Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Askan G, Basturk O. Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasitpn.html. Accessed January 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Intraductal, grossly solid and cystic, tubule forming, epithelial neoplasm with high grade dysplasia and no overt mucin production (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- First described in 2004 by Tajiri et al. under the name of intraductal tubular carcinoma (Pancreas 2005;30:115)
- Renamed in 2009 by Jamaguchi et al. as intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1164)
- Previous (2010) and current (2019) WHO classify as a distinct intraductal neoplasm of the pancreas
- Accounts for 3% of intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1812)
Essential features
- A rare and distinct type of pancreatic intraductal neoplasm
- Highly cellular, complex tubular or cribriform growth pattern
- Focal papillary growth may be seen
- Intracellular mucin is typically not detectable or is very minimal
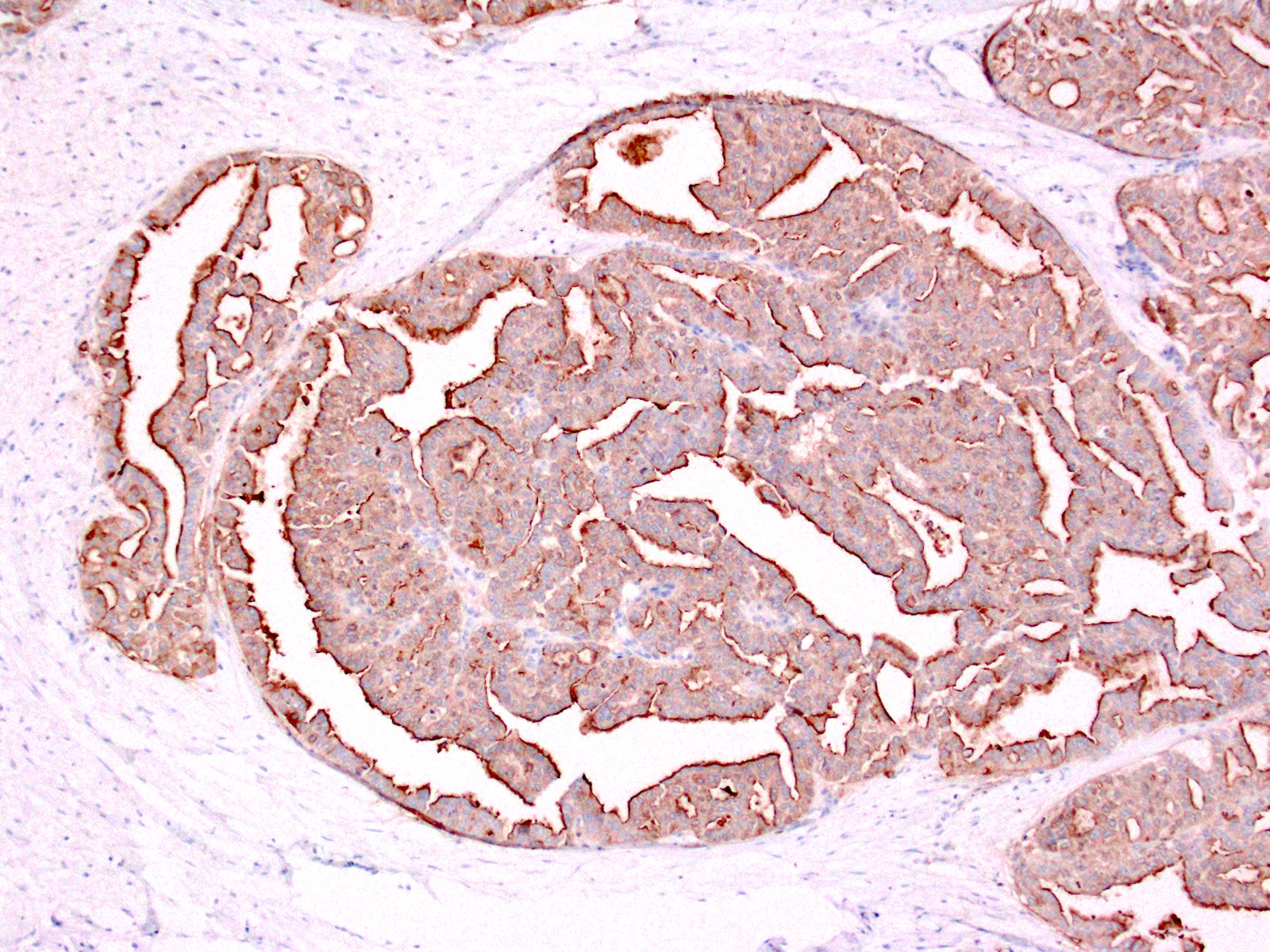
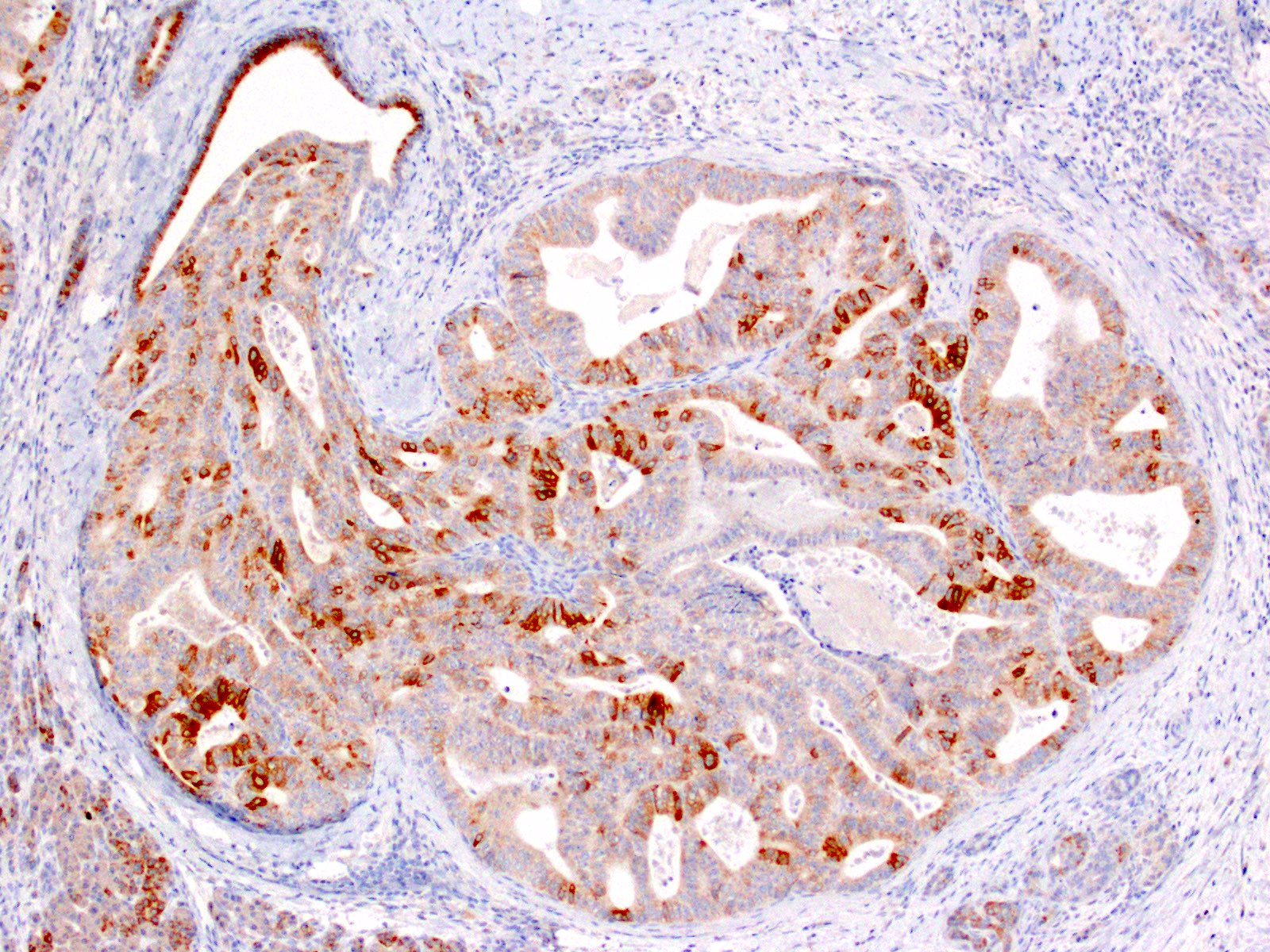
- Positive for MUC1 and MUC6; negative for MUC5AC
- Lacks genetic alterations commonly seen in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs)
- Favorable overall outcome even if associated with invasive carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
Terminology
- Older term is intraductal tubular carcinoma (not recommended)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Mean age: 55 years (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- F:M = 17:14 (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- Accounts for 3% of intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1812)
Sites
- 50% occur in head, 15% occur in tail and 30% involve entire gland of the pancreas (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:9672)
- Also occurs in bile ducts (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1249)
Etiology
- No known etiological factors
Clinical features
- Nonspecific symptoms: abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, steatorrhea
- Jaundice is not common
Radiology description
- 2 tone duct sign on CT image and cork of wine bottle sign on MRCP examination as characteristic imaging findings that represent their intraductal growth (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2012;36:710, Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e14426)
- Intraductal solid tumor within dilated main pancreatic duct mimicking IPMN (Diagn Interv Radiol 2019;25:251)
- Irregular main pancreatic duct dilatation may lead to misdiagnosis of chronic pancreatitis (Diagn Interv Radiol 2019;25:251)
Prognostic factors
- Exhibits relatively indolent behavior even if associated with invasive carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
Case reports
- 23 year old woman with incidental asymptomatic retroperitoneal cystic lesion (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2019;12:1041)
- 43 year old woman with epigastric pain (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:11)
- 62 year old man with epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting (J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:PD14)
- 72 year old man with recurrent pancreatitis (Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;48:122)
- 73 year old man with nausea and persistent abdominal pain (World J Surg Oncol 2017;15:203)
Treatment
- Treated primarily by surgical resection
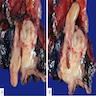
Gross description
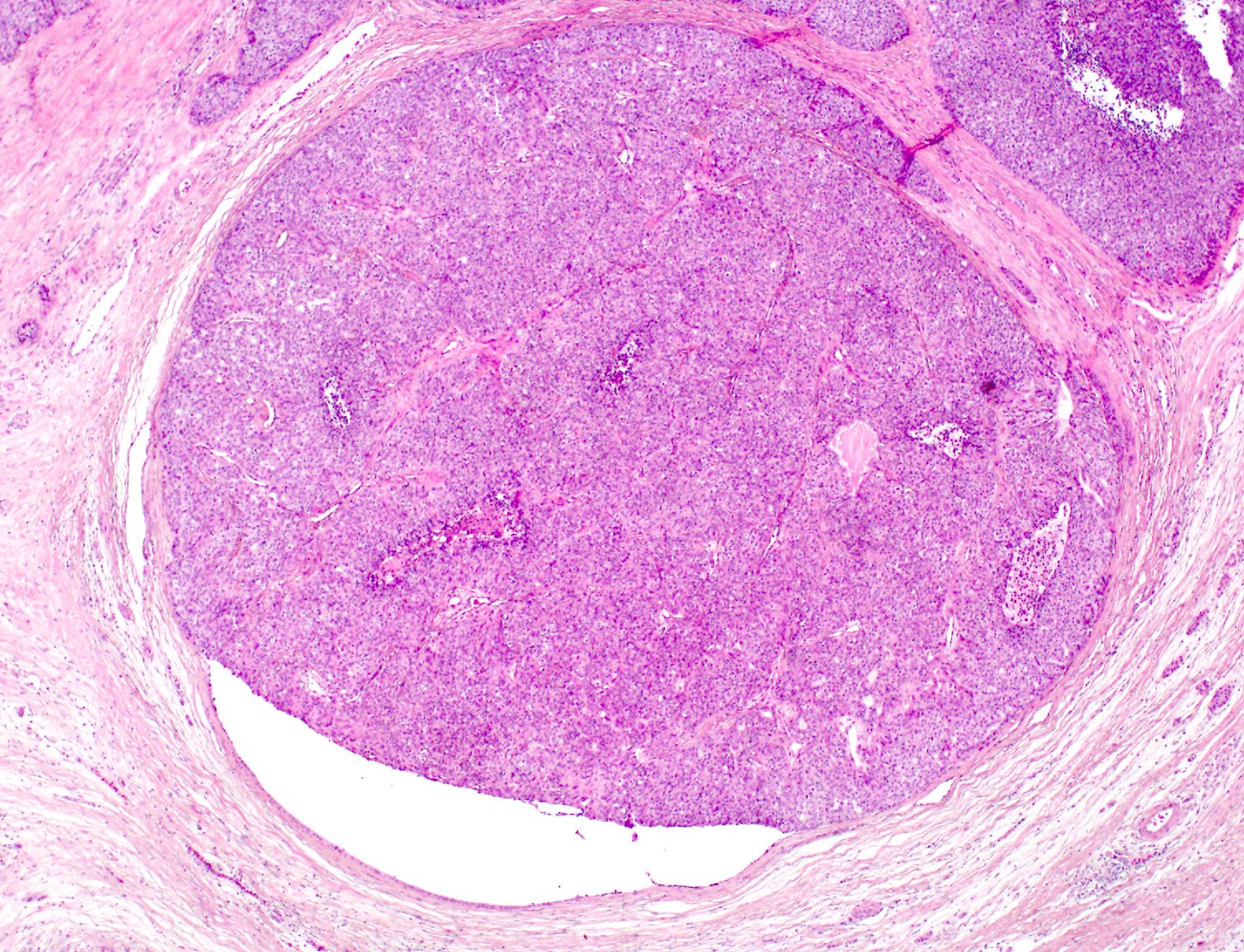
- Multinodular, polypoid, solid or fleshy mass within dilated main pancreatic duct (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- Cyst formation is less common
- Median size: 4.5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- Multifocality may be seen (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:9672)
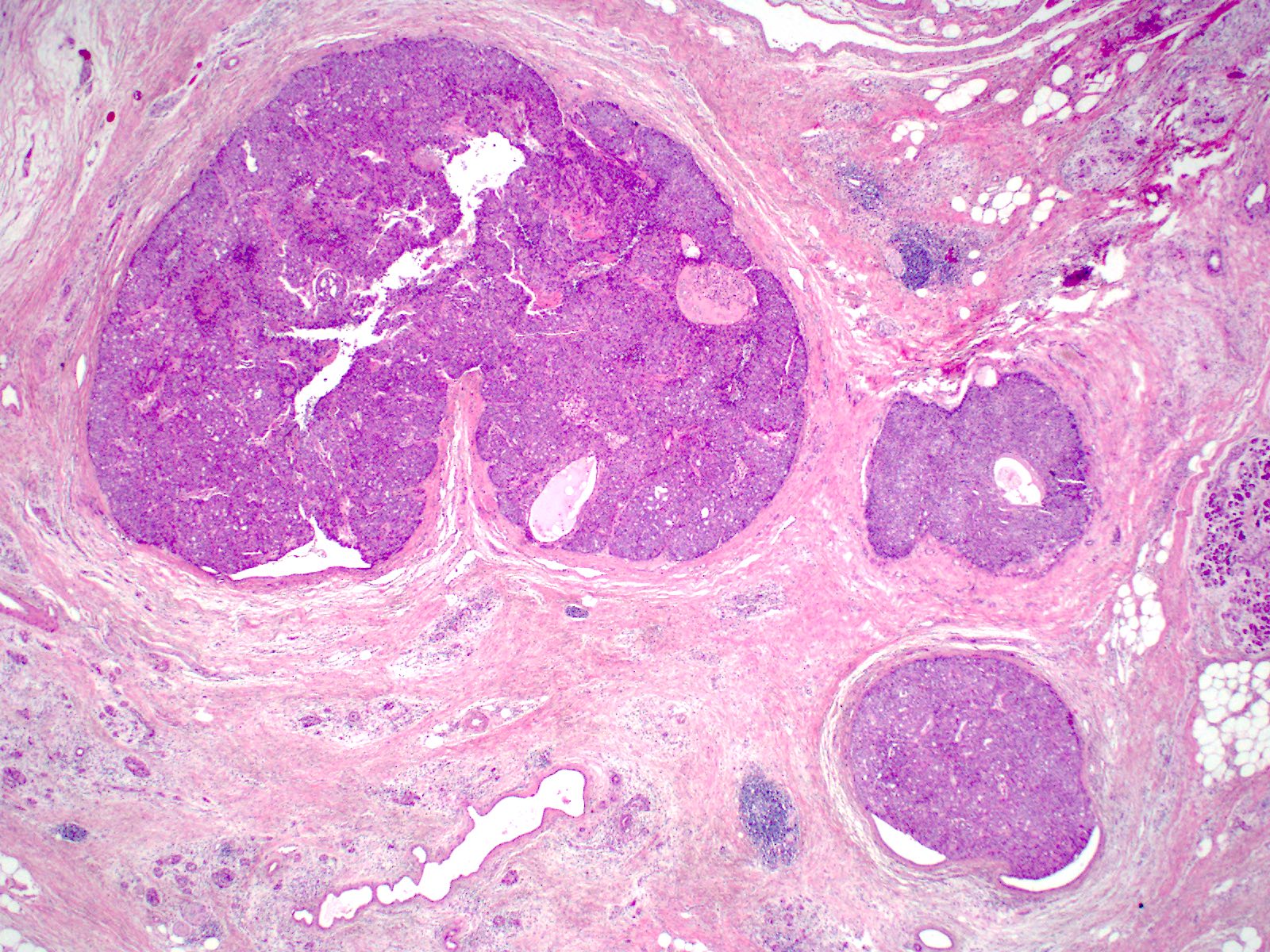
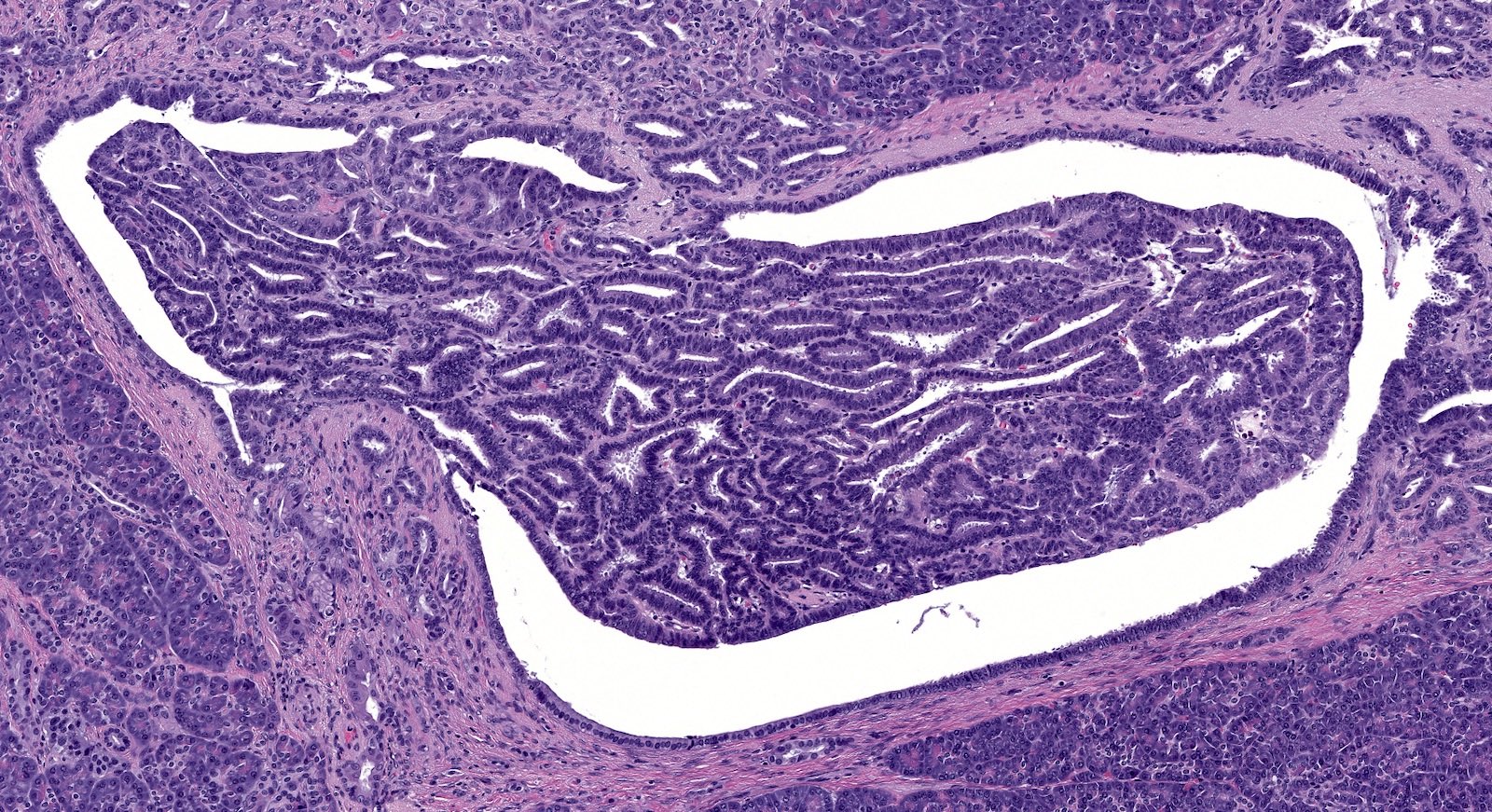
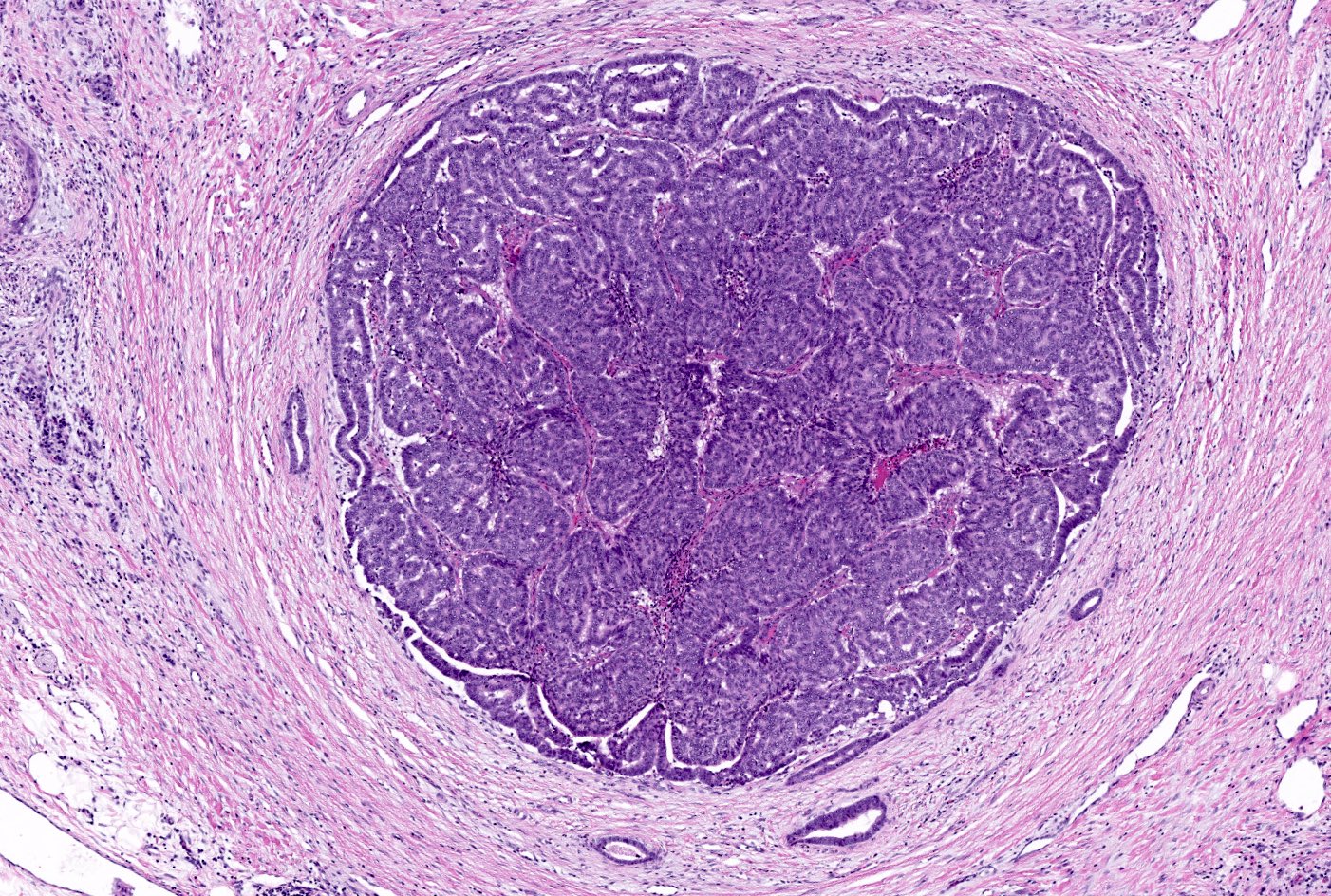
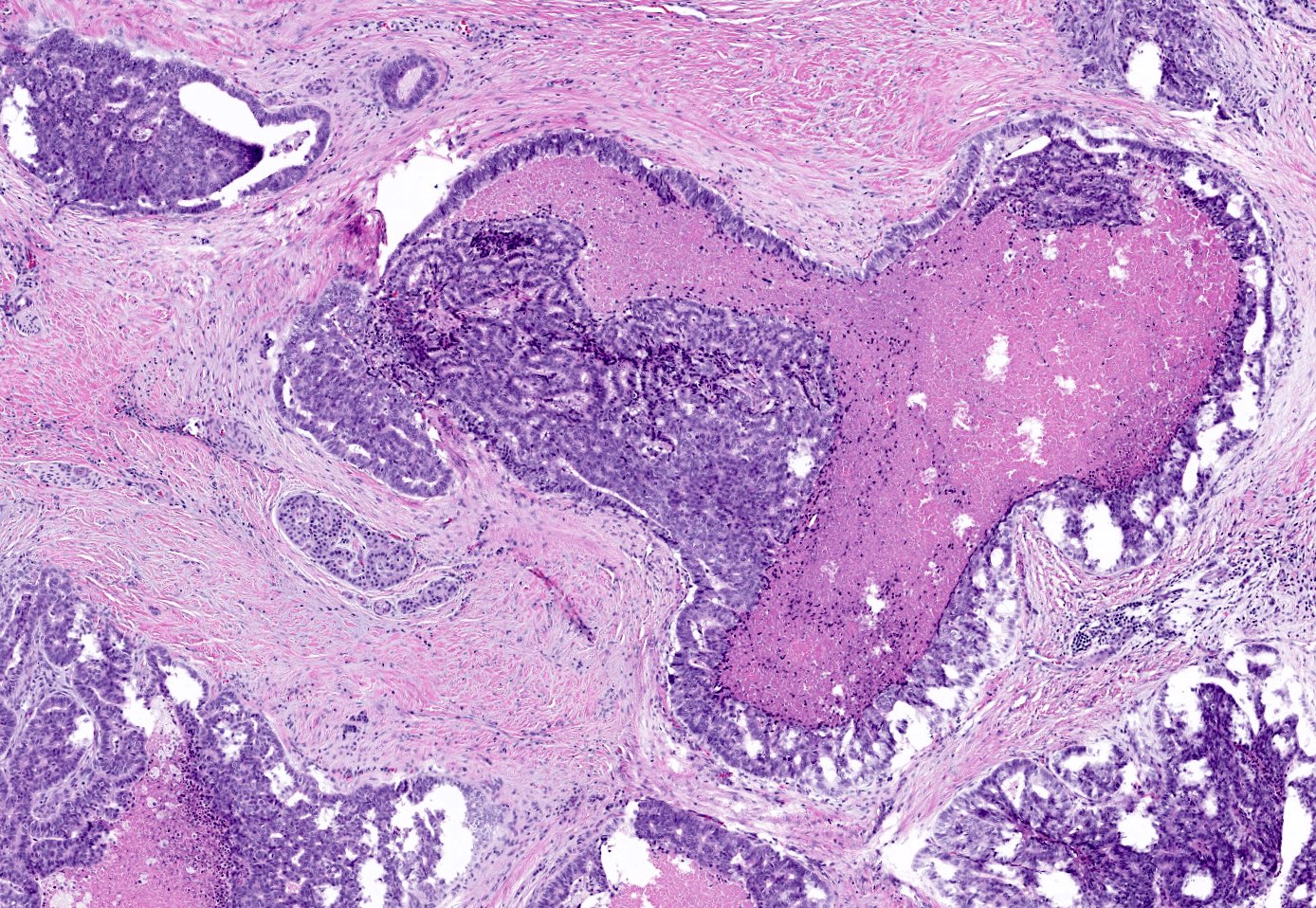
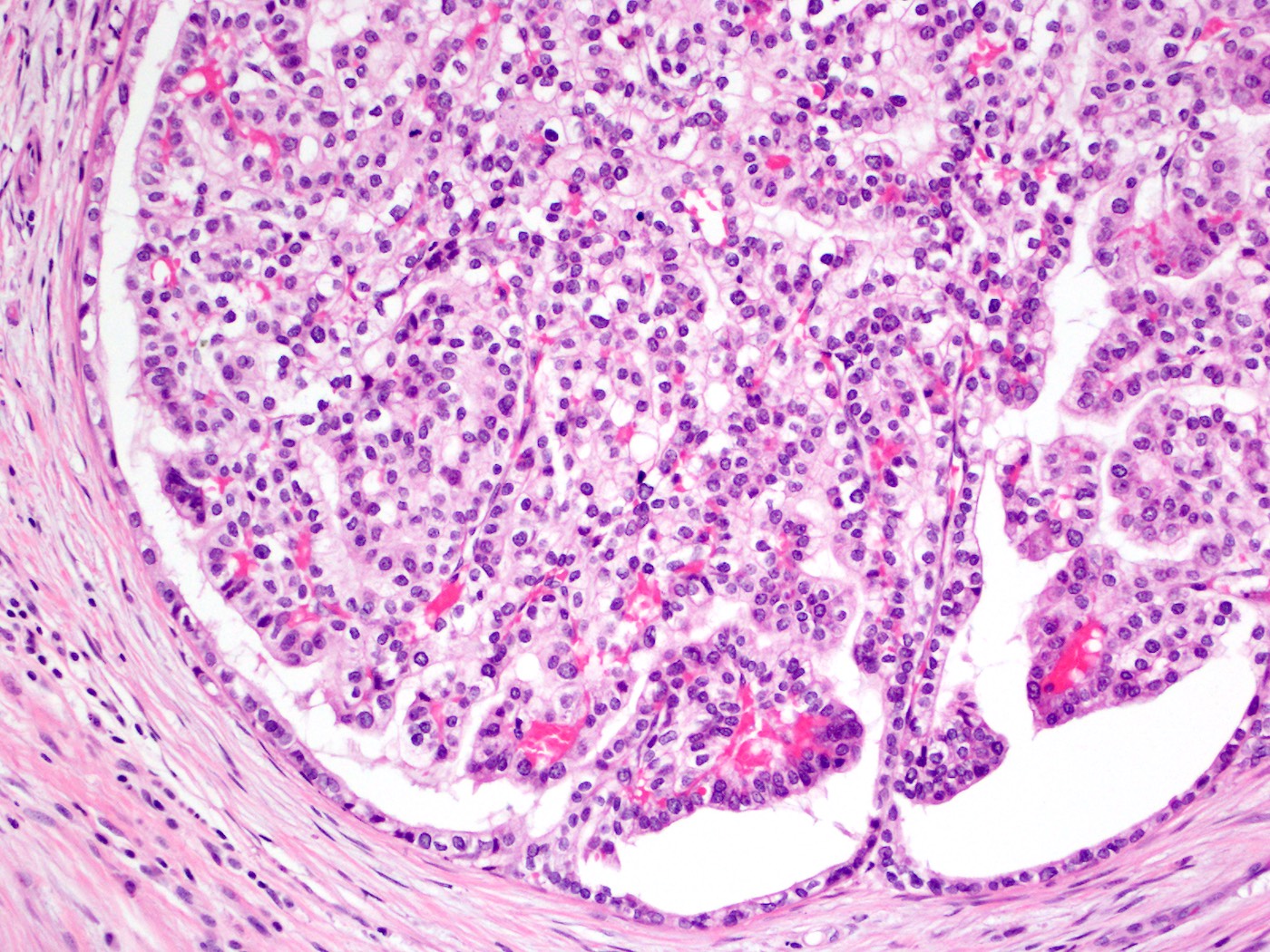
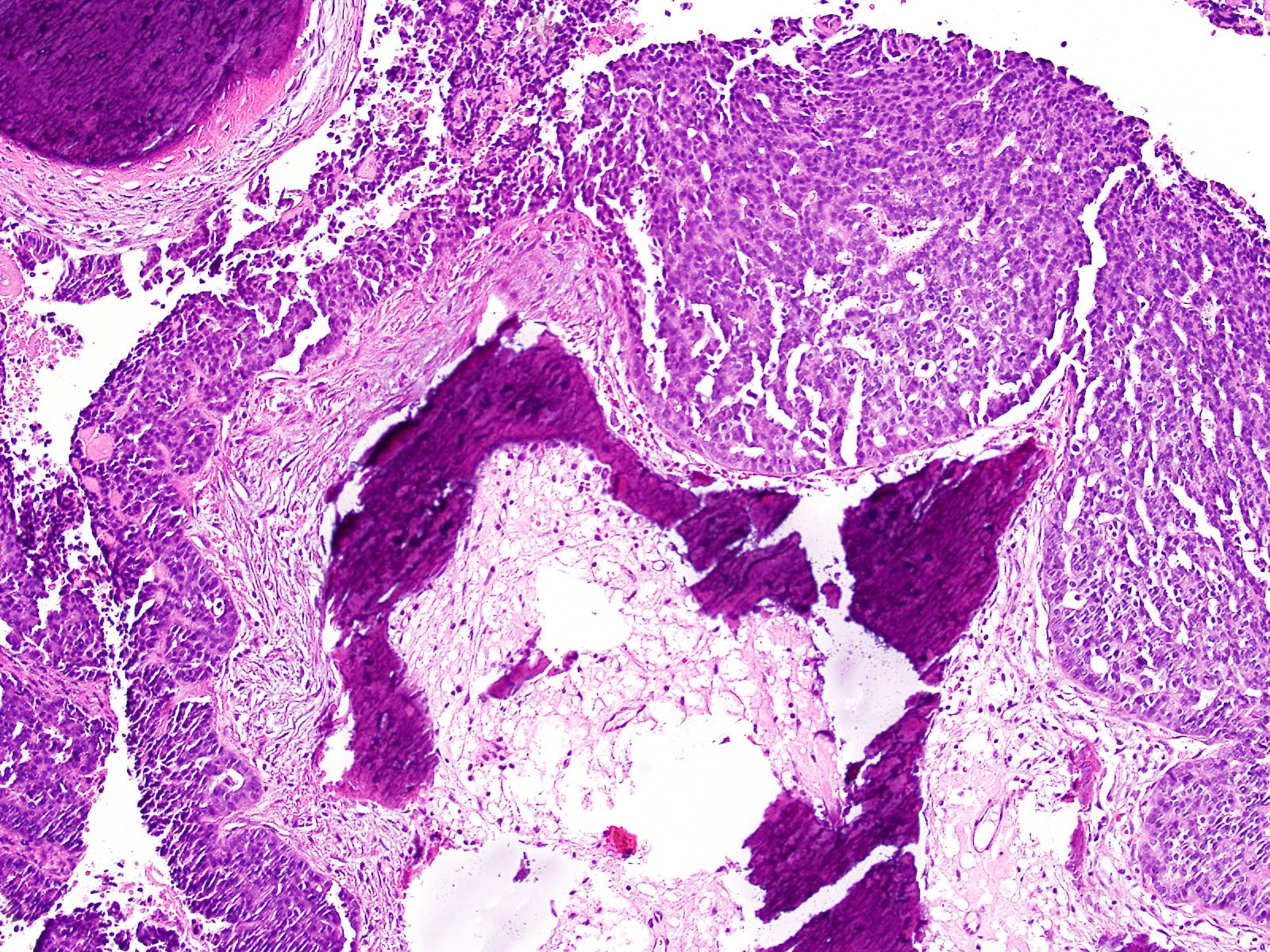
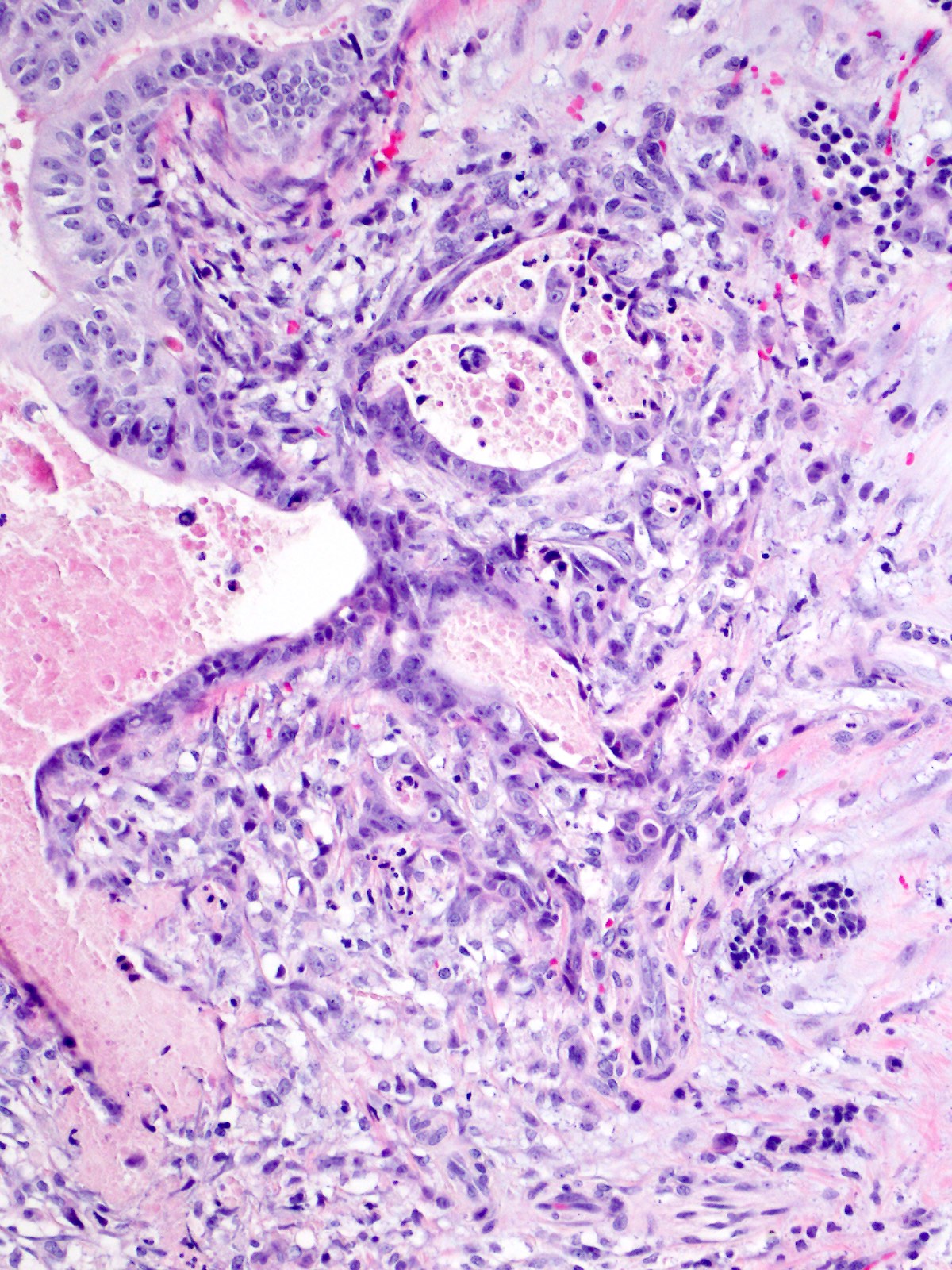
Microscopic (histologic) description
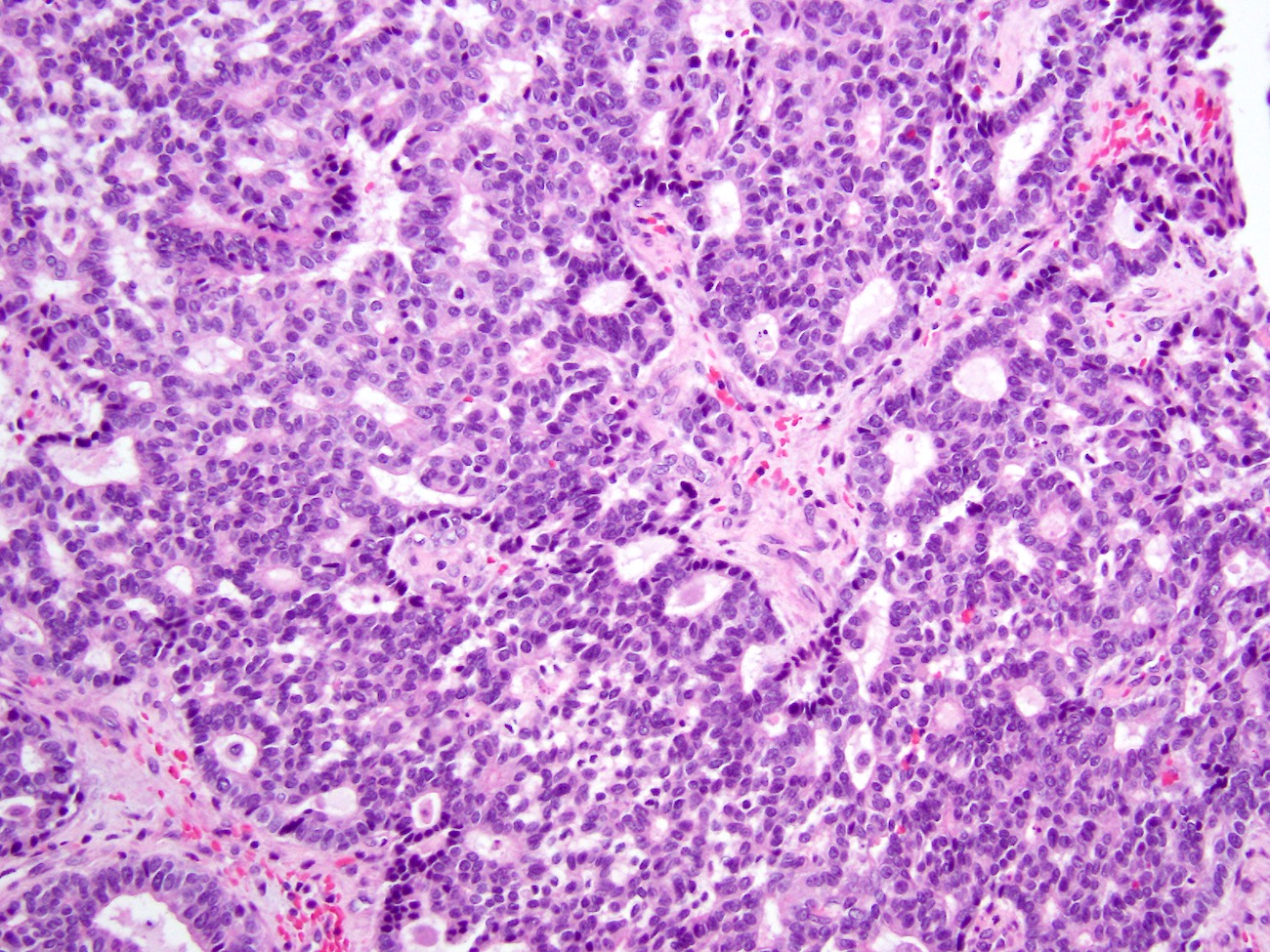
- Circumscribed nodules of back to back tubular glands surrounded by fibrotic stroma; however, the intraductal location of at least some of the nodules is evidenced by continuity of the neoplastic epithelium with nonneoplastic ductal epithelium
- Tubules are lined by cuboidal or columnar epithelium with a modest amount of eosinophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm
- Nuclei are small, round to oval and moderately to markedly atypical with readily identifiable mitotic figures
- Intracellular mucin production is typically not detectable or is very minimal
- Intraluminal secretions and necrosis, often with comedo-like pattern, are present
- Clear cell changes, cartilaginous or osseous metaplasia may be seen (Diagn Pathol 2014;9:11, Pathol Int 2012;62:339, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313, Pathol Int 2015;65:501)
- Associated invasive carcinoma is seen in about 70% of cases as individual cells or small angulated nonmucinous glands surrounded by usually desmoplastic stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Gokce Askan, M.D. and Olca Basturk, M.D.
Cytology description
- Large cribriform and tubular clusters with luminal spaces and scanty intracytoplasmic mucin (Diagn Cytopathol 2014;42:314, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:366)
Positive stains
Negative stains
- MUC2 and MUC5AC (Pancreas 2004;29:116, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313, Pancreas 2005;30:115, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1164)
- Acinar markers (trypsin, chymotrypsin) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
- Neuroendocrine markers (a few scattered cells may be positive for chromogranin or synaptophysin) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:313)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- In general, ITPNs lack KRAS, GNAS and BRAF mutation (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1760, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1164, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1812, J Pathol 2013;231:335)
- PIK3CA, PIK3CB, INPP4A, PTEN may be mutated in ITPNs (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1760, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1164, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1812, J Pathol 2013;231:335)
- Recently, it has been shown that certain chromatin remodeling genes (MLL1, MLL2, MLL3, BAP1, etc.) may be mutated in ITPNs and a subset of the cases harbors FGFR2 and STRN-ALK fusions (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1760)
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas and duodenum, pancreaticoduodenectomy:
- Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of pancreas (ITPN) (see comment)
- Comment: The pancreas was submitted entirely for microscopic evaluation and no associated invasive carcinoma is identified. The neoplasm involves the main pancreatic duct and measures 4 cm in greatest dimension. Adjacent pancreas reveals atrophy. Surgical margins are free of neoplasm. 15 benign lymph nodes are identified (0/15).
- Pancreas and duodenum, pancreaticoduodenectomy:
- Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of pancreas (ITPN) associated with an invasive ductal carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: ITPN involves the main pancreatic duct. The entire tumor measures 5 cm in greatest dimension; the invasive carcinoma component measures 0.7 cm in greatest dimension (suggestion for if multifocal invasion is present: the invasive carcinoma accounts for 25% of entire tumor and is estimated to measure 1.25 cm in greatest dimension). Adjacent pancreas reveals atrophy. Surgical margins are free of ITPN and invasive carcinoma. 14 benign lymph nodes are identified (0/14).
- Reference: Ann Surg 2016;263:162
Differential diagnosis
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, pancreatobiliary type:
- More delicate papillae that are lined with highly atypical cuboidal cells
- Positive for MUC5AC
- KRAS mutations are common
- Acinar cell carcinoma intraductal variant:
- Eosinophilic zymogen granule containing cytoplasm and single prominent central nucleolus
- Mitotically very active
- Positive for trypsin, chymotrypsin and BCL10
- Neuroendocrine neoplasm, with intraductal growth pattern:
- Salt and pepper chromatin pattern
- Positive for chromogranin and synaptophysin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas?
- Jaundice is one of the most common symptoms
- Papilla and mucin formation are common histologic features
- They are positive for MUC5AC
- They commonly have KRAS, GNAS and BRAF mutations
- They have relatively indolent prognosis even when associated with invasive carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
E. They have relatively indolent prognosis even when associated with invasive carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN)
Comment Here
Reference: Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN)
Board review style question #2
Which one of the following stains is negative in intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas?
- CK7
- CK19
- MUC5AC
- MUC1
- MUC6
Board review style answer #2