Table of Contents
Definition / general | Grossing - penectomy specimens | Grossing - circumcision | Features to report | Features to report by organization | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample gross description report | Diagrams / tables | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Hakim SW, Flood TA. Grossing & features to report. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumgrossingpenect.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- This topic describes how to gross specimens obtained from penectomy and partial penectomy procedures
- Essential clinical history: clinical diagnosis, procedure performed, prior biopsies
Grossing - penectomy specimens
- In the fresh state, cut the proximal resection margin en face
- 3 important areas of the resection margin need to sampled:
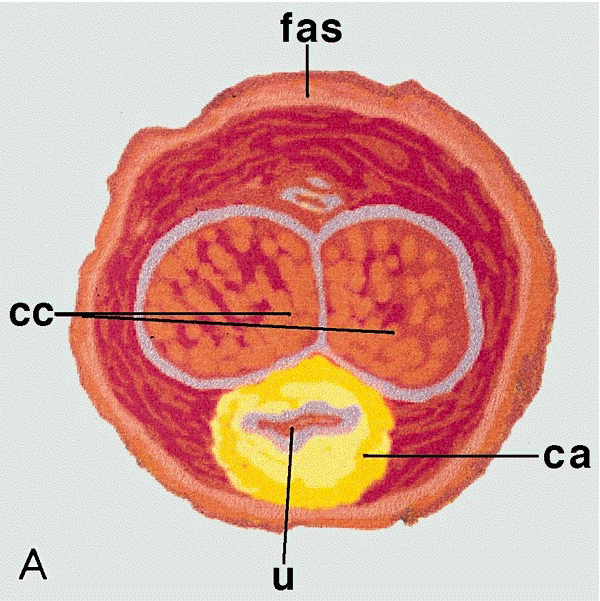
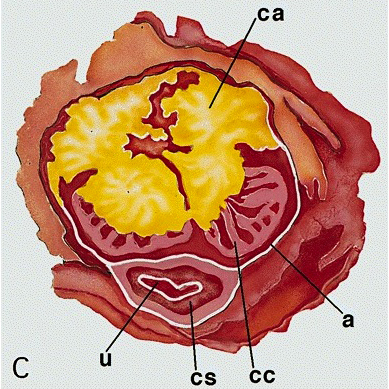
- Proximal urethra and surrounding periurethral cylinder composed of epithelium, subepithelial connective tissue (lamina propria), corpus spongiosum and penile fascia
- Urethra may be retracted but it is important to locate it and submit its circumference entirely
- Corpora cavernosa separated and surrounded by tunica albuginea and Buck fascia
- Skin of shaft with underlying corporal dartos
- Proximal urethra and surrounding periurethral cylinder composed of epithelium, subepithelial connective tissue (lamina propria), corpus spongiosum and penile fascia
- Fix the remaining specimen in 10% buffered formalin overnight
- After fixation, section the glans and shaft longitudinally (sagittally) in 2 halves, using the meatus and anterior urethra as a guide
- Do not probe the urethra as doing so can result in distortion of the urethral mucosa
- If foreskin is present:
- Measure its length and identify the presence / absence of phimosis
- If not affected by tumor, separate the foreskin, leaving a 3 mm margin from the coronal sulcus and include it as a circumcision specimen
- Do not remove foreskin if it is affected by tumor
- Document the tumor size, location, color, growth pattern and distance from resection margin
- Take a photograph of the specimen showing the maximum tumor depth of invasion
- Map the photograph according to sections submitted
- Section each half longitudinally along the specimen's longest axis, at 3 - 5 mm intervals
- Submit entirely the section which depicts the deepest anatomical level infiltrated by tumor
- If tumor affects multiple anatomical compartments, submit at least 3 sections of each compartment affected
- Sections should always attempt to include adjacent nontumoral mucosa
Grossing - circumcision
- Benign circumcision specimens:
- Sample with routine sections (1 - 2), including any grossly identified lesions / abnormalities
- Circumcision specimens containing tumor / suspicious for tumor:
- Lightly stretch and pin the specimen to cardboard / sheet of cork
- Fix in 10% buffered formalin overnight
- Measure and describe the specimen:
- Identify color and consistency
- Identify areas of flattening / thickening / induration
- Describe focal lesions, hemorrhage, exudates and edema
- Describe the tumor and its relation / distance to surgical resection margins
- Ink the mucosal and cutaneous margins of resection with different colors
- Take a photograph of the specimen
- Section the specimen transversally
- Map the photograph according to sections submitted, labeling each section in a clockwise fashion
- Submit the entire tumor and sample each surgical resection margin
