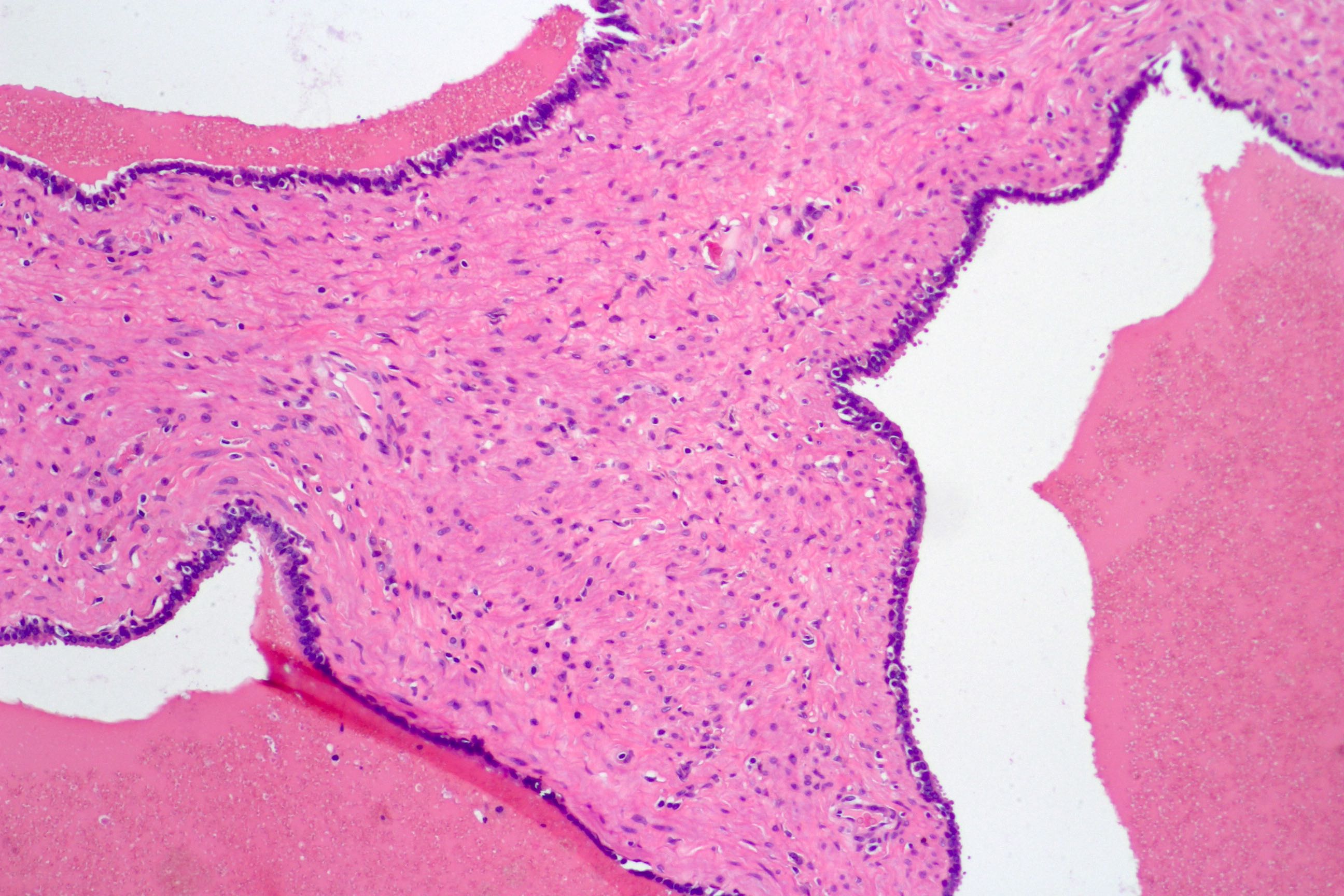
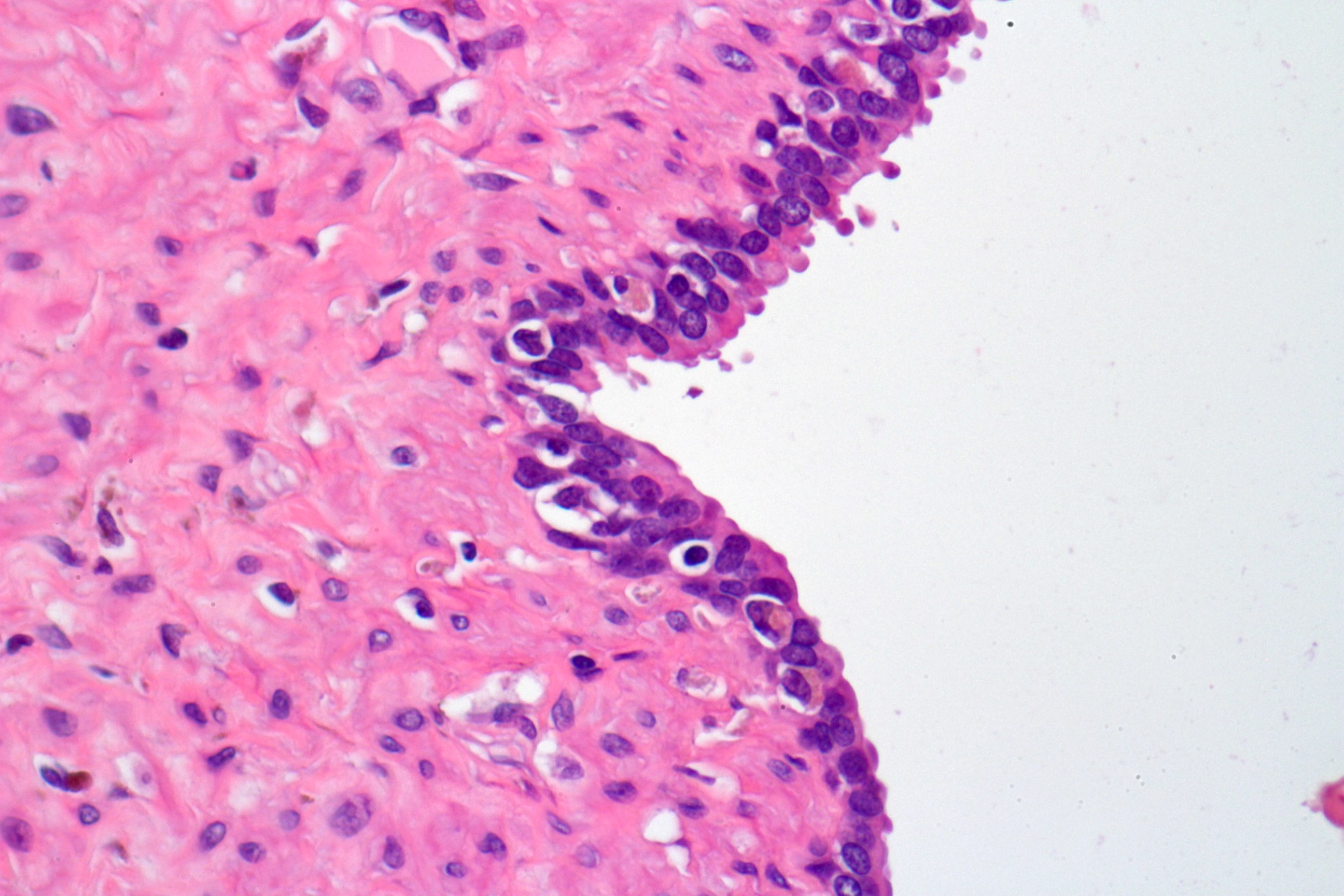
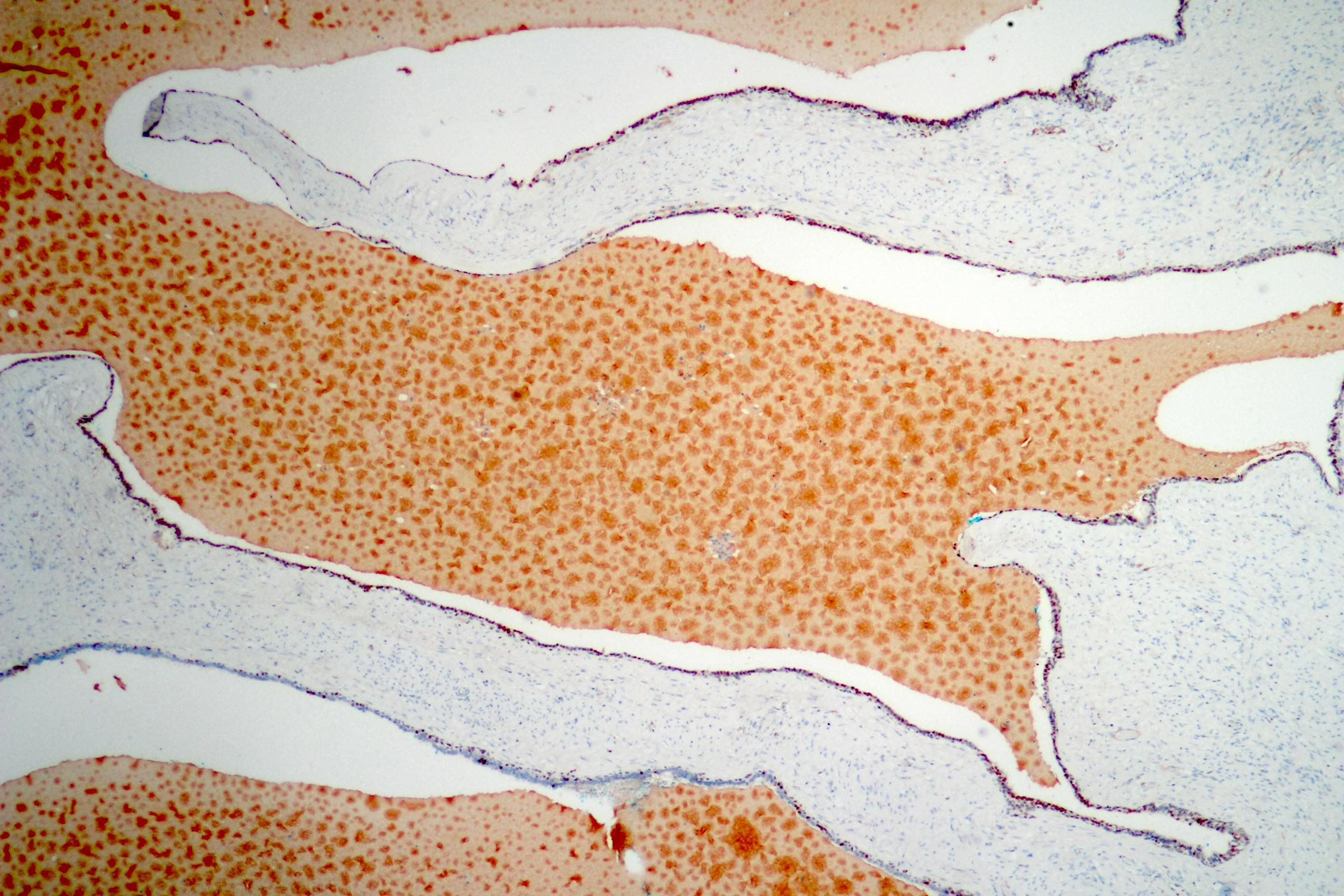
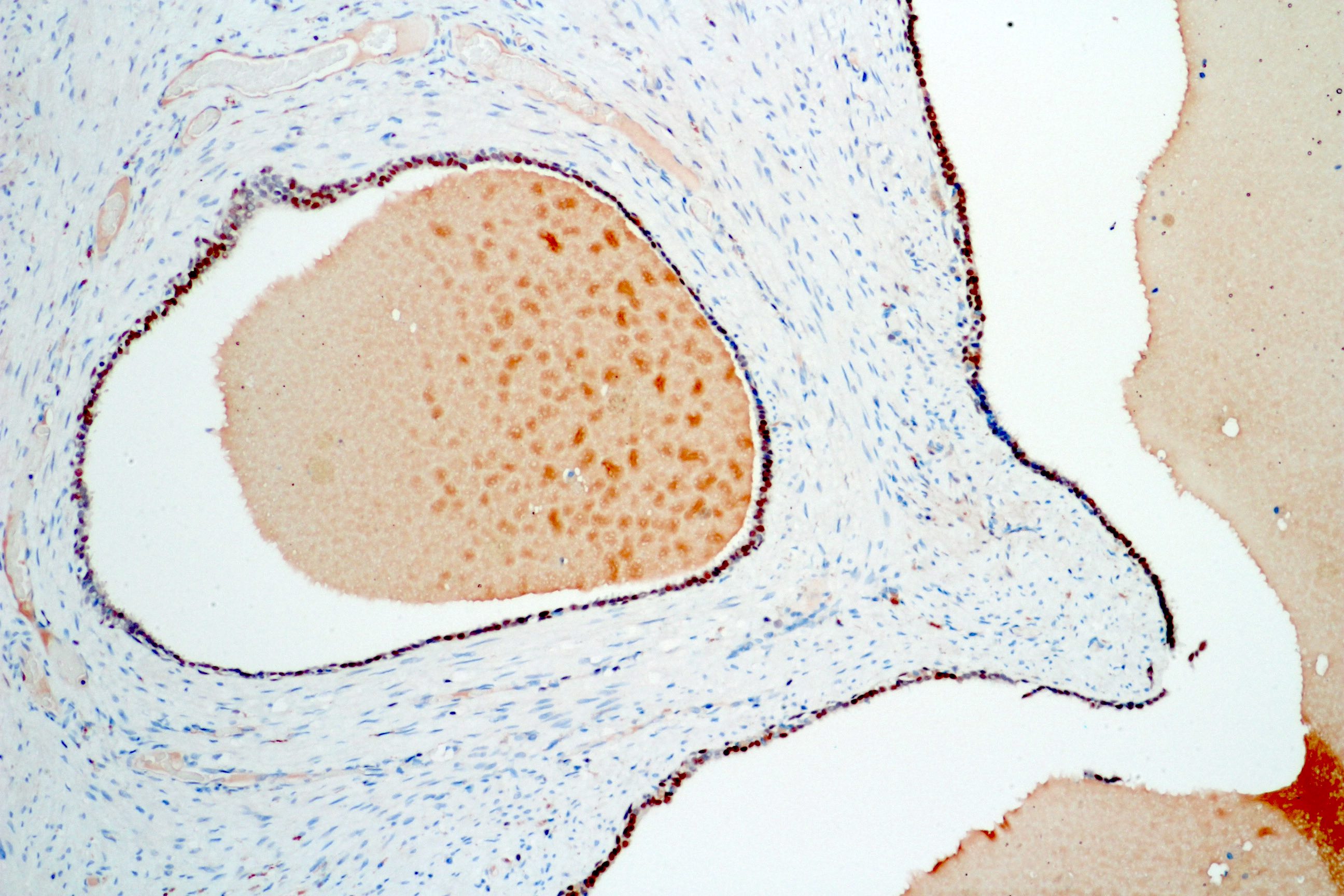
- Glandular spaces of varying sizes are lined by cuboidal cells without atypia (Adv Anat Pathol 2015;22:113)
- Lobular pattern, forming branching lumina and cysts that contain granular intraluminal secretions
- No hypercellularity or atypia in stromal cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Epithelial lining stains for pancytokeratin and CK7
- Basal cells express high weight molecular keratins
- Stromal cells may stain for smooth muscle actin
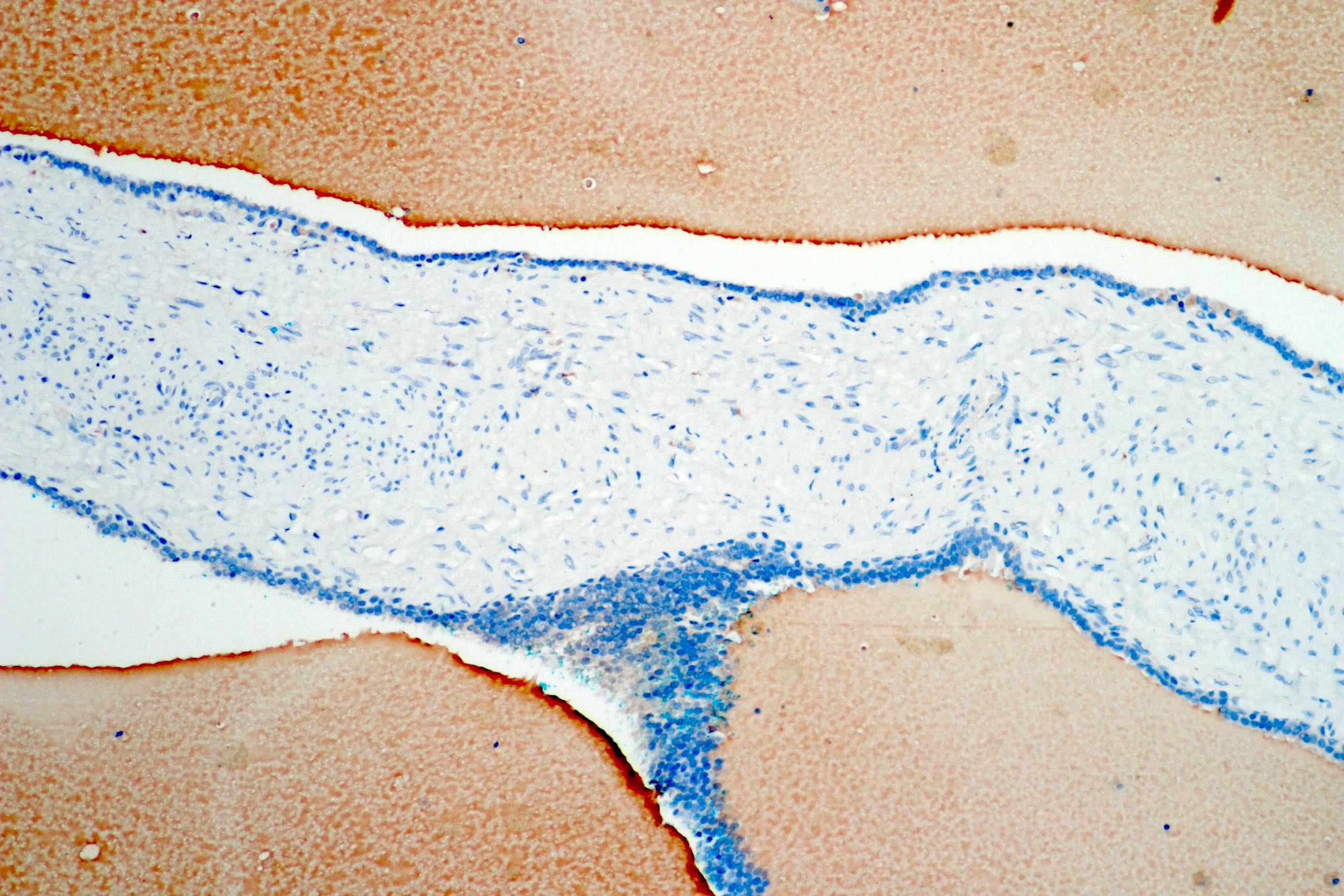
- Normal epithelial lining of a seminal vesicle usually strongly expresses GATA3; however this marker is also positive in the prostate and should be interpreted with caution (Actas Urol Esp 2017;41:577)
- Normal and neoplastic seminal vesicle epithelium is strongly positive for PAX8 (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1837, Hum Pathol 2017;69:123)
Negative stains
- Epithelial cells usually do not express PSA, prostein / P501S or calretinin
- Stromal cells are negative for S100
Sample pathology report
- Prostate and seminal vesicles, radical prostatectomy:
- Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle (see comment)
- Comment: This is a benign neoplasia. Surgical resection is considered curative.
Differential diagnosis
- Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the seminal vesicle:
- Stromal hypercellularity
- Prostatic stromal tumor of uncertain malignant potential entrapping glands:
- Centered in the prostate, entrapped prostatic glands express PSA and other markers of prostatic differentiation
- Adenomatoid tumor:
- Expresses mesothelial markers such as calretinin
- Mesothelial cysts:
- Express mesothelial markers such as calretinin
- Cystic ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate:
- Pseudostratified and atypical epithelial neoplastic cells
- Primary seminal vesicle carcinoma:
- Atypical cells
- Tumor centered in a seminal vesicle
- Adenocarcinomas usually show papillary glandular and trabecular growth patterns
- Exclusion of other primary sites and immunophenotype excluding primary prostate adenocarcinoma
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What major criterion favors the diagnosis of mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the seminal vesicle over cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle?
- Expression of PSA in epithelial cells
- Expression of smooth muscle actin in stromal cells
- Stromal proliferation and hypercellularity
- Tumor grossly centered in the seminal vesicle
Board review style answer #1
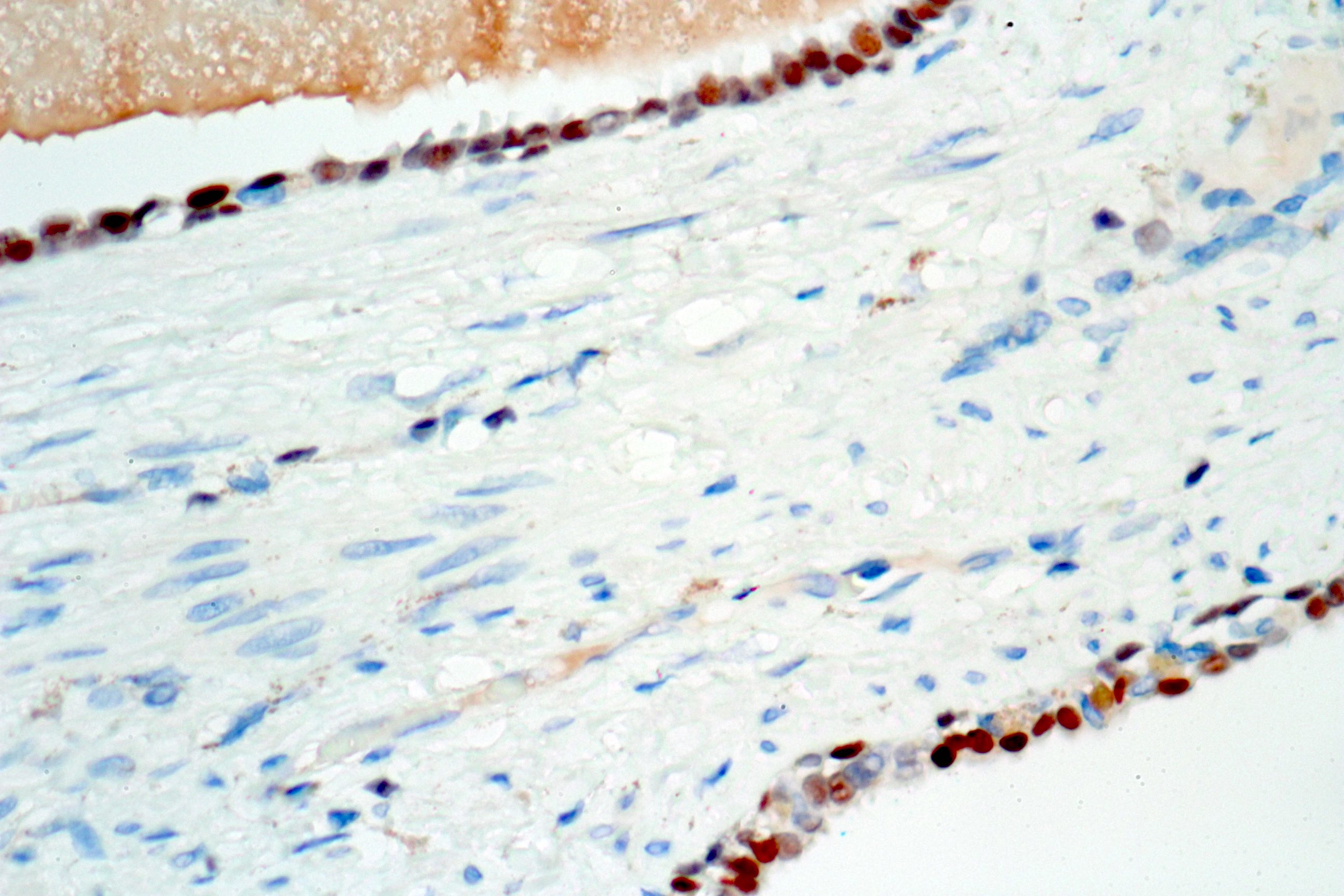
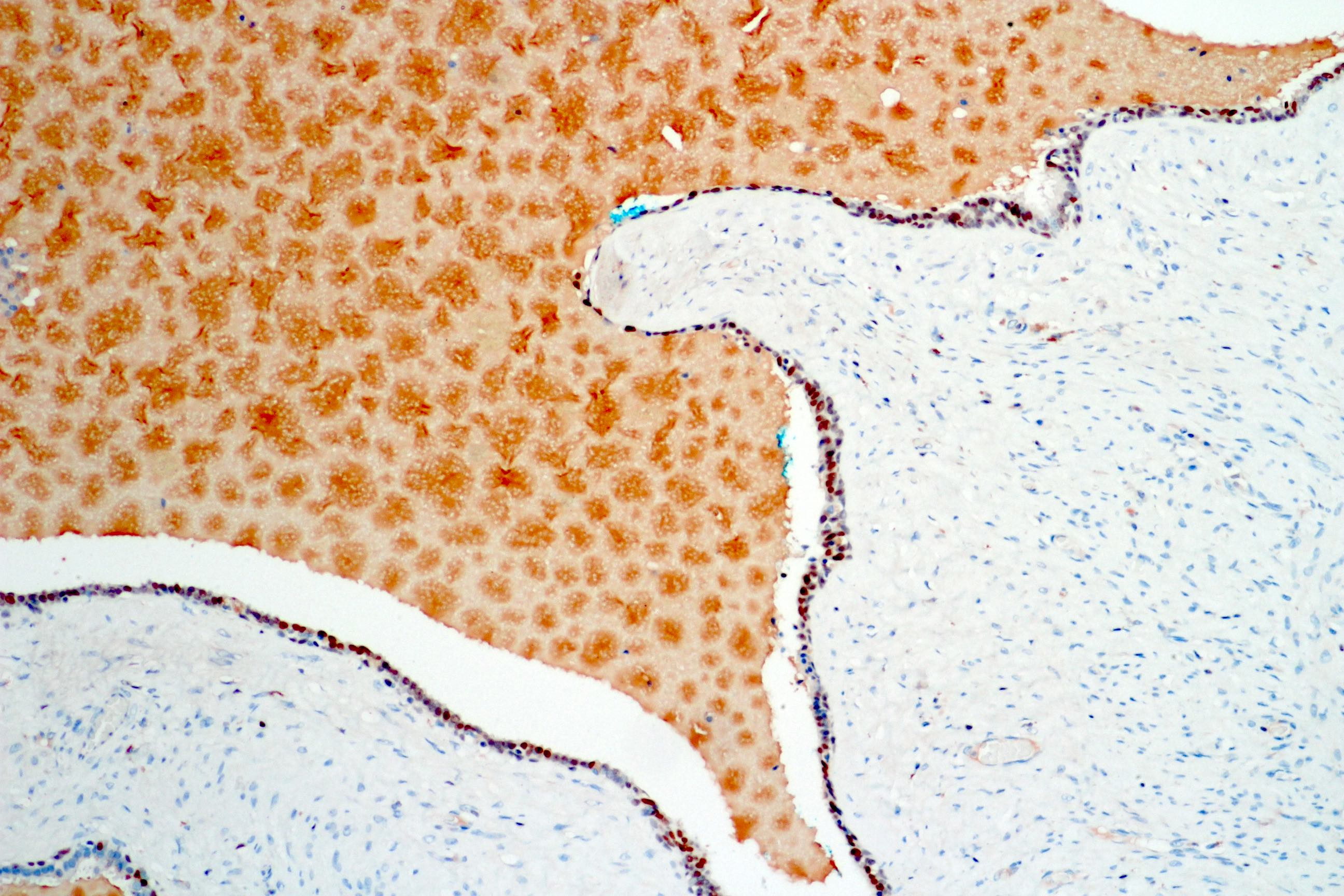
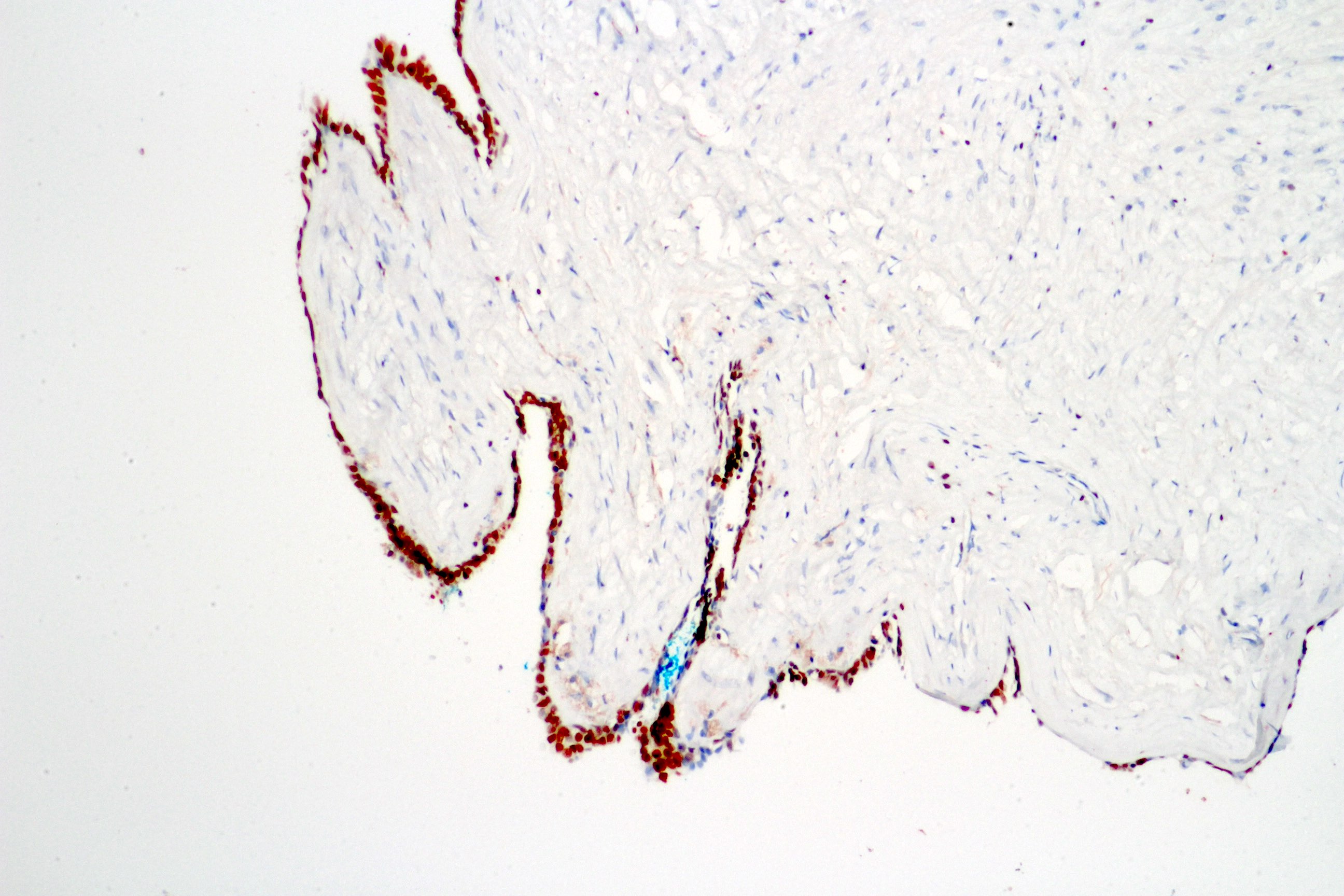
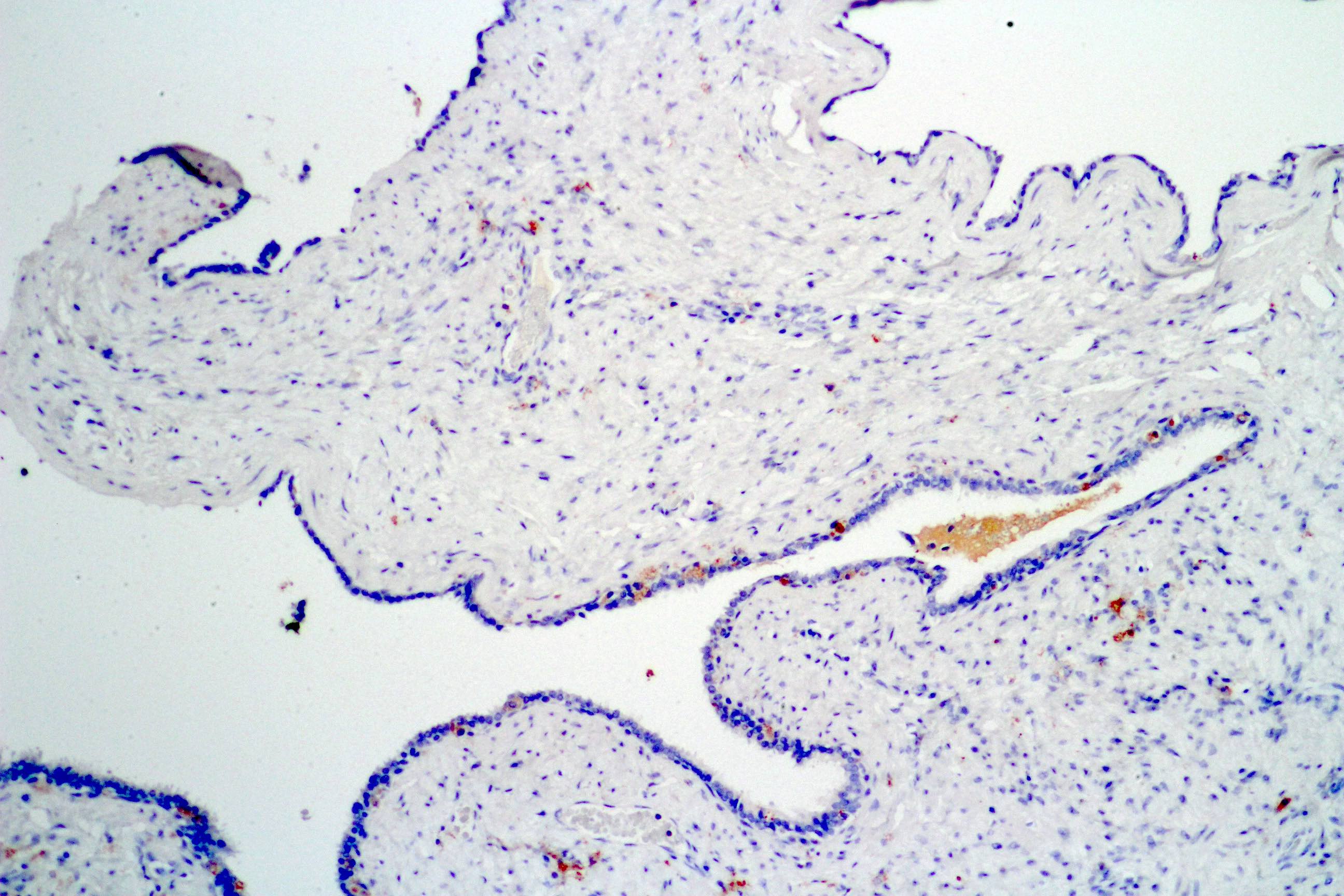
C. Stromal proliferation and hypercellularity. Seminal vesicle cystadenoma shows no stromal hypercellularity (image shown above).
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Board review style question #2
Which feature of immunohistochemistry favors the diagnosis of benign mesothelial cysts over cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle?
- Expression of calretinin in epithelial cells
- Expression of GATA3 in epithelial cells
- Expression of pankeratins in epithelial cells
- Expression of smooth muscle actin in stromal cells
Board review style answer #2
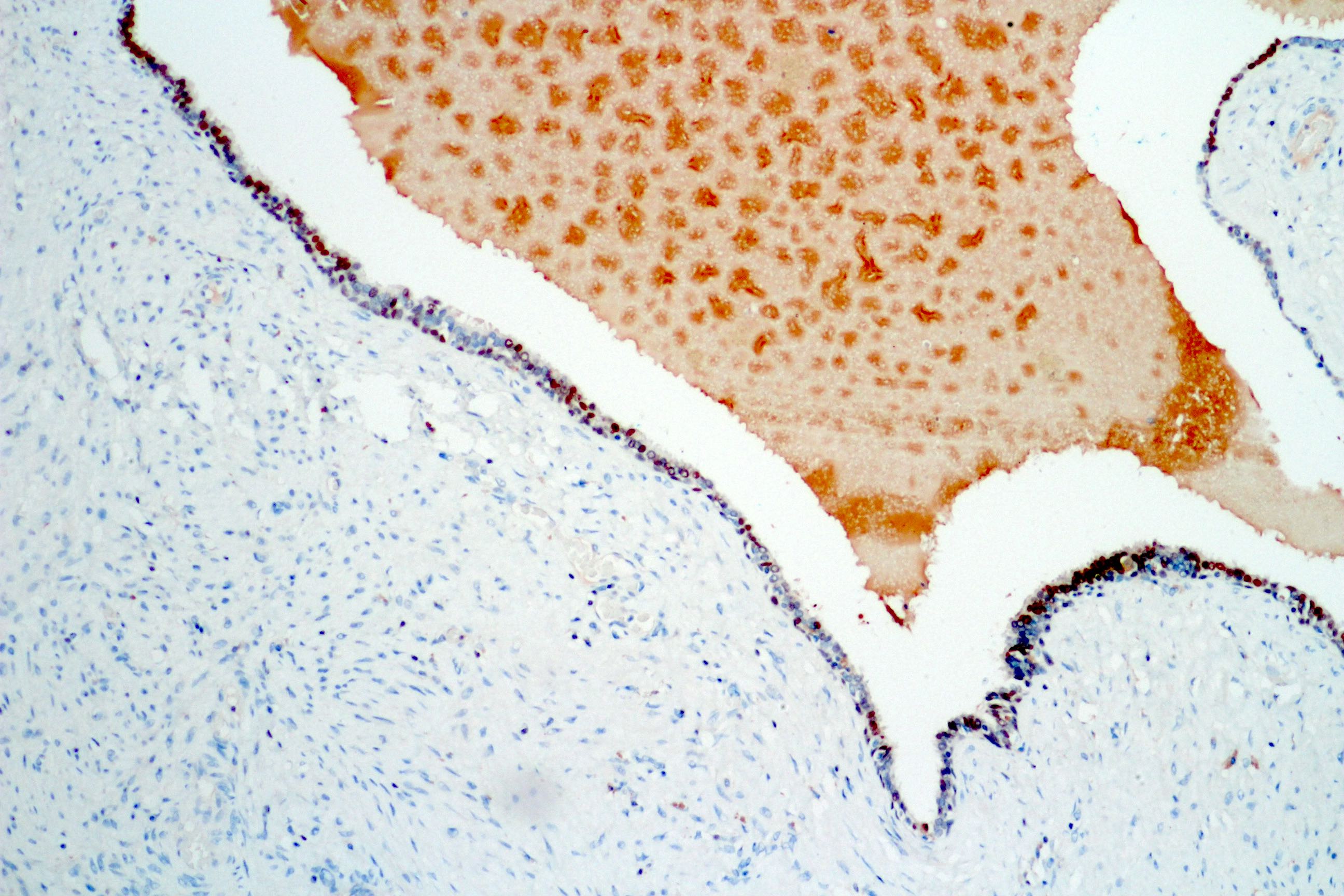
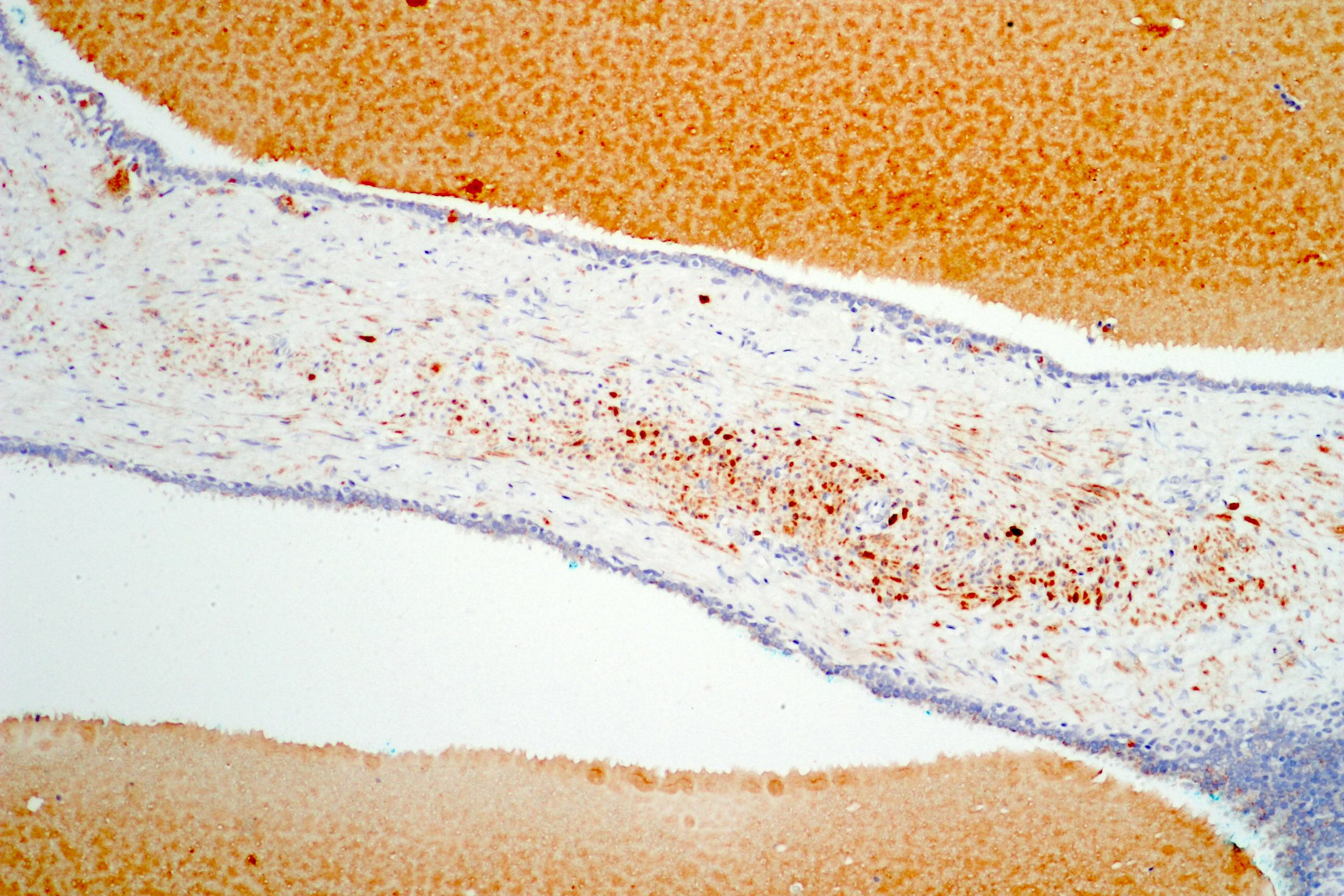
A. Expression of calretinin in epithelial cells. Seminal vesicle cystadenoma is negative for calretinin in the photo above.
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cystadenoma