Table of Contents
Terminology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Uses by pathologists | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Avadhani V. Benign mesothelial proliferations (pleura). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pleurab9mesothelial.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Terminology
- Also called simple mesothelial hyperplasia
Pathophysiology
- Normal mesothelial surface has single layer of flat cuboidal epithelium
- Irritation of pleural surface causes simple hyperplasia of mesothelium
Etiology
- Due to asbestos, benign pleural effusion, benign pleural plaque, collagen infections, drug reactions, pneumothorax, pulmonary infarct, trauma, vascular disease
Uses by pathologists
- If malignancy cannot be excluded, use diagnosis of "atypical mesothelial hyperplasia" and recommend rebiopsy if clinically suspicious (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1217)
Case reports
- 43 year old woman with pleural multicystic mesothelial proliferation (Tuberk Toraks 2013;61:47)
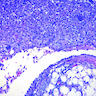
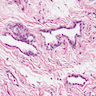
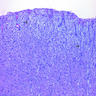
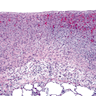
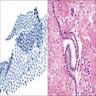
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mesothelial cells form conspicuous layer of regularly spaced, bland cuboidal cells along pleural surface; normally, mesotheial cells present only along surface and not in underlying tissue
- Distinct nucleoli may be present
- Likely benign if papillary excrescences with tufts of cells with bland tubule-like nonbranching structures, no fibrovascular cores
- Capillaries are parallel to each other and perpendicular to pleural surface (in malignancy, the capillaries are haphazard)
- Necrosis may be seen but usually accompanied with inflammatory cells and debris (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1421)
Microscopic (histologic) images
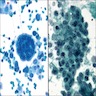
Cytology description
- Usually mesothelial cells will be numerous, dispersed or present in small clusters
- Clusters of > 12 cells is unusual in simple hyperplasia
- Binucleation, multinucleation, mitosis, prominent nucleolus can be seen in benign proliferations
- Two or more mesothelial cells are often separated by "window" or a narrow space
- Benign mesothelial cells usually have characteristic "skirt" or "halo" at pale outer rim of cell
Cytology images
Positive stains
- Immunostains do not differentiate benign and malignant mesothelial cells as both are positive for keratin
- However, immunostains can demonstrate invasion into underlying tissues
Differential diagnosis
Additional references