Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagnosis | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Steele J, Hecht JL. Decidual arteriopathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentadecidualvasculopathy.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pattern of injury to maternal vessels of the decidua that occurs in late pregnancy
- Features thickening or fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall, endothelial swelling and detachment, loose collection of perivascular lymphocytes
Essential features
- Closely associated with preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction
- 2 forms: early / hypertrophic type and advanced / severe type with fibrinoid necrosis
- Alteration is independent of endovascular trophoblast and is best seen away from the placental bed in the membrane roll
- Likely caused by excess antiangiogenic proteins secreted by trophoblast
Terminology
- Decidual arteriopathy
- Decidual vasculopathy
ICD coding
Sites
- Decidua along the placental membranes
Pathophysiology
- Represents chronic endothelial injury and remodeling in maternal vessels, usually in the setting of preeclampsia or growth restriction with maternal vascular malperfusion
- Early lesions (hypertrophic type) show mural thickening due to continuous endothelial damage and repair
- Endothelial damage is caused by trophoblastic secretion of circulating soluble antiangiogenic factors that accumulate in the amniotic fluid, such as soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFLT) and soluble endoglin (sENG), in response to oxidative and hypoxic stress; local inflammatory cytokines such as interferon (INF) gamma may also play a role
- Independent of trophoblast conversion of spiral arterioles in the implantation site
- Although both processes are associated with maternal vascular malperfusion, decidual arteriopathy is not a failure of physiologic transformation of spiral arteries
- Failure of physiologic transformation of spiral arteries involves direct contact between endovascular trophoblast in the implantation site
- Decidual arteriopathy is a paracrine effect in the decidua of the free membranes (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2017;216:287.e1)
- Decidual arteriopathy is not a form of hypertension related vascular remodeling; wall thickening in early lesions of decidual arteriopathy is accompanied by loss of smooth muscle (loss of desmin staining) rather than hypertrophy as seen in chronic hypertension
- Form of hypertrophic decidual arteriopathy has been noted in patients with chronic hypertension unrelated to preeclampsia or growth restriction; such lesions do not seem to progress to acute atherosis
Etiology
- Diabetes (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:773)
- Smoking (Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2016;29:733)
- Other risk factors for preeclampsia or growth restriction (Placenta 2016;42:37, Placenta 2012;33:630)
Diagnosis
- Histologic examination of the membranes
Gross description
- Sections of membrane roll should be taken in areas of preserved decidua (roughened surface of the membranes)
- Affected vessels may appear prominent on transillumination of the membranes
Microscopic (histologic) description
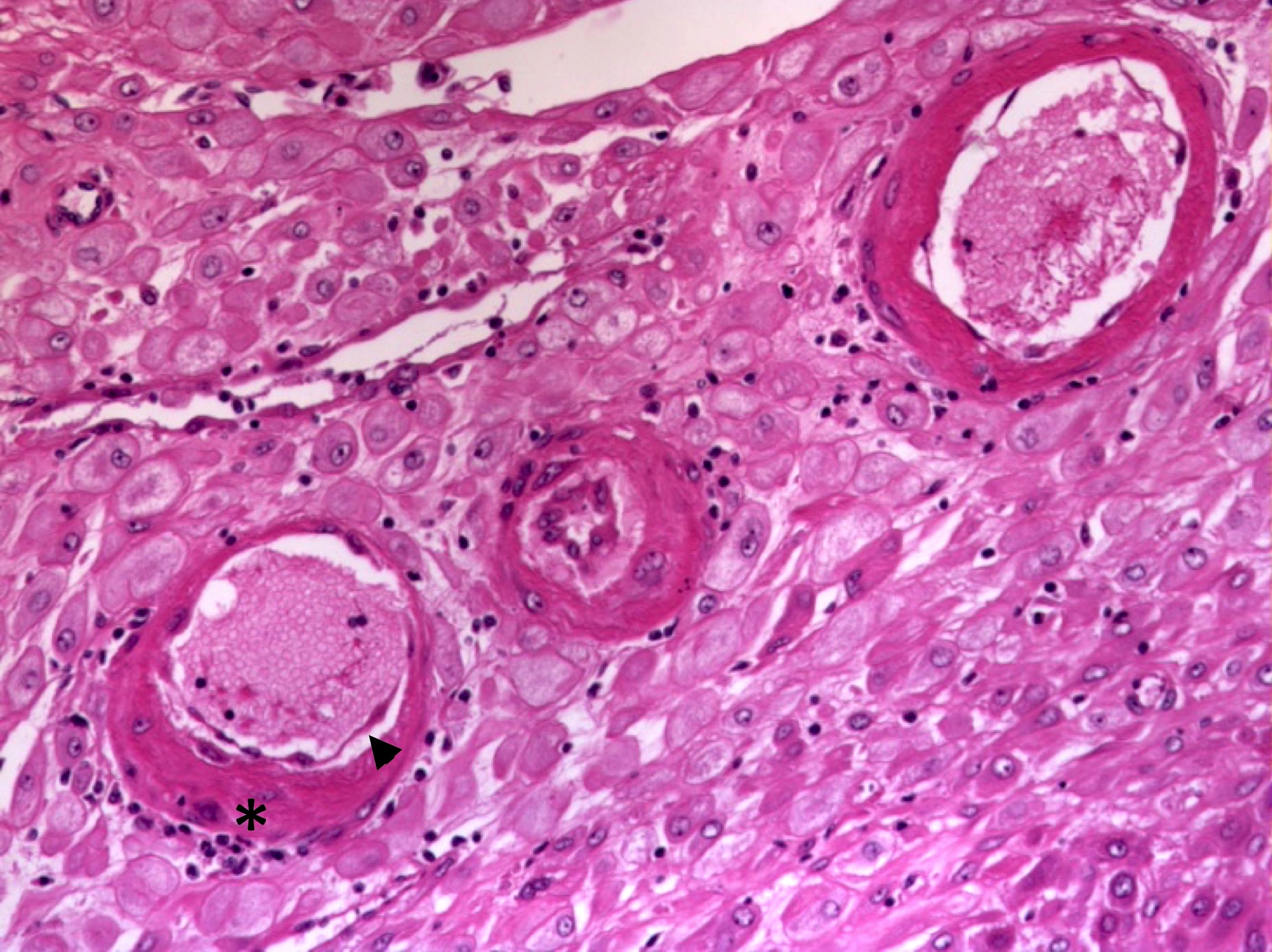
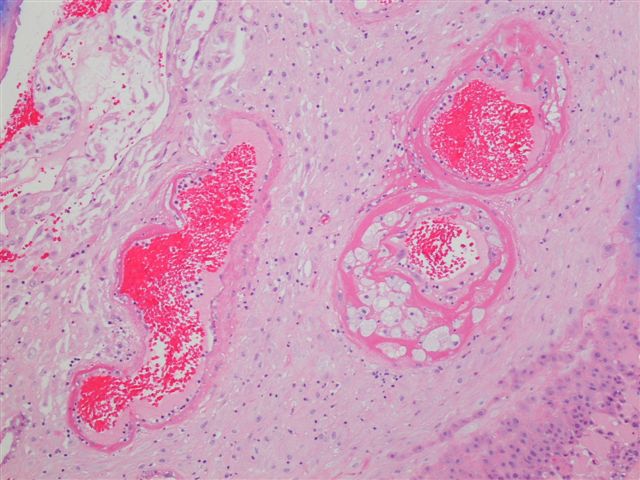
- 2 forms: hypertrophic decidual arteriopathy (HDA) and severe decidual arteriopathy with fibrinoid necrosis (SDA)
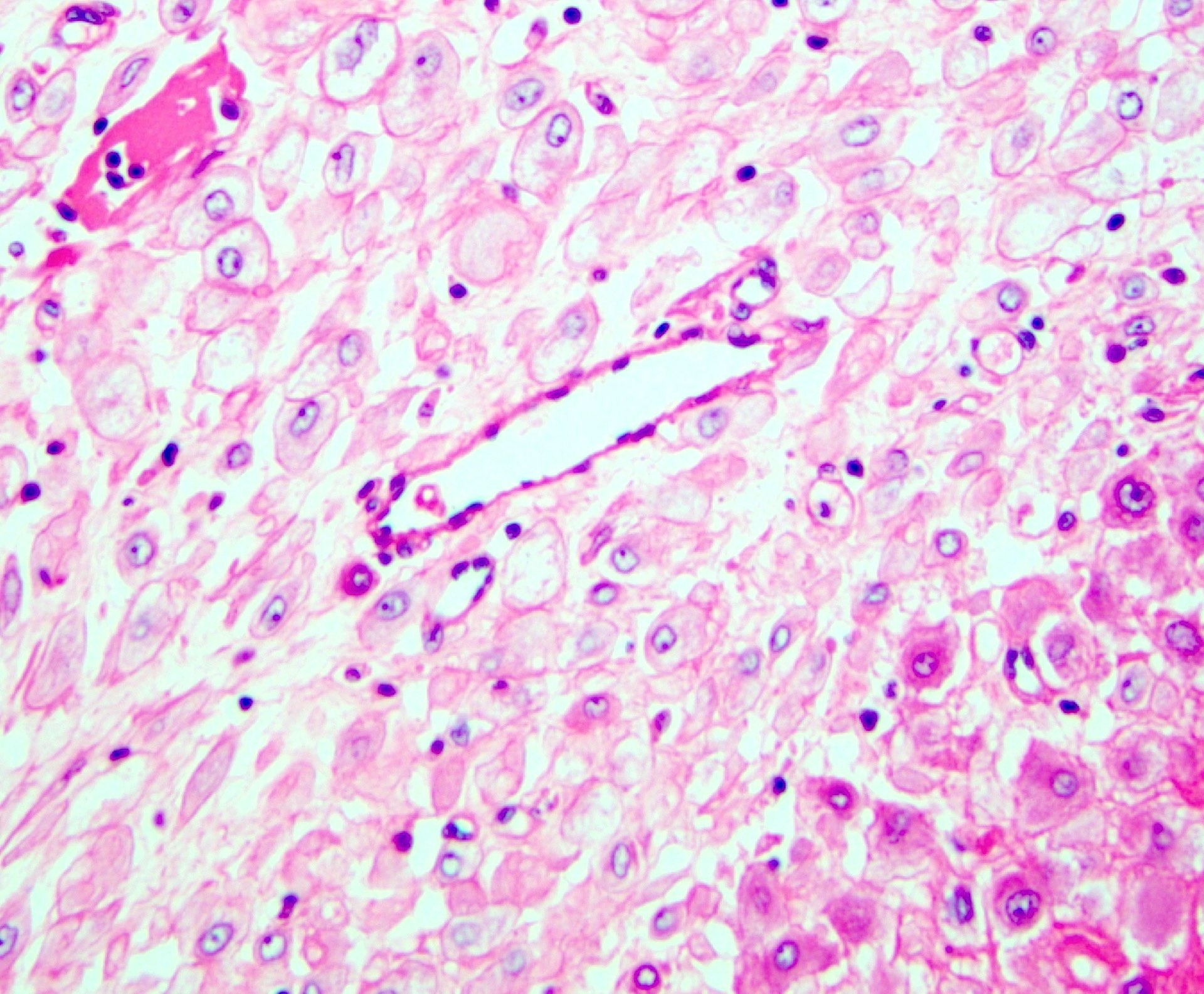
- Hypertrophic decidual arteriopathy:
- Small arteries with thickened walls, swollen endothelial cells that detach into the lumen and a sparse collection of perivascular lymphocytes
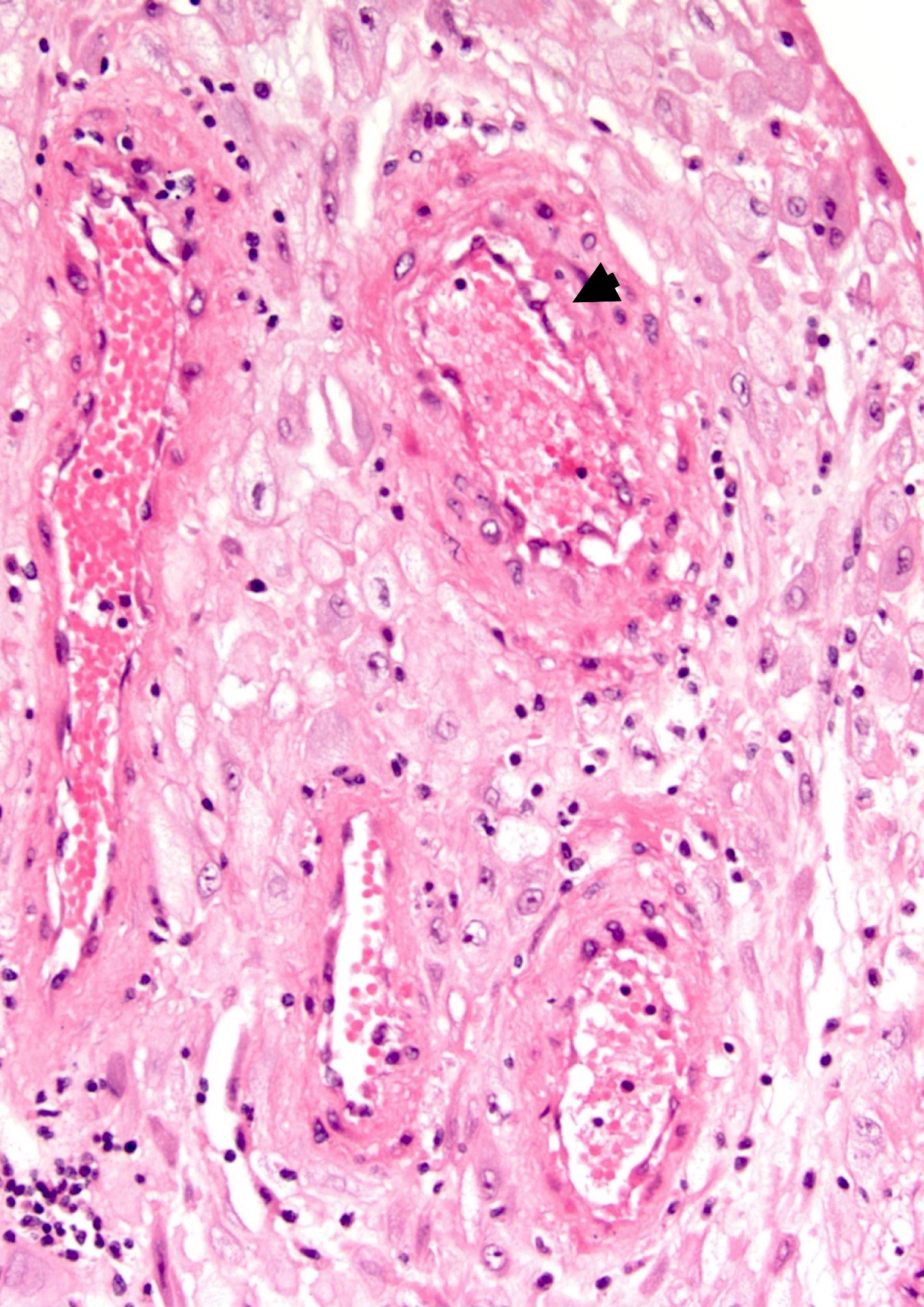
- Severe decidual arteriopathy:
- Characterized by fibrinoid necrosis of vessel wall (amorphous eosinophilic vessel wall)
- With or without foamy macrophages (atherosis)
- Reference: Placenta 2016;42:37
Microscopic (histologic) images
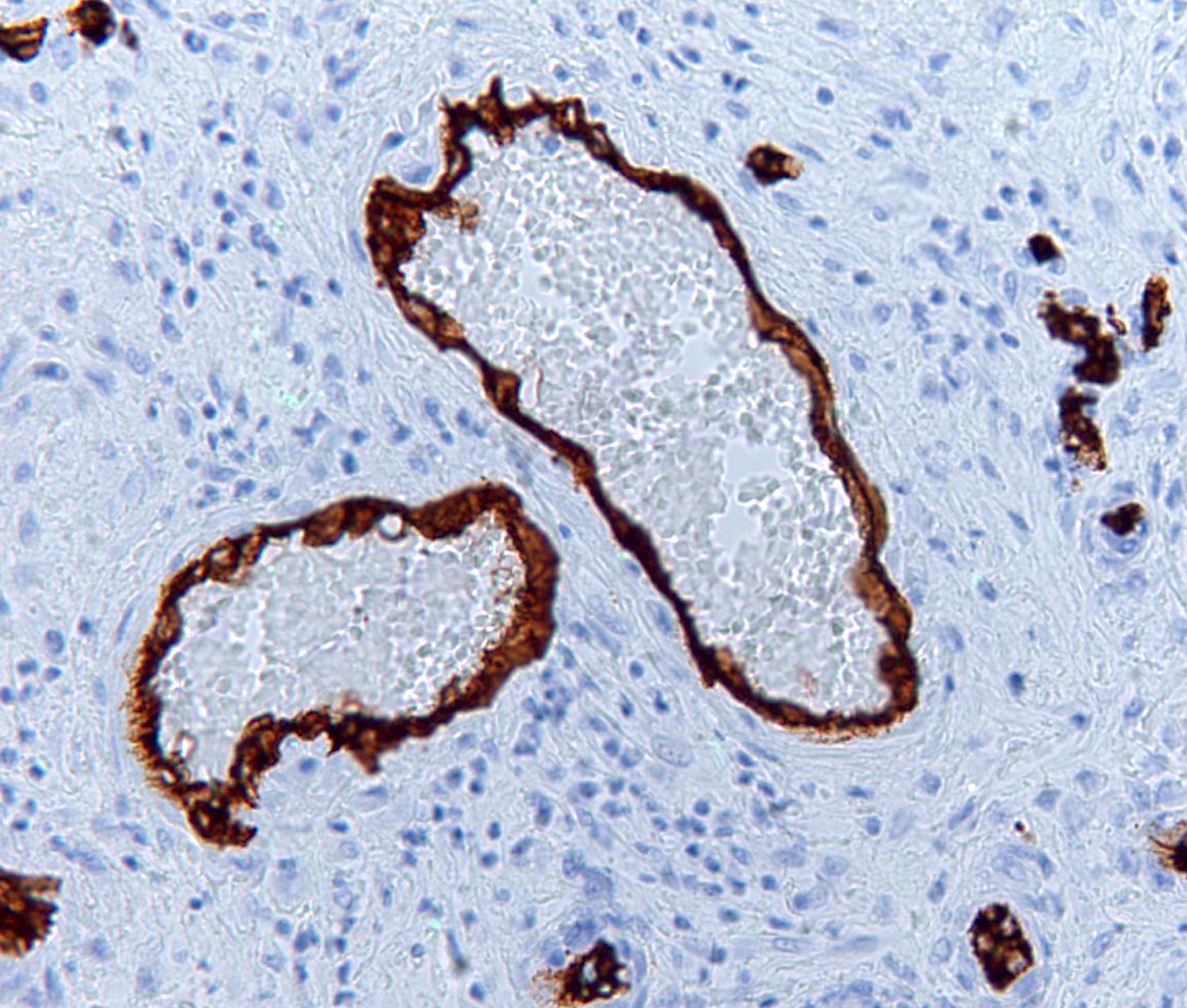
Contributed by Jonathan L. Hecht, M.D., Ph.D.
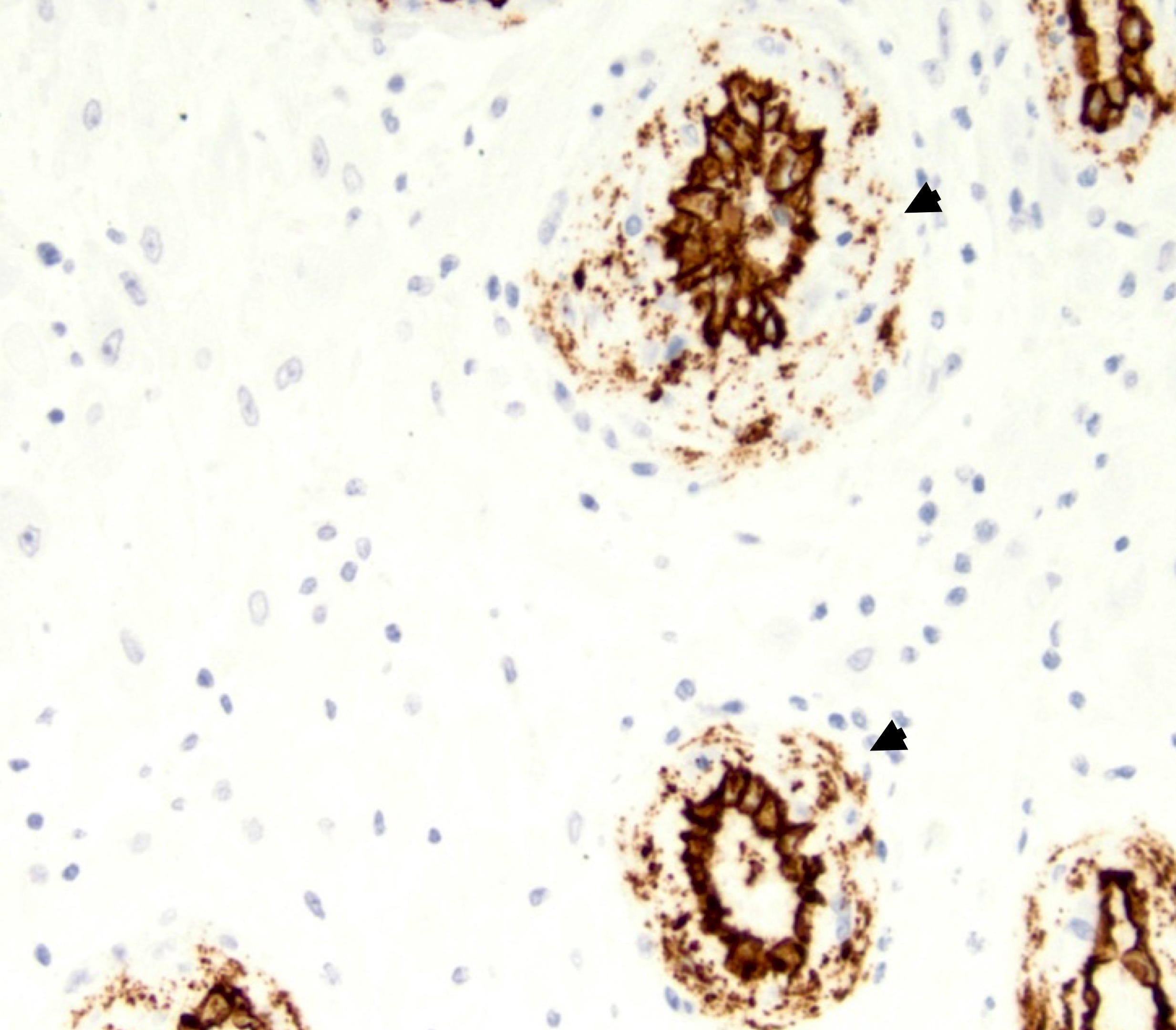
Contributed by Yan Lemeshev, M.D.
Immunofluorescence description
- Immunofluorescence is not used for clinical diagnosis
- Characteristic staining pattern is endovascular deposition of immunoglobulin, complement and perivascular leakage of fibrin
- Atherosis with deposition of IgM and C3 resembles vascular lesions in transplant rejection, suggesting maternal antifetal rejection (Placenta 1983;4 Spec No:489)
- However, this pattern can also be seen in the context of diabetes and chronic hypertension due to local intravascular coagulation (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:773)
Positive stains
- CD34: particulate / granular (starburst) pattern in and around the vessel wall (Placenta 2016;42:37)
Negative stains
- Desmin: loss or fragmentation of staining in hypertrophic decidual arteriopathy (Placenta 2016;42:37)
Videos
Placental lesions
Sample pathology report
- Singleton placenta at _ weeks gestational age; _ g (_ percentile):
- Membranes with decidual arteriopathy
Differential diagnosis
- Normal muscular decidual arteries:
- Thick muscular walls
- Lack endothelial disruption and perivascular lymphocytes
- Highlighted with desmin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 34 year old woman who is pregnant with her third child and has 2 children (G3P2002) presents at 39 weeks for delivery. Histologic examination of the membrane roll reveals small arteries with detached endothelial cells and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Which immunohistochemical stain would best highlight the fragmentation of smooth muscle within the vessel walls?
- Caldesmon
- Desmin
- MyoD1
- Myogenin
- Smooth muscle actin
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
32 year old G3P1102 presents at 39 weeks for delivery. Histologic examination of the membrane roll reveals small arteries with detached endothelial cells and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Which predisposing factor is this mother most likely to have?
- Gestational hypertension
- Increased exercise during pregnancy
- Infection during pregnancy
- Low body weight
Board review style answer #2