- References: Eur Urol 2004;46:434, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1091, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:994
Features to report
- Features to report are according to the College of American Pathologists Cancer Protocols (CAP: Cancer Protocol Templates [Accessed 24 January 2023])
- Foreskin: presence and type (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:994)
- Uncircumcised
- Phimosis
- Circumcised
- Uncircumcised
- Number of lymph nodes examined and involved
- Specimen size
- Tumor site
- Glans
- Foreskin (mucosal surface or skin surface)
- Coronal sulcus
- Skin of shaft
- Penile urethra
- Tumor size (greatest dimension + additional dimensions)
- Tumor focality
- Unicentric
- Multicentric
- Macroscopic features
- Flat
- Ulcerated
- Polypoid
- Verruciform
- Necrosis
- Hemorrhage
- Tumor deep borders
- Pushing
- Infiltrative
- Anatomic level of involvement: macroscopic and microscopic
- Glans
- Involving subepithelial connective tissue (lamina propria)
- Involving corpus spongiosum
- Involving tunica albuginea
- Involving corpus cavernosum
- Involving distal (penile) urethra
- Foreskin
- Involving subepithelial connective tissue (lamina propria)
- Involving tunica albuginea
- Involving corpus cavernosum
- Involving distal (penile) urethra
- Shaft
- Involves skin
- Involves dartos
- Involves Buck fascia
- Involves corpus spongiosum
- Involves corpus cavernosum
- Involves proximal urethra
- Glans
- Gross assessment of surgical resection margins
- Tumor type (invasive, noninvasive, in situ)
- Histological type
- Benign and precursor squamous lesions
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Squamous cell carcinoma precursors, HPV associated
- Penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN), HPV associated
- Squamous cell tumors and precursors, HPV independent
- Differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN), HPV independent
- Invasive epithelial tumors of the penis and scrotum
- Invasive squamous epithelial tumors
- HPV associated squamous cell carcinoma
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
- Warty carcinoma
- Clear cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma
- Non-HPV associated squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma, usual type
- Verrucous (including carcinoma cuniculatum)
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma
- Sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma, NOS
- HPV associated squamous cell carcinoma
- Other epithelial tumors
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Paget disease, extramammary
- Other scrotal tumors
- Basal cell carcinoma of the scrotum
- Invasive squamous epithelial tumors
- Benign and precursor squamous lesions
- Histological grade
- Well differentiated (G1)
- Moderately differentiated (G2)
- Poorly differentiated (G3); % present (J Urol 2001;165:1138)
- Tumor thickness
- Lymphovascular invasion
- Perineural invasion
- Presence of associated lesions
- Squamous hyperplasia
- PeIN (differentiated, basaloid, warty, warty basaloid)
- Lichen sclerosus
- Depth of invasion (Mod Pathol 2001;14:963)
- From deepest malignant cell to highest overlying dermal papilla
- Note: if tumor replaces most of penis, measure tumor thickness from nonkeratinized tumor surface to the deepest point of invasion
- Prognostic index optional (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1049)
Features to report by organization
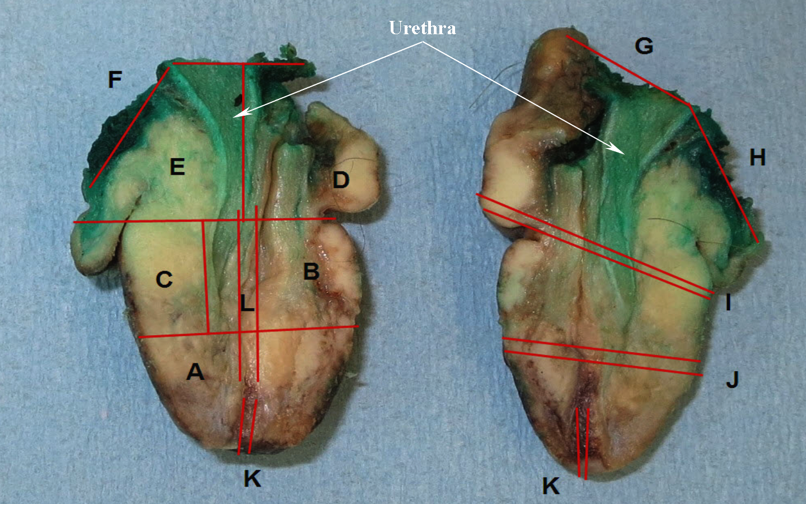
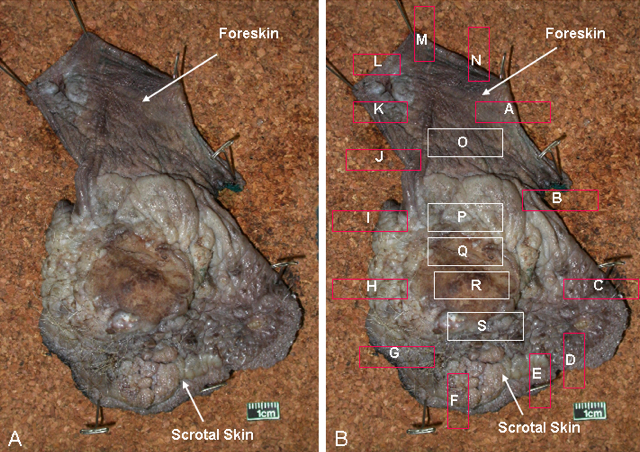
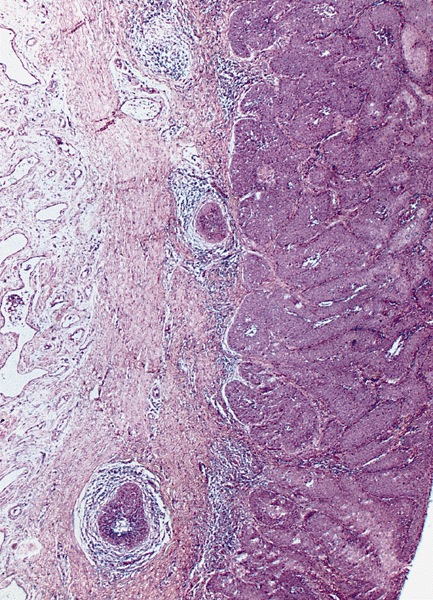
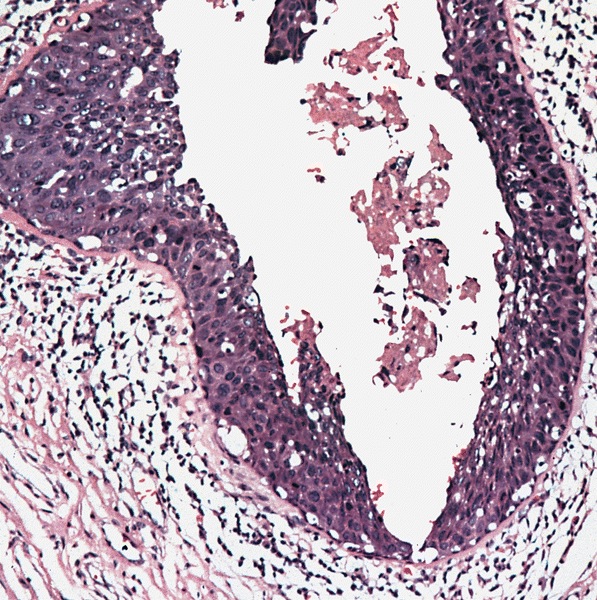
Gross images
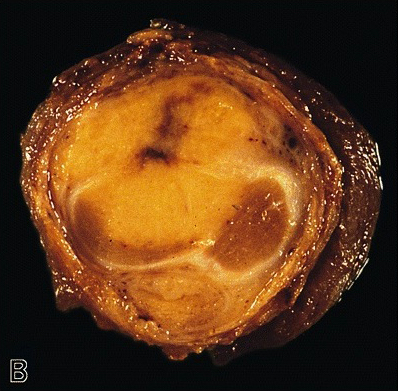
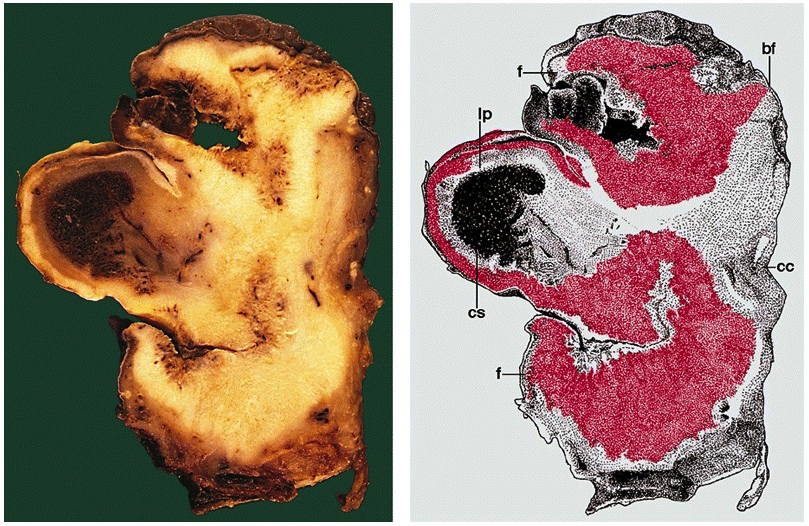
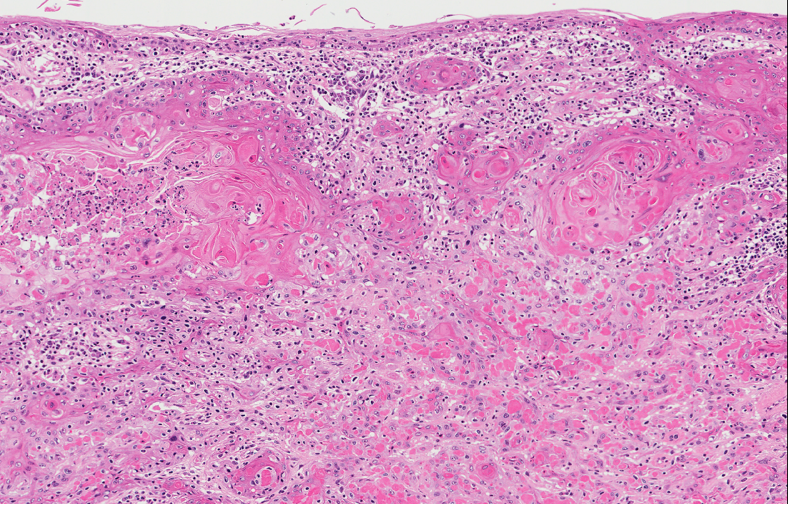
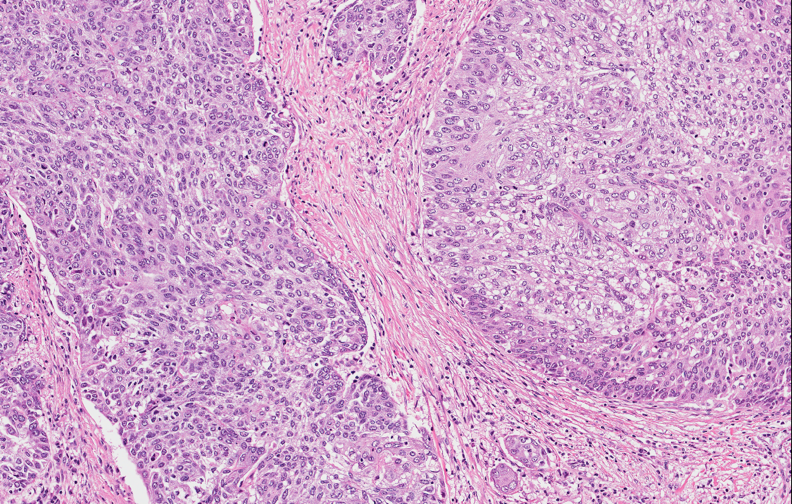
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample gross description report
- Specimen labeled as the requisition and with the matching Co-Path tag as penis consists of a portion of penis and measures 5.5 cm in length by up to 4.3 x 3.5 cm in diameter.
- On the skin surface, a white ulcerated / granular mass in distal portion measuring up to 3.8 cm in length and involves up to 70% of luminal circumference, which is 1.5 cm from the proximal resection margin.
- The margin is inked with silver nitrate, skin margin inked green. On longitudinal sectioning, the tumor partially involves the distal 2 cm of the corpus cavernosum and spongiosum.
- The proximal shaft / urethral is free of tumor.
- Macroscopic digital photos taken and representative sections are submitted as follows:
- B1 - B4: the entire longitudinal section of specimen including proximal resection margin, into 4 quadrants, in toto
- B5 - B6: the remainder of proximal resection margin bisected in toto, en face
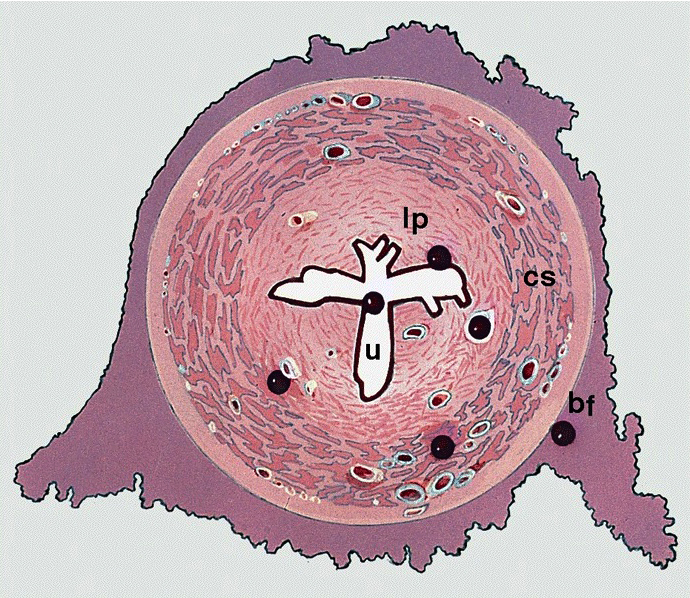
Diagrams / tables
Additional references
Board review style question #1
You are grossing a partial penectomy and note that the tumor affects multiple anatomical compartments. How would you approach gross evaluation of the specimen?
- Submit 2 - 3 representative sections per centimeter of specimen
- Submit at least 3 sections of each affected compartment
- Submit the section of the highest stage compartment
- Submit the specimen in toto
Board review style answer #1
B. Submit at least 3 sections of each affected compartment
Comment Here
Reference: Penis & scrotum - Grossing & features to report
Comment Here
Reference: Penis & scrotum - Grossing & features to report