Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Booth AL, Gonzalez RS. Clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasclearcellendocrine.html. Accessed January 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon morphologic variant of pancreatic well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL) and multiple endocrine neoplasia type I (MEN I) syndrome
Essential features
- Clear, vacuolated cytoplasm due to accumulation of lipid, glycogen or mucin
- Characteristic salt and pepper nuclear chromatin features
- Can be easily misdiagnosed due to morphologic similarities with primary and metastatic tumors of the pancreas
Terminology
- Also known as lipid rich variant
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C25.4 - malignant neoplasm of endocrine pancreas
Epidemiology
- Adults ages 40 - 60
- No sex predilection
- Syndromic patients may present at an earlier age (Pathol Res Pract 2016;212:747)
Sites
- Most commonly in the head of the pancreas
Pathophysiology
- In VHL, the disease results from deletions or mutations in the VHL tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p25.5 (Mod Pathol 2011;24:S66)
- Mutations in MEN1 on chromosome 11q result in loss of function of tumor suppressor protein menin (Mod Pathol 2011;24:S66)
- Sporadic tumors consistently result from allelic loss of chromosome 11q
Clinical features
- Patients with VHL or MEN I may be screened following clinical suspicion
- Patients may present for evaluation of abdominal symptoms or abnormal laboratory results
- Some cases may be found incidentally on imaging (Mod Pathol 2011;24:S66)
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in VHL or MEN I are typically nonfunctional (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:963)
Diagnosis
- Imaging may identify a suspicious mass
- Definitive diagnosis is made following endoscopic biopsy or surgical resection
Radiology description
- Hyperintense, enhancing mass, well circumscribed with sharp borders on computed tomography (Radiographics 2010;30:1445)
Prognostic factors
- Worse prognosis with high Ki67 proliferative index, tumor size > 2 cm, nonfunctioning tumors, tumor necrosis and poor response to chemotherapy (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:586, Mod Pathol 2011;24:S66)
Case reports
- 29 year old man with liver and pancreatic lesions (Diagn Cytopathol 2009;37:365)
- 32 year old woman with abdominal pain and a pancreatic mass (Cytojournal 2016;13:7)
- 47 year old woman presenting with a mass in the pancreatic tail (Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2017;38:83)
- 60 year old woman with pancreatic cysts and octreotide avid lesions (Virchows Arch 2013;463:593)
- 64 year old man with a nodule in the head of the pancreas (Cytopathology 2013;24:197)
Treatment
- Surgical resection and chemotherapy (Mod Pathol 2011;24:S66)
Gross description
- Most often solid, solitary, homogenous, tan to yellow (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:602)
- If extensive fibrosis present, may be gray and firm (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:586)
- Hereditary syndromes may present with multiple tumors
- Rarely a cystic component can be seen (Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2017;38:83)
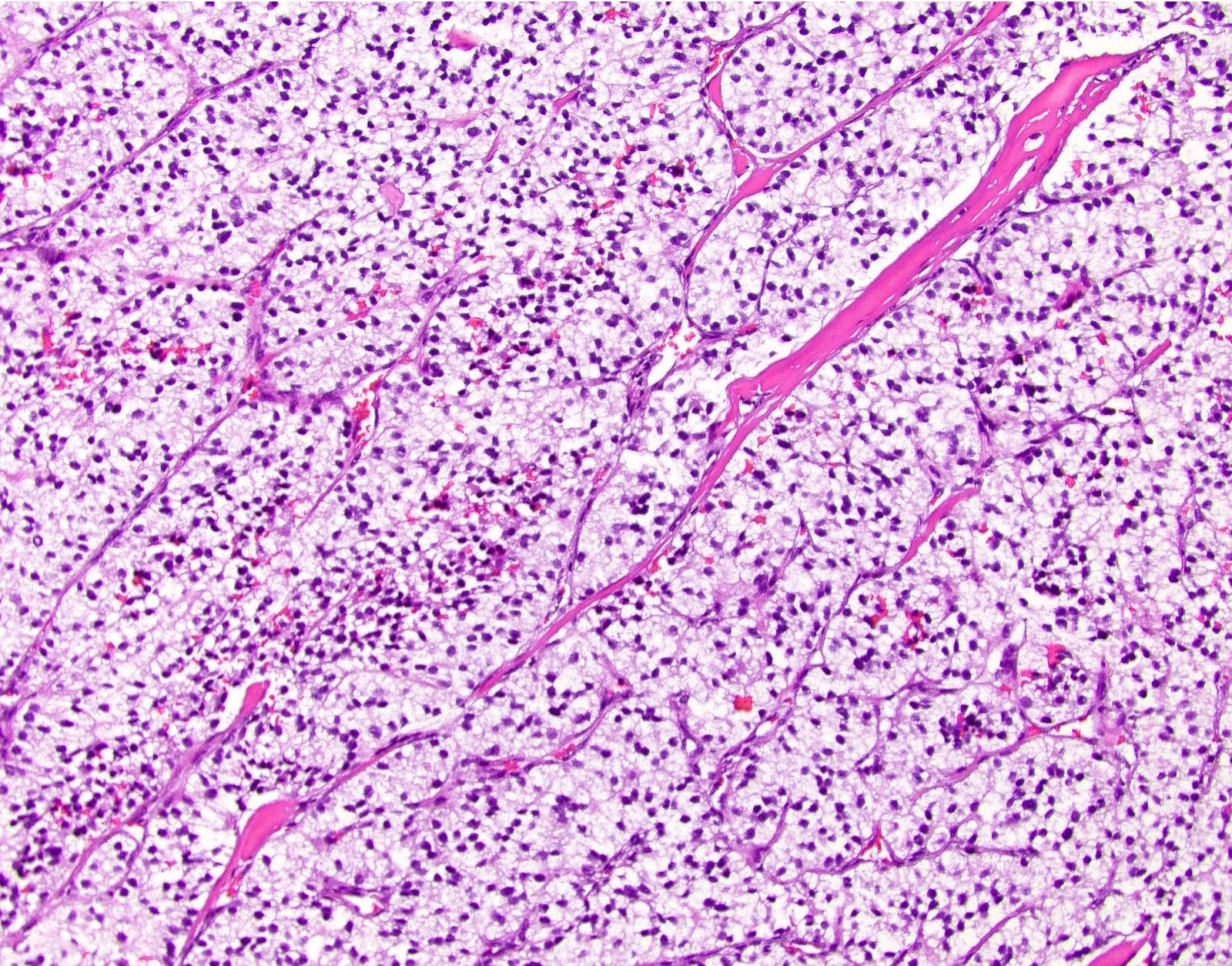
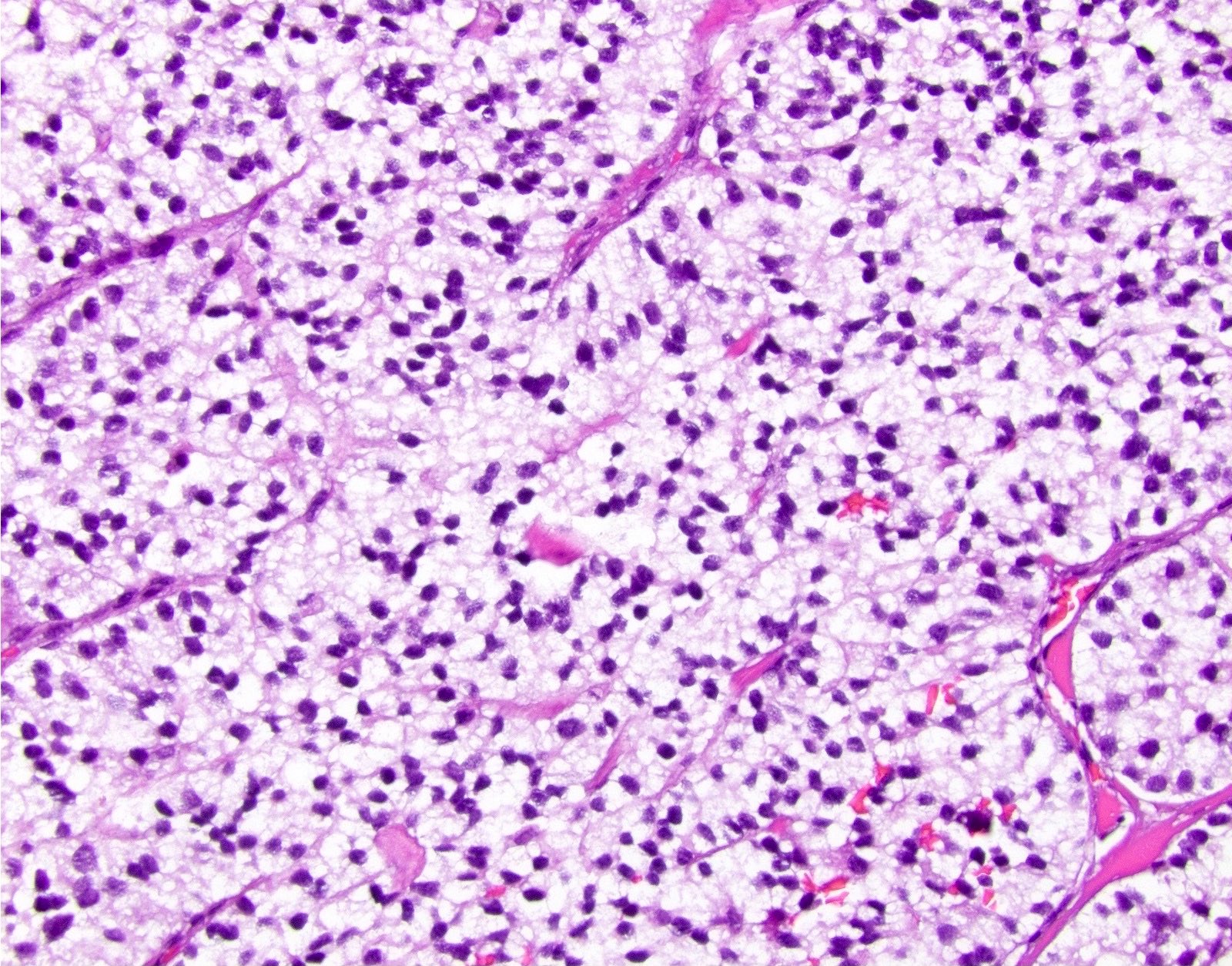
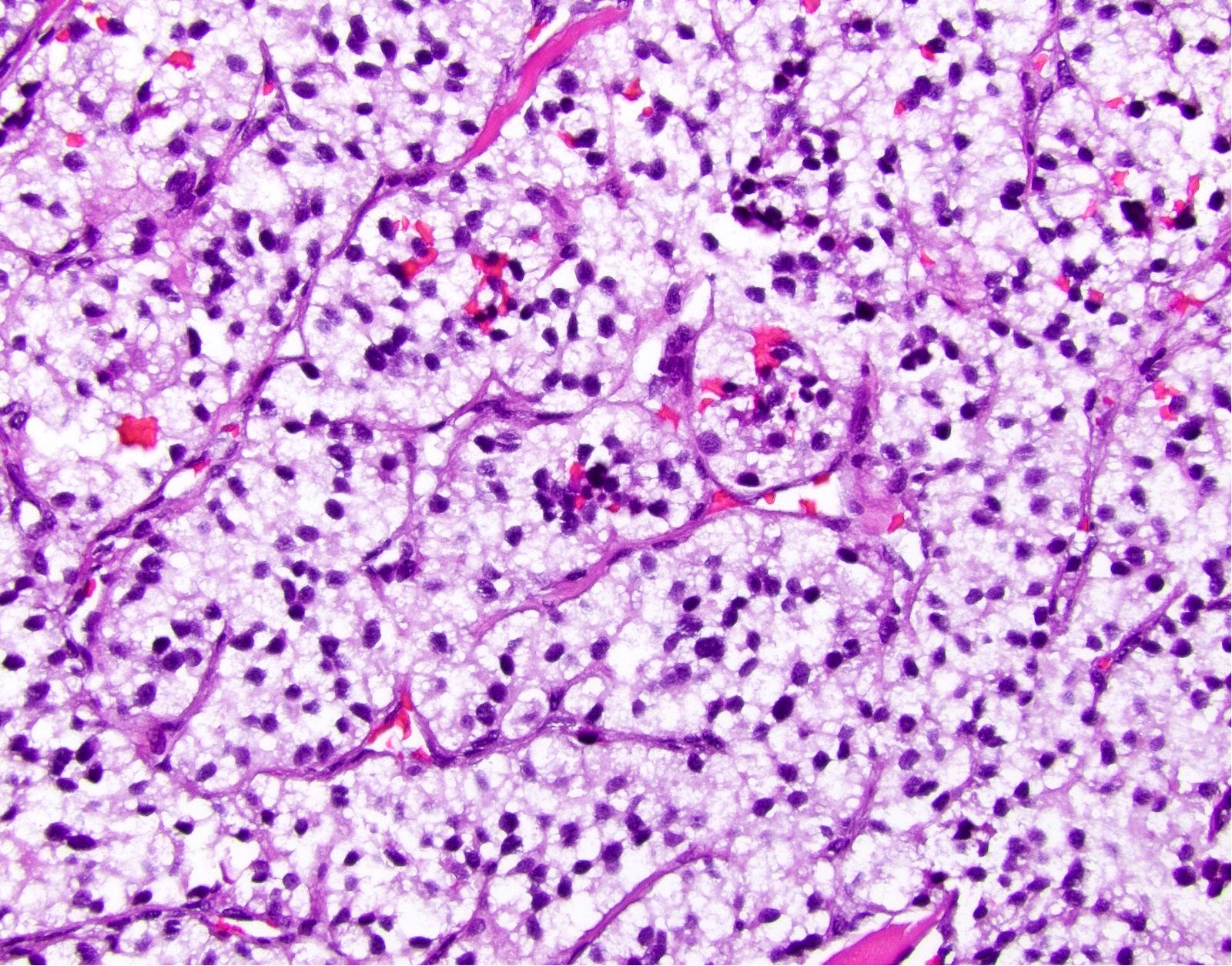
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solitary, well circumscribed
- Widely variable architectural patterns: nested, trabecular, glandular, ribbon-like, tubuloacinar, mixed patterns are common; however, there is usually a dominant pattern (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:963)
- Small / medium round, polygonal cells with clear, vacuolated cytoplasm due to lipid accumulation
- Central nucleus with characteristic salt and pepper chromatin pattern and inconspicuous nucleoli (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:350)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Isolated or small clusters of round monomorphic tumor cells (Cytopathology 2013;24:197)
- Numerous small cytoplasmic vacuoles imparting a foamy appearance
- Eccentric nuclei with fine nuclear chromatin, without prominent nucleoli (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:586)
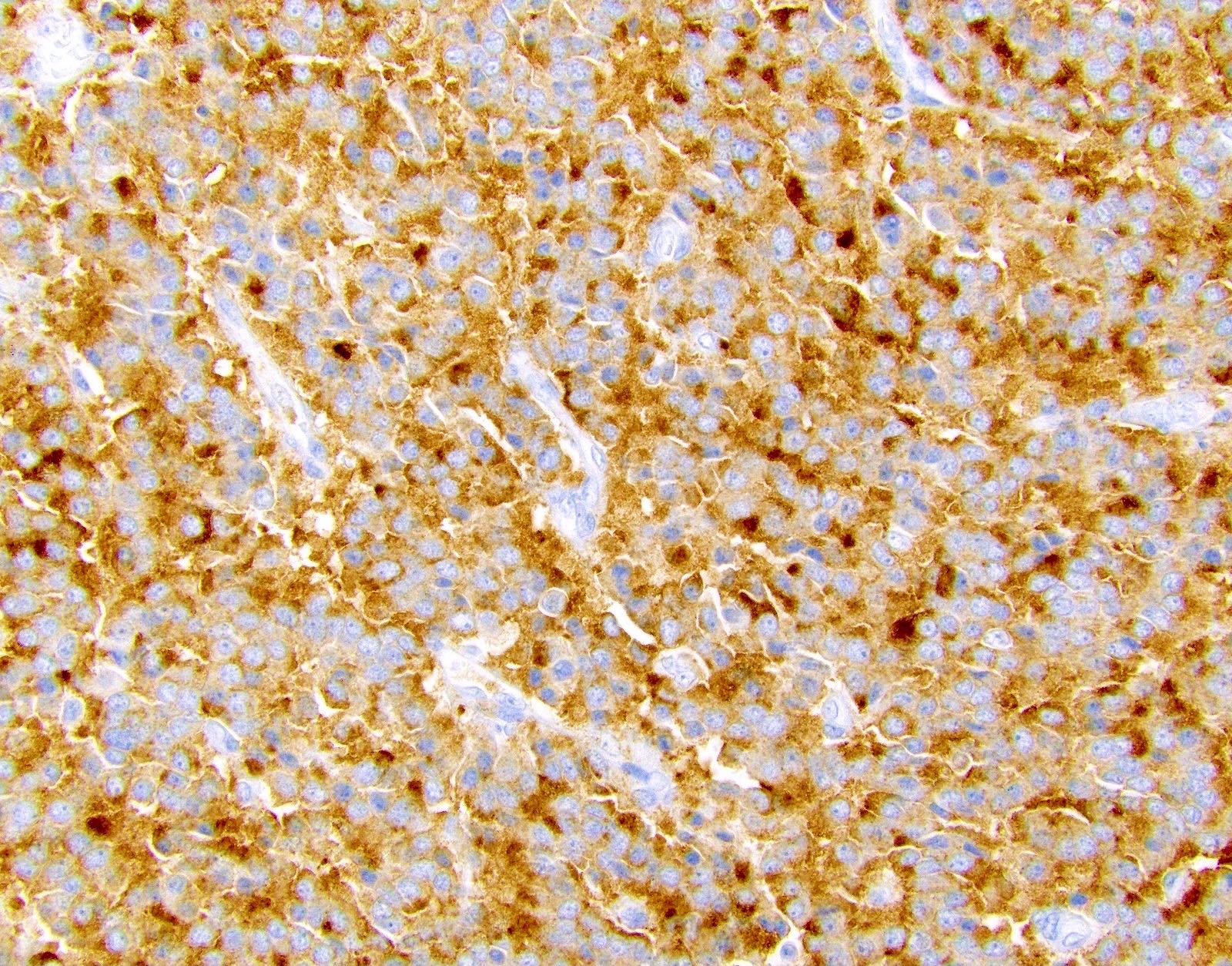
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Variably sized cytoplasmic lipid globules and dense neurosecretory granules (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:350)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Autosomal dominant mutation in VHL tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p25.5 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1080)
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type I
- Autosomal dominant germline mutation in MEN1 tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11q13
- Sporadic tumors may arise from chromosomal alterations, epigenetic changes or functional genomic alterations
