Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Kitson A, Shi J. Simple mucinous cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasmucnoncyst.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mucinous pancreatic cyst with minimal cytologic atypia, grossly > 1 cm, lined by single layer of gastric type flat epithelium without ovarian type stroma
Essential features
- Unilocular or multilocular mucinous cyst (> 1 cm) with single layer of columnar or cuboidal cells and low grade dysplasia
- Paucicellular fibrotic wall with no ovarian type stroma or lymphoid band
- Cyst rarely communicates with pancreatic duct
- High cyst fluid CEA, low amylase
- KRAS and KMT2C mutations in a subset of cases
- Follows benign clinical course, no reported progression to carcinoma
Terminology
- Also called mucinous nonneoplastic cyst, first proposed by Kosmahl et al. in 2002 (Mod Pathol 2002;15:154)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K86.2 - cyst of pancreas
Epidemiology
- 2 - 3.4% of pancreatic resections, 2.2 - 6.7% of pancreatic cyst resections and 7.6 - 10.3% of pancreatic mucinous cyst resections (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- Mean age: 64 (range, 20 - 88) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
- More common in females, F:M = 2.8:1 to 4:1 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
Sites
- Body, tail (53 - 69%)
- Head, neck, uncinate (31 - 47%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic or incidental (41 - 49%), abdominal pain (34 - 44%), jaundice (4 - 7%), back pain (11%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Size: 1 - 12 cm (mean 2.5 cm) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
Diagnosis
- CT or MRI of abdomen
- EUS with FNA or biopsy
- Cyst fluid analysis
- Cytology
- Surgical specimen (StatPearls: Pacreatic Cysts [Accessed 8 June 2020])
Laboratory
- Cyst fluid: often elevated CEA, mean 6,797 ng/mL (range, 11 - 64,000 ng/mL) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Low amylase (unless connected to duct)
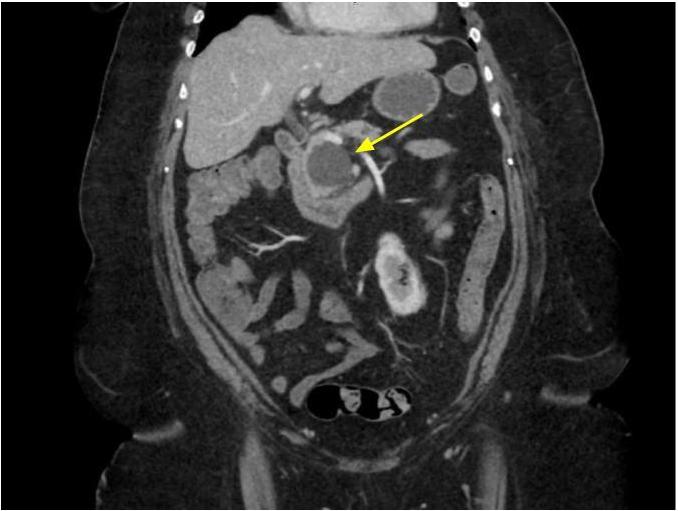
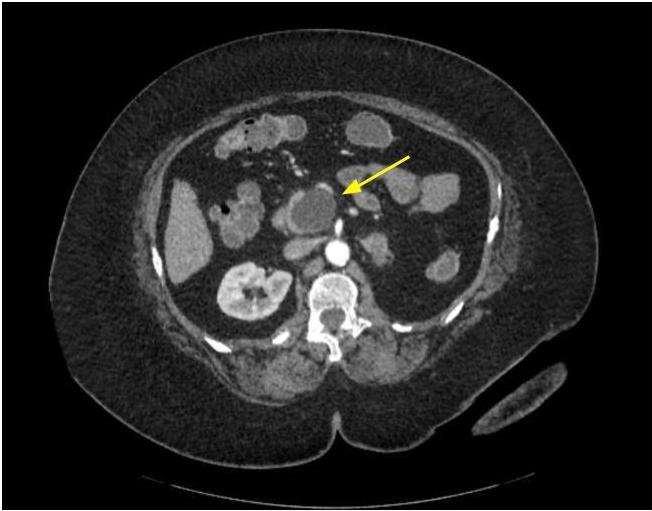
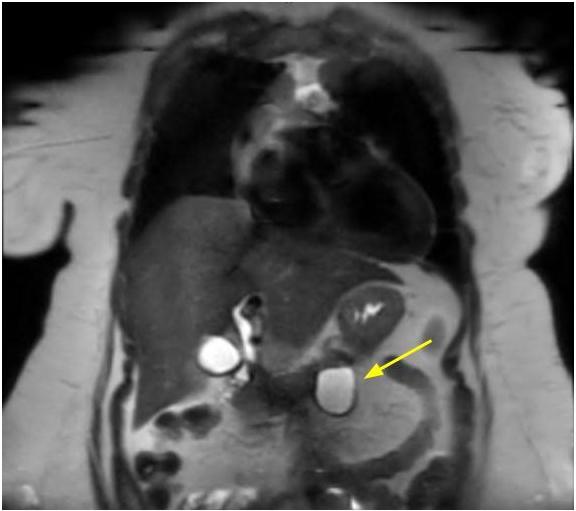
Radiology description
- CT / MRI:
- Unilocular (55 - 59%), multilocular or septated (41 - 45%)
- Rare communication with pancreatic duct (3 - 7%) or mural nodule (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Upstream main pancreatic duct dilatation (Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017;42:2827)
- Low signal intensity of cyst fluid on T1 weighted, high on T2 weighted and low on diffusion weighted
- Most with thin cyst wall but can have cyst wall enhancement
- EUS:
- Septate in 26.3%, solid component in 10.5%, possible communication with pancreatic duct in 21% (Pancreas 2012;41:813)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Overall benign behavior with no recurrence or malignant transformation (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1730, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330)
Case reports
- 52 year old man with hematochezia and active bleeding from ampulla (Korean J Gastroenterol 2017;70:301)
- 71 year old woman with a cystic tumor in the body of the pancreas (World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:2045)
- 75 year old man with pancreatic cyst (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:264)
Treatment
- Often treated with surgical resection due to preoperative imaging indistinguishable from other mucinous neoplasms
- Surveillance
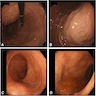
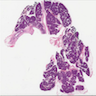
Clinical images
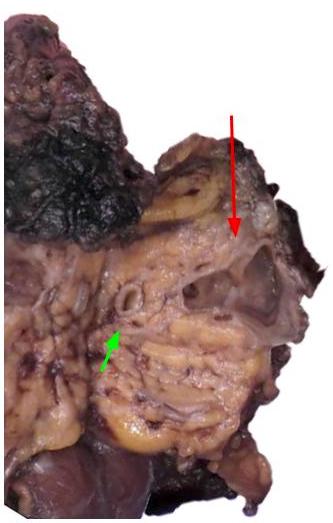
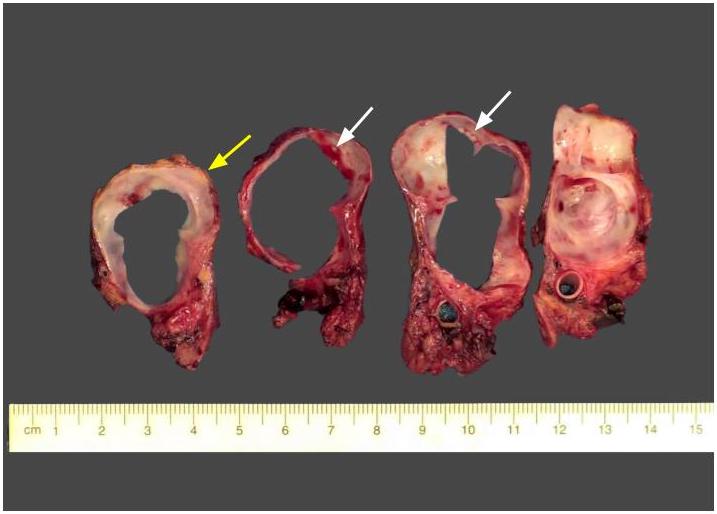
Gross description
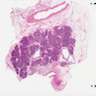
- Unilocular or multilocular cyst, mean size 2.5 cm, range 1.0 - 12 cm (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- No or rare communication with pancreatic duct (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Usually clear or serous fluid, ~33% with mucinous fluid, rarely serosanguinous or brown-green thick fluid (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
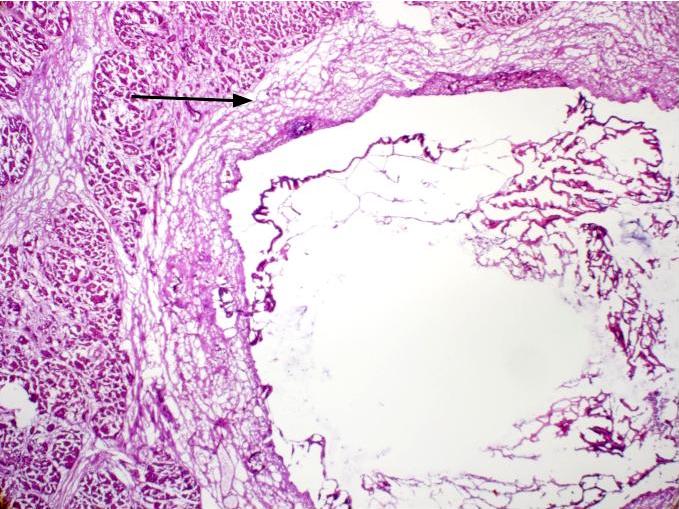
- Smooth cyst lining, no or minimal focal papillary excrescences (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Submit entire lining (or extensive sampling if large cyst) to rule out high grade dysplasia or invasive carcinoma
Gross images
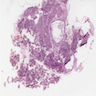
Frozen section description
- > 1 cm unilocular or multilocular cyst
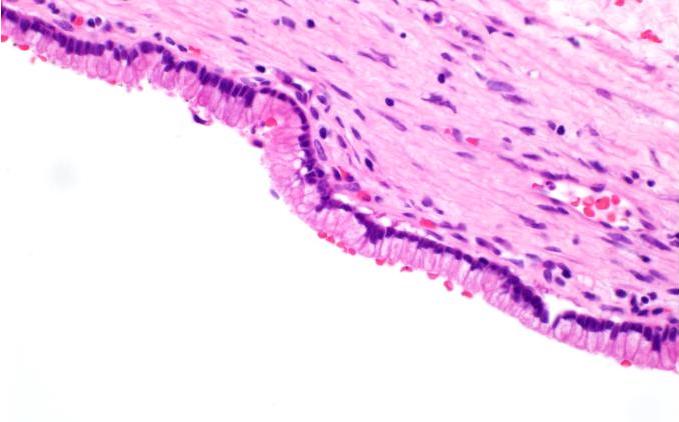
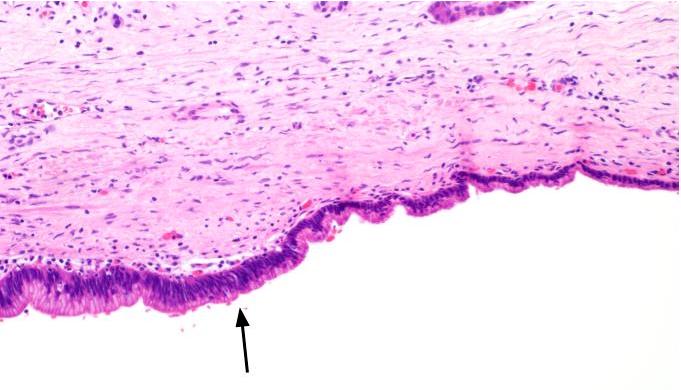
- Flat gastric type mucinous epithelium
- No significant atypia
- No ovarian type stroma
Frozen section images
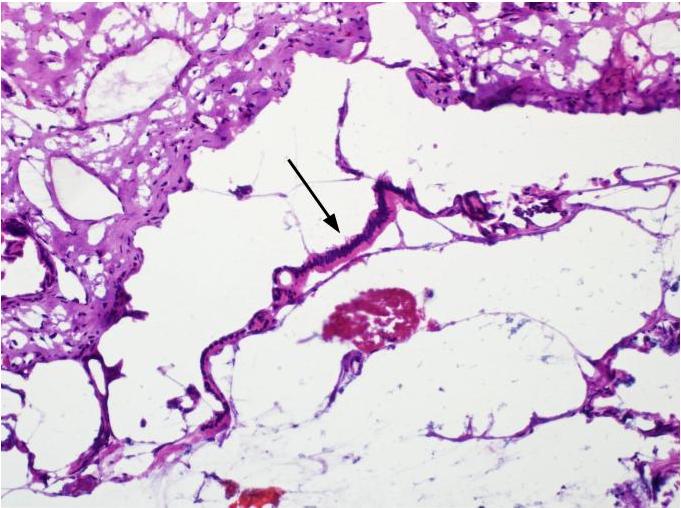
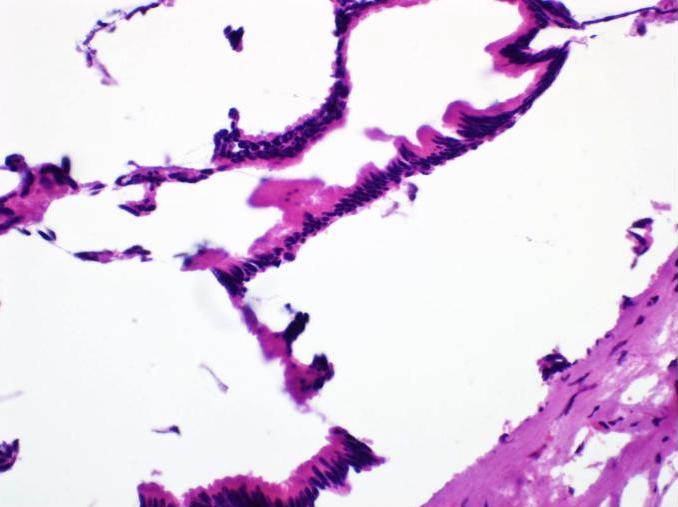
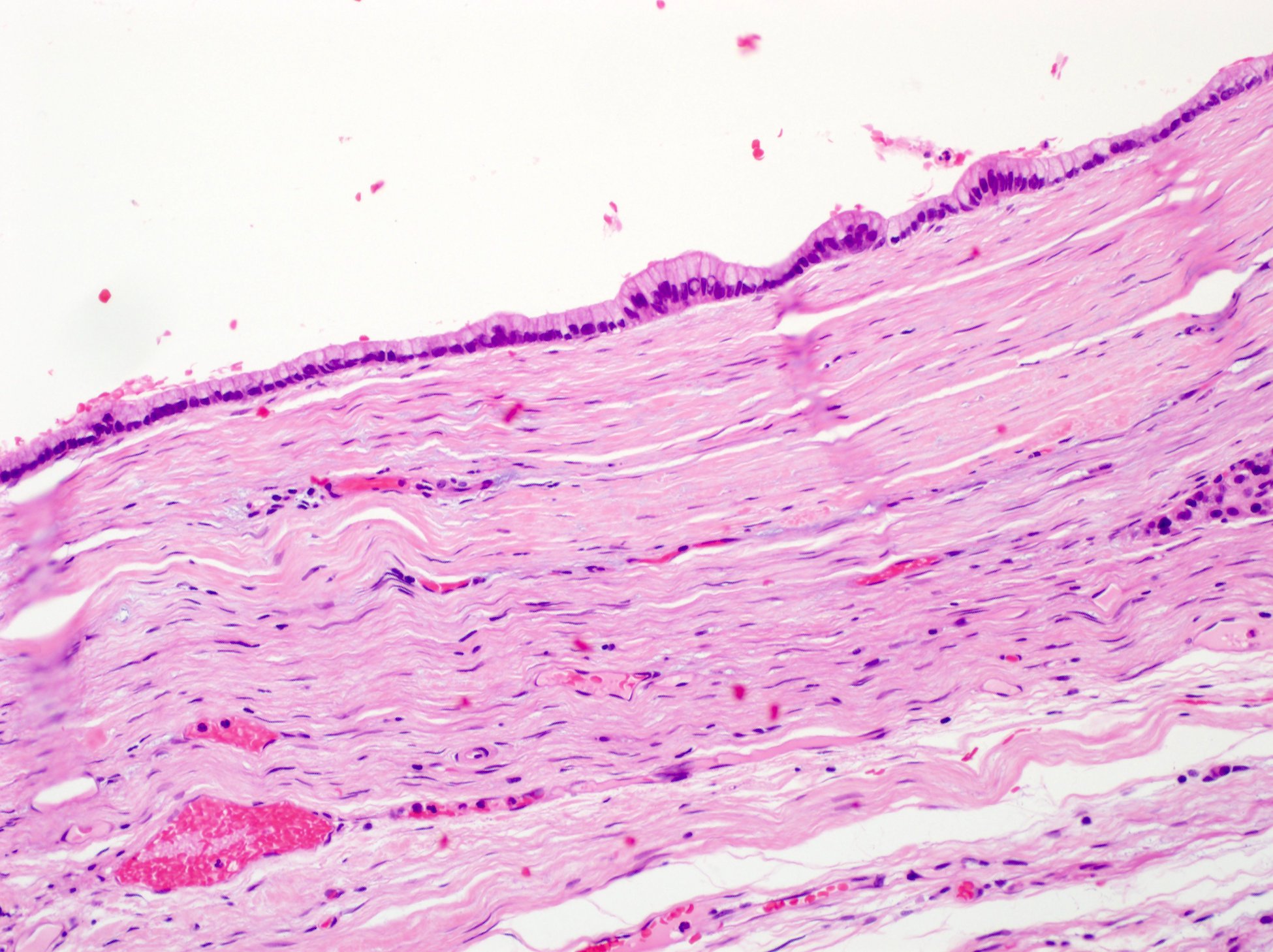
Microscopic (histologic) description
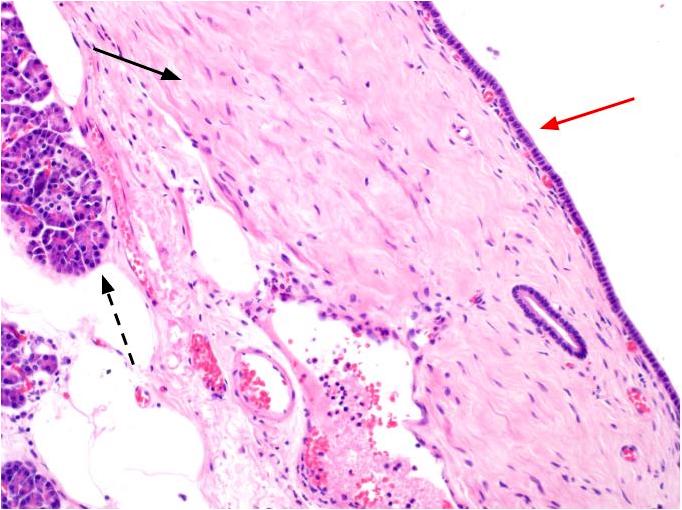
- Flat monolayer of columnar mucinous epithelium or attenuated cuboidal epithelial cells, often resembling gastric type mucinous epithelium (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Low grade dysplasia, which may mimic low grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN)
- Focal high grade dysplasia in 8% cases in one study (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- No or minimal papillary architecture (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Paucicellular fibrotic wall with no ovarian type stroma or lymphoid band (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Degenerative changes in cyst wall common:
- Hyalinization, myxoid stroma, hemorrhage, calcifications, macrophage clusters, granulation-like tissue (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
- Flat honeycomb sheets / nests of cuboidal or columnar cells without significant atypia (100%) (Pancreas 2013;42:27, Pancreas 2012;41:813)
- Round to oval nuclei, small to slightly enlarged, 1 - 2 inconspicuous nucleoli, fine granular chromatin, smooth nuclear contour, nuclear grooves (43.5%), nuclear pseudoinclusions (26.1%) (Pancreas 2013;42:27)
- Delicate, vacuolated cytoplasm (60.9%), variable in amount (Pancreas 2013;42:27)
- May show papillary architecture (10.5%), acini formation (10.5%), 3D clusters (5.3%), single cell pattern (5.3%), goblet cells (17.4%) (Pancreas 2013;42:27)
- Background mucin, macrophages (43.5%), rarely stroma (17.4%) (Pancreas 2013;42:27)
- Limitations: may not be representative of entire cyst lining
- Unremarkable mucin
Positive stains
- MUC5AC (77 - 90%), MUC6 (74 - 93%), MUC1 (35 - 37%), CK7 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
Negative stains
- MUC2, retained SMAD4 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- CDX2 (can be focal)
- p53
