Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Chaux A, Cubilla AL. Pearly penile papules. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumpapglands.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign condition of 20 - 30% of normal young and middle aged males, asymptomatic
Terminology
- Also called hirsutoid papillomas, papillomatosis of glans corona
Epidemiology
- Prevalence of 38% in men < 25 years old and 11% in men > 50 years old (Int J STD AIDS 2009;20:768)
Etiology
- Hyperplastic, reactive
- Not related to HPV (J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;49:50)
Clinical features
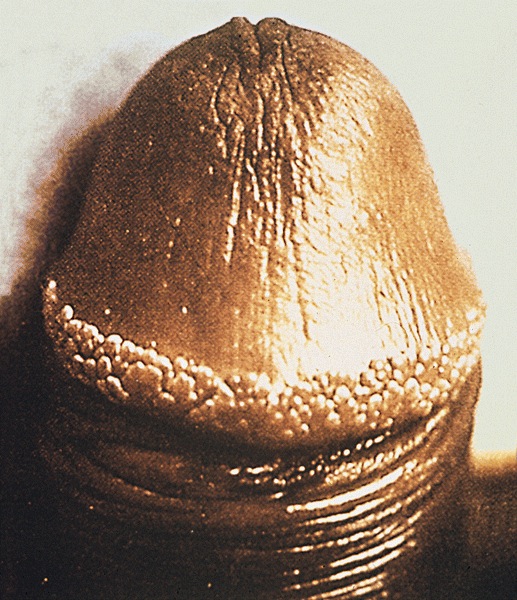
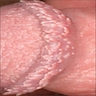
- Multiple pearly gray-white fibroepithelial papillomas, 1 - 2 mm and in dorsal glans corona
- Usually arranged in 2 - 3 rows
- Rarely covers most of glans
- Reduced prevalence in circumcised men
- Has been confused with Tyson glands, which don't exist in humans (Wikipedia: Preputial Gland [Accessed 2 April 2018])
Treatment
- None required; disappears with age; CO2 laser if patients request removal (Dermatol Surg 2002;28:617)
- Also cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, podophyllin or curettage
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
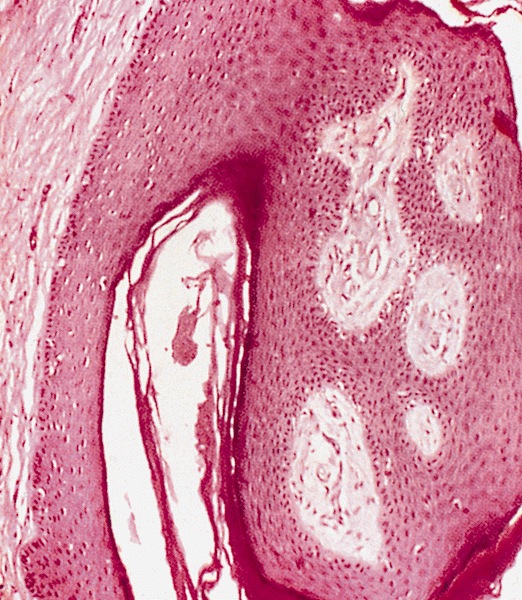
- Hyperkeratosis associated with a fibrovascular stroma, simulating an angiofibroma
- No koilocytosis, no significant inflammation
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Condyloma acuminatum: nonuniform, not arranged in rows and has HPV related changes
- Syphilis: ulcer with indurated and punched out base, marked plasmacytic inflammation and serologic evidence of syphilis