Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Hung YP. Localized mesothelioma (pleura). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pleuralocmalmesothelioma.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Localized mesothelioma is a rare malignant mesothelial tumor that is microscopically identical to diffuse mesothelioma
- Unlike diffuse mesothelioma, localized mesothelioma is solitary and circumscribed, with no radiologic, intraoperative, gross or microscopic evidence of diffuse serosal involvement
Essential features
- Solitary and circumscribed, with no radiologic, intraoperative, gross or microscopic evidence of diffuse serosal involvement
- Microscopically identical to diffuse pleural mesothelioma
- Can be subclassified into epithelioid, biphasic and sarcomatoid histotypes
- Mesothelial immunophenotype
Terminology
- Not recommended: localized malignant mesothelioma
- Not recommended: solitary malignant mesothelioma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- < 1% of all mesothelial tumors (Mod Pathol 2020;33:271)
- < 200 published cases of localized pleural mesothelioma (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281)
Sites
- Most cases reported involve the pleura; the remainder of the cases involve the peritoneum, including mesenteric, perigastric, perisplenic or other intra-abdominal sites (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:1352)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown at this time
Etiology
- Associations with exposure to asbestos reported in some cases (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281)
Clinical features
- Wide age range and male predilection (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:357, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:866, Mod Pathol 2020;33:281)
Diagnosis
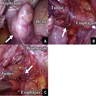
- Diagnosis of localized mesothelioma cannot be rendered based on the histologic findings alone and requires correlation with clinical and radiologic findings, in order to ascertain that the tumor is solitary and circumscribed, with no evidence of diffuse serosal involvement
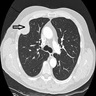
Radiology description
- Solitary localized serosal or subserosal mass (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281)
Prognostic factors
- More indolent than diffuse mesothelioma (Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2013;16:533)
- Potential favorable prognostic factors: epithelioid histotype, small tumor size and low grade cytology / mitotic index (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:1352)
Case reports
- 48 year old man with a localized splenic mass (Int J Surg Pathol 2014;22:451)
- 69 year old woman with a solitary intra-abdominal mass (Case Rep Pathol 2019;2019:2732674)
- 72 year old woman with a solitary mass adjacent to the diaphragm and esophagus (Ann Thorac Surg 2021;112:e57)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
- Adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy in some patients (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:1352)
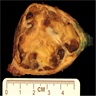
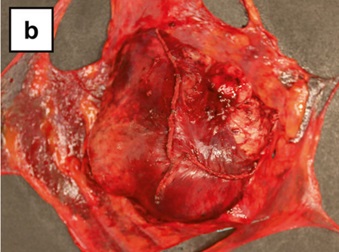
Gross description
- Circumscribed; can be encapsulated or nonencapsulated
- Tumor size ranging from < 2 cm to ~ 20 cm (Mod Pathol 2020;33:281)
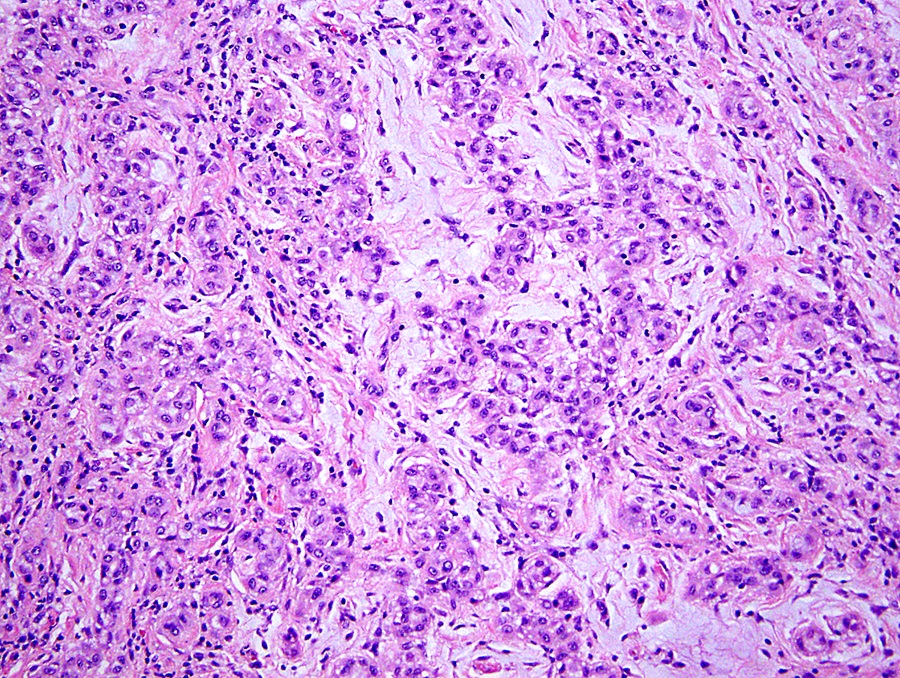
