Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Etiology | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Electron microscopy imagesCite this page: Chaux A, Cubilla AL. Molluscum contagiosum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotummolluscum.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
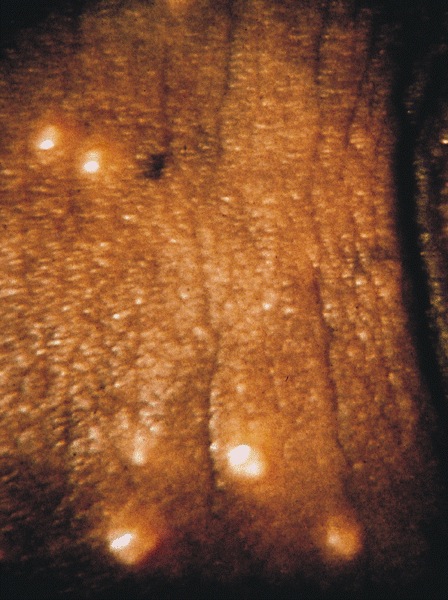
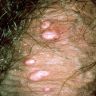
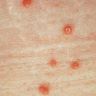
- Dome shaped papule with central umbilication, caused by DNA poxvirus called molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) (eMedicine: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 March 2018])
Sites
- In children ages 1 - 5 years, occurs commonly on almost all body sites, including trunk, arms and legs
- In adults, is considered a sexually transmitted disease, often due to MCV2 virus
Etiology
- Caused by DNA poxvirus, which only infects humans
- Spreads by skin to skin contact, autoinnoculation (spread to neighboring areas by touch), sexual transmission or by handling objects with the virus on them
Case reports
- 65 year old HIV+ man with genital lesions appearing after institution of HAART therapy, as part of the immune reconstitution syndrome (Dermatol Online J 2007;13:6)
Treatment
- Usually resolves within months in people with a normal immune system
- Virus lives only in lesions - once they are gone, patient is cured, unless reinfected
- Treatment is similar to that for warts - cryotherapy, acid, electrocautery, curetting or laser therapy; also topical trichloroacetic acid, cantharidin, retinoic acid or imiquimod
Clinical images
Gross description
- 3 - 6 mm dome shaped pearly painless papule with central umbilication
Microscopic (histologic) description
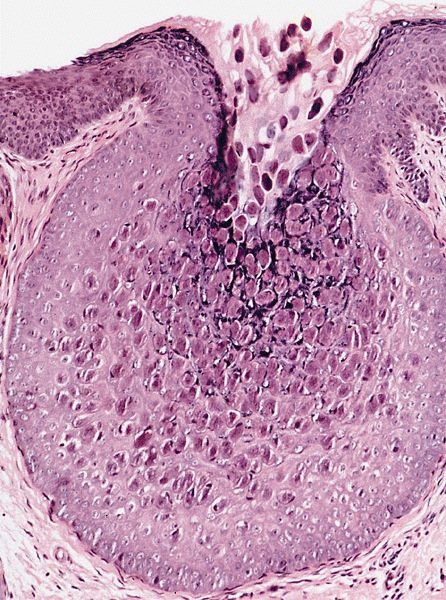
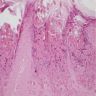
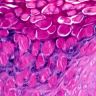
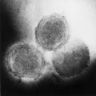
- Prominent Henderson-Patterson (molluscum) bodies (intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions containing virus particles) in keratinocytes of stratum spinosum and granulosum
- Epidermal lobular acanthosis with inverted epidermal hyperplasia
Microscopic (histologic) images