Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Arole V, Chen W. Acinar cystic transformation. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasacinarcellcystadenoma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, nonneoplastic cystic lesion of the pancreas lined by benign appearing acinar and ductal epithelium
Essential features
- First described in 2002; recognized by WHO in 2010 (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:698)
- Clinically indolent; no cases of metastasis have been reported
- Most cases found incidentally; though may be symptomatic
- Cyst epithelium of acinar cystic transformation (ACT) consists of bland acinar and ductal epithelium, without mitoses, atypia and necrosis
Terminology
- Other names include acinar cell transformation and acinar cell cystadenoma
ICD coding
- ICD-11: DC30.0 - cyst of pancreas
Epidemiology
- Rare; so far < 130 cases reported in the literature (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
- Female predominance (65.3%) with no age predilection
Sites
- Found in all sites of the pancreas; can diffusely involve the gland
- More common in head of pancreas
Pathophysiology
- Most studies report nonneoplastic dilatation of the acinar and ductal epithelium (Oncol Lett 2014;8:852, J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
- May arise from a heterogeneous background (Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:379)
- Evolving from acinar microcysts
- Secondary to underlying obstructive lesions
- Subset may possibly be neoplastic
Etiology
- Unknown; some may occur due to obstruction
- No longer thought to represent the benign counterpart to acinar cell cystadenocarcinoma
Clinical features
- Often found incidentally on imaging
- Abdominal pain (42.1%), weight loss (4.9%), pancreatitis (4.9%), palpable mass (3.3%), jaundice (2.5%) (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
Diagnosis
- Requires clinical, radiologic and pathologic correlation
Radiology description
- Nonspecific but the presence of 5 or more cysts, clustered peripheral small cysts, presence of cyst calcifications and absence of communication with the main pancreatic duct are supportive (Eur Radiol 2014;24:2128)
Prognostic factors
- Clinically benign; there is no evidence of recurrence, malignant transformation or association with acinar cell carcinoma
- Minority of cases involve controversial / high risk histomolecular features, including intralesional pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) (4%), chromosomal gains and somatic mutations of KRAS and SMO genes (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with epigastric pain and 5 cm cystic lesion in tail of pancreas (Surg Case Rep 2016;2:39)
- 43 year old woman with recurrent attacks of acute pancreatitis found to have diffuse involvement of pancreas by small multiple cysts (< 1 cm in maximum diameter) (Int J Surg Pathol 2022;30:697)
- 52 year old man with a pancreatic tail mass found incidentally on routine imaging for renal cell carcinoma followup (Korean J Radiol 2011;12:129)
- Largest systematic review of literature (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
Treatment
- Benign; no need of surgical resection (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740)
- Some are resected for symptomatic relief or to exclude other cystic neoplasms associated with malignancy
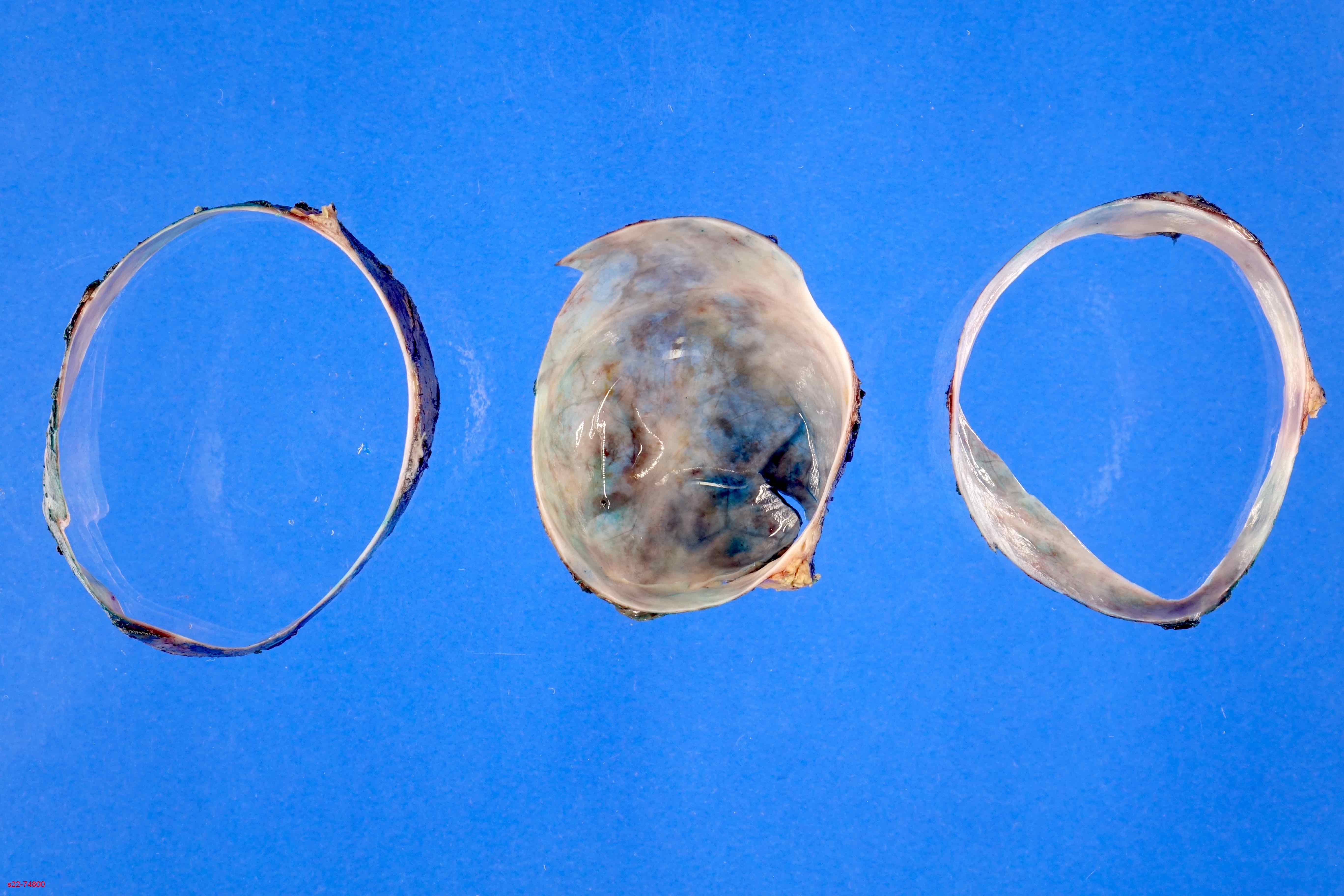
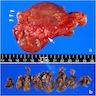
Gross description
- Unifocal > multifocal, multilocular > unilocular
- Average size ~5 cm (range: 2 - 20 cm)
- Typically does not communicate with ductal system, though rare cases have been reported
- Thin walled cyst containing clear white serous watery fluid
- Solid areas or papillary excrescences on cyst wall are typically absent
- References: J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740, Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:379, Esposito: Pathology of the Pancreas, 1st Edition, 2022
Gross images
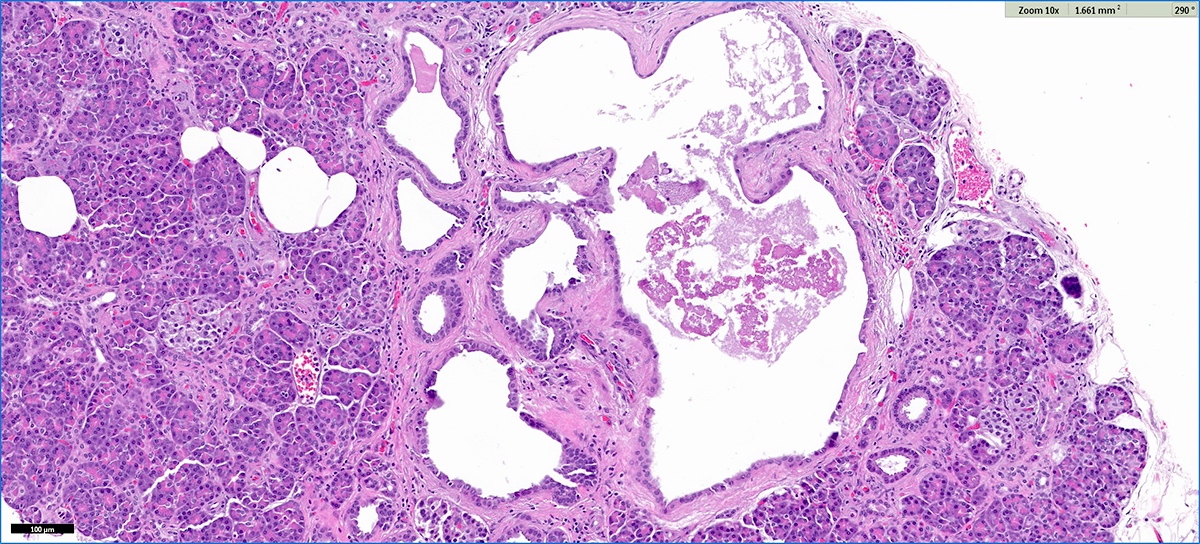
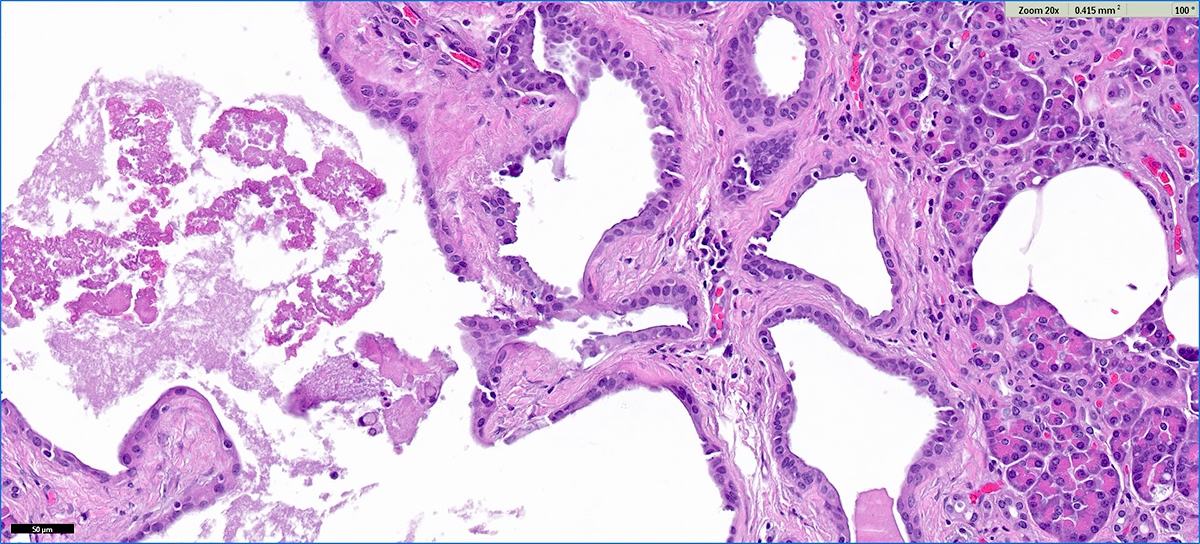
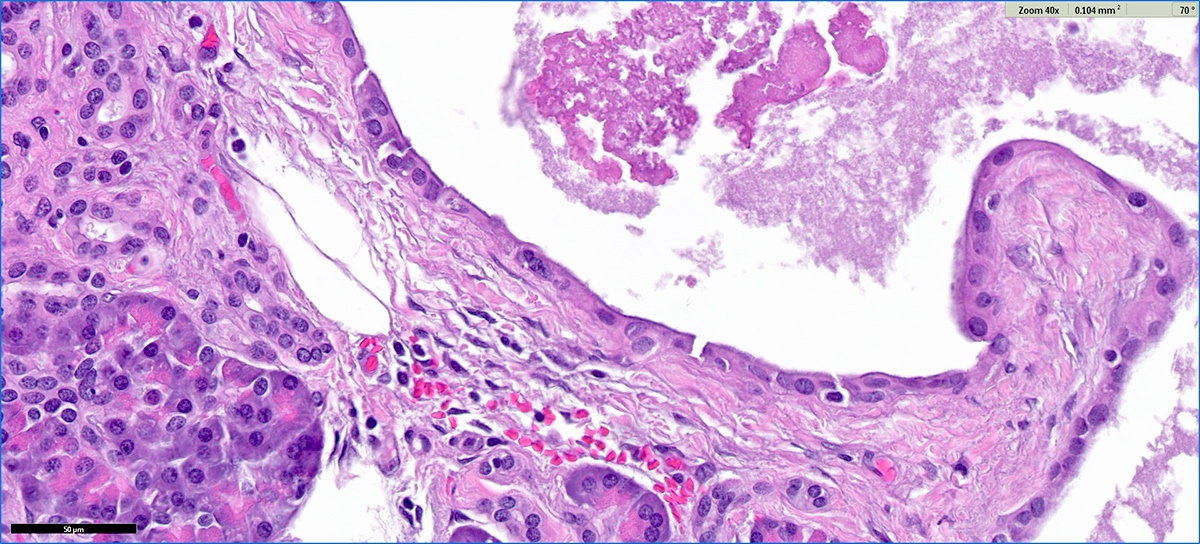
Microscopic (histologic) description
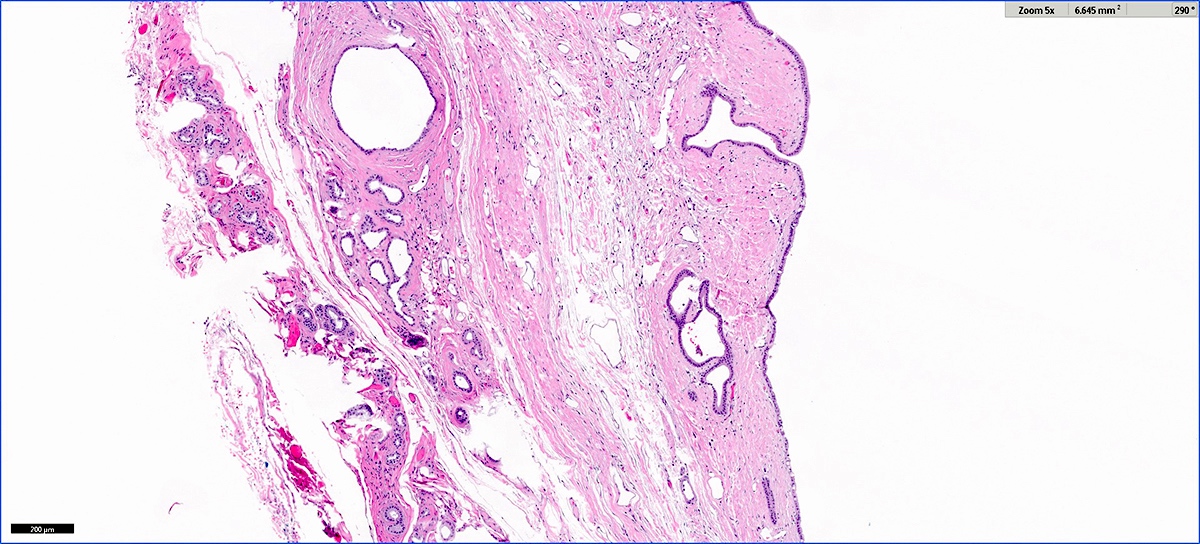
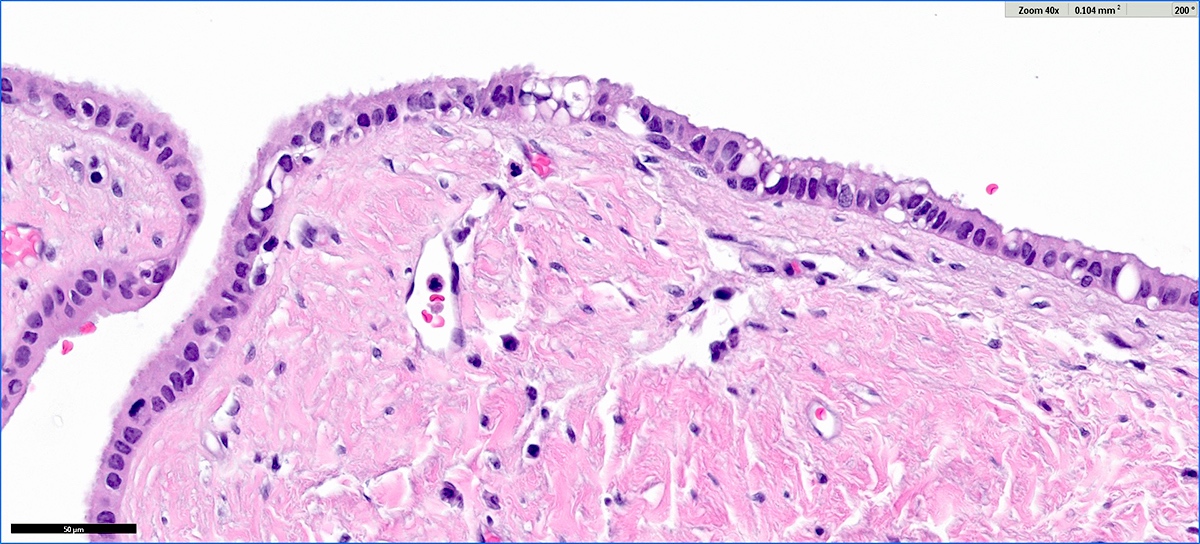
- Cysts of variable sizes lined by bland flattened cuboidal acinar cells with apical granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and dense basophilic basal cytoplasm
- Ductal epithelium can be admixed with the acinar cells
- May contain corpora amylacea-like dense eosinophilic lamellar concretions
- Multilocular cyst often demonstrates incomplete septa and club-like pseudopapillae
- Low Ki67 proliferation (≤ 3%) and nuclear atypia is minimal
- Cyst lining may show focal mucinous or clear cell change
- Negative for ovarian type stroma, necrosis or infiltrative growth
- References: J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740, Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:379, Esposito: Pathology of the Pancreas, 1st Edition, 2022
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Vidya Arole, M.D. and Wei Chen, M.D., Ph.D.
Cytology description
- Lesional epithelium indistinguishable from normal acinar and ductal cells
- Smears usually low cellularity, containing cells resembling benign acinar or ductal epithelial cells
- Smears / FNA specimens often interpreted as benign or nondiagnostic
- Eosinophilic concretions can mimic mucinous secretions
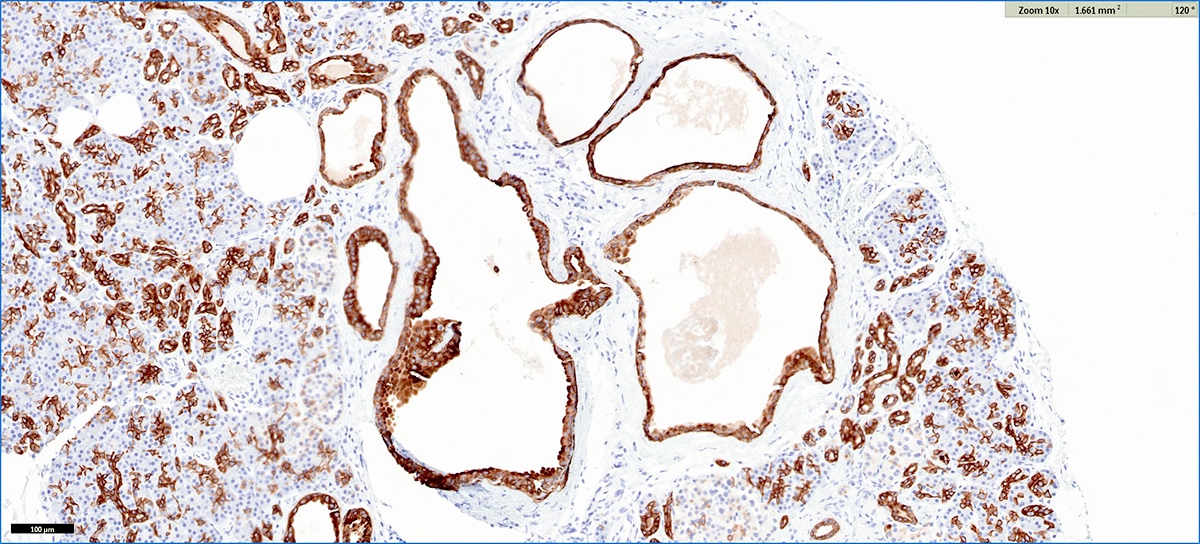
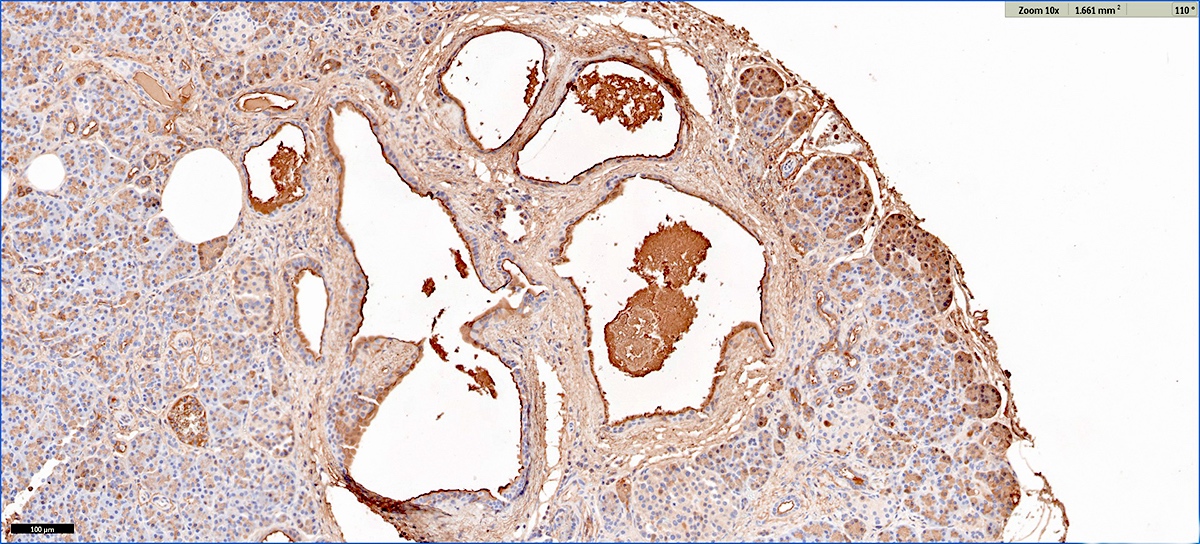
Positive stains
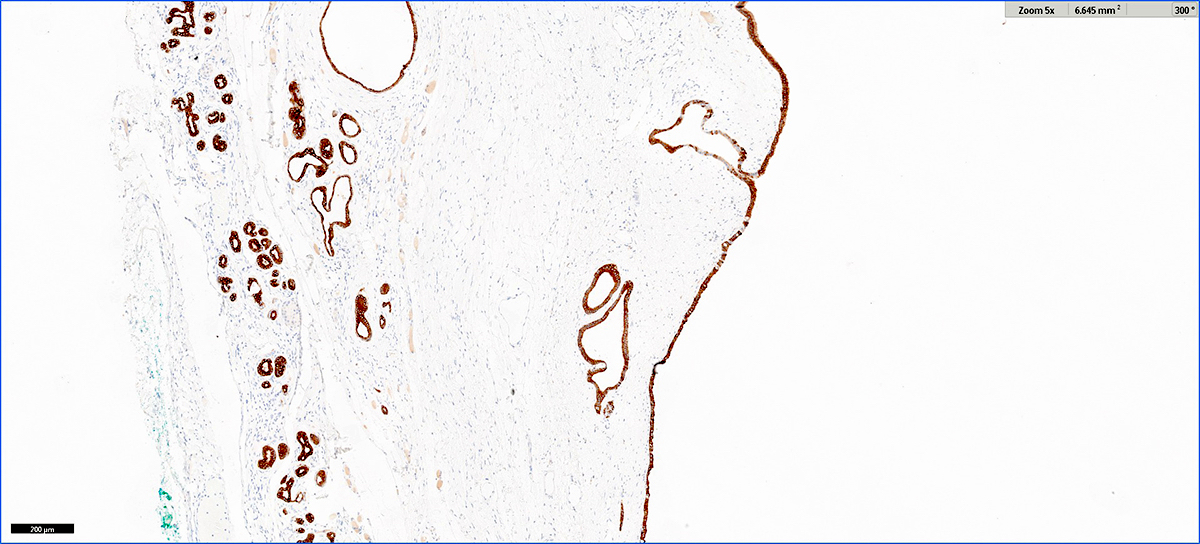
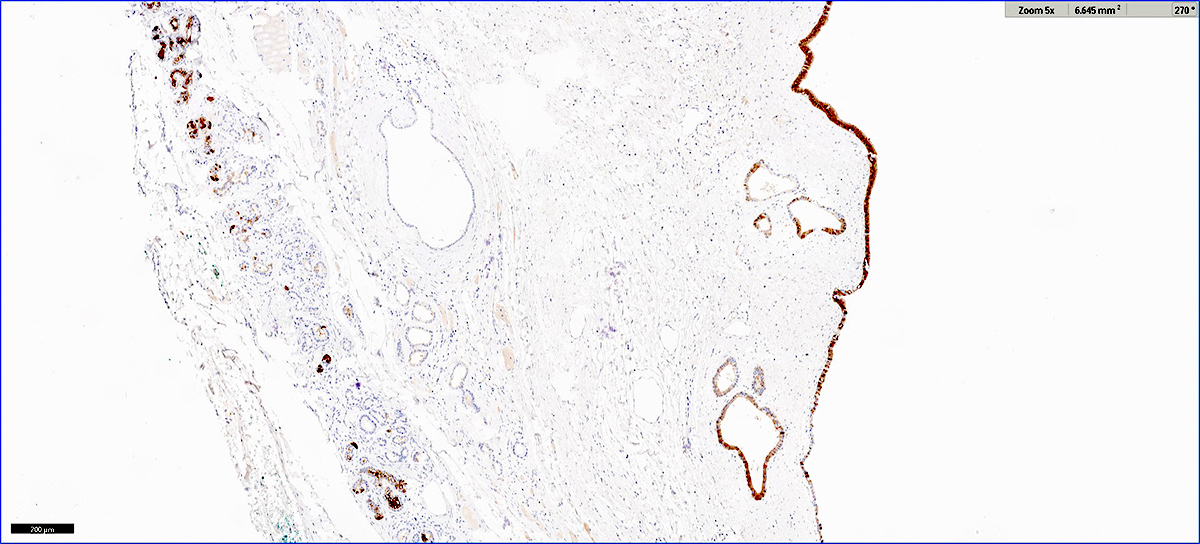
- Trypsin, chymotrypsin, lipase, CAM 5.2, CK7, CK8, CK18
- Apical cytoplasm with PAS positive, diastase resistant granules
- CK19 will stain intervening patches of the ductal epithelium
- References: J Clin Pathol 2023;76:740, Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:379, Esposito: Pathology of the Pancreas, 1st Edition, 2022
Negative stains
- Alpha amylase, synaptophysin, chromogranin
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Single report of array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) reported the following chromosome gains: 1p, 3p, 5q, 6p, 7q, 8, 10q, 11, 14, 20 and X (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1579)
- Random X chromosome inactivation observed in 5/5 cases, favoring nonneoplastic origin (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1329)
- In molecular analysis of 4 ACT cases, all cases had wild type status for KRAS and CTNNB1 genes (Oncol Lett 2014;8:852)
- Next generation sequencing (NGS) performed on 9 ACT cases demonstrated driver mutations in 2 cases: one case a likely pathogenic mutation in SMO gene and the other a pathogenic mutation in KRAS gene (Am J Surg Pathol 2023;47:379)
Sample pathology report
- Distal pancreas and spleen, distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy:
- Acinar cystic transformation, 3.8 cm, pancreatic tail (see comment)
- Proximal pancreatic resection margin is uninvolved
- Benign spleen with no diagnostic abnormality
- Comment: Sections show a multilocular cyst lined by bland cuboidal cells with granular cytoplasm. Eosinophilic concretions are present in the cyst. On immunohistochemical staining, the cyst epithelium is positive for both trypsin and CK19. The findings support the diagnosis of acinar cystic transformation.
Differential diagnosis
- Cystic variant of acinar cell carcinoma (acinar cell cystadenocarcinoma):
- May have similar histology but mitotic activity is conspicuous and there is clear atypia
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms:
- Mucinous, papillary lining and connection to ductal systems favors IPMN
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm:
- Ovarian type stroma is diagnostic; absent in cystic acinar cell lesions
- Cyst lining is typically mucinous but may be nonmucinous; does not contain acinar cells
- Serous cystadenoma:
- Areas with attenuated cytoplasm may mimic ACT
- Serous cystadenoma contains rich subepithelial vascular network, which is typically absent in ACT
- Should be negative for trypsin
- Squamoid cyst of pancreatic ducts:
- Cystically dilated ducts are lined by a squamous / transitional epithelium, not acinar cells
- May contain acidophilic concretions
- Retention cyst:
- Cyst > 1 cm lined by flat (not papillary) epithelium and connected to pancreatic ductal system; secondary to obstruction (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1730)
- Cyst epithelium may show mucinous change, negative for acinar cells / trypsin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
This is an incidental cyst found in the distal pancreas. On immunohistochemical staining, the cyst epithelium is positive for both CK19 and trypsin. Ki67 proliferation is low (< 3%). What is the diagnosis?
- Acinar cystic transformation
- Cystic acinar cell carcinoma
- Cystic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
Board review style answer #1
A. Acinar cystic transformation. The photograph demonstrates a cystic lesion lined by bland nonmucinous epithelium and filled with eosinophilic concretions. The positive CK19 and trypsin indicate ductal and acinar differentiation. The overall histomorphology and immunoprofile support the diagnosis of acinar cystic transformation of the pancreas. Answer D is incorrect because the cyst epithelium is nonmucinous. Answer B is incorrect because acinar cell carcinoma would have a much higher proliferation rate than 3%. Answer C is incorrect because solid pseudopapillary neoplasm should be negative for trypsin.
Comment Here
Reference: Acinar cystic transformation
Comment Here
Reference: Acinar cystic transformation