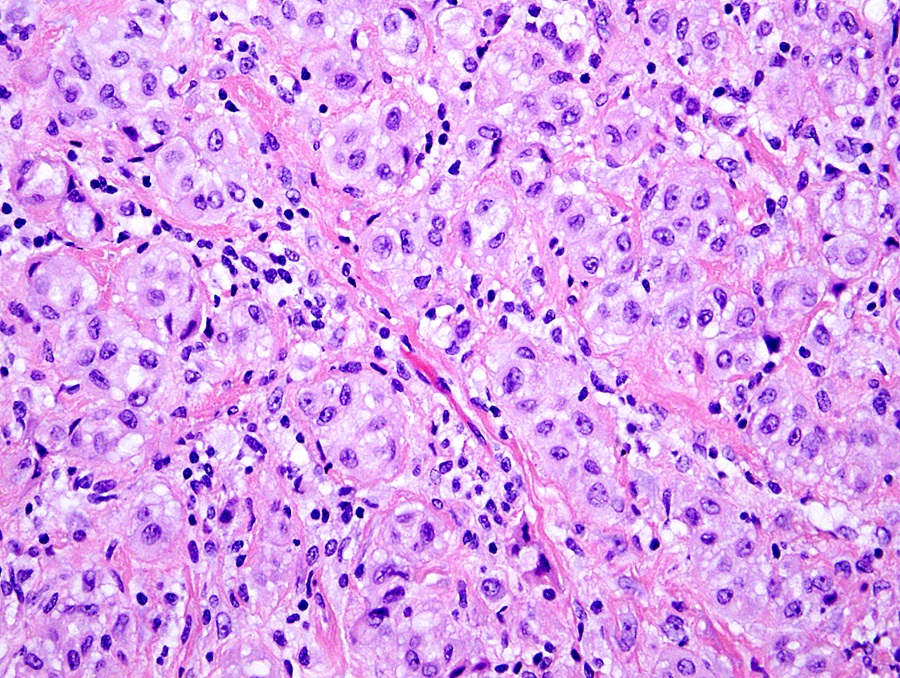
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Histologically identical to diffuse mesothelioma
- Comprises epithelioid, biphasic and sarcomatoid histologic types
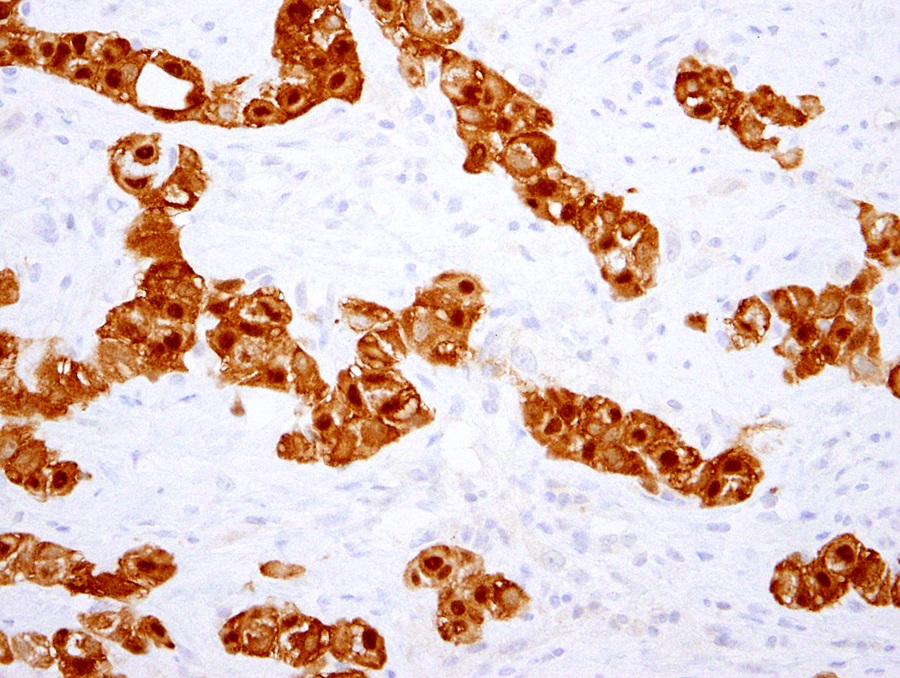
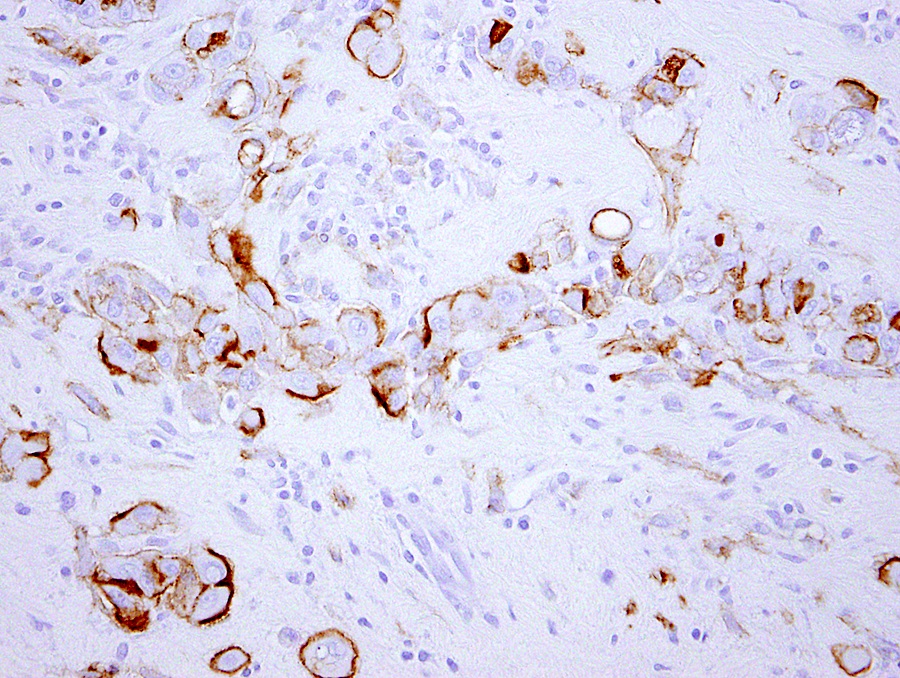
Microscopic (histologic) images
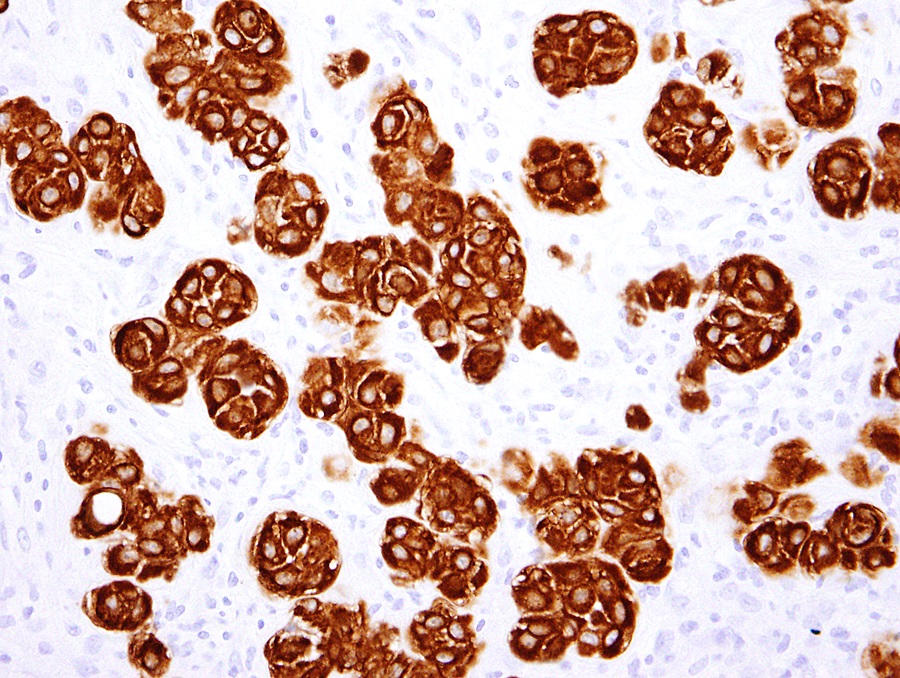
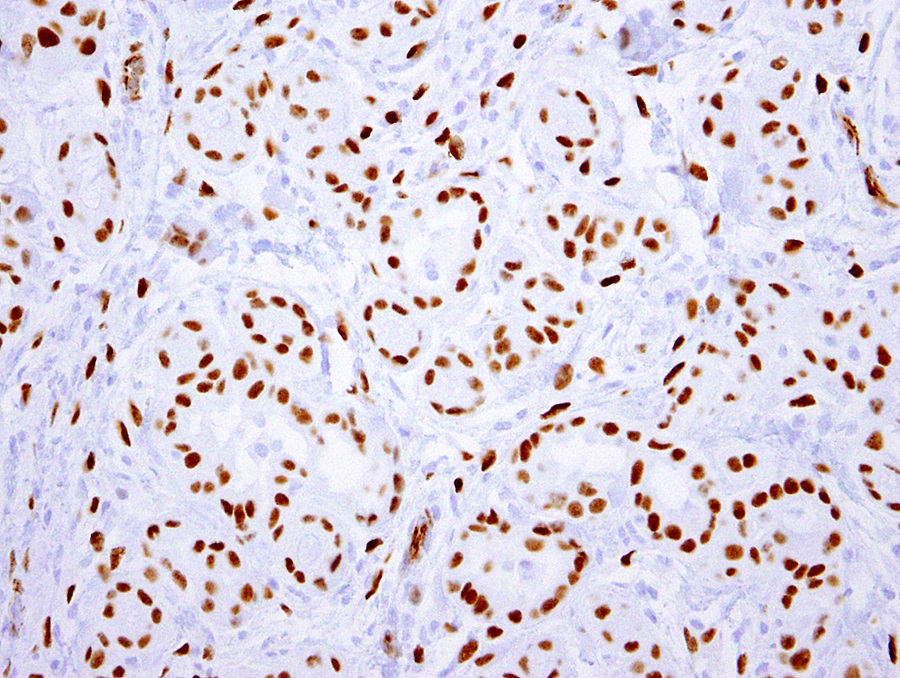
Positive stains
- WT1
- Calretinin
- D2-40
- HEG1 (membranous)
- BAP1 (loss of nuclear staining) seen in a subset of cases
- References: Mod Pathol 2020;33:271, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1143
Negative stains
- Claudin4
- MOC31
- BerEP4
- TTF1
- PAX8 (expression in 10 - 20% of mesotheliomas)
- References: Virchows Arch 2007;451:669, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1675
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Genomically heterogeneous with multiple subgroups (Mod Pathol 2020;33:271)
- Alterations involving BAP1, CDKN2A or NF2
- Mutations involving TRAF7
- Genomic near haploidization, with extensive loss of heterozygosity involving most chromosomes except chromosomes 5 and 7
Sample pathology report
- Pleura, pleurectomy:
- Localized pleural biphasic mesothelioma (see comment)
- Comment: Radiologic findings and intraoperative findings were reviewed. Radiologically, intraoperatively and grossly, this tumor is solitary and circumscribed. Microscopically, it is biphasic, with ~70% epithelioid component and ~30% sarcomatoid component. By immunohistochemistry, the tumor cells in both components are positive for AE1 / AE3 keratins, WT1, calretinin and D2-40 (patchy) and are negative for TTF1, MOC31 and claudin4, with complete loss of BAP1 nuclear staining, supporting the above diagnosis. Resection margin is negative for tumor. Tumor is 0.2 cm from the resection margin.
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic carcinoma:
- Diffuse mesothelioma:
- Microscopically identical to localized mesothelioma
- Diffuse involvement of the serosa, as noted radiologically or intraoperatively
- Adenomatoid tumor:
- Benign mesothelial tumor that arises most commonly near the genital tract
- Microcystic appearance at low magnification
- Recurrent mutations in TRAF7 (Mod Pathol 2018;31:660, Hum Pathol 2021;111:59)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements is true about localized mesothelioma?
- It involves only the pleura
- Its histopathologic features are identical to those of diffuse mesothelioma
- Loss of BAP1 nuclear staining is present in all cases
- Radiologic and intraoperative correlation is not needed to render this diagnosis
Board review style answer #1
B. Its histopathologic features are identical to those of diffuse mesothelioma. As such, its diagnosis requires correlation with radiologic, intraoperative and gross findings to ascertain that the tumor is indeed solitary with no diffuse serosal involvement. Answer D is incorrect because radiologic and intraoperative correlation is needed to render the diagnosis of localized mesothelioma. Answer A is incorrect because localized mesothelioma can involve the pleura and other serosal membranes including the peritoneum. Answer C is incorrect because the loss of BAP1 nuclear staining is seen in only a subset of localized mesotheliomas.
Comment Here
Reference: Localized mesothelioma
Comment Here
Reference: Localized mesothelioma