Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gupta N. Leiomyoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorleiomyoma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Accounts for 0.5 - 1% of all benign ovarian tumors
- Associated with synchronous leiomyomas of uterus
- Do not recur locally or metastasize, even if mitotically active
Epidemiology
- Age varies between 20 and 65 years
- About 16% occur after menopause (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2005;31:257)
Pathophysiology
- Arises from smooth muscle cells in ovarian hilar blood vessels
- Other possible origins include cells in ovarian ligament, smooth muscle cells or multipotential cells in ovarian stroma, undifferentiated germ cells, or cortical smooth muscle metaplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1436)
Clinical features
- Abdominal pain, mass, vaginal discharge
Laboratory
- CA125, CA19-9 and CEA are within normal range
Radiology description
- Transvaginal ultrasonography: solid mass
- MRI T1 and T2 weighted images: well circumscribed low signal intensity mass (Eur Radiol 1998;8:1444)
Case reports
- 21 year old woman with bilateral massive ovarian leiomyomata (Mod Pathol 1992;5:586)
- 31 year old woman with primary ovarian leiomyoma associated with endometriotic cyst presenting with symptoms of acute appendicitis (Diagn Pathol 2009;4:25)
- 79 year old woman with leiomyoma of the ovary presenting with Meigs' syndrome (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2005;31:257)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
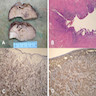
Gross description
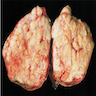
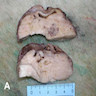
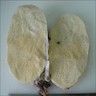
- Solid lobulated mass, median 3 cm (range 0.3 - 20 cm), often in hilar region
- Cut surface is gray-white, whorled
Gross images
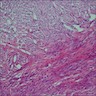
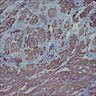
Microscopic (histologic) description
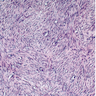
- Irregular bundles and whorling of spindle shaped cells with no atypia or pleomorphism
- Degenerative changes like hyaline degeneration and myxomatous changes can be seen
- May be cellular, have prominent mitotic activity or occasionally have bizarre nuclei or myxoid stroma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis