Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Mubeen A, Gopinath A. Seromucinous cystadenoma and adenofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovaryseromucinouscystadenoma.html. Accessed January 13th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign ovarian epithelial tumors exhibiting admixture of 2 or more Müllerian type epithelia (mucinous, serous and endometrioid), each accounting for at least 10% of the epithelium
Essential features
- Benign ovarian neoplasms with admixture of 2 or more Müllerian type epithelia, each accounting for 10% or more
- Mucinous, serous and endometrioid cell types
- Mean age 62 years (Histopathology 2021;78:445)
- Association with endometriosis
Terminology
- Müllerian mucinous cystadenoma (preferred by some authors to reflect association with endometriosis, endometrioid and clear cell tumors rather than serous tumors of the ovary)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D27 - benign neoplasm of ovary
Epidemiology
- Rare tumors
Clinical features
- Detected incidentally during work up of other gynecological diseases
- May present with an abdominal mass, abdominal pain or swelling
- Unilateral / bilateral (bilateral in 40% of cases) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2022;41:68)
- Mean size is 9 cm, generally smaller than intestinal type neoplasms (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2022;41:68)
Diagnosis
- Microscopic examination
Radiology description
- Unilocular / multilocular cystic masses (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2019;43:119)
Treatment
- Surgery (cystectomy or oophorectomy)
Gross description
- Cystic masses (unilocular or multilocular)
- Seromucinous cystadenofibroma are solid with a fibrous cut surface
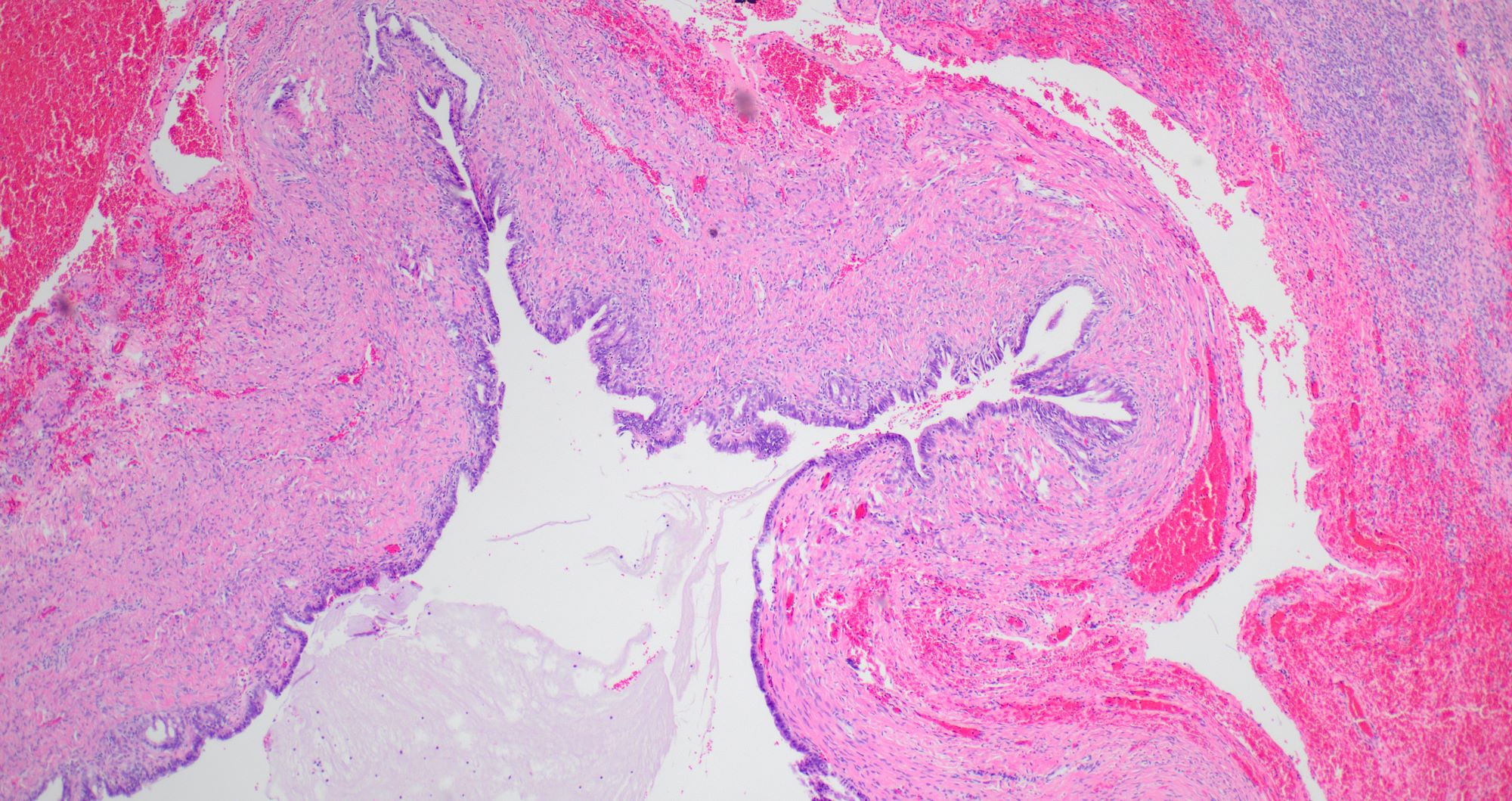
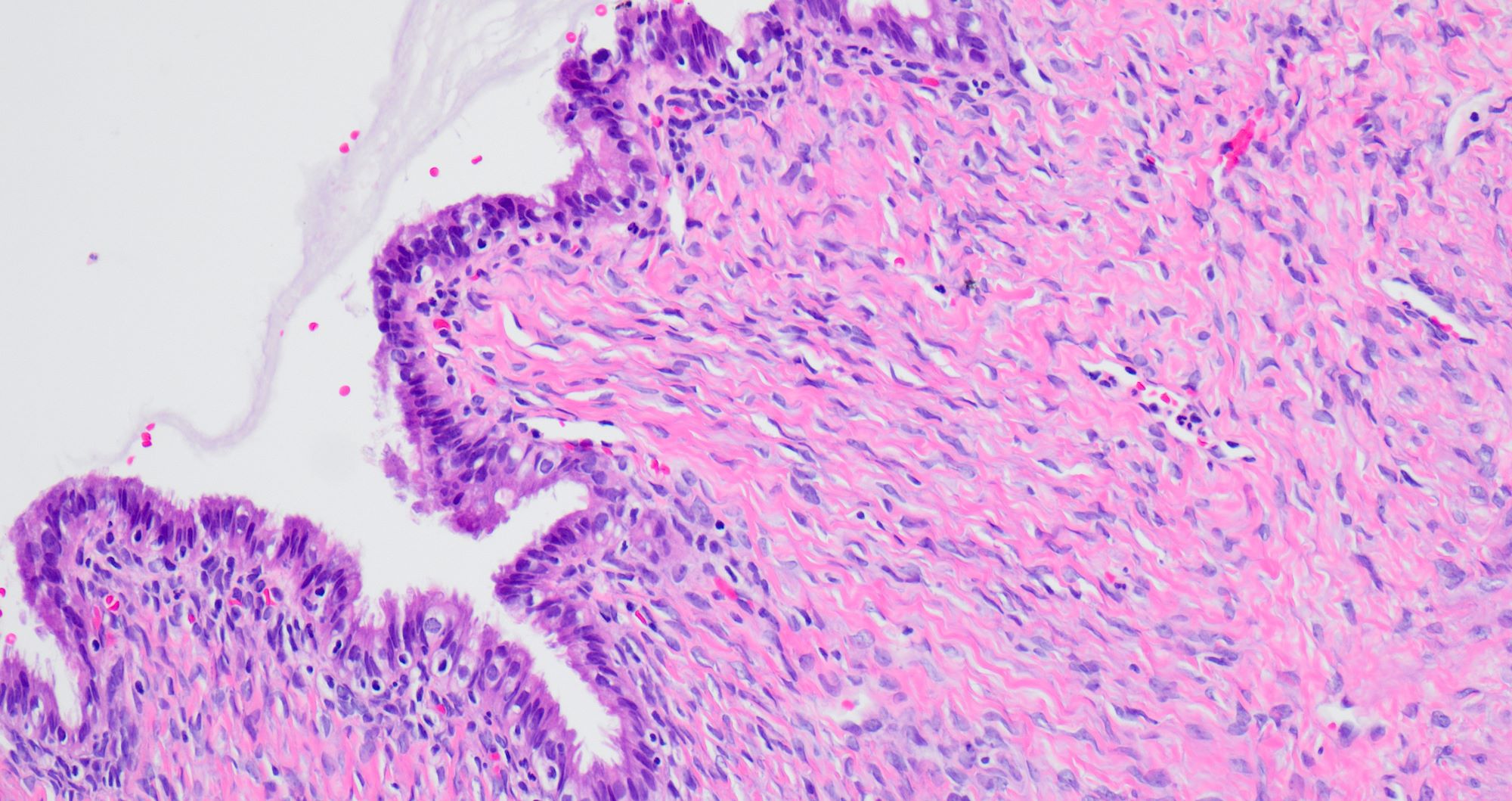
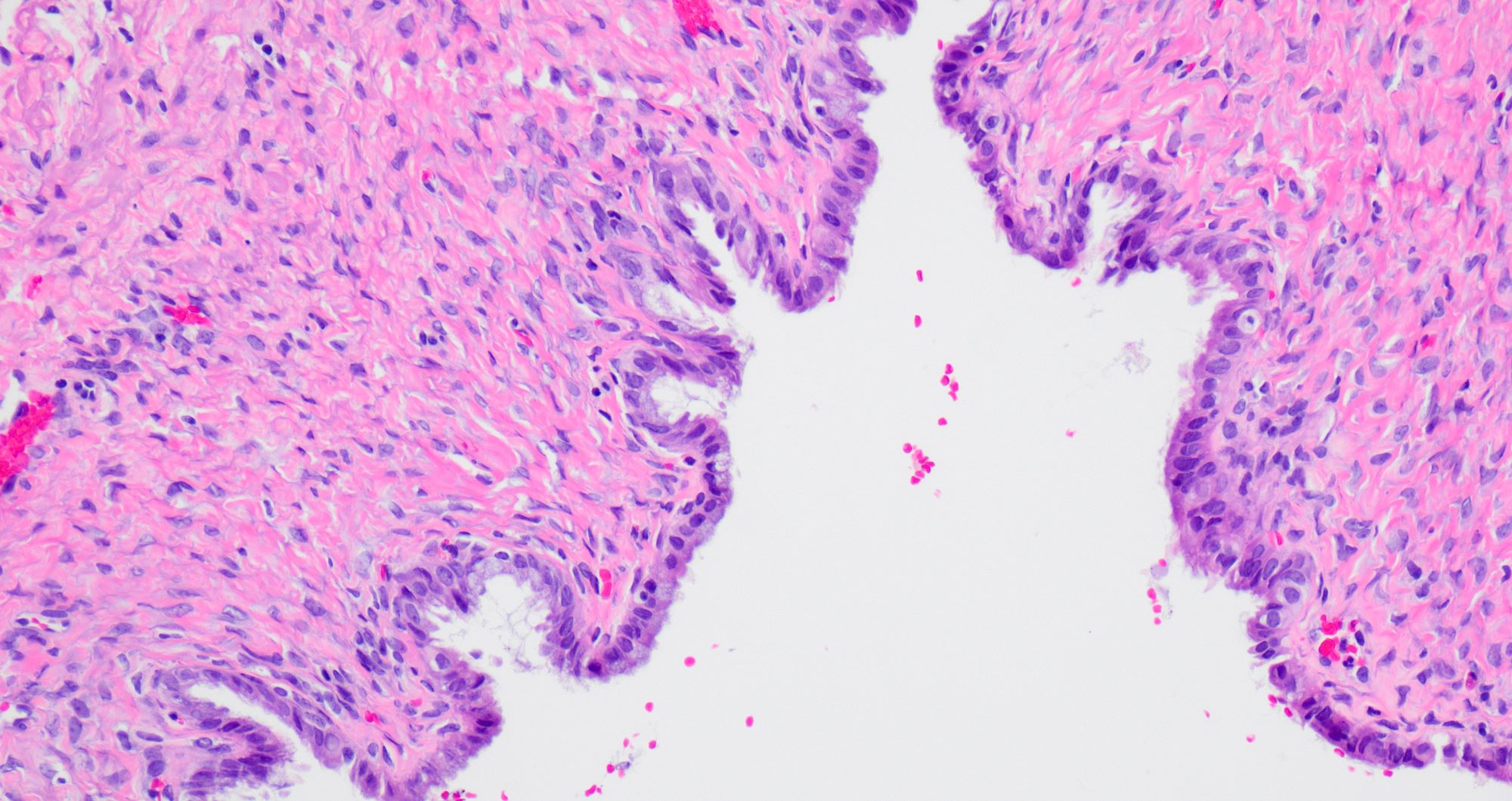
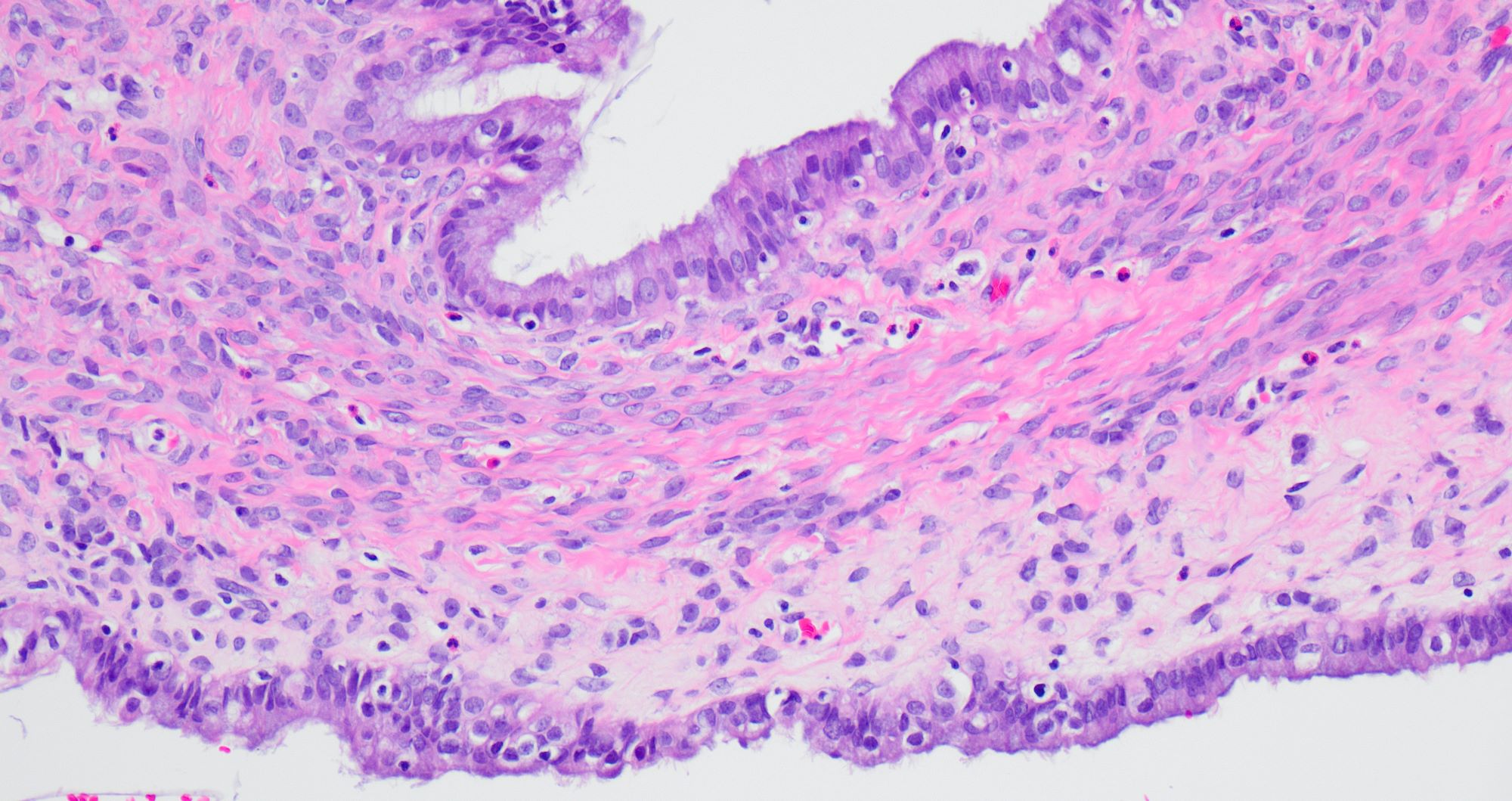
