Table of Contents
Aphallia | Chordae (chordee) | Concealed penis | Diphallia | Epispadias | Hypospadias | Clinical images | Lateral curvature | Median raphe cysts | Microscopic (histologic) images | Micropenis | Torsion | Webbed penisCite this page: Chaux A, Cubilla AL. Congenital anomalies. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumcongen.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Aphallia
- Agenesis of penis caused by failure in embryologic development of genital tubercle
- Very rare, incidence of 1 per 10 million male births; < 100 cases reported
- Associated with other GU abnormalities and with musculoskeletal and cardiopulmonary defects
- Can classify based on site of urethral meatus (J Urol 1989;141:589)
- Case reports: associated with urethrorectal fistula (Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2008;19:435), various anomalies (J Pediatr Surg 2010;45:E13)
Chordae (chordee)
- Fibrous band associated with hypospadias or epispadias that causes bending of penis
Concealed penis
- Also called hidden or buried penis
- Penis is normally developed but hidden under fat in suprapubic region, scrotum, perineum and thigh
- May be complication of circumcision
- In adults, surgical repair may be complicated (J Sex Med 2009;6:876)
Diphallia
- Duplication of penis
- Occurs in 1 per 5 million male births
- Associated with hypospadias, bifid scrotum, bladder duplication (Cir Pediatr 2008;21:235) and renal agenesis
Epispadias
- Urethra opens onto dorsal surface of penis
- Very rare, incidence of 1/300,000 male births
- Part of exstrophy-epispadias complex (Orphanet J Rare Dis 2009;4:23)
- Not related to hypospadias (has a different embryologic defect)
- Penopubic epispadias (opening in penopubic junction) is most common, associated with urinary incontinence
- Treatment is surgical
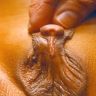
Hypospadias
- Most common congenital abnormality of male external genitalia other than cryptorchidism
- Urethra opens onto ventral surface of penis or scrotum
- 3 - 5/1000 live male births
- Due to failure of fusion of urethral folds; may be due to mutations in MAMLD1 (CXorf6) gene (Horm Res 2009;71:245)
- Urethral opening is usually near glans
- Hypospadias and epispadias are associated with abnormal descent of testes, urinary tract malformations, obstruction, urinary tract infections and possibly infertility if orifices are near base of penis
- Treatment is usually surgical unless hypospadias is minor (eMedicine: Hypospadias [Accessed 28 March 2018])
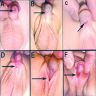
Classified by location of opening of meatus (see first clinical image below):
- A: anterior (inferior surface of glans)
- B: coronal (in balanopenile furrow)
- C: distal third of shaft
- D: penoscrotal (at base of shaft in front of scrotum)
- E: scrotal (on scrotum or between the genital swellings)
- F: perineal (behind scrotum or genital swellings)
Clinical images
Lateral curvature
- Due to hypo / hyperplasia of one corpora cavernosa
- Surgical treatment is often effective (J Urol 2008;179:1495)
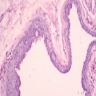
Median raphe cysts
- Relatively common
- Due to anomalies in development of urethral groove, trapped epithelial cells or migration of epithelial cells after closure of genital folds
- Usually in foreskin or glans; may also be present in frenulum
- Lined by squamous, columnar, mucus producing, apocrine-like or distal urethra type epithelium
- Case report: 43 year old man with an asymptomatic nodule on glans (Dermatol Online J 2005;11:37)
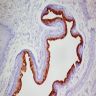
Microscopic (histologic) images
Micropenis
- Penis small but normal ratio of shaft length to circumference
- Defined as stretched length < 2.5 standard deviations below mean for age (Wikipedia: Micropenis [Accessed 28 March 2018], eMedicine: Microphallus [Accessed 28 March 2018])
- Usually associated with endocrine abnormalities (insufficient androgen stimulation during embryologic growth of external genitalia, Arch Dis Child 1991;66:1033)
Torsion
- Fibrous tissue surrounding corpus spongiosum or short urethra causes rotational defect of penile shaft
- Isolated neonatal torsion occurs in 27%, usually to left (J Pediatr Urol 2007;3:495)
- Can be surgically corrected in adults, although patients often tolerate it without complaint (J Sex Med 2008;5:735)
Webbed penis
- Scrotal skin extends to ventral portion of penis and hides it