Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Jabbar A, Lanjewar S, Gupta R. Exaggerated placental site. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentaexagg.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Exuberant infiltration of the endometrium and myometrium by implantation site intermediate trophoblast
Essential features
- Exaggeration of normal physiologic process, with infiltration of the endometrium and superficial third of myometrium by implantation site intermediate trophoblast
- Can be associated with normal pregnancy or abortions, molar pregnancy and sometimes presents as postpartum bleeding
- Ki67 labeling index is near 0%
- Ki67 labeling index can be 0 - 5 % in exaggerated placental site (EPS) of molar pregnancies (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: O43.899 - other placental disorders, unspecified trimester
Epidemiology
- Incidence is 1.6% of first trimester spontaneous and elective abortions (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2014;33:339, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
Sites
- Uterus
Pathophysiology
- Exaggeration of normal physiologic process
- Intermediate trophoblasts (IT) invade through endometrium into the superficial third of myometrium (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
- Normal structure of endometrial glands, myometrium and vessels is usually maintained
- Ki67 indices of near zero indicate increased number of intermediate trophoblasts in EPS is not a result of de novo proliferation of IT in the implantation site (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- Increased Ki67 in molar pregnancy may be a spillover effect IT in the trophoblastic columns of hydatiform moles (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- Although histologically the same, increased Ki67 labelling index in complete molar implantation site represents related but different lesions (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
Clinical features
- Can occur in normal pregnancy or following an abortion (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:609)
- Causes postpartum bleeding, uterine atony (J Reprod Med 2013;58:448, Tohoku J Exp Med 2014;234:77)
Diagnosis
- Histologic examination
Radiology description
- May present as echogenic lesion in the uterine cavity (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:609)
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis following curettage
Case reports
- 26 year old woman presented with complete mole and coexistent exaggerated placental site reaction (Niger Med J 2014;55:180)
- 34 year old woman primigravida with intrauterine fetal demise and suspected placenta previa (Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2012;51:440)
- 35 year old woman with intractable massive postpartum hemorrhage after removal of retained placenta (Tohoku J Exp Med 2014;234:77)
- 39 year old woman with an echogenic mass in uterine cavity following elective abortion (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:609)
Treatment
- Curettage is curative; no follow up is required (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
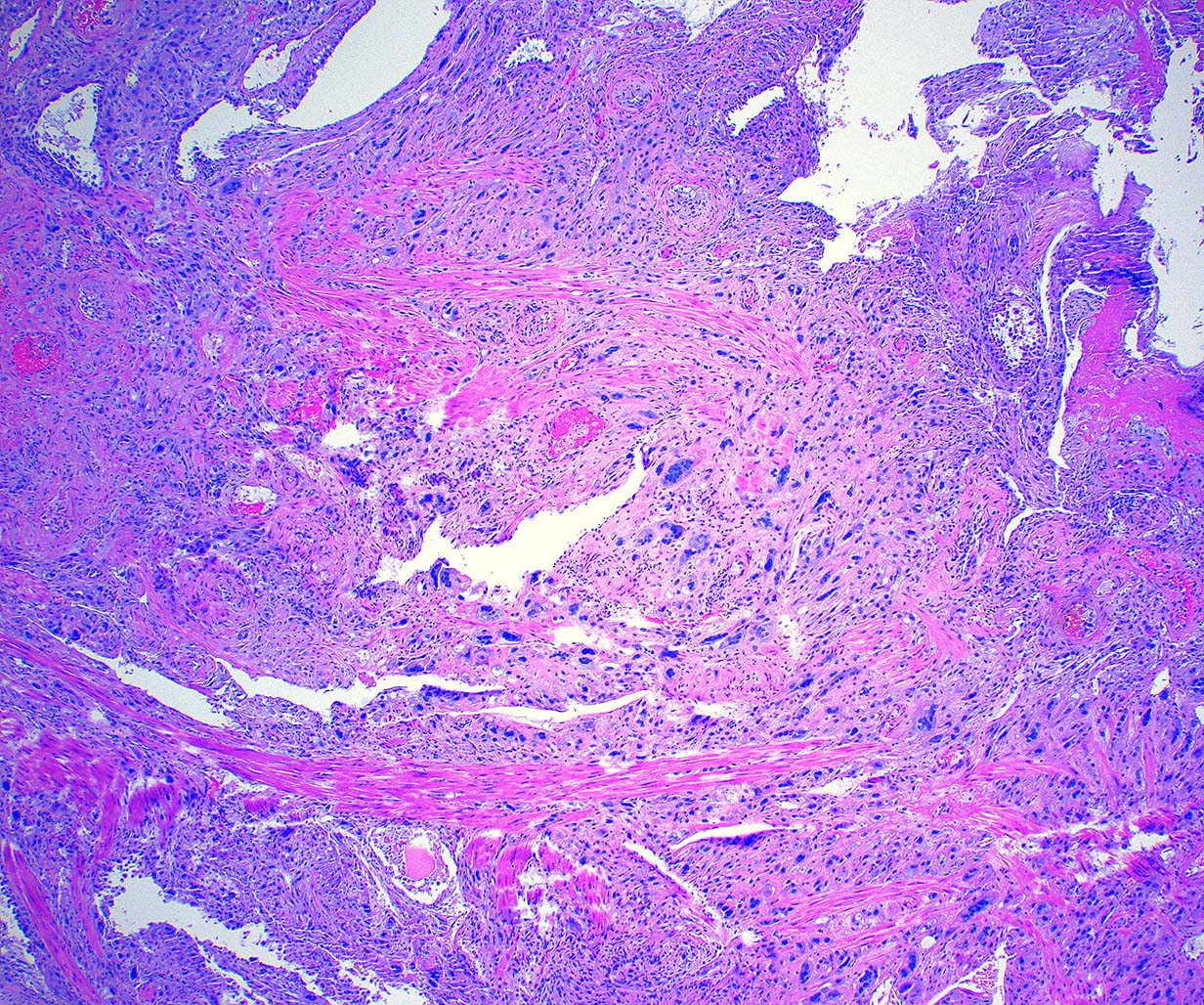
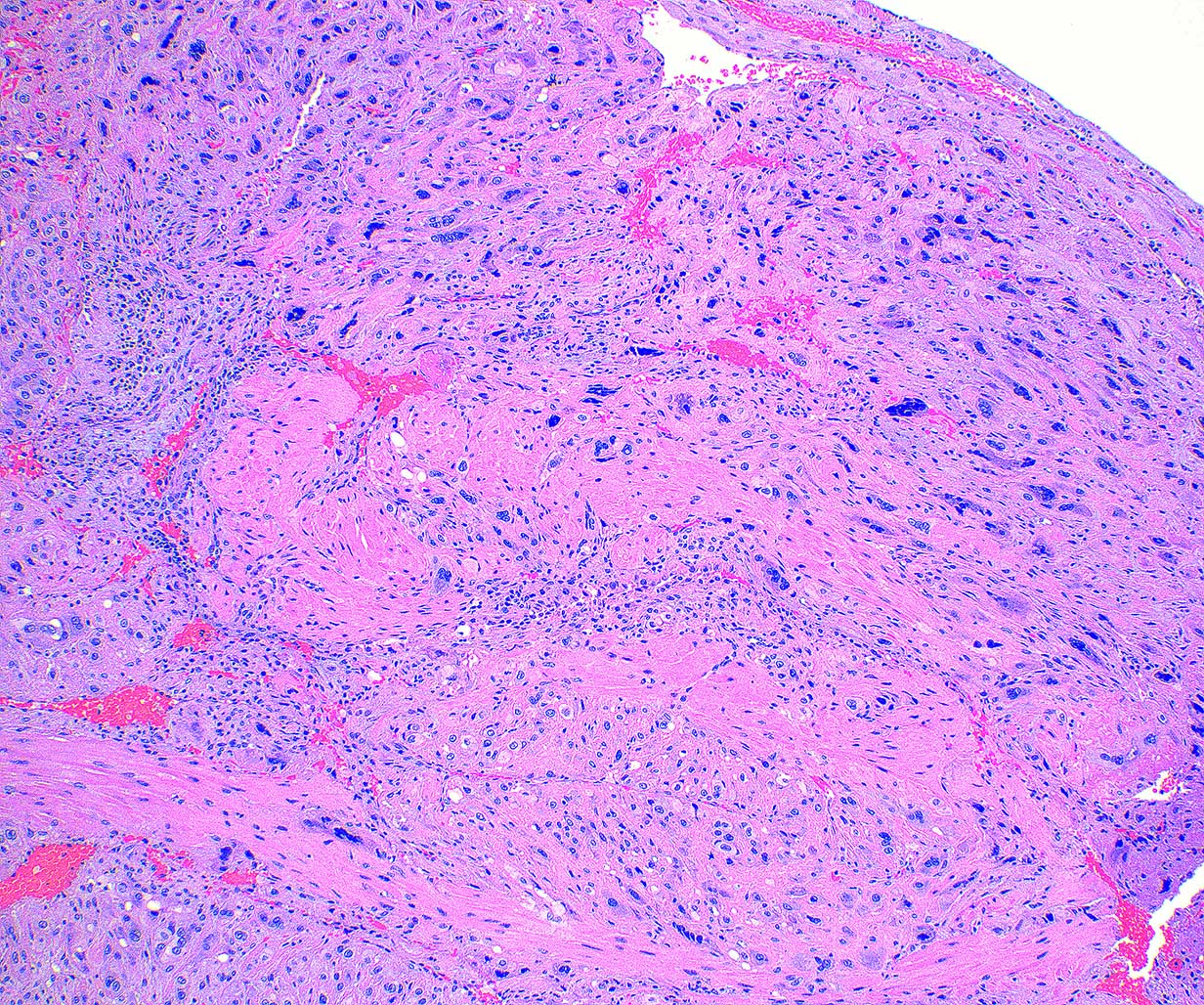
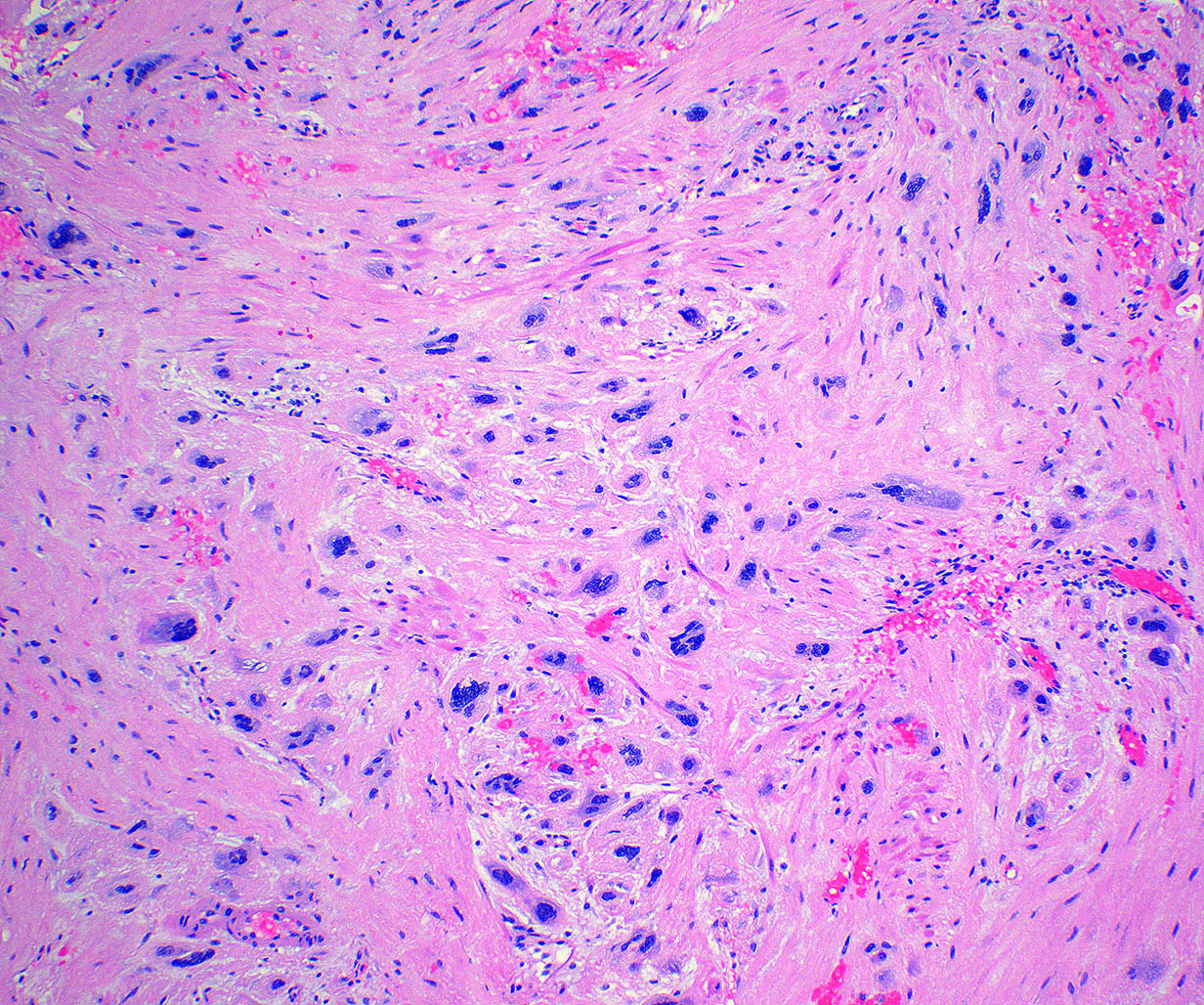
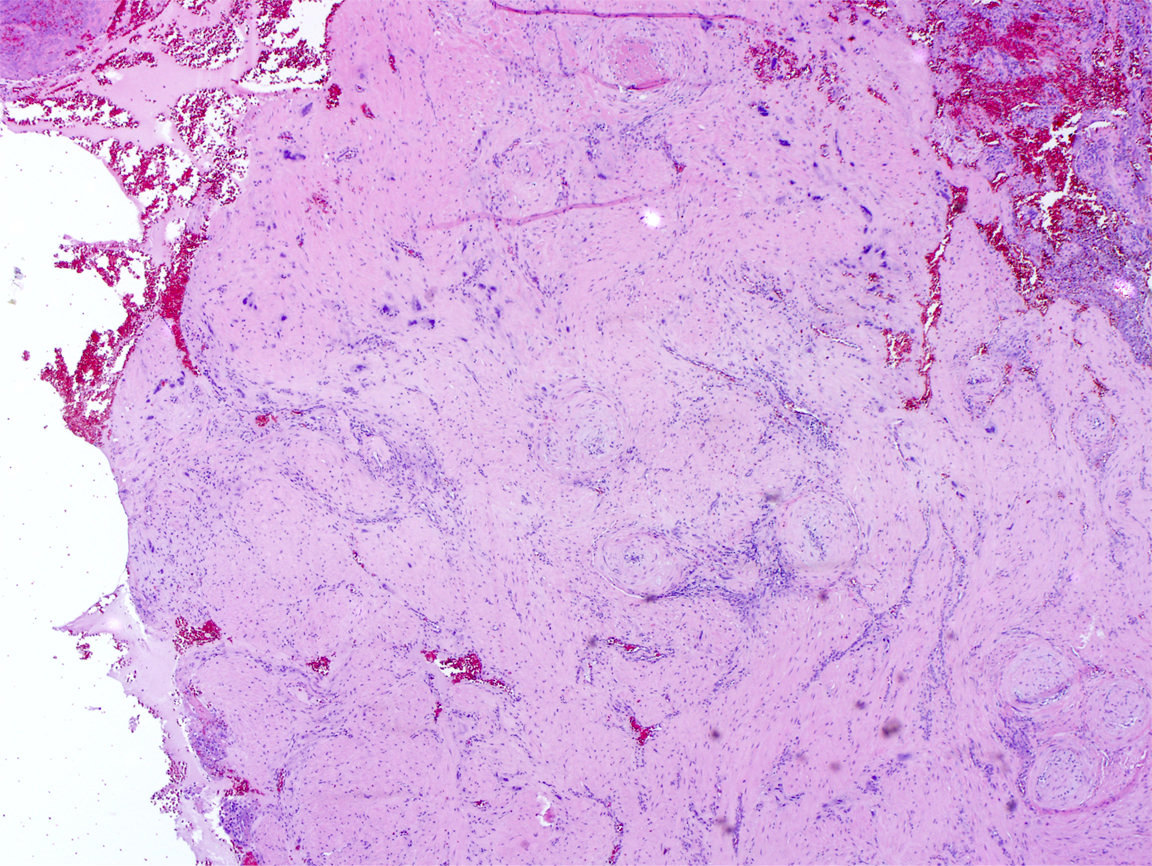
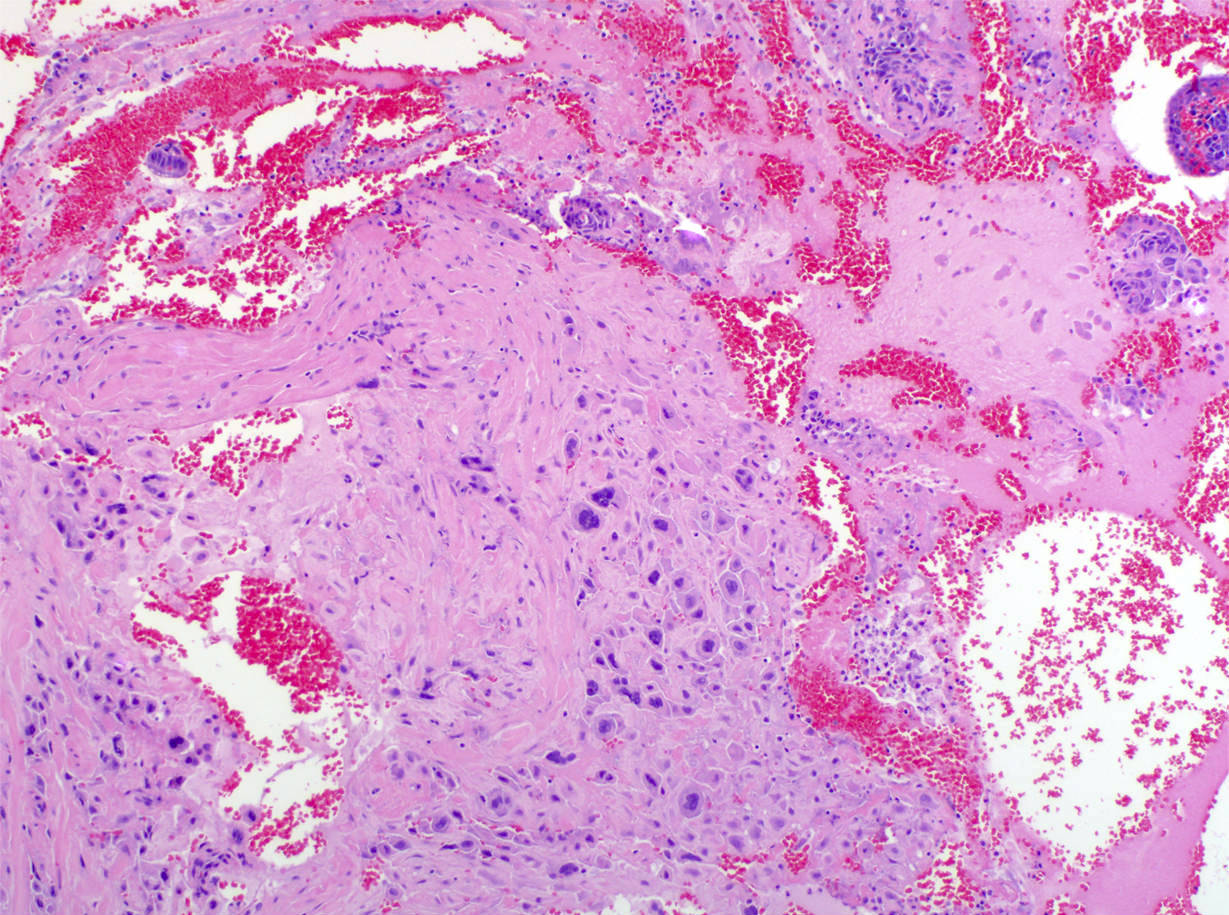
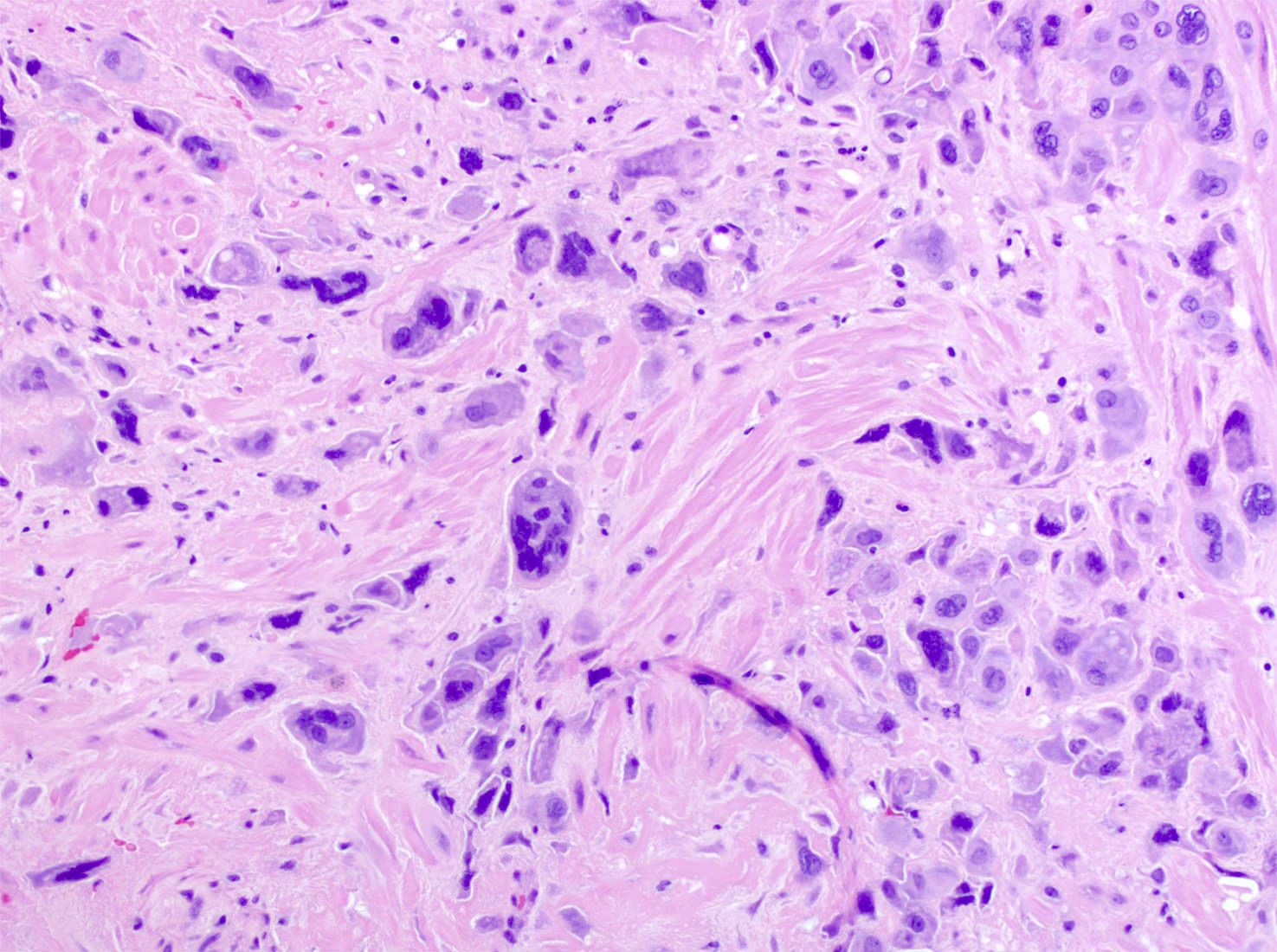
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Extensive infiltration of endometrium and myometrium by implantation site intermediate trophoblasts which are often multinucleate (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
- Endometrial glands and spiral arterioles can show invasion by trophoblasts
- Smooth muscle cells of myometrium are separated by cords, nests and individual trophoblastic cells
- Despite diffuse infiltration, there is not necrosis or mitoses
- Trophoblastic cells share similar morphologic features of normal implantation site intermediate trophoblasts; these cells contain abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
- Chorionic villi are morphologically unremarkable
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- HPL (diffuse), MUC4, CK18, HLA-G (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2014;33:339)
- MEL-CAM / CD146, inhibin, PLAP (weak) (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- Double staining of Ki67 and HLA-G is a useful method in the differential diagnosis of exaggerated placental site versus placental site trophoblastic tumor and placental site trophoblastic tumor versus choriocarcinoma (Hum Immunol 2007;68:272)
Sample pathology report
- Uterus, endometrium, dilatation and curettage:
- Exaggerated placental site
Differential diagnosis
- Choriocarcinoma:
- Comprised of syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts
- Extensive hemorrhage and necrosis
- hCG positive
- Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor:
- Well circumscribed nodular expansile masses with necrosis
- Mononucleate trophoblastic cells arranged in nests and cords (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2001;20:31)
- Strongly positive for p63, focally positive for HPL and MEL-CAM / CD146; negative for MUC4
- Placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT):
- Confluent sheets of trophoblastic cells
- Increased mitoses (Ki67 is 10 - 15%) (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- PSTT can be confused with molar implantation site; Ki67 labelling index of molar implantation site is 3 - 5% (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- HLA-G immunostaining highlights growth patterns of intermediate trophoblasts and can distinguish placental site trophoblastic tumor and an exaggerated placental site
- In a placental site trophoblastic tumor, the cells form confluent masses, whereas in an exaggerated placental site, the IT cells infiltrate the endomyometrium as single cells and cords of cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:914)
- Placental site nodule:
- Nodular with well circumscribed, surrounding thin rim of chronic inflammatory cells and occasionally decidual cells
- Ki67: trophoblast nuclear staining < 5% in placental site nodule (Hum Pathol 1998;29:27)
- p63 positive
Board review style question #1
Exaggerated placental site (shown in the image above) is characterized by which of the following features?
- Absence of villi
- Presence of necrosis and mitoses
- Proliferation of chorionic type intermediate trophoblasts with invasion of myometrium
- Proliferation of implantation type intermediate trophoblasts with invasion of myometrium
Board review style answer #1
D. Proliferation of implantation type intermediate trophoblasts with invasion of myometrium
Comment Here
Reference: Exaggerated placental site
Comment Here
Reference: Exaggerated placental site
Board review style question #2
Ki67 labeling index in exaggerated placental site is
- Near 0%
- Near 5%
- Near 15%
- Near 100%
Board review style answer #2