Videos
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: overview
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas and duodenum, Whipple procedure:
- Clear cell pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, WHO grade 1 (see synoptic report and comment)
- Comment: The patient's clinical history of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome is noted. The clear cell variant of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor is more common in this setting. Immunohistochemical stains for synaptophysin and chromogranin are positive and the Ki67 index is approximately 2.0%.
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic:
- Renal cell carcinoma, clear cell type:
- Positive for AE1/AE3, CD10, PAX8, CAIX
- Negative for neuroendocrine markers (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1080)
- Renal cell carcinoma, clear cell type:
- Primary:
- Ductal adenocarcinoma with clear cell features:
- Positive for AE1 / AE3
- Negative for neuroendocrine markers
- Serous cystadenoma, solid variant:
- Positive for PAS, AE1 / AE3, vimentin
- Negative for synaptophysin
- Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm, clear cell variant:
- Positive for beta catenin (nuclear and cytoplasmic), CD10, CD56, vimentin
- Variable neuroendocrine markers
- Loss of E-cadherin (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:586)
- Clear cell sugar tumor / PEComa:
- Ductal adenocarcinoma with clear cell features:
- Peripancreatic region:
- Adrenocortical tumors:
- Positive for inhibin, MelanA
- Weak with AE1 / AE3
- Negative for chromogranin A (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:586)
- Clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Positive for Arginase1, HepPar1
- Negative for neuroendocrine markers
- Adrenocortical tumors:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following statements regarding clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor is true?
- A diagnosis should not stimulate genetic evaluation for the VHL syndrome
- Frequently immunoreactive for cytokeratins
- Immunohistochemistry can distinguish from histologically similar metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in VHL disease
- Only seen in the setting of VHL disease
- Tumors associated with VHL syndrome and MEN1 syndrome are often functional tumors
Board review style answer #1
C. Immunohistochemistry can distinguish clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumors from histologically similar metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in VHL disease
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor
Board review style question #2
- A patient is diagnosed with a clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor. What genetic mutation is likely to be present?
- Mutation in APC tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 5q21-22
- Mutation in c-KIT proto-oncogene gene on chromosome 4q11-4q13
- Mutation in CDH1 gene on chromosome 16q22.1
- Mutation in MET proto-oncogene located on chromosome 17q31.1-34
- Mutation in VHL tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p25.5
Board review style answer #2
E. Mutation in VHL tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p25.5
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell pancreatic endocrine tumor