Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Nilforoushan N, Vang R. Mucinous borderline tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorborderlinemucinous.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Noninvasive mucinous neoplasm with complex architecture and gastrointestinal type differentiation
Essential features
- Ovarian tumors with mucinous epithelium of gastrointestinal type and epithelial proliferation (tufting, stratification and villus formation) involving > 10% of tumor
- Mild cytologic atypia, resembling low grade dysplasia of intestinal epithelium
- May be associated with intraepithelial carcinoma (foci with high grade cytologic atypia) and microinvasion (stromal invasion by single cells or small nests, measuring < 5 mm)
- > 90% of tumors are unilateral
- KRAS mutations are the most frequent molecular alterations
Terminology
- Mucinous borderline tumor
- Previously classified as atypical proliferative mucinous tumor or mucinous tumor of low malignant potential
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8472/1 - mucinous cystic tumor of borderline malignancy
Epidemiology
- Mean age: 45 years (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1995;14:198)
- Second most common subtype of ovarian borderline tumor in Western countries and the most common subtype in Asia (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2011;30:218)
Sites
- Ovary; less frequently in retroperitoneum
Pathophysiology
- May arise from mucinous cystadenoma
- Also associated with Brenner tumor and mature cystic teratoma (Mod Pathol 2020;33:722)
Clinical features
- Symptoms most often are related to pelvic mass
Diagnosis
- May be suggested by pelvic ultrasound
- Definitive diagnosis deferred to oophorectomy
Laboratory
- Patients may have increased CA 125, CEA or CA19-9 levels
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis; stage I at diagnosis
- Mucinous borderline tumor with intraepithelial carcinoma: 95 - 100% overall survival rate (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1447)
- Recurrences may occur following cystectomy
- Tumors with microinvasion are associated with recurrence rate of 5% (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:546)
- Anaplastic carcinoma and sarcoma mural nodules are associated with adverse clinical behavior and increased mortality rate; however, anaplastic carcinoma in unruptured stage I tumors does not necessarily carry an adverse prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:383, Int J Gynecol Pathol 1994;13:62)
- Sarcoma-like mural nodule does not have effect on prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1467)
Case reports
- 42 year old woman with ovarian borderline mucinous tumor accompanied by low grade endometrial stromal sarcoma with myxoid change (Eur J Med Res 2017;22:52)
- 53 year old woman with mucinous borderline tumor with pulmonary and pleural metastasis (Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:571348)
- 59 year old postmenopausal woman with primary signet ring cell carcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation arising in mucinous borderline tumor (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2019;31:100522)
Treatment
- Surgery with staging
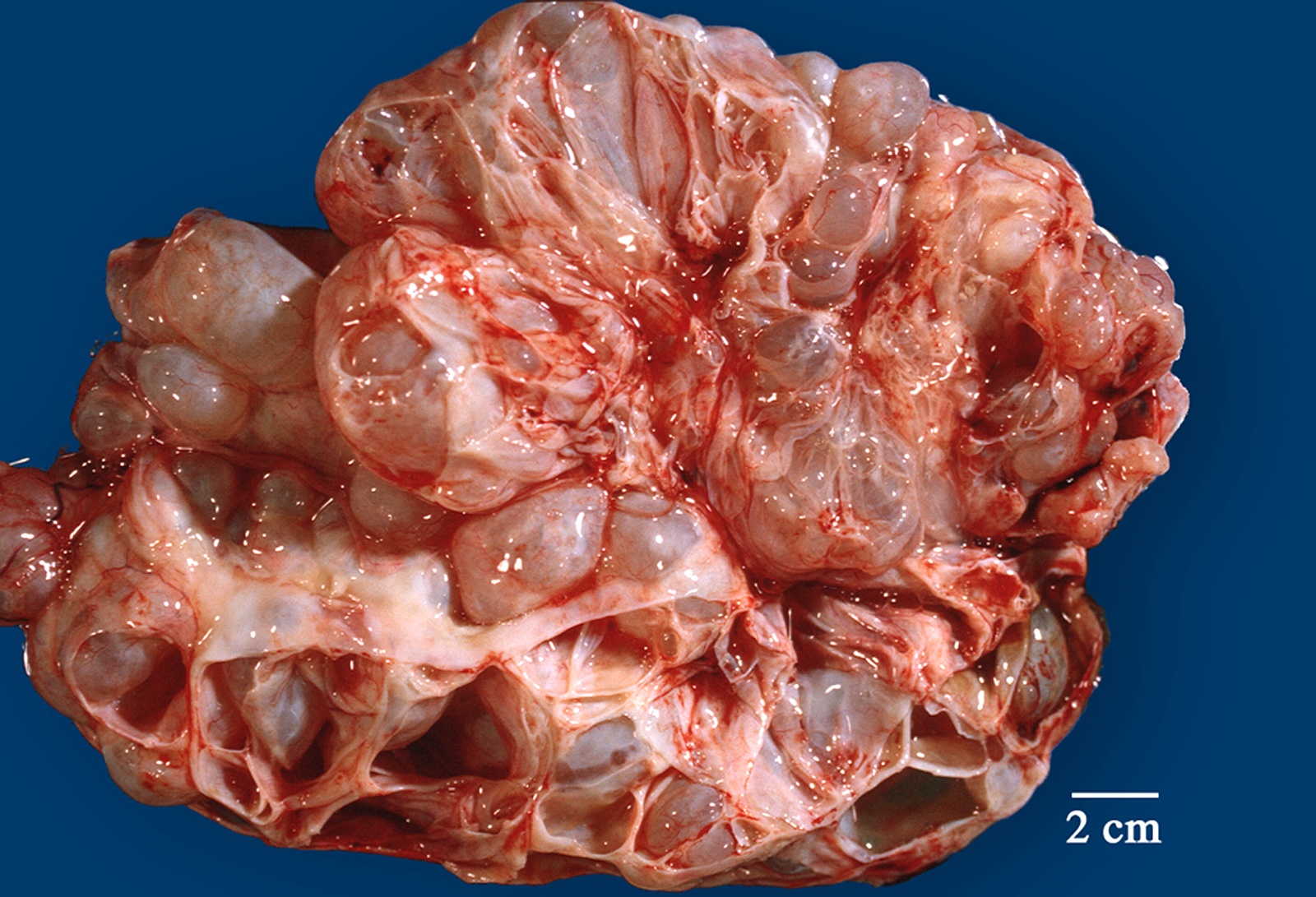
Gross description
- > 90% of the tumors are unilateral (Gynecol Oncol 2005;97:80)
- Mean size: 22 cm; some tumors can measure as large as 50 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:128)
- Cysts are multiloculated with mucinous contents and smooth external surface
- Solid areas and necrosis may be present
Frozen section description
- Complex architecture with tufting and villus formation
- Glands with luminal mucin
- Mucinous epithelium of gastrointestinal type with goblet cells
- Mild cytologic atypia with nuclear stratification, hyperchromasia and mitotic activity
Frozen section images
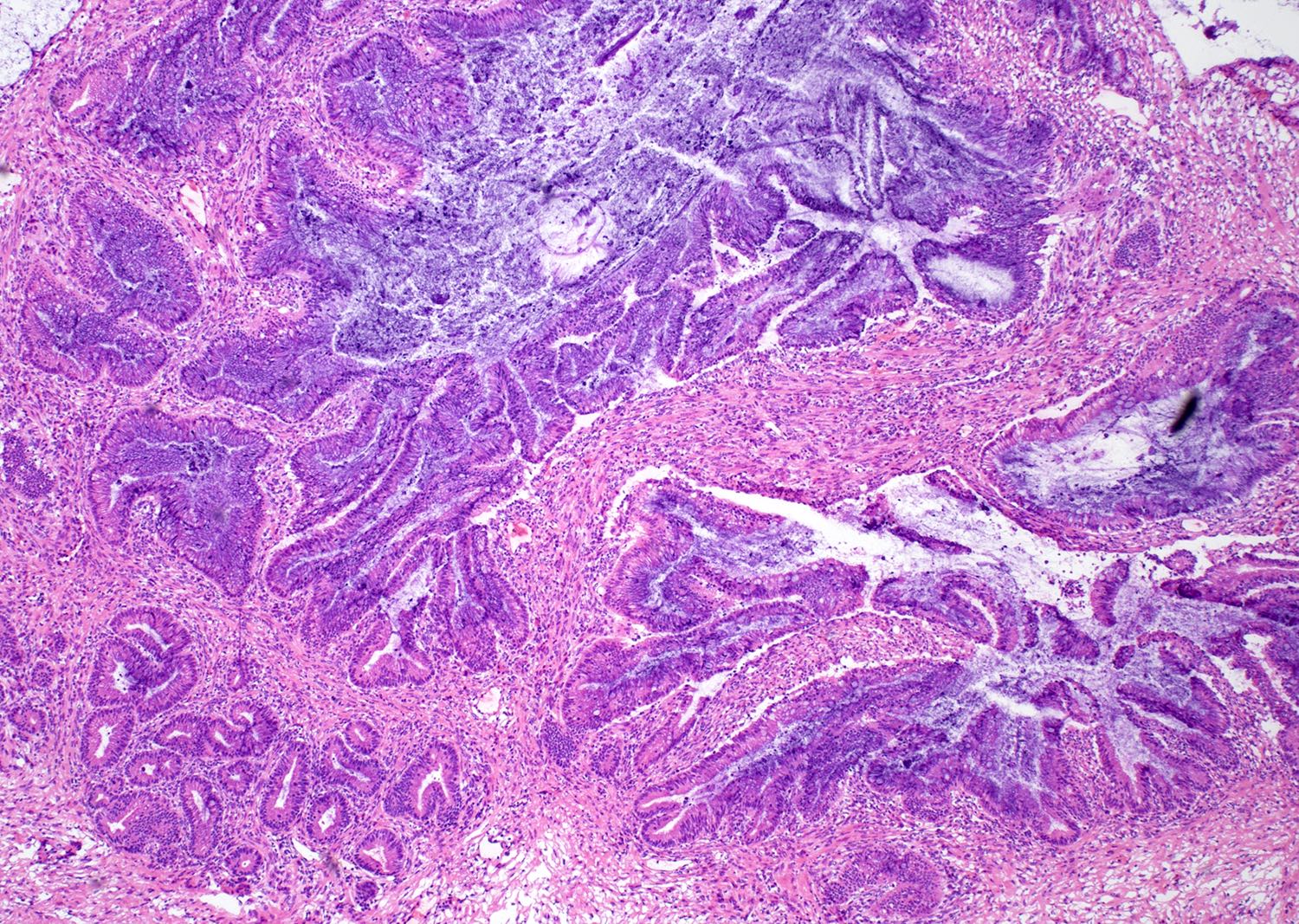
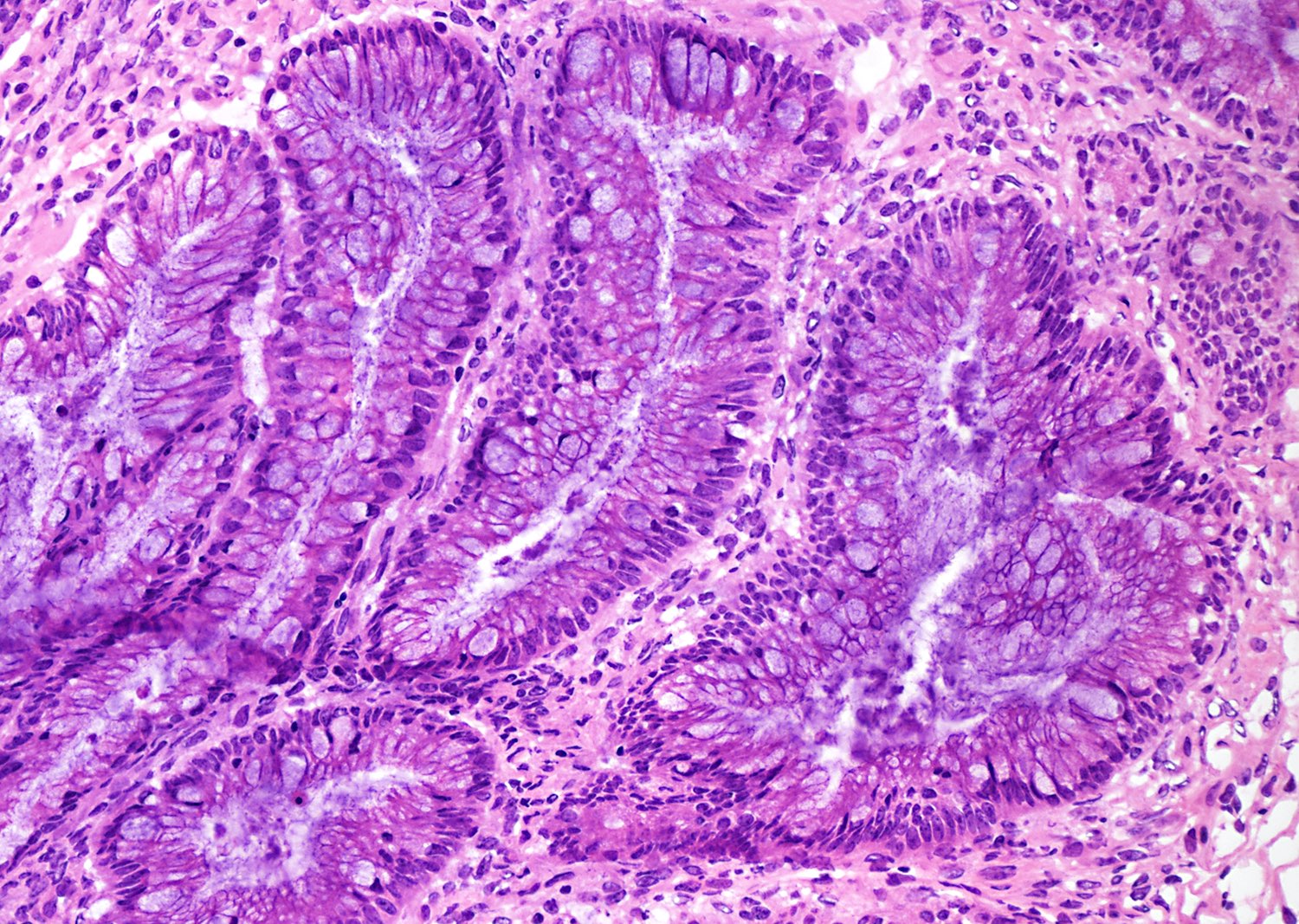
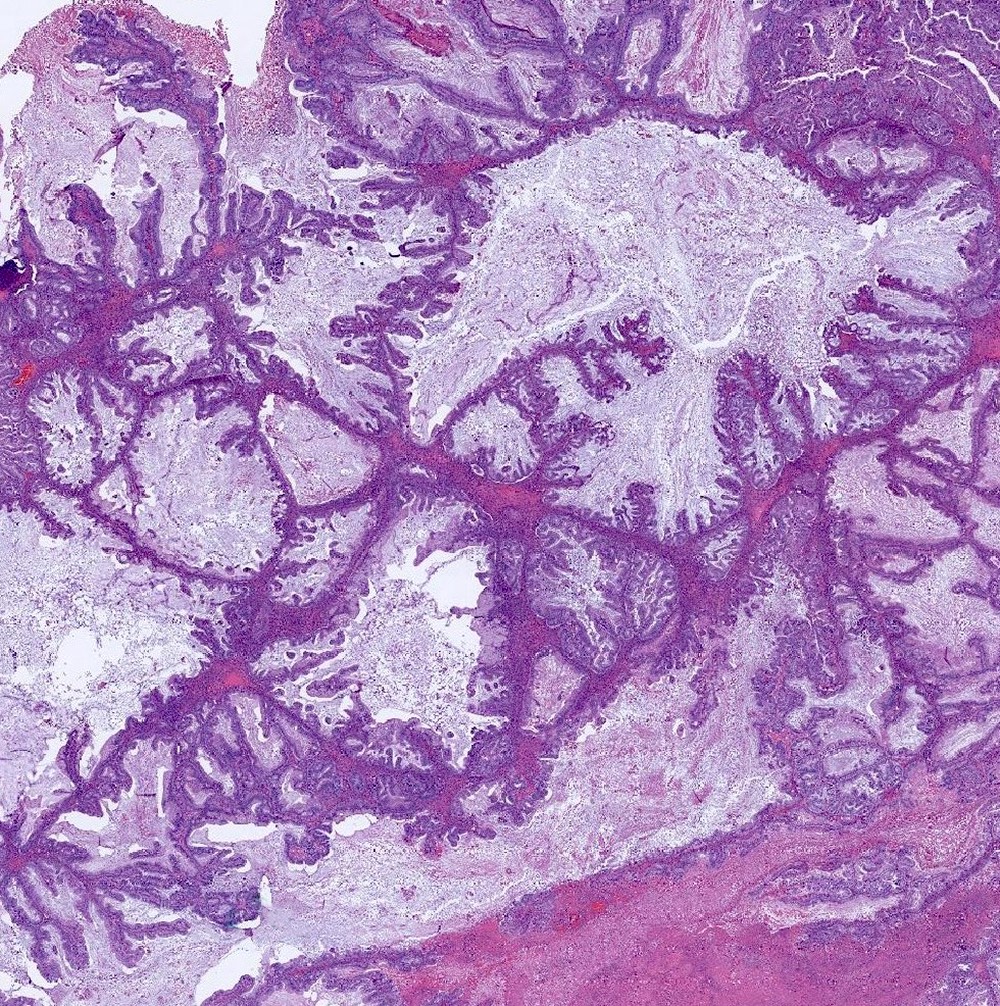
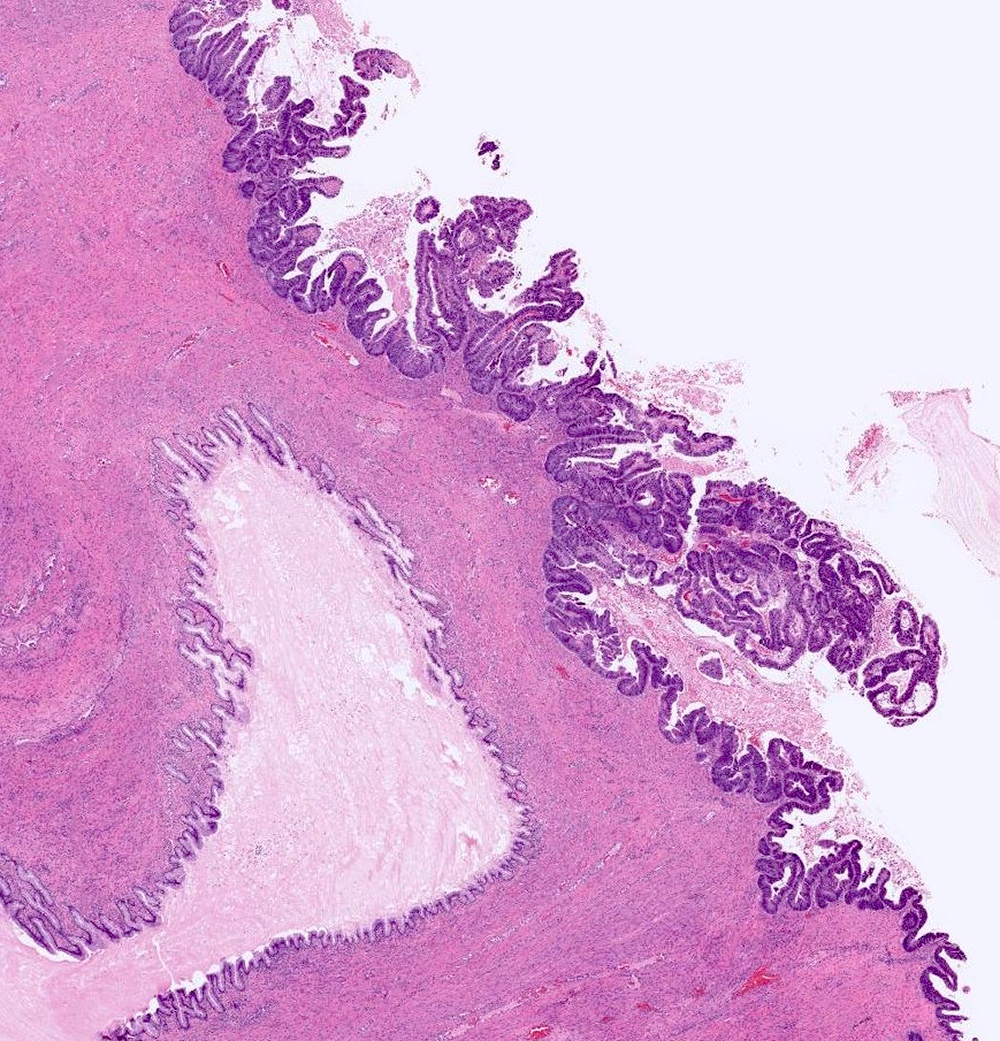
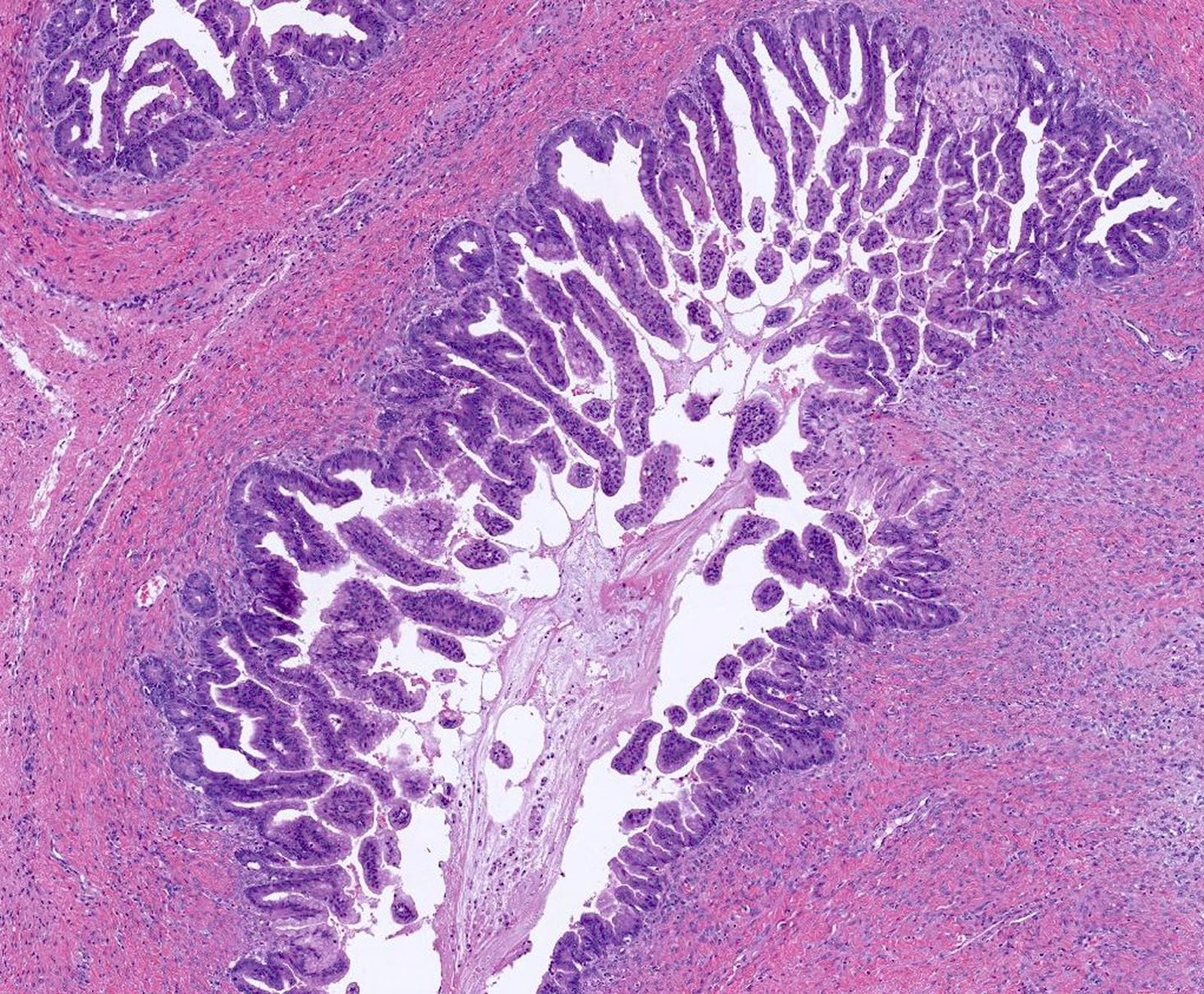
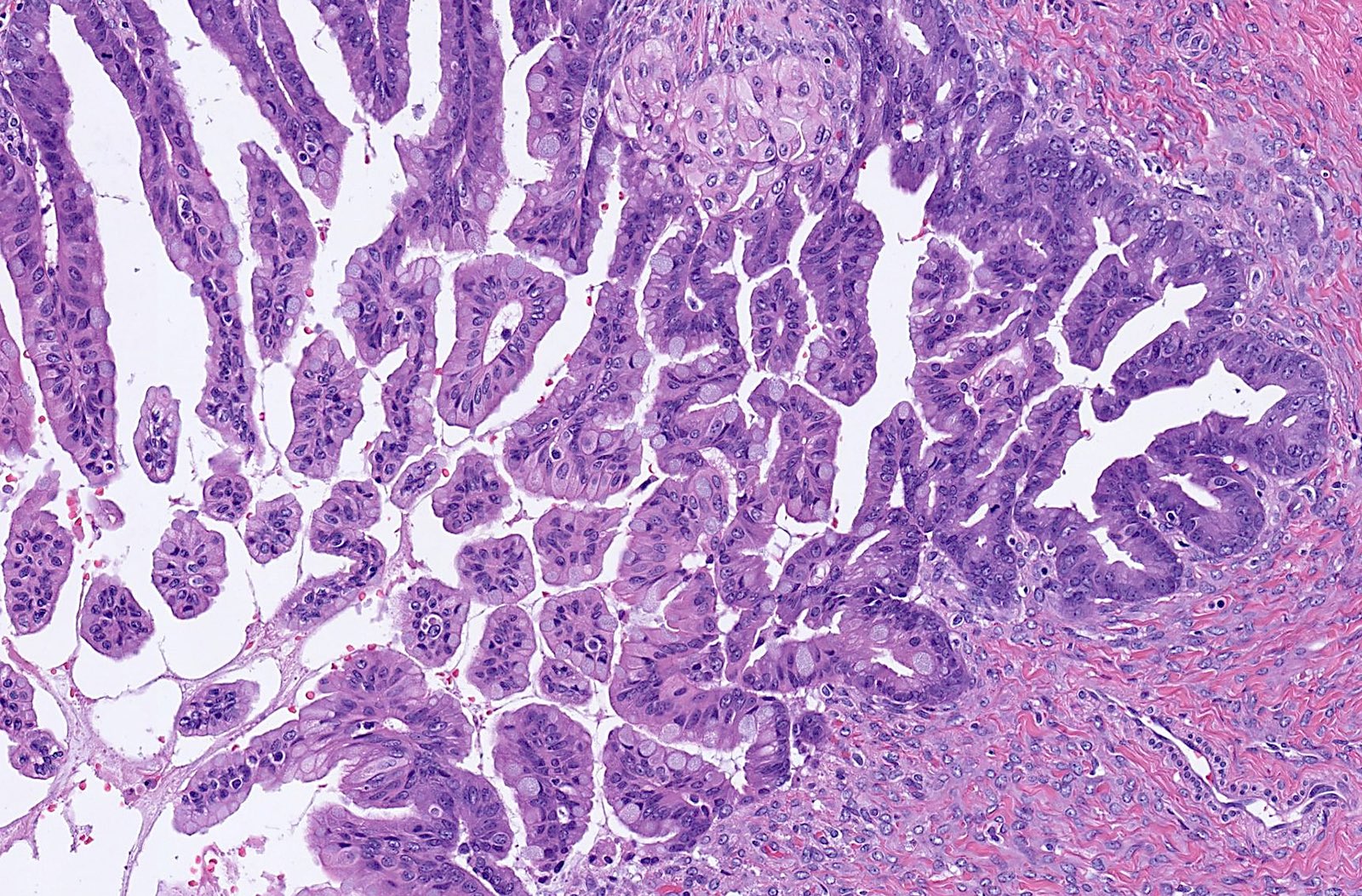
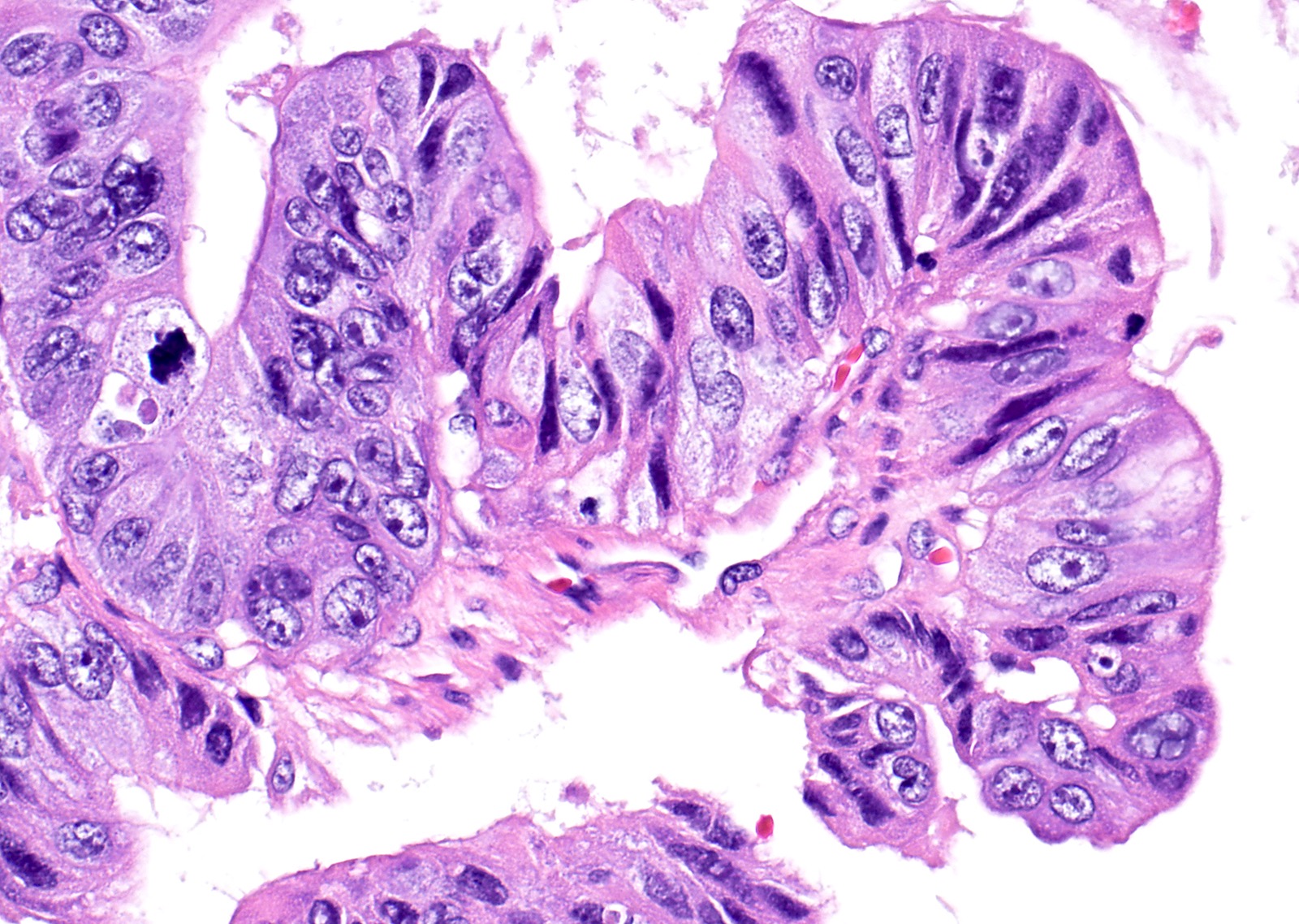
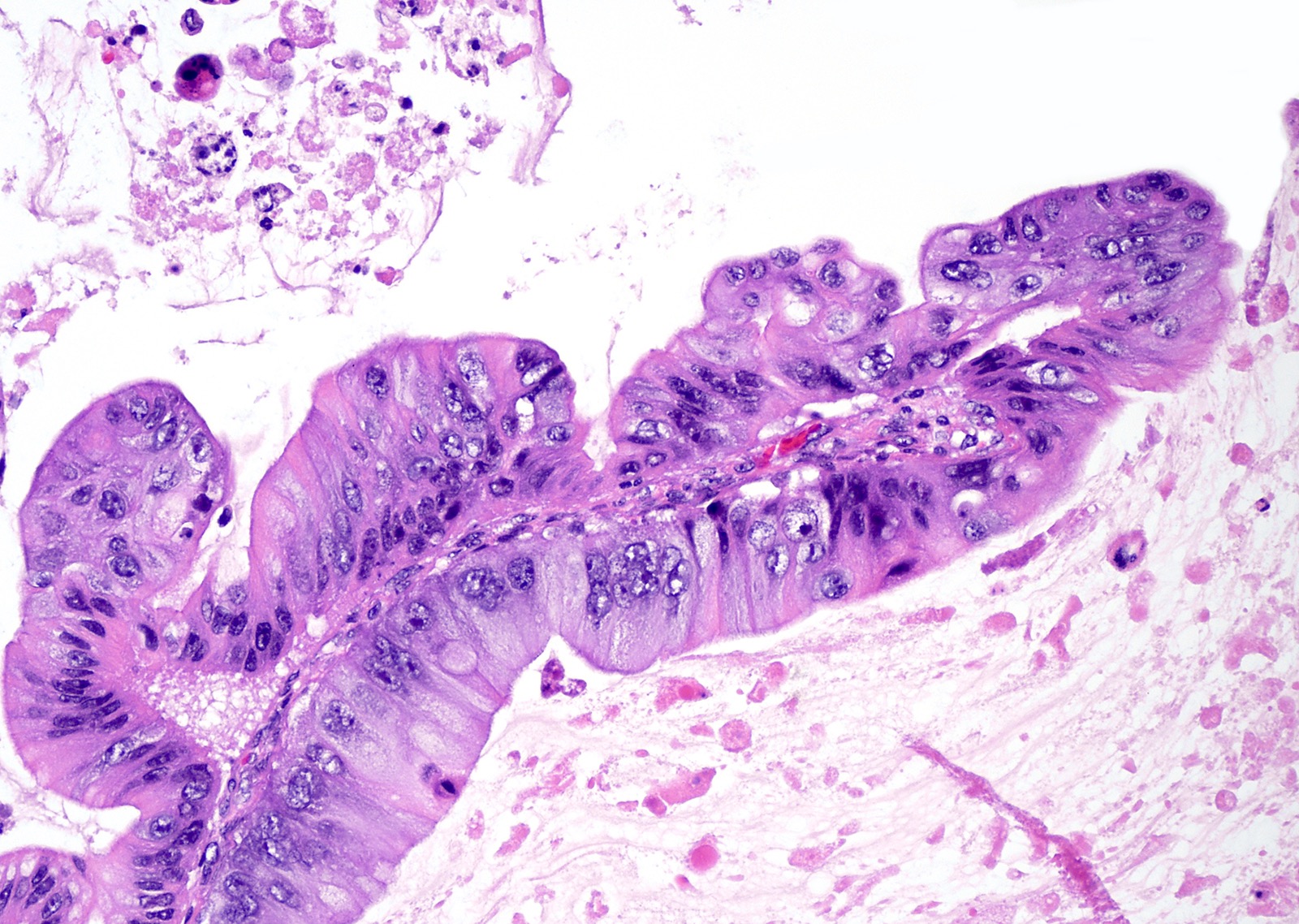
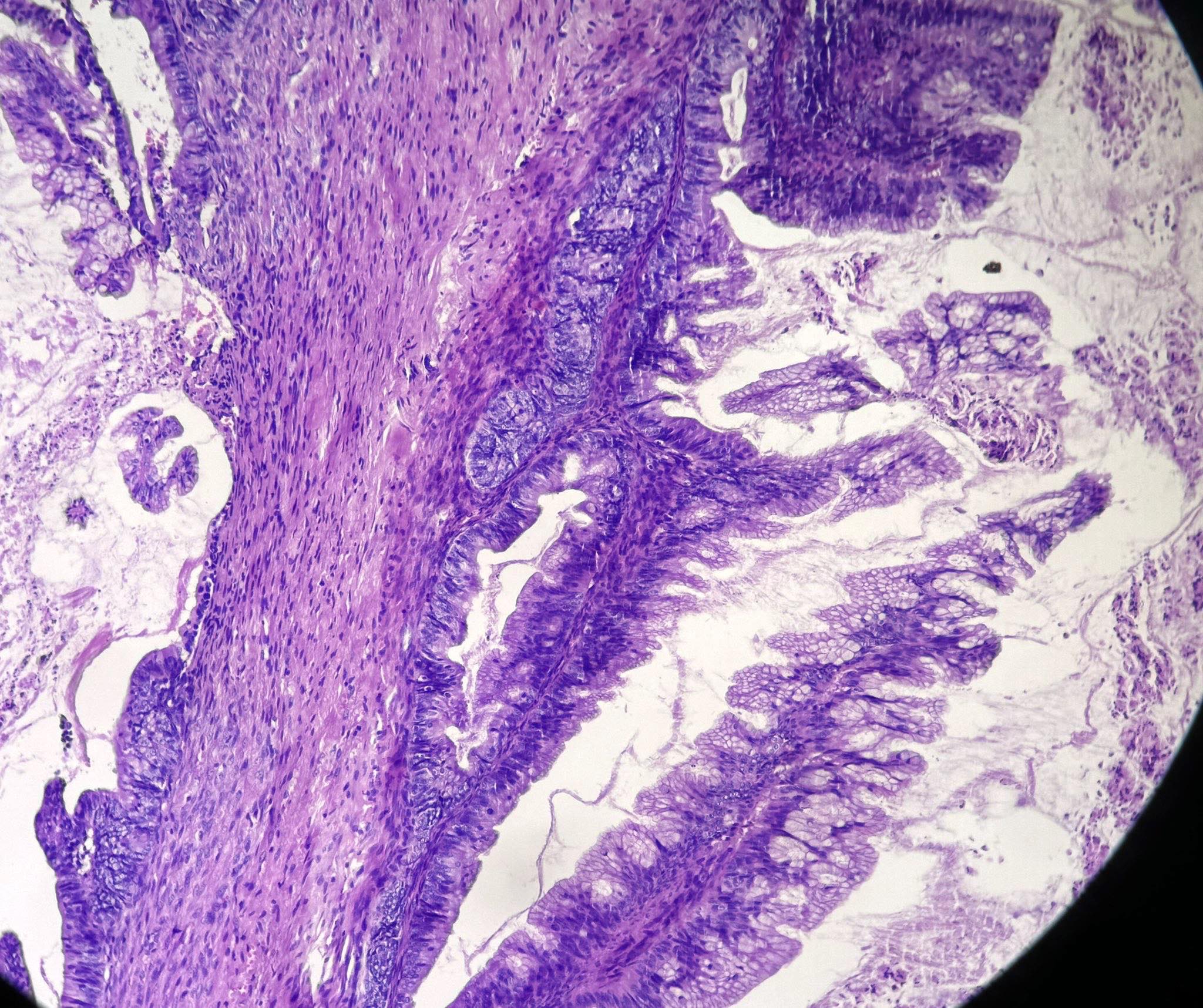
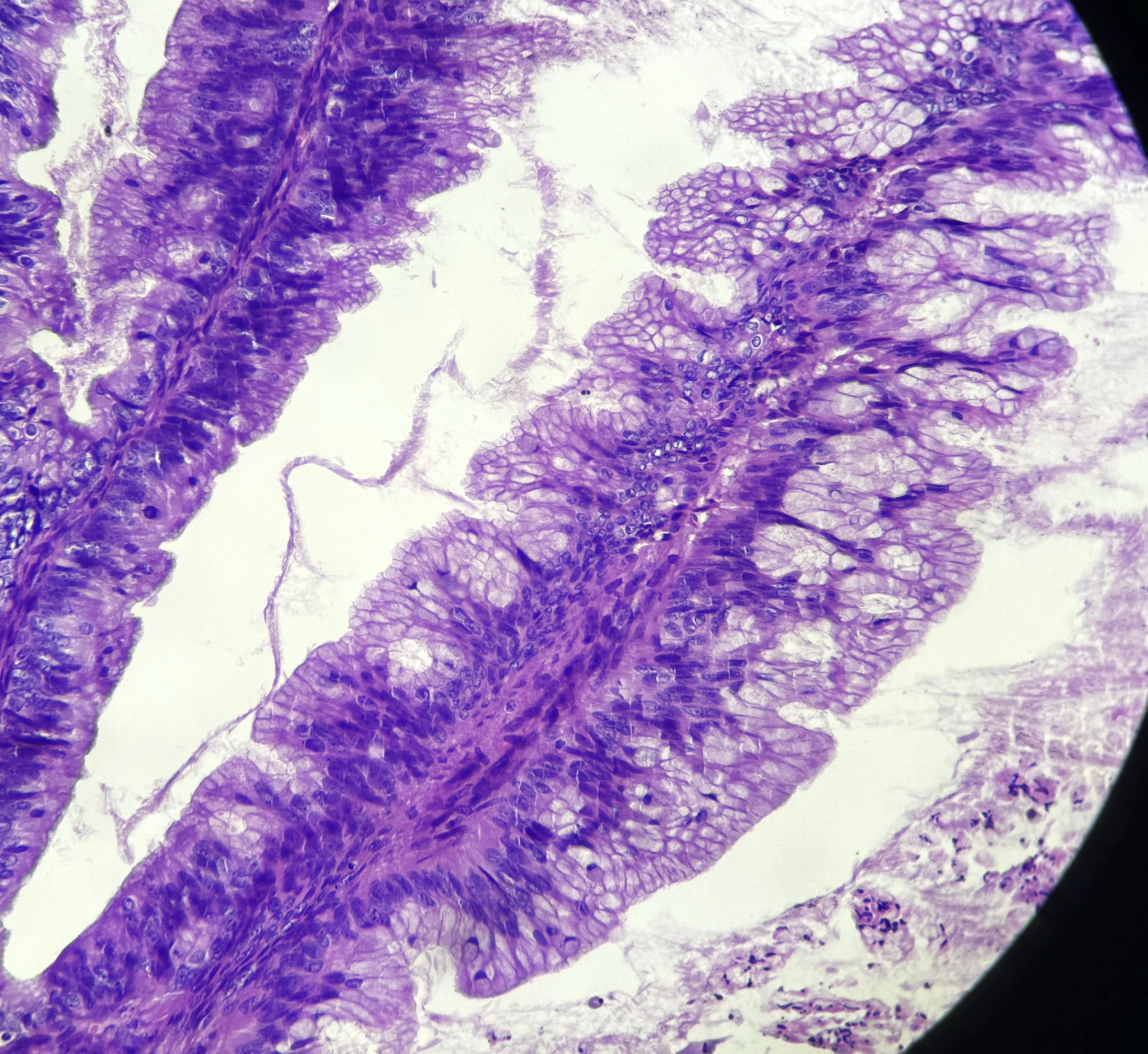
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Complex architecture with tufting and villus formation
- Epithelium resembles low grade dysplasia of the intestine with goblet cells, neuroendocrine cells and occasional Paneth cells
- Neoplastic cells have hyperchromasia, crowding, stratification and mitotic activity
- Glands with luminal mucin
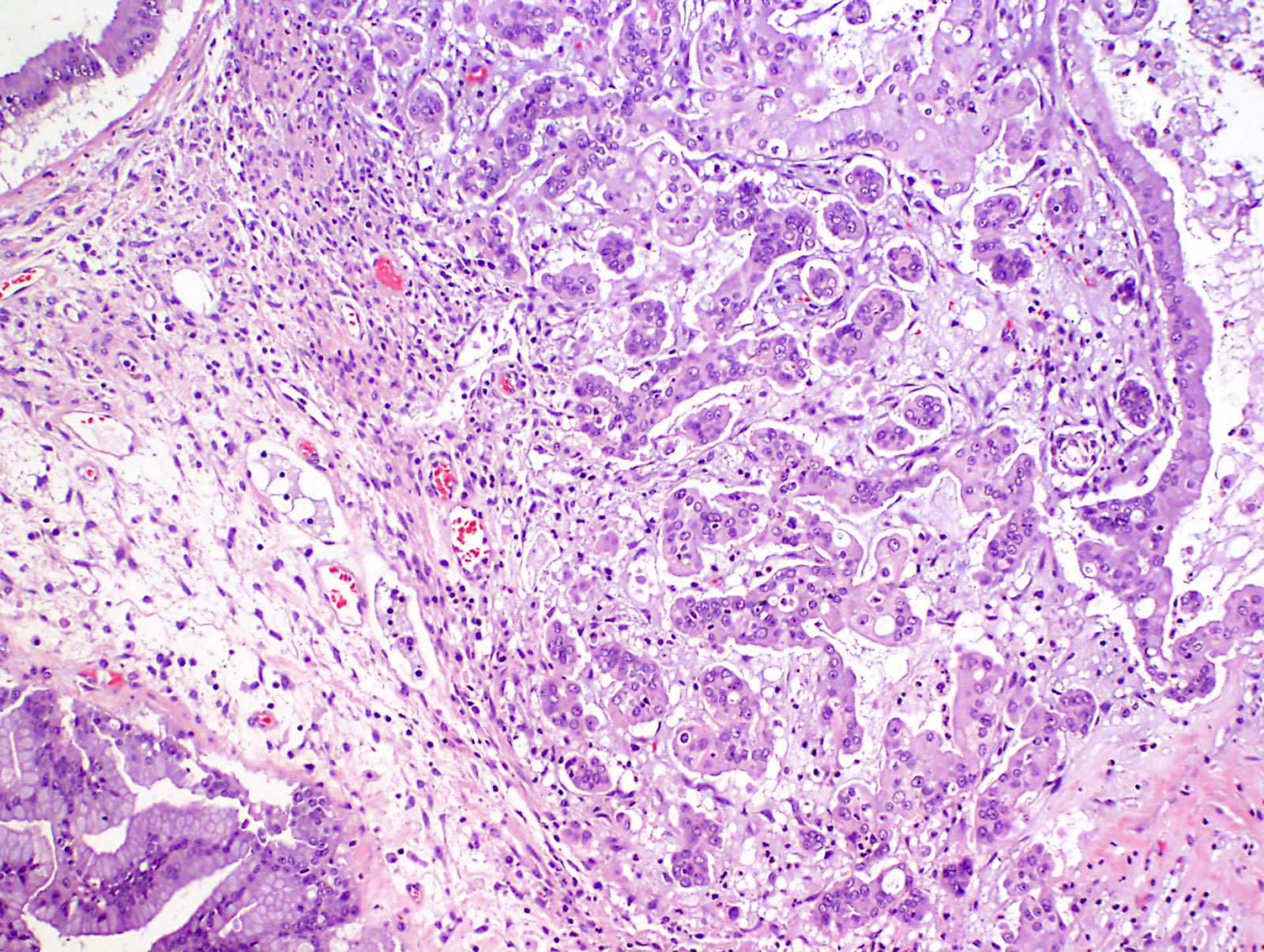
- With intraepithelial carcinoma:
- Resembles high grade dysplasia of intestines
- No stromal invasion
- With microinvasion:
- Foci of stromal invasion, measuring < 5 mm in the greatest dimension
- Degree of cytologic atypia is mild and similar to borderline tumor
- Areas of mucin extravasation with inflammatory response are not diagnostic of invasion
- With mural nodule:
- Classified as sarcoma-like, anaplastic carcinoma and sarcoma (Cancer 1979;44:1327)
- Sarcoma-like nodule (reactive): spindled and round cells, multinucleated giant cells and marked inflammation
- Anaplastic carcinoma: rhabdoid, pleomorphic and spindle cells
- Sarcoma: usually without specific differentiation but there are some reports of rhabdomyosarcomatous and leiomyosarcomatous differentiation (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1994;13:62)
- Classified as sarcoma-like, anaplastic carcinoma and sarcoma (Cancer 1979;44:1327)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Clusters of epithelial cells with nuclear stratification, mild to moderate cytologic atypia and mucinous cytoplasm
Positive stains
- CK7
- CK20 (variable)
- CDX2 (variable) [the extent of expression of CK7 is greater than that of CK20 or CDX2] (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1130)
- PAX8 (focal)
- SATB2 is positive in a small subset of cases, including mucinous tumors associated with teratoma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:249, Mod Pathol 2019;32:1834)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- KRAS mutations are identified in 30 - 75% of the tumors (Genome Med 2015;7:87)
- TP53 mutations are present in lower frequency
Sample pathology report
- Ovary, left (oophorectomy):
- Mucinous borderline tumor
- Ovary, right (oophorectomy):
- Mucinous borderline tumor with intraepithelial carcinoma
- Ovary, left (oophorectomy):
- Mucinous borderline tumor with microinvasion
Differential diagnosis
- Seromucinous borderline tumor:
- Admixture of Müllerian type epithelium with endocervical type mucinous epithelium, including serous or ciliated cells
- Associated with endometriosis
- Low grade mucinous neoplasm of appendiceal origin:
- Mucinous epithelium with tall mucinous cells, scalloping, subepithelial clefts, dissecting mucin pools
- Metastatic pancreatobiliary carcinoma:
- Diffuse intraepithelial carcinoma, foci of invasive carcinoma
- Microinvasive carcinoma:
- Stromal invasion morphologically resembles invasive mucinous carcinoma but measuring < 5 mm
- Invasive component has complex architecture and high grade cytologic atypia
- Mucinous cystadenoma:
- Cysts and glands with simple lining composed of nonstratified mucinous epithelium
- Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with mucinous differentiation:
- Mucinous carcinoma with expansile growth pattern:
- Confluent growth pattern with glandular crowding without intervening stroma, measuring ≥ 5 mm
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What is the most common mutation associated with ovarian mucinous borderline tumors?
- BRAF
- CDKN2A
- KRAS
- TP53
Board review style answer #1
C. KRAS. KRAS mutations are present in 30 - 75% of mucinous borderline tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous borderline tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous borderline tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding microinvasion in mucinous borderline tumor?
- Associated with adverse clinical behavior
- Associated with mucin extravasation with inflammatory response and histiocytes
- Cytologic atypia is severe and similar to intraepithelial carcinoma
- Foci of stromal invasion measuring < 5 mm in the greatest dimension
Board review style answer #2
D. Foci of stromal invasion measuring < 5 mm in the greatest dimension. Cytologic atypia in microinvasion is mild to moderate, similar to adjacent borderline tumor. Presence of severe atypia warrants the diagnosis of microinvasive carcinoma. Mucin extravasation with inflammatory response and histiocytes is associated with gland rupture and not diagnostic of microinvasion. Overall, mucinous borderline tumors have excellent prognosis. Microinvasion is not associated with adverse behavior.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous borderline tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous borderline tumor