Table of Contents
Definition / general | Etiology | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Ziadie MS. Fetal thrombotic vasculopathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentafetalthrombotic.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Thrombosis of fetal vessels results in fibrosis of downstream villi
- Implies an increased risk for neurologic injury, growth restriction, oligohydramnios and renal / systemic thrombosis (Hum Pathol 1999;30:759)
- Clinical abnormalities associated with 30%+ avascular villi (Hum Pathol 1995;26:80)
Etiology
- May be associated with maternal diabetes, hypercoagulable disorders (Hum Pathol 2000;31:1036), maternal diabetes or perinatal liver disease
Gross description
- Large thrombi of chorionic vessels may be visible
- Areas of involvement may appear pale and firm
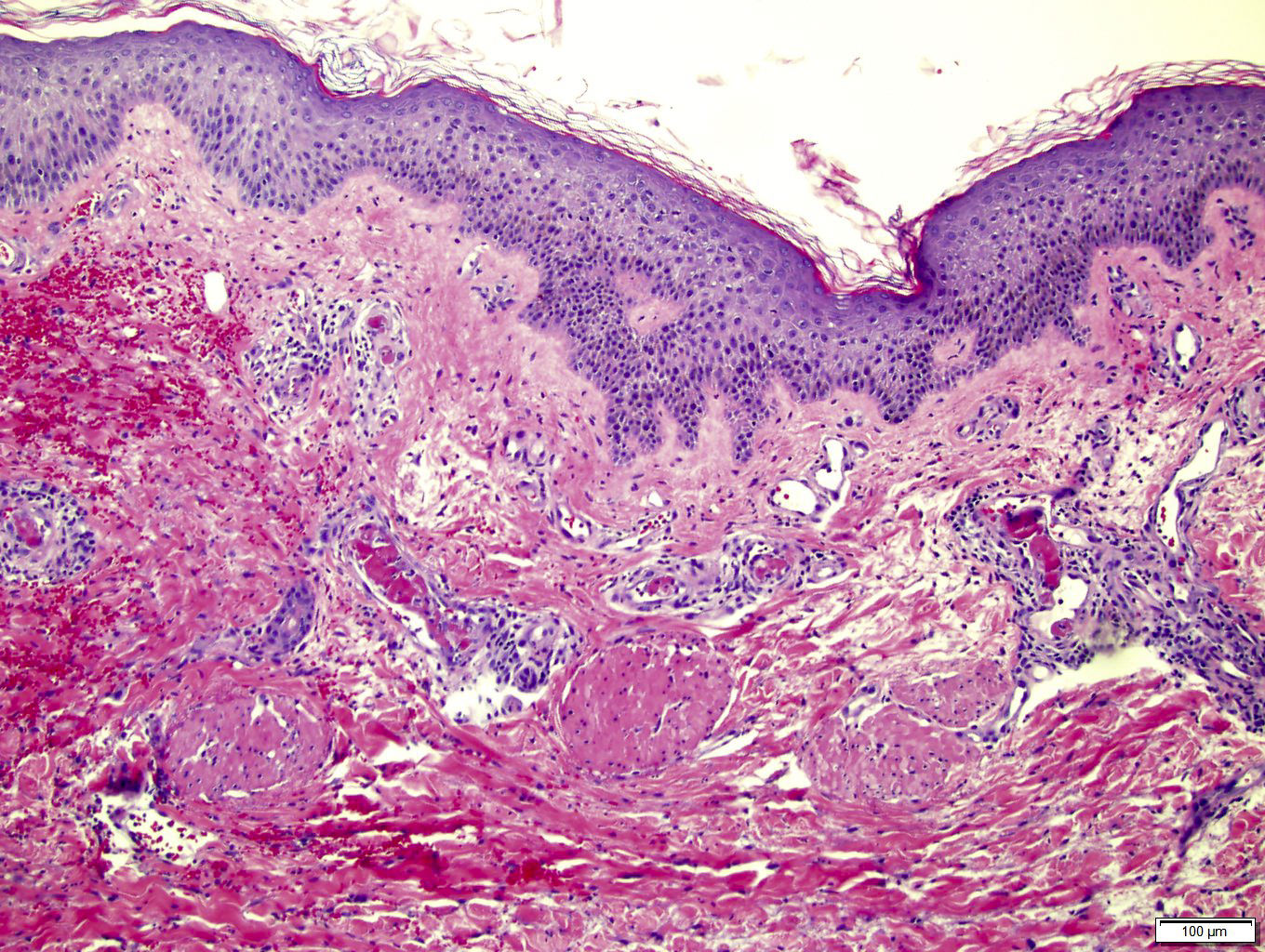
Microscopic (histologic) description
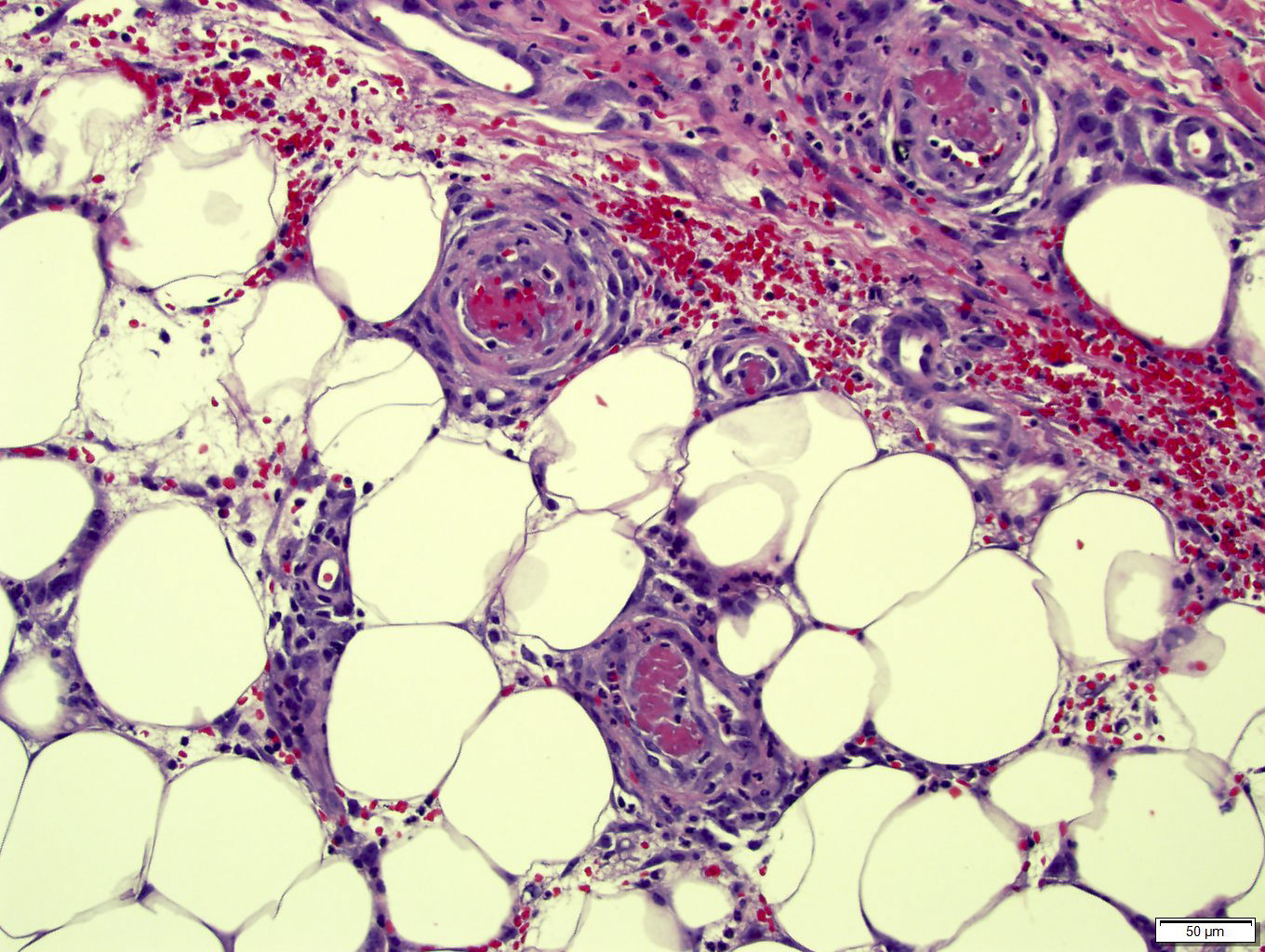
- Occlusive thrombi in large stem vessels are accompanied by downstream changes including organization, septation, red cell extravasation, endothelial destruction, loss of vascularity and ultimately fibrosis
- Trophoblastic basement membrane mineralization is common
- Grading is based on the number of affected villi: focal (3 - 5 avascular villi), intermediate (6 - 19 villi) or large ( > 20 villi)
- Massive or extensive involvement is defined as 25 - 50% affected parenchyma
- Changes are similar to those seen in intrauterine fetal demise but are focal rather than diffuse
- Associated pathologic findings may include meconium staining, villous chorangiosis and infarction