Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chellappan R, Leal SM. Balamuthia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/parasitologybalamuthia.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Taxonomy: genera Balamuthia, family Balamuthiidae
- Single celled, free living amoeba discovered from brain tissue fragments of a mandrill baboon (old world monkey) that died from a neurological condition at San Diego Zoo Wild Animal Park in California in 1986 (Clin Microbiol Rev 2008;21:435)
- Rare cause of chronic granulomatous amebic encephalitis, disseminated disease or skin lesions in immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals
- Enters nasal passages or ulcerated broken skin
- Hematogenous dissemination to the central nervous system (CNS)
- Similar disease spectrum as Acanthamoeba
Essential features
- 2 stage life cycle (Trop Parasitol 2015;5:15)
- Trophozoite: 12 - 60 μm in diameter, infective, pleomorphic, uninucleated / binucleated, with 1 - 3 nucleoli (helps differentiate from Acanthamoeba) and long, slender pseudopodia
- Cyst: 6 - 30 μm, dormant round cells that form under harsh conditions; double walled with wrinkled fibrous outer wall (exocyst); 1 or 2 nuclei
Epidemiology
- Isolated from soil, dust, fresh water
- Human exposure is common but infection is rare
- > 100 confirmed cases in the U.S.; > 200 worldwide (CDC: Parasites - Balamuthia mandrillaris - Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE) - General Information [Accessed 15 December 2022])
- Given the difficulty of diagnosing infection, many undiagnosed infections are suspected
- Cases in the Southwestern U.S. and Latin America (Peru), with limited cases in Asia, Australia and Europe, have involved the development of facial skin lesions
- Increased risk in Hispanic ethnicity and immunocompromised conditions: diabetes, HIV / AIDS, solid organ transplant, liver cirrhosis, renal failure and cancer (Clin Infect Dis 2019;68:1815)
Sites
- Skin, brain, spinal cord
Pathophysiology
- Entry via nasal passages or broken skin; rarely organ donation with dissemination to the CNS (Trop Parasitol 2015;5:15)
- It is transmitted on contact with skin wounds and cuts or when dust containing the parasite is breathed (e.g., during gardening)
- Organisms are difficult to eradicate with tropism to blood vessels
- Initial acute inflammatory response develops into chronic granulomatous inflammation with persistent perivascular ameba involving CD4 and CD8 T cells, epithelioid histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells
- In immunocompromised patients, granulomas may or may not be present
Clinical features
- Skin:
- Involvement of face, palate, extremities and trunk (Clin Infect Dis 2019;68:1815)
- Single or disseminated chronic plaque-like ulcerated skin lesion; may be mistaken for chronic fungal or mycobacterial infection and progress to CNS disease
- CNS:
- Granulomatous amebic encephalitis:
- Indolent progression initially over weeks to months
- Usually fatal with 90% mortality
- Hematogenous spread from skin or nasal passages (Clin Infect Dis 2019;68:1815)
- Meningoencephalitis: fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, lethargy with neurological deficits including ataxia, impaired speech, focal deficit and seizures
- Granulomatous amebic encephalitis:
Diagnosis
- Identification of cysts or trophozoites in brain or skin biopsy
Laboratory
- Skin:
- Biopsy and microscopic evaluation of formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue
- Direct microscopic examination with Calcofluor white dye
- RT-PCR on fresh tissue is required for definitive diagnosis
- CNS:
- Cerebrospinal fluid (BMC Microbiol 2008;8:210)
- High lymphocytes, low glucose, high protein
- Extremely rare to identify amebae on cerebrospinal fluid
- Biopsy and microscopic evaluation of FFPE tissue
- RT-PCR on fresh tissue or cerebrospinal fluid required for definitive diagnosis
- In the U.S., the CDC offers RT-PCR for B. mandrillaris and morphologic mimics Naegleria fowleri and Acanthamoeba species
- Negative cerebrospinal fluid RT-PCR result does not rule out intraparenchymal brain infection
- Cerebrospinal fluid (BMC Microbiol 2008;8:210)
- CDC ID pathology branch offers immunohistochemical staining
- Antibodies in serum
- Indirect immunofluorescence assay (CDC: Parasites - Balamuthia mandrillaris - Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE) - Diagnosis & Detection [Accessed 15 December 2022])
- Culture requires special media and is not available in clinical labs
Case reports
- 3 year old girl with B. madrillaris granulomatous amebic encephalitis (Am J Trop Med Hyg 2021;104:1836)
- 52 year old woman diagnosed with B. mandrillaris showing unusual lab and radiological findings (Arch Neurol 2000;57:1210)
- 72 year old immunocompetent woman with Balamuthia encephalitis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:466)
Treatment
- Miltefosine in combination with drugs such as flucytosine, pentamidine, fluconazole, sulfadiazine and either azithromycin / clarithromycin (Clin Infect Dis 2010;51:e7)
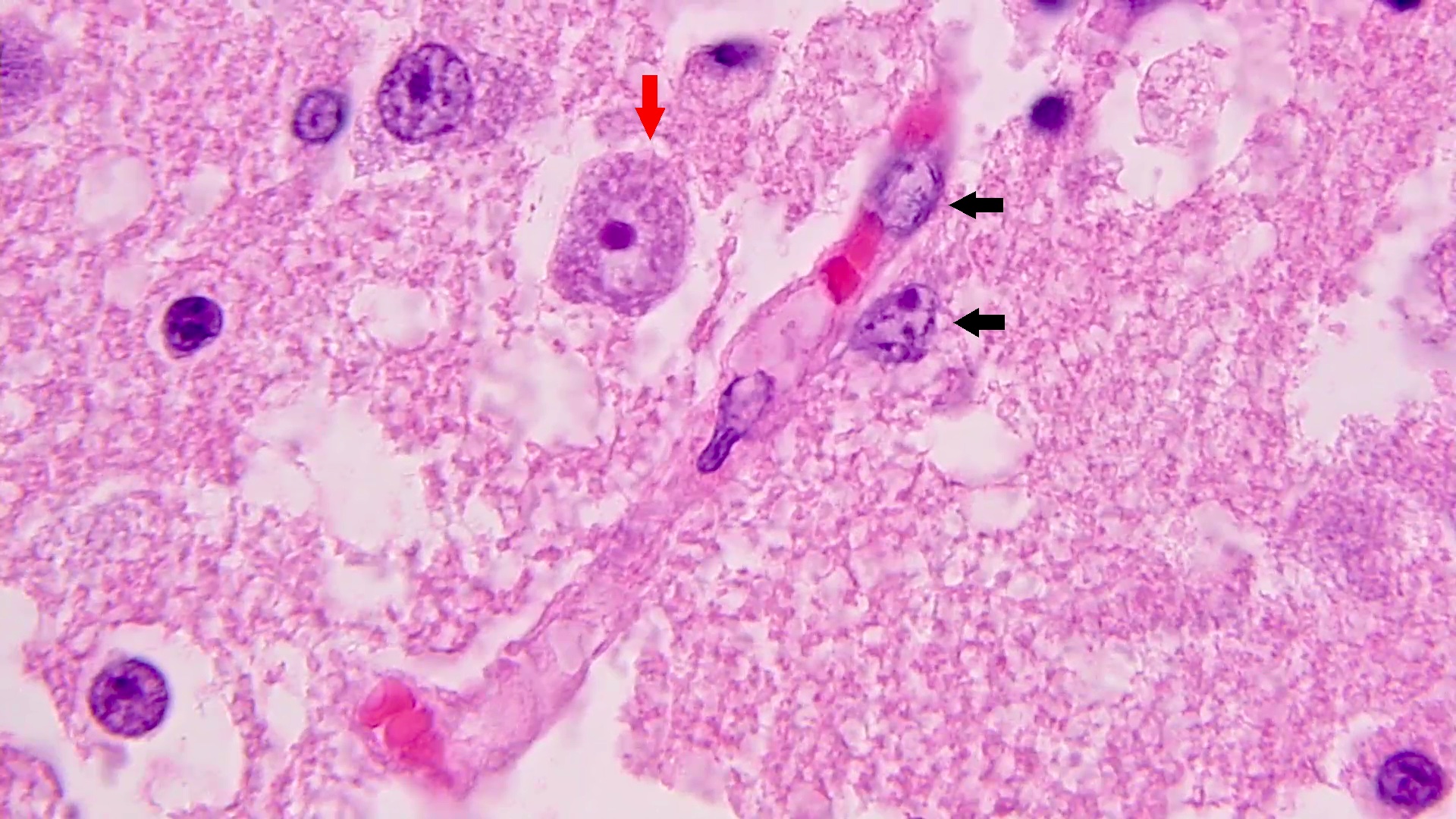
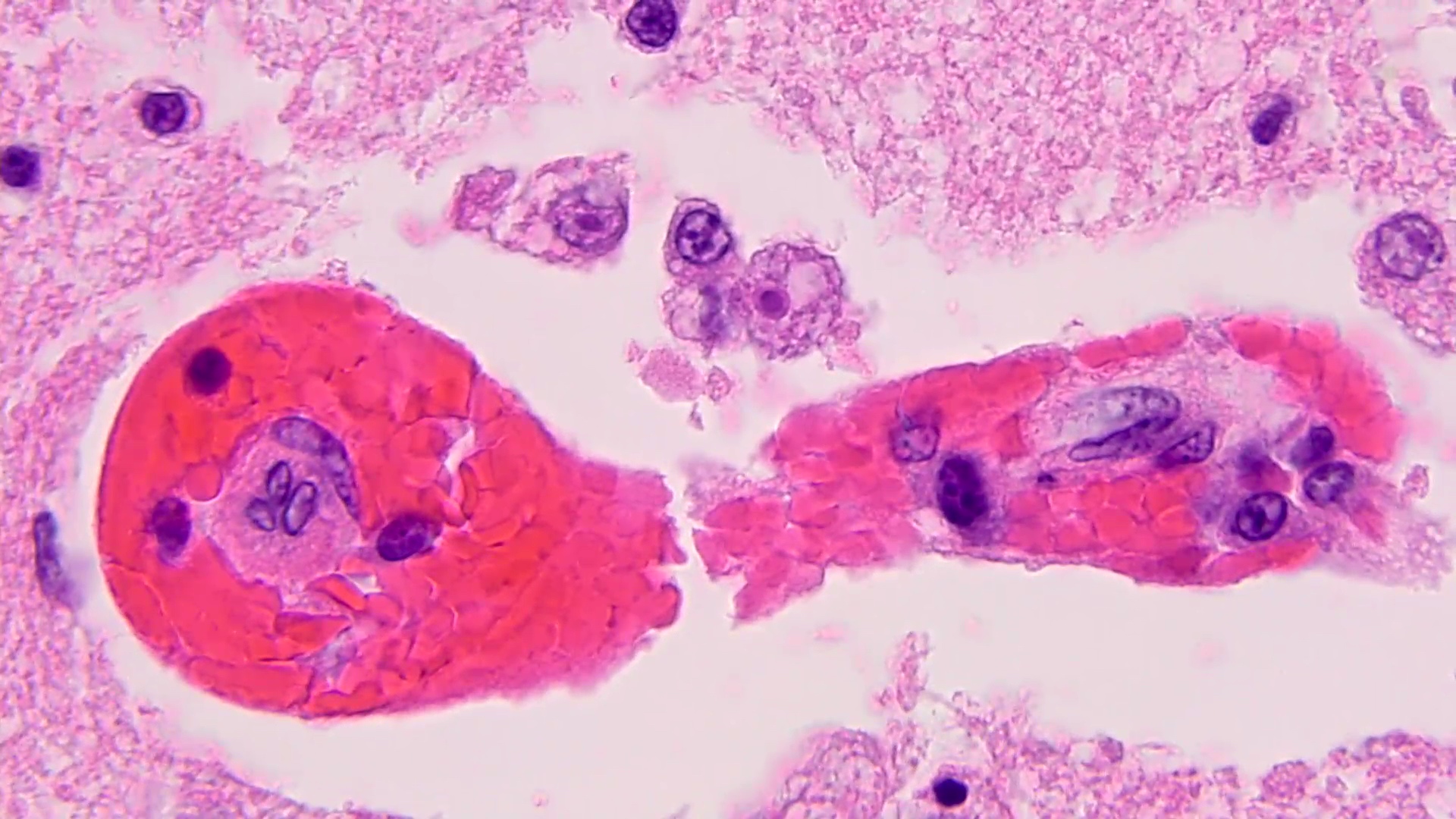
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Chronic granulomatous inflammation with cysts or trophozoites surrounding blood vessels
- Cysts have 2 walls: wrinkled fibrous outer exocyst and inner endocyst and appear hexagonal, spherical or star shaped
- Refractive granules may be present in the inner wall with no pores
- May be uninucleate / binucleate
- Trophozoites are pleomorphic with long pseudopodia
- May be uninucleate / binucleate with multiple nucleoli in infected tissue
- Reference: Trop Parasitol 2015;5:15
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Tuberculosis:
- Acid fast bacilli within granulomatous inflammation
- Acanthamoeba:
- Inner wall (endocyst) with hexagonal, spherical, star shaped or polygonal morphology
- Molecular identification often necessary for definitive distinction
- Naegleria:
- Acute illness and inflammation are predominant
- Cysts do not form in human tissues
- Granular cytoplasm with many vacuoles, single large nucleus and dense karyosome with no margination
- Sappinia pedata:
- Binucleated trophozoites and cysts
- Only 1 reported case in Texas (JAMA 2001;285:2450)
- Neurocysticercosis:
- Cysticerci present
- Pathognomonic calcaneous corpuscles within cestode tissue
- Histoplasma:
- Intracellular, uniformly sized, oval to round budding yeasts
- Mold infection:
- Infiltrating hyphae
- Aspergillus and neurotropic dematiaceous molds
- Reference: Emerg Microbes Infect 2020;9:1379
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 13 year old girl presented with a 1 year history of a cutaneous skin lesion and recent onset of dizziness, blurry vision, diplopia and worsening headaches. Brain CT showed hypodense regions in the left lateral ventricle and a brain biopsy revealed granulomatous inflammation and the perivascular organisms shown above. What microscopic features can be used to distinguish this organism from Acanthamoeba species?
- Endocyst structure
- Exocyst structure
- Multiple nucleoli
- Vacuolated cytoplasm
Board review style answer #1
A. Endocyst structure. Balamuthia mandrillaris resembles Acanthamoeba and may require molecular identification for definitive identification in granulomatous CNS lesions. However, the inner wall (endocyst) of Acanthamoeba may exhibit hexagonal, spherical, star shaped or polygonal morphology that distinguishes it from the more uniform endocyst of Balamuthia species.
Comment Here
Reference: Balamuthia
Comment Here
Reference: Balamuthia
Board review style question #2
A 58 year old man presented with 2 month history of sporadic headaches that have increased in frequency. Fundoscopy showed bilateral papilledema and retinal hemorrhages. Brain CT showed a hypodense lesion in right temporal lobe. It was suspected to be brain tumor and resected. Amebic trophozoites were identified. What test can confirm the diagnosis?
- Cerebrospinal fluid microscopy
- Culture on agar
- Real time (RT) PCR
- Serology
Board review style answer #2
C. Real time PCR can detect up to a single organism per reaction and distinguish between Acanthamoeba, Balamuthia and Naegleria. PCR on fresh tissue is optimal. PCR on cerebrospinal fluid can be helpful to render the diagnosis but does not rule out intraparenchymal infection if negative.
Comment Here
Reference: Balamuthia
Comment Here
Reference: Balamuthia