Table of Contents
Definition / general | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gupta N. Breast carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumormetatstaticbreastcarc.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Usually incidental finding associated with (a) staging, (b) oophorectomy for patient with BRCA mutation or strong family history of breast cancer, or (c) therapeutic oophorectomy (induced hormone suppression for hormone receptor+ breast carcinoma)
- Ovarian involvement is seen in ~30% of therapeutic oophorectomies for advanced breast cancer, and at autopsy in ~10% of breast cancer cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:277)
- Involvement by lobular carcinoma (36%, including signet-ring cell type) is more frequent than ductal carcinoma (2.6%) (Br J Cancer 1984;50:23, Adv Anat Pathol 2007;14:149)
- Metastatic disease frequently arises up to 5 years post diagnosis, median 11.5 months, and is related to breast cancer stage (Br J Cancer 1984;50:23)
Pathophysiology
- High rates of hormone receptor+ breast cancer and premenopausal status suggest that hormone regulation is important in metastases to ovary
Clinical features
- Ovarian involvement is usually asymptomatic
- May have GI symptoms of abdominal pain, distension or pressure, abnormal uterine bleeding or mass (Gynecol Oncol 2003;90:397, Gynecol Oncol 2005;98:235)
Radiology description
- USG: mostly bilateral ovarian involvement by solid tumors 10 cm in size or less
Case reports
- 58 year old woman (J Cytol 2009;26:144)
- Two case reports and review of three additional cases (Cancer 1981;48:210)
- Sixteen cases reported as part of a cohort of patients with breast cancer and ovarian disease (Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:449)
Treatment
- Diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma to the ovary is usually done on salpingo-oophorectomy specimens:
- Subsequent treatment is commonly not necessary
- More extensive surgery (contralateral salpingo-oophorectomy, hysterectomy, lymph node dissection) may be considered if obvious or suspected residual tumor and no other sites of metastatic involvement on imaging
- Minimal (e.g., palliative debulking) can also be considered
- Surgery is defined as "optimal" when largest residual tumor mass is <2 cm (J Korean Med Sci 2009;24:114)
Gross description
- 80% are bilateral
- Multiple solid tumor nodules with soft consistency
- Involvement of ovarian surface and superficial cortex is common
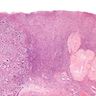
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Morphology mirrors the architecture and cytomorphology of the breast primary (including histologic grade)
- Lobular carcinoma: small cords and clusters of tumor cells in ovarian cortex, single cells in between normal cortical stroma; histiocytoid or signet ring cell morphology can be seen
- Ductal carcinoma: tubules / glands or solid nests of tumor cells in a variable fibrous stroma
Microscopic (histologic) images
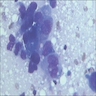
Cytology description
- Cell clusters have high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, moderate cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei, conspicuous nucleoli
Positive stains
- GATA3 is consistently positive in mammary carcinomas (Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:57)
- It is consistently positive in ER positive tumors but is also positive in 69% of ER negative tumors (Am J Clin Pathol 2014;14:648)
- ER, PR and HER2 are not always expressed; expression usually mirrors that of the primary mammary tumor
- Variable (~50%) GCDFP and mammaglobin staining (Hum Pathol 1991;22:368, Mod Pathol 2007;20:208, Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:103)
Negative stains
- PAX8: usually positive in most ovarian carcinomas subtypes (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1566)
- WT1: positive in only 2% of breast metastases versus 63% of ovarian tumors, but also negative in ovarian clear cell, mucinous and endometroid subtypes
- CA125: weak / negative in breast carcinomas, 90% of ovarian carcinomas are CA125+ (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1482)
Differential diagnosis
- Primary ovarian adenocarcinoma: PAX8+, CA125+
- Metastatic carcinoma from other sites (GI tract): history of known primary and IHC for primary site (CK20, CDX2, TTF1, Napsin A)