Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Simon C. Amnion nodosum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentaamnionnodosum.html. Accessed January 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nodules of fetal skin, hair and fat found on the amnion
Essential features
- Deposition of fetal squames as nodules of surface of amnion
- Associated with severe prolonged oligohydramnios, anhydramnios
Terminology
- Vernix granuloma
Sites
- Amnion of the chorionic disc, placental membranes or umbilical cord
Pathophysiology
- From vernix that has been rubbed into defects of the amniotic surface
- Most likely first step is reactive amnionic epithelium due to decreased / absent amniotic fluid
- Vernix is then able to attach to the defect (Baergen: Benirschke's Pathology of the Human Placenta, 7th Edition, 2021)
Etiology
- Result of deficient amniotic fluid over a prolonged period of time
Clinical features
- Pregnancies complicated by severe oligohydramnios, including
- Cases of fetal renal agenesis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1829)
- Placenta of the donor twin ("suck twin") in twin to twin transfusion syndrome
- Cases of fetal sirenomelia (Arch Dis Child 1960;35:250)
Diagnosis
- Gross and histopathologic examination
Case reports
- Baby with bilateral renal agenesis and oligohydramnios (Proc R Soc Med 1958;51:512)
- 19 year old woman with no prenatal care who gave birth to a fetus with sirenomelia and renal agenesis (Arch Dis Child 1960;35:250)
- 33 year old woman with missed abortion and fetus with congenital ichthyosis (Am J Clin Pathol 1977;67:567)
Gross description
- Multiple firm, circumscribed, round to ovoid, raised, shiny, yellow nodules visible on the amniotic surface (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1829)
- 1 - 5 mm in diameter
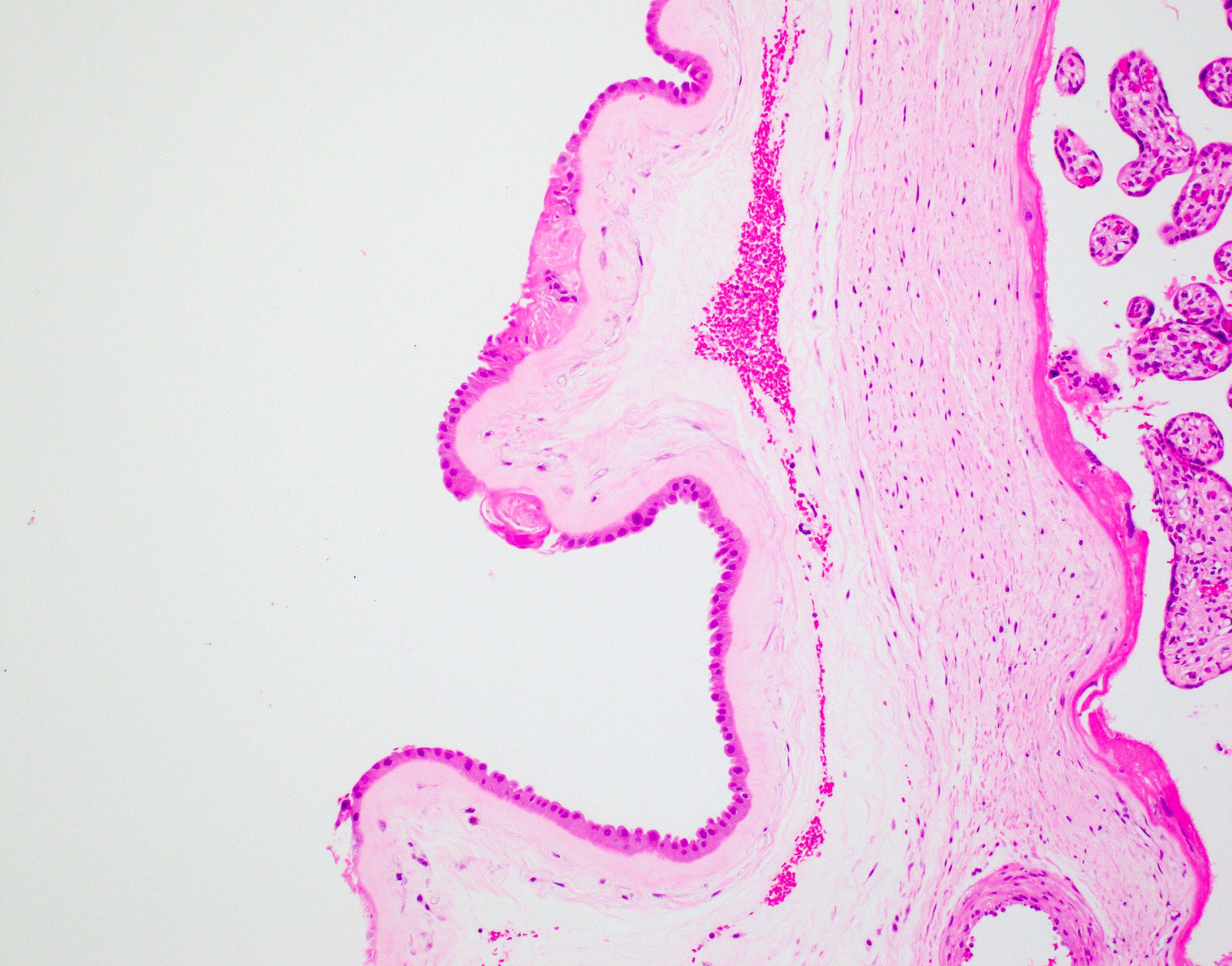
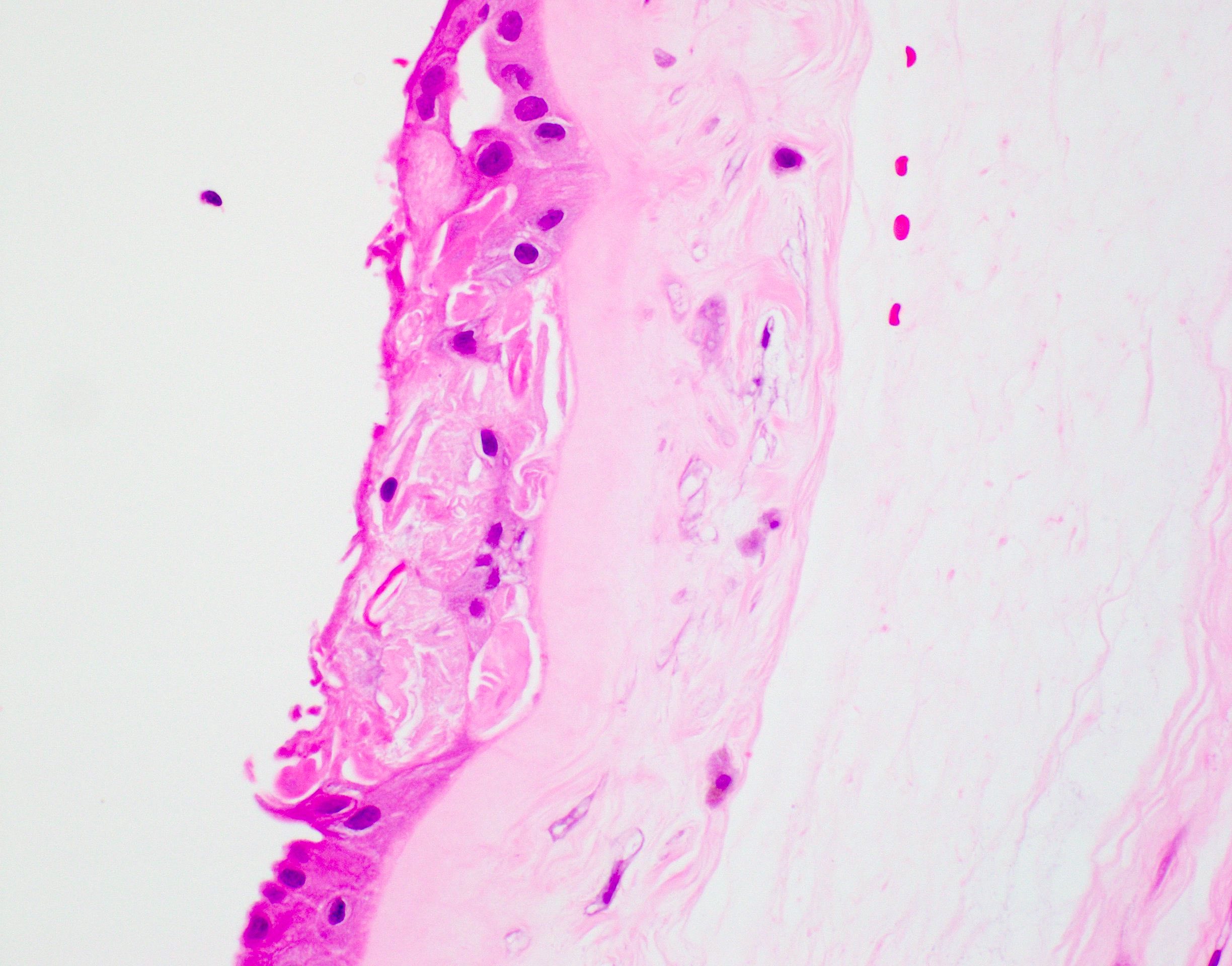
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Composed of varying proportions of squamous cells (occasionally keratinized), fat and hair embedded in degenerative amorphous acidophilic debris (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1829)
Positive stains
- Fetal skin cells within the amnion nodosum will stain positive for keratins
Electron microscopy description
- Nodules are composed mostly of closely packed bundles of fibrillary material of high electron density and cellular elements of various kinds (Arch Pathol 1974;98:39)
- Basement membrane of amnion epithelium is usually present under the nodules
Sample pathology report
- Placenta, delivered:
- Third trimester placenta 330 grams (tenth to twenty fifth percentile)
- Umbilical cord: unremarkable 3 vessel cord
- Fetal membranes and maternal decidua: amnion nodosum
- Placental disc: villous maturation appropriate for gestational age; intervillous thrombus
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous metaplasia:
- Grossly typically more plaque-like, patchy and hydrophobic
- Microscopically keratinizing metaplasia of the amnion
- Chorion nodosum (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2006;9:353):
- Similar nodules
- Develop on the chorion
- Associated with early amnion rupture / amniotic bands
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Amnion nodosum is most commonly associated with which congenital anomaly / malformation?
- Renal agenesis
- Tracheoesophageal fistula
- Trisomy 18
- Ventricular septal defect
Board review style answer #2