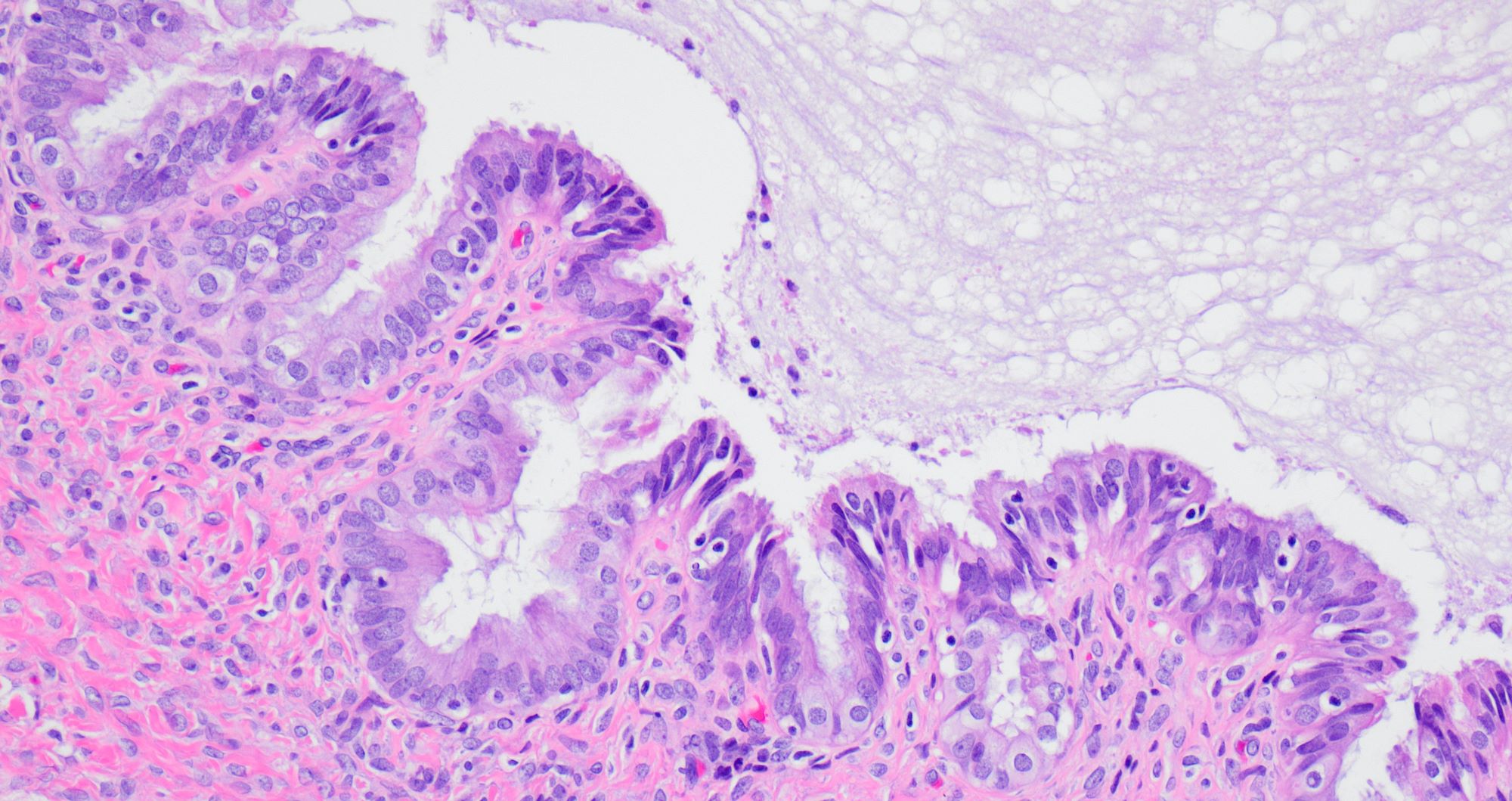
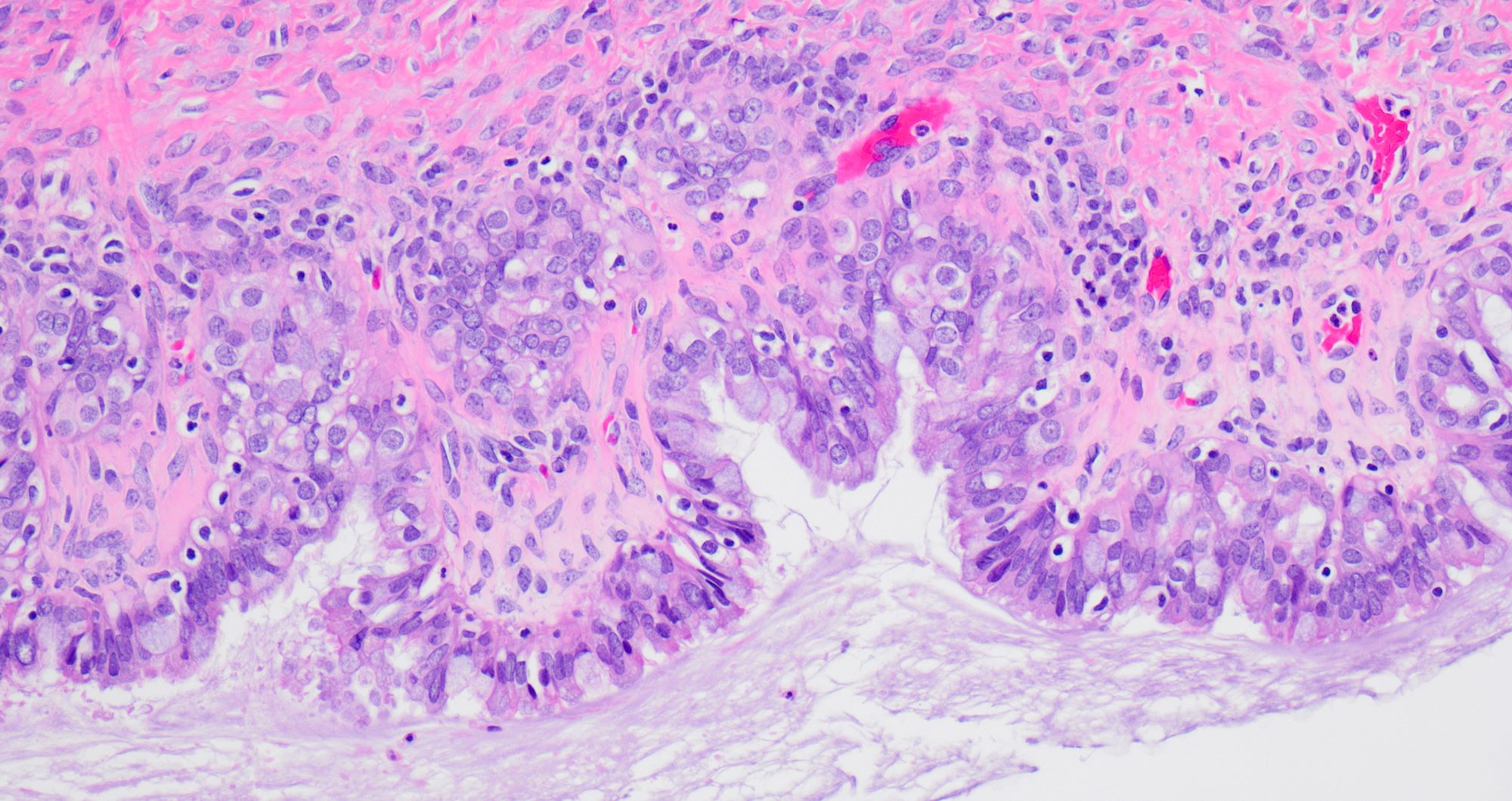
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Single layered epithelial lining with occasional stratification
- Cell types: mucinous (endocervical in appearance), serous (ciliated), endometrioid (nonserous, nonciliated), hybrid morphology (serous and mucinous) (Histopathology 2021;78:445)
- Variable degree of papillae (epithelial papillary tufting or broader papillae with fibrovascular core) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2022;41:68)
- Neutrophilic infiltrate may be present
- Endometrioid epithelium may have squamous metaplasia
- Some tumors have a prominent fibrous stromal component (classified as seromucinous adenofibroma)
- Associated with endometriosis in 27 - 36% of cases (Histopathology 2021;78:445, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2022;41:68)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Right ovary, cystectomy / oophorectomy:
- Seromucinous cystadenoma
Differential diagnosis
- Serous cystadenoma:
- Lined by nonstratified tubal type epithelium
- Mucinous cystadenoma:
- Lined by nonstratified mucinous epithelium with intestinal differentiation (goblet cells)
- Seromucinous borderline tumor:
- Epithelial proliferation > 10%, complex architecture, papillae with hierarchical branching, edematous papillae with neutrophils
- Metastatic tumors:
- Low grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, endocervical adenocarcinoma, etc.
- Morphology and immunohistochemical panels are helpful
- Low grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, endocervical adenocarcinoma, etc.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Seromucinous cystadenoma of ovary is associated with which of the following conditions?
- Endometriosis
- Hypercalcemia
- Isochromosome 12p
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Board review style answer #1