Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Thakral C. Peripheral giant cell granuloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityperipheralgiantcellgranuloma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
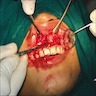
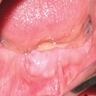
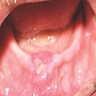
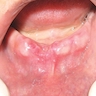
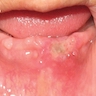
- Reactive gingival mass resembling pyogenic granuloma, which pushes teeth aside and may erode alveolar bone or involve periodontal membrane
- Arises from periodontal ligament enclosing root of tooth
- Central giant cell granuloma: similar to peripheral giant cell granuloma but multiloculated
Terminology
- Also called giant cell epulis, giant cell reparative granuloma, osteoclastoma, myeloid epulis
Epidemiology
- Usually women, 30s to 50s, although may involve children or elderly patients without teeth
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with lesion in maxillary anterior region (Contemp Clin Dent 2012;3:S118)
- 53 year old man, 57 and 81 year old women with lesion in same location as edentulous mandible (Eur J Dent 2010;4:329)
Central giant cell granuloma:
- 15 year old girl with lesion mimicking adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (Contemp Clin Dent 2011;2:249)
Treatment
- Excision with curettage of base of lesion extending into adjacent periodontal membrane
- Recurs if not completely excised or source of irritation not removed (10% recurrence rate)
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
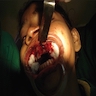
Gross description
- Nodular, pedunculated, inflammatory lesion up to 1.5 cm that protrudes from gingiva at site of chronic inflammation
- Covered by gingival mucosa or ulcerated
