Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) descriptionCite this page: Kowalski PJ. Hematoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentahematoma.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
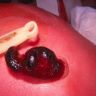
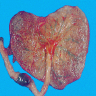
- Extravasation of blood from an umbilical vessel that subsequently accumulates in Wharton jelly
Terminology
- Hematoma or hemorrhage should be distinguished from umbilical cord thrombosis, which can be seen in association with a cord hematoma
Epidemiology
- Uncommon and estimated to occur in 1 per 5,000 - 13,000 deliveries
Sites
- Hematomas typically occur at the fetal end of the umbilical cord
Etiology
- Typically unknown but may be due to a ruptured umbilical vein varix (cystic vascular dilatation), trauma including therapeutic procedures (amniocentesis, cordocentesis, etc.) and cord abnormalities, such as traction occurring with short umbilical cords
Clinical features
- Blood loss or compression of fetal vessels can lead to circulatory compromise, fetal distress and fetal death
- Fetal mortality is estimated at 40 - 50% when umbilical cord hematoma is present
Diagnosis
- Fetal heart tracings can show decreased variability and an absence of accelerations (J Perinatol 2009;29:517)
Radiology description
- Ultrasound can reveal cord expansion with a heteroechoic to hyperechoic mass or discordant umbilical artery Doppler waveforms
Case reports
- Spontaneous umbilical cord hematoma (Am J Forensic Med Pathol 2008;29:185)
- Fetal death due to umbilical cord hematoma (J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2005;18:387)
- Umbilical cord hematoma secondary to in utero intravascular transfusion for Rh isoimmunization (Fetal Ther 1987;2:65)
Treatment
- Induction of delivery can be undertaken if fetal compromise is present
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nonspecific and variable hemorrhage involving Wharton jelly
- Less commonly, evidence of vascular disruption, cystic changes or aneurysmal dilatation