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- KRAS mutations in 13 - 55% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- KMT2C (MLL3) mutations in 62% (Hum Pathol 2020;101:1)
- BRAF, RNF43, CDKN2A, SMAD4 mutations in 8% (Hum Pathol 2020;101:1)
- TP53 mutations in 15% (Hum Pathol 2020;101:1)
- Loss of heterozygosity at 10q (PTEN) or 17q (ubiquitin E3 ligase ring finger 43 / RNF43) reported in 2 cases (Hum Pathol 2016;55:159)
- Clonality analysis with HUMARA gene showed polymorphism (Hum Pathol 2010;41:513)
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas, resection:
- Simple mucinous cyst (see comment)
- Comment: Many of these lesions have KRAS mutation. Although there is no consensus, many authors consider this entity a neoplastic process. However, they tend to have a benign behavior with no reported recurrence or malignant transformation after resection.
Differential diagnosis
- Intraductal pancreatic mucinous neoplasm (IPMN):
- Increased amylase in cyst fluid (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- More commonly head of pancreas
- More papillary architecture
- Communicates with pancreatic duct
- Can have high grade dysplasia or be associated with invasive carcinoma
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN):
- Almost exclusively in women
- Body and tail of pancreas
- Can have papillary epithelium
- Can have high grade dysplasia
- Ovarian type stroma (progesterone receptor / PR positive) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1330, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:121)
- Can be associated with invasive carcinoma
- Retention cyst:
- Cystic dilation of pancreatic duct
- Intraluminal obstruction (Clin Endosc 2015;48:31)
- Lymphoepithelial cyst:
- Squamous or columnar epithelium
- Lymphocytes and germinal centers within the wall
- Epidermoid cyst:
- Keratinizing squamous epithelium
- Squamoid cyst:
Board review style question #1
- A 62 year old woman presents with an incidental cystic lesion in the head / uncinate process of the pancreas on imaging. The cyst does not communicate with the pancreatic duct. Upon grossing of the Whipple resection specimen, a 4.6 cm multiloculated cyst with smooth lining is present in the head / uncinate. Representative H&E image of the cyst lining is shown. Which of the following is true regarding this entity?
- High grade dysplasia is often present
- KRAS mutations have been demonstrated in a subset of cases
- Often communicate with pancreatic duct
- Ovarian type stroma is diagnostic of this entity
- Papillary architecture is common
Board review style answer #1
B. KRAS mutations have been demonstrated in a subset of cases
Comment Here
Reference: Simple mucinous cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Simple mucinous cyst
Board review style question #2
- A 2.3 cm multiloculated cyst with smooth lining located in the head of the pancreas was removed during surgery. It does not connect with the main pancreatic duct. The pathologist observes that the cyst lining is composed of a single layer of columnar mucinous cells with no papillary architecture or high grade dysplasia. The surrounding cyst wall is fibrotic and paucicellular with no ovarian type stroma. No ductal obstruction is present. What is the best diagnosis for this entity?
- Intraductal pancreatic mucinous neoplasm
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
- Retention cyst
- Simple mucinous cyst
Board review style answer #2