Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) descriptionCite this page: Riddle N, Shutter J., Islam S. Torsion. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytubetorsion.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
Ovary:
Fallopian tube:
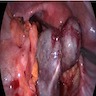
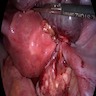
- Rare; partial or complete rotation of ovarian vascular pedicle, causing obstruction to venous outflow and arterial inflow
- In children, ovary is often normal (Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005;159:532)
Fallopian tube:
- "Twisting" of fallopian tube that blocks blood flow, causing ischemia and associated edema and pain
- Often accompanies torsion of adjacent ovary (often with a cyst) but may be isolated to tube
Epidemiology
Fallopian tube:
- Occurs in women of all ages
- 2/3 involve right tube
Etiology
Fallopian tube:
- Usually associated with a mass / cyst causing rotation / obstruction
- Also PID, hydrosalpinx, tubal ligation or adhesions
- Occasionally no identifiable cause
Clinical features
-
Ovary:
- Presents with abdominal pain, patients need emergency ultrasound and laparoscopy (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2008;21:201)
- Predisposing factors: large cyst, neoplasms (benign or malignant), pelvic inflammatory disease; also associated with in vitro fertilization
- sharp lower abdominal pain, fever, tachycardia, leukocytosis (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010;89:1354)
Fallopian tube:
Radiology description
- Fallopian tube: ultrasound usually shows adnexal mass with heterogeneous echogenicity and cystic component with fluid levels
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with isolated fallopian tube torsion (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;185:1590)
- 32 year old woman at 32 weeks gestation with nausea, pain and vomiting (J Med Case Reports 2008;2:378)
Treatment
Ovary:
Fallopian tube:
- Cases during pregnancy (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:683)
- Recommended to attempt to preserve ovary, since most are viable (Clin Obstet Gynecol 2006;49:459)
Fallopian tube:
- May resolve or tube may become necrotic and calcified with autoamputation of tube and ovary
- Often requires surgical excision
Gross description
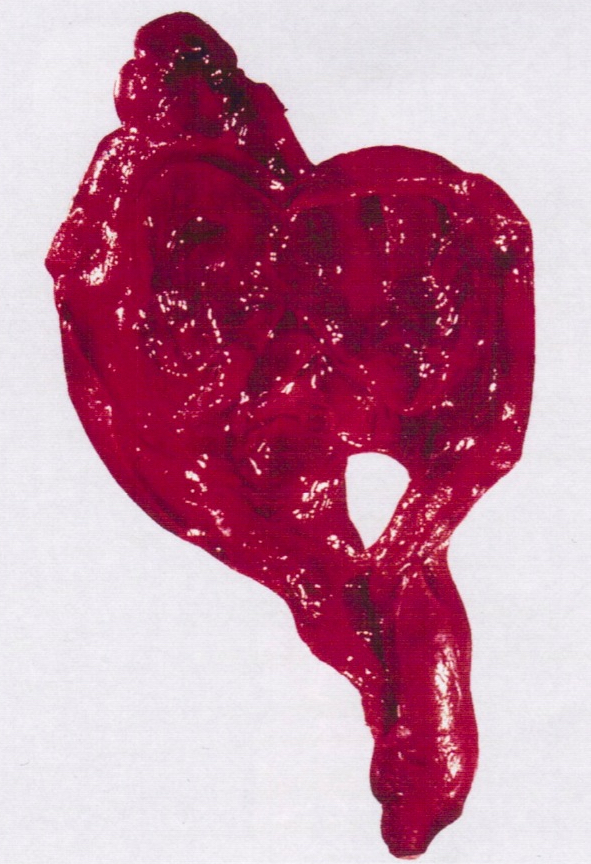
- Fallopian tube: swollen, dusky fallopian tube, with or without associated mass / cyst
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Fallopian tube: ischemic necrosis of mucosa and wall