Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gupta N. Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumornephroblastoma.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- See also topics in Kidney tumor chapter: Childhood Wilms, Adult Wilms
- Extrarenal Wilms tumor are very rare, mostly seen in children
- Occur mostly in reteroperitoneum and very rarely in ovary
- Hypothesis for origin of these tumors is still debated
Epidemiology
- To date, limited case reports:
- 14 months (Journal of Gynecologic Surgery 2012;28:306)
- 3.5 years (J Pediatr Surg 2002;37:127)
- 21 years (Hum Pathol 2000;31:761)
- 56 years (Cancer 1988;61:1460)
Sites
- Usually retroperitoneal and inguinal regions (J Pediatr Surg 2002;37:127)
Pathophysiology
- Hypotheses regarding the origin: see J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 2007;12:145
- From ectopic metanephric blastema
- From primitive mesodermal tissue
- Connheim's cell rest theory
Clinical features
- Palpable mass
Diagnosis
- The diagnostic criteria necessary to establish the diagnosis include absence of primary kidney tumor and supernumerary kidney (radiologically and surgically)
Radiology description
- USG and CT: solid mass with cystic components (J Pediatr Surg 2002;37:127)
Prognostic factors
- When matched with the appropriate stage, prognosis is similar to its renal counterpart (J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 2007;12:145)
Treatment
- Excision and chemotherapy
- Similar staging and treatment protocol to renal Wilms tumor (J Clin Oncol 1991;9:167)
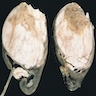
Gross description
- Solid large mass with cystic cavities
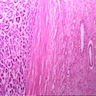
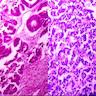
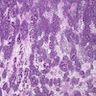
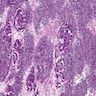
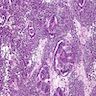
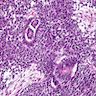
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sheets of undifferentiated blastemal component with or without epithelial, mesenchymal differentiation and anaplastic features
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis