Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Saab S. Chorangiomatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentachorangiomatosis.html. Accessed November 27th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Nonexpansile proliferation of anastomosing capillaries at the periphery of stem villi or immature intermediate villi
- Closely related to chorangiosis and chorangioma and associated with advanced maternal age, extreme prematurity and multiple gestation; it is less common in those of African American ancestry (Hum Pathol 2000;31:945)
Essential features
- Also called multifocal chorangiomatosis and multifocal diffuse chorangiomatosis
- No gross findings; therefore, radiologic detection on antenatal evaluation is not possible
- 2 subgroups: patchy (multiple foci, occupying < 10x microscopic field) and extensive (multiple foci with at least one > 4x microscopic field)
- Fetal growth restriction, congenital malformation and adverse fetal outcomes associated with more extensive lesions
Terminology
- Multifocal chorangiomatosis and multifocal diffuse chorangiomatosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: O43.813 - placental infarction, third trimester
Epidemiology
- Maternal factors associated with multifocal chorangiomatosis include advanced maternal age and multiparity; it is less common in those of African American ancestry
- Fetal outcomes can include growth restriction, congenital anomalies and stillbirth
Pathophysiology
- Rare disorder without a clearly defined etiology or pathophysiology
- Suspected to be due to fetal developmental anomalies or abnormal fetal blood flow
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is made on histologic evaluation of the placenta as there are no radiologic or grossly evident findings
Prognostic factors
- Patchy multifocal chorangiomatosis has been associated with fetal growth restriction and prematurity
- Extensive multifocal chorangiomatosis has been associated with macrosomia, congenital anomalies and stillbirth
Case reports
- Premature infant delivered at 31 weeks gestational age with hydrops and multifocal intestinal stenosis (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2006;49:600)
- Premature male infant delivered at 32 weeks gestation with placentomegaly, cardiomegaly and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2017;36:457)
- Newborn with multifocal chorangiomatosis with disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, hydrops and massive umbilical vein thrombosis (J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2022;35:4009)
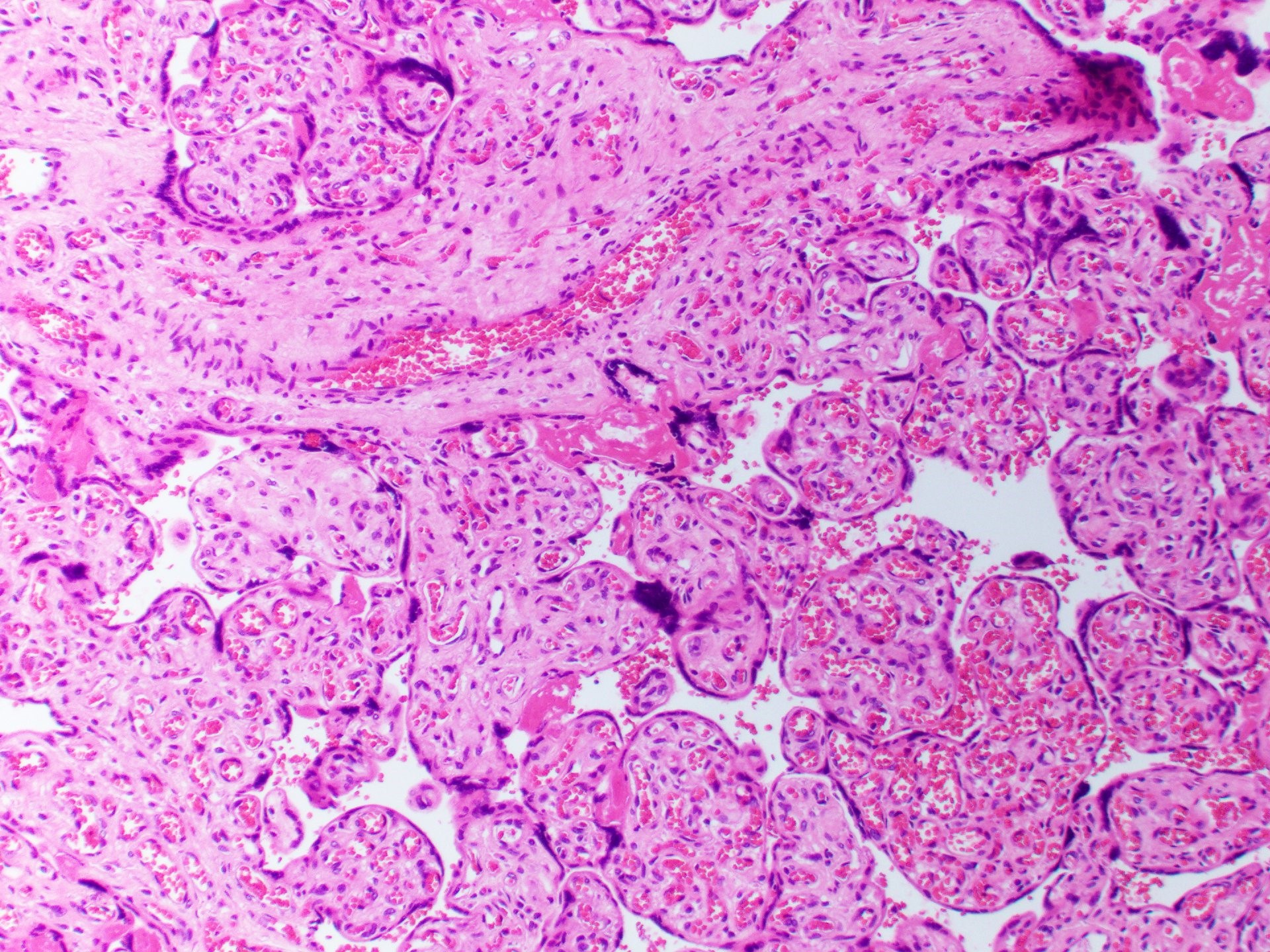
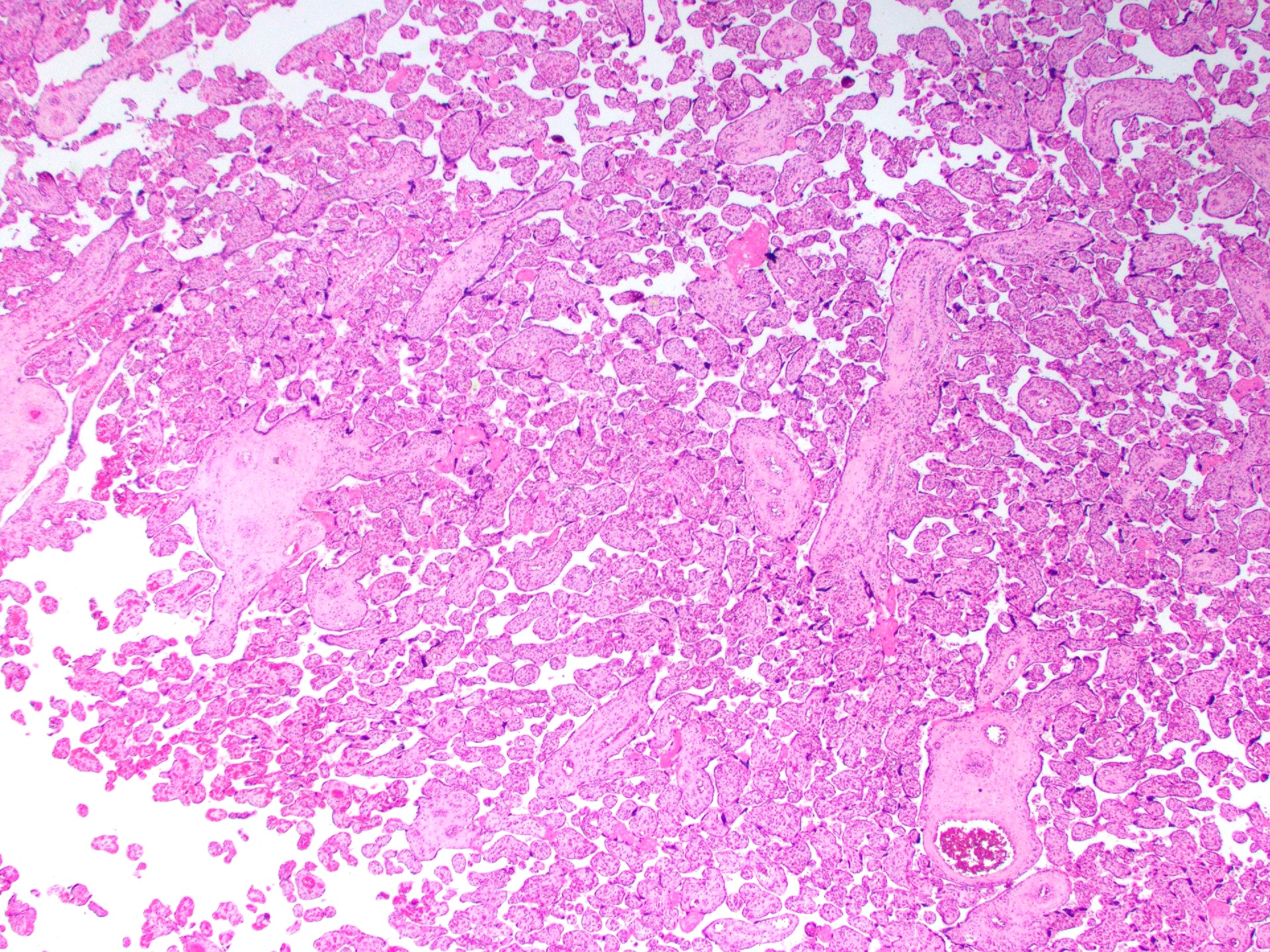
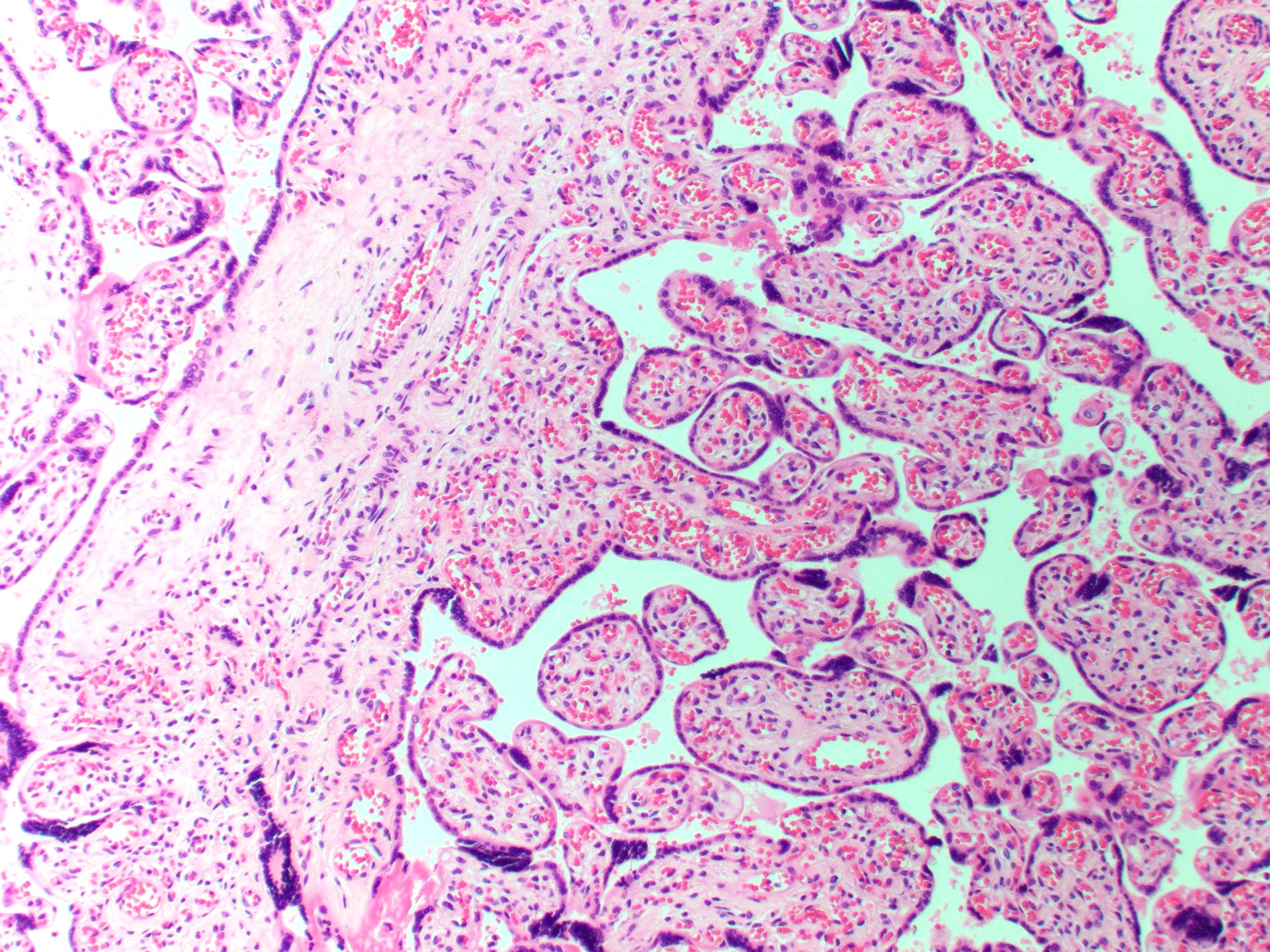
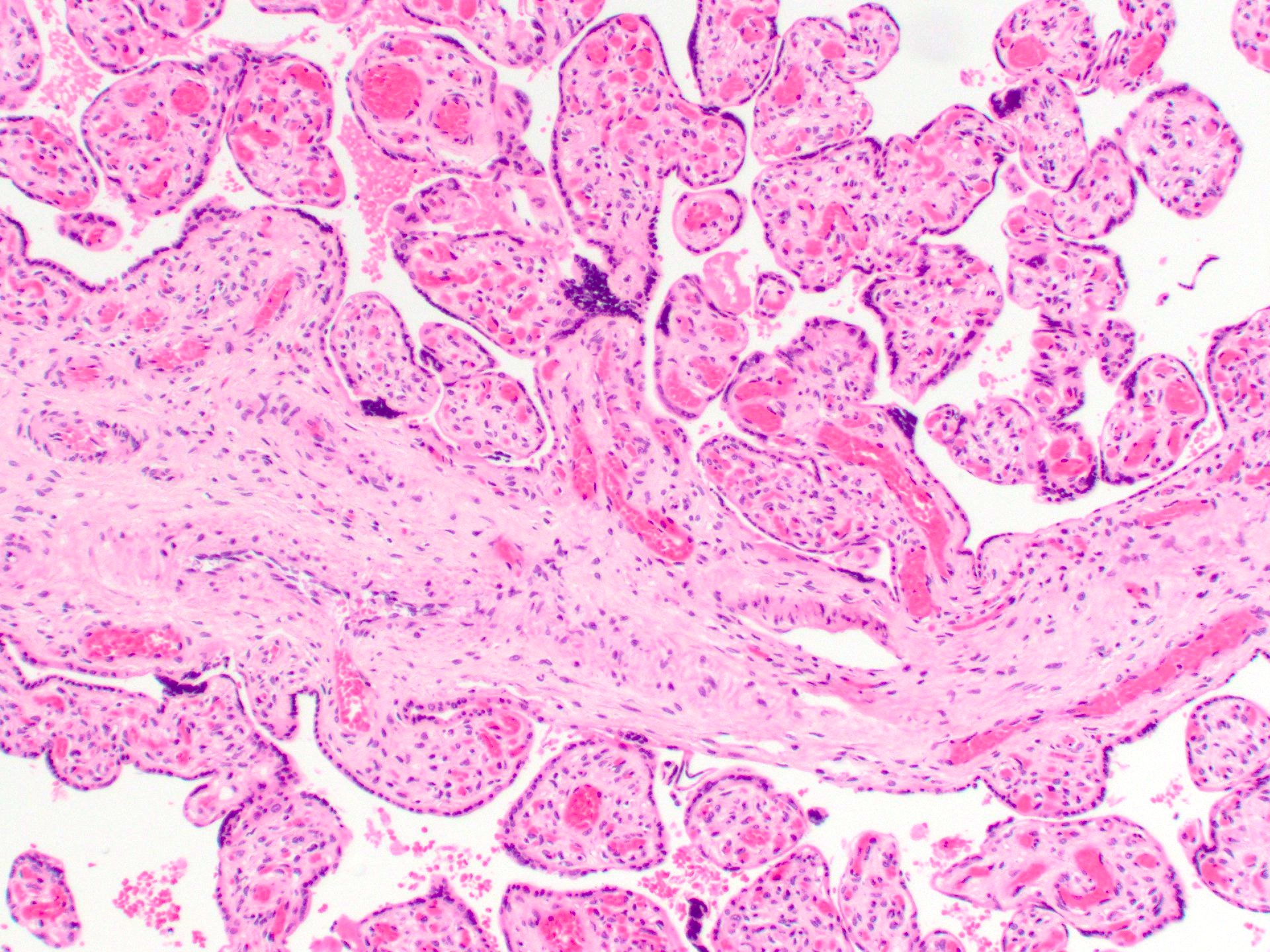
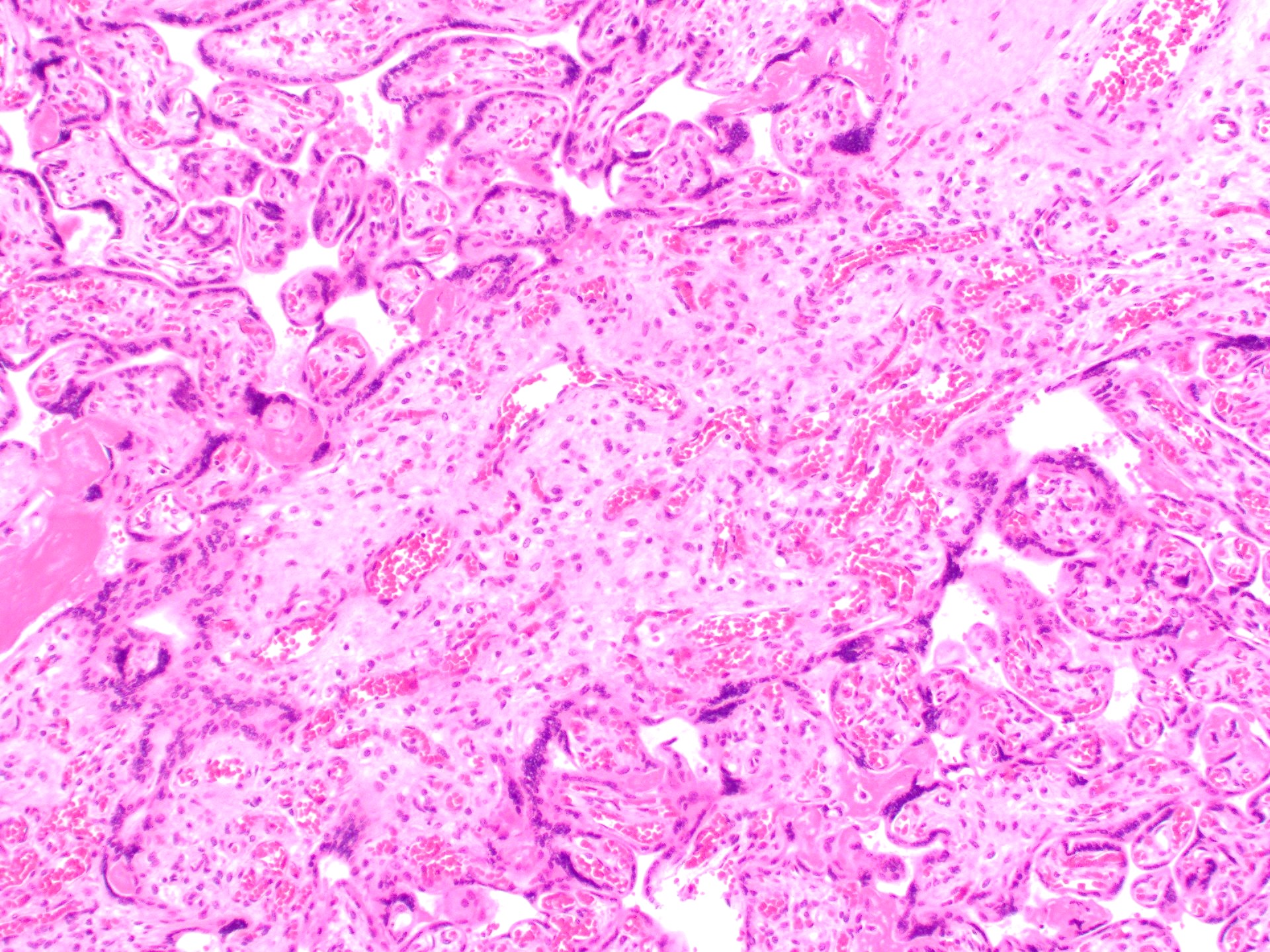
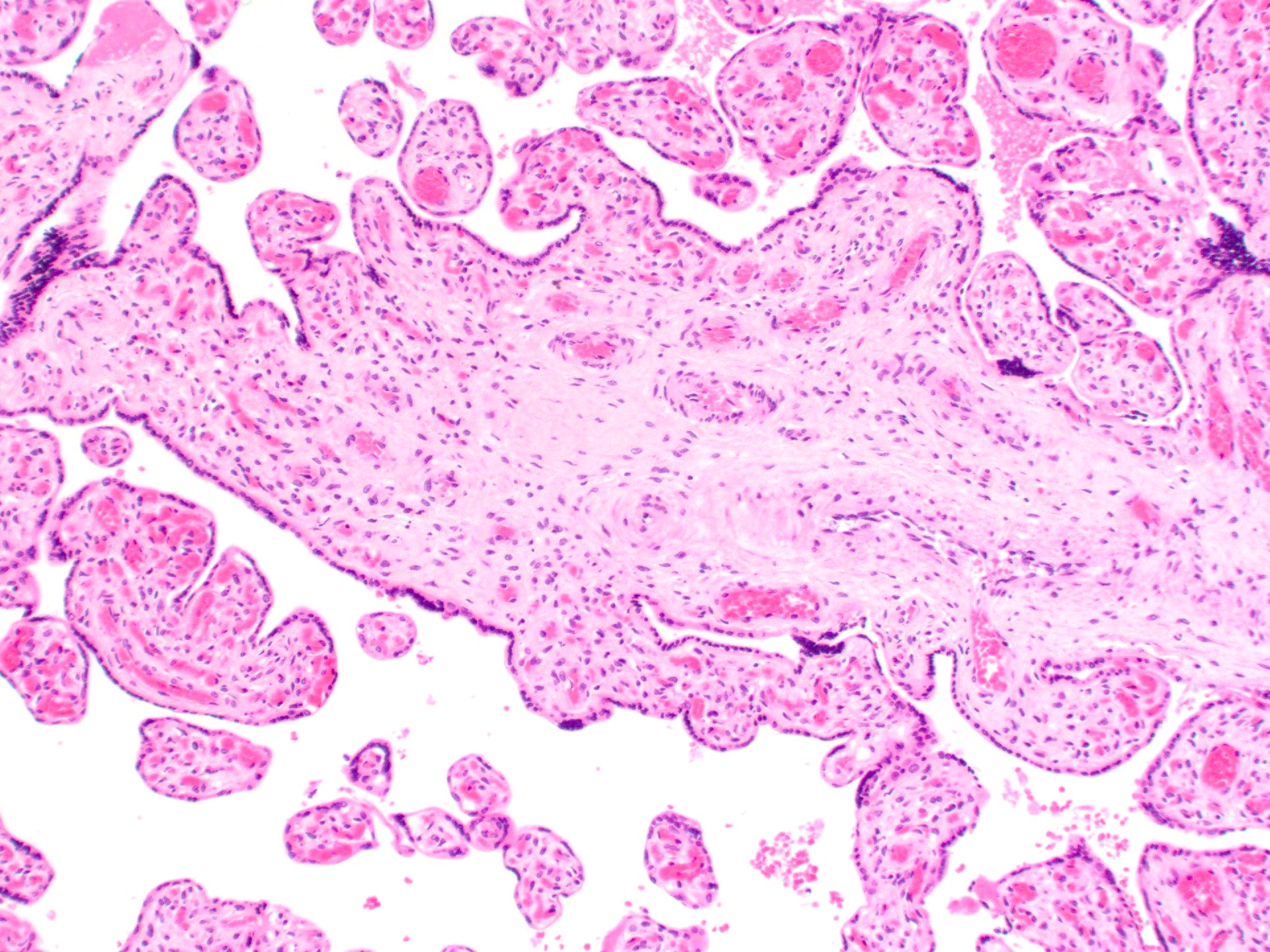
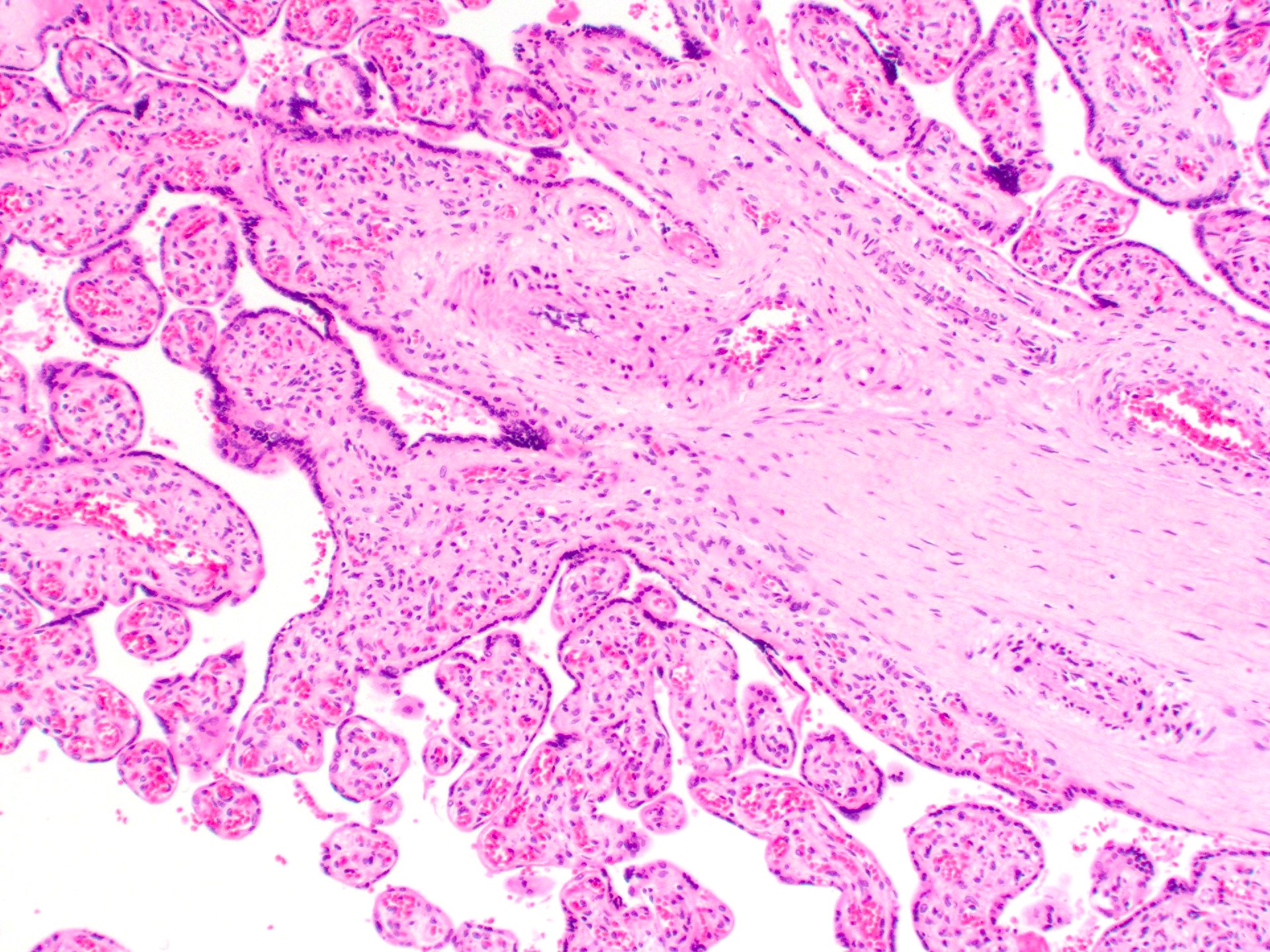
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Anastomosing vascular proliferation along the edges of stem vessels and immature intermediate villi comprised of capillaries surrounded by pericytes and small, muscularized arterioles
- Often with coexistent chorangiosis
- 2 subtypes
- Patchy: multiple foci occupying < 10x microscopic field
- Extensive: multiple, more diffuse foci with at least one > 4x microscopic field
- Reference: Hum Pathol 2000;31:945
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Placenta:
- Chorangiosis and multifocal chorangiomatosis
- Immature (early third trimester) placenta, 256 g
Differential diagnosis
- Chorangioma:
- Benign, well circumscribed, nodular capillary proliferation
- Localized chorangiomatosis:
- Chorangioma that has spread to involve several contiguous primary stem villi (wandering chorangioma)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following describes the lesion shown above?
- A capillary proliferation localized to a group of contiguous primary stem villi
- A localized capillary proliferation which when > 3 cm can result in polyhydramnios and intrauterine growth restriction
- Enlarged villi with irregular contours, increased stroma, trophoblast inclusions and irregularly distributed arterioles, venules and capillaries
- Foci of excessive capillary proliferation present at the edges of stem and intermediate villi that can be associated with advanced maternal age, preterm birth and multiparty
- Multifocal or diffuse increase in villous diameter with increased stromal cellularity and the presence of nonperipheral villous capillaries
Board review style answer #1
D. Foci of excessive capillary proliferation present at the edges of stem and intermediate villi that can be associated with advanced maternal age, preterm birth and multiparty. Answer A is incorrect because it describes localized chorangiomatosis (wandering chorangioma). Answer B is incorrect since it describes a giant chorangioma, which has a high prevalence of poor fetal outcomes related to polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth restriction, cardiomegaly, high output heart failure and fetal hydrops. Answer C is incorrect because it describes dysmorphic villi. Answer E is incorrect because it describes immature villi.
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangiomatosis
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangiomatosis
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about multifocal chorangiomatosis?
- Can be categorized as patchy or extensive
- Can be seen in placentas of mothers living at high altitudes
- Localized, nodular capillary proliferation
- Placentas are enlarged with segmentally abnormal proximal villi showing stromal overgrowth and vascular abnormalities affecting small and large villous vessels
Board review style answer #2
A. Can be categorized as patchy or extensive. Answer B is incorrect because it describes chorangiosis. Answer D is incorrect because it describes placental mesenchymal dysplasia. Answer C is incorrect because it describes chorangioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangiomatosis
Comment Here
Reference: Chorangiomatosis