Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Varughese L, Malliah R. Choriocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorchorio.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare primary ovarian tumor; < 1% of primitive ovarian germ cell tumors
- May develop from ovarian pregnancy (gestational choriocarcinoma), as a germ cell tumor (pure or mixed, non-gestational choriocarcinoma) or as a surface epithelial tumor with choriocarcinomatous differentiation
Epidemiology
- Primary ovarian choriocarcinomas are more common in children and adolescents
- After puberty, origin from an ovarian ectopic pregnancy cannot be excluded
Clinical features
- Presentation similar to ectopic or tubal pregnancy
- Abdominal enlargement
- Pain, sometimes hemoperitoneum
- Isosexual precocity, menstrual abnormalities, androgenic changes
Laboratory
- Markedly elevated serum β hCG
- Monitoring serum levels of β hCG is helpful in predicting recurrence and response to therapy
Radiology description
- On imaging, appears as vascular solid tumor with cystic, hemorrhagic, necrotic areas
Prognostic factors
- In contrast to gestational choriocarcinomas, non-gestational choriocarcinomas are difficult to treat, generally unresponsive to chemotherapy
- Metastases to lungs, liver, bone and viscera are common at diagnosis
Case reports
- 19 year old woman with pure choriocarcinoma of ovary diagnosed by FNA (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2009;52:417)
- 48 year old woman with pure choriocarcinoma of ovary (J Gynecol Oncol 2011;22:135)
Treatment
- Surgery, chemotherapy
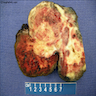
Gross description
- Hemorrhagic, soft, tan with necrosis
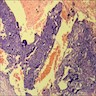
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Composed of cytotrophoblast, intermediate trophopblast and multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast around periphery of blood channels
- Cytotrophoblasts have clearly defined cytoplasmic borders, are mononucleated with vesicular nuclei and distinct nucleolus
- Syncytiotrophoblasts contain basophilic to amphophilic cytoplasm with mutiple nuclei
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Cytokeratin, CD10, human placental lactogen, EMA
- Syncytiotrophoblasts are hCG+
Negative stains
- CD31, CD34 (Mod Pathol 2011;24:646)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Gestational choriocarcinomas have component of paternal chromosomes, often aneuploid, but hyperploidy and other variations have been described (Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology)
Differential diagnosis
- Adrenocortical carcinoma: see UC Davis-Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Malignant pheochromocytoma
- Metastatic choriocarcinoma
- Mixed germ cell tumor with choriocarcinoma component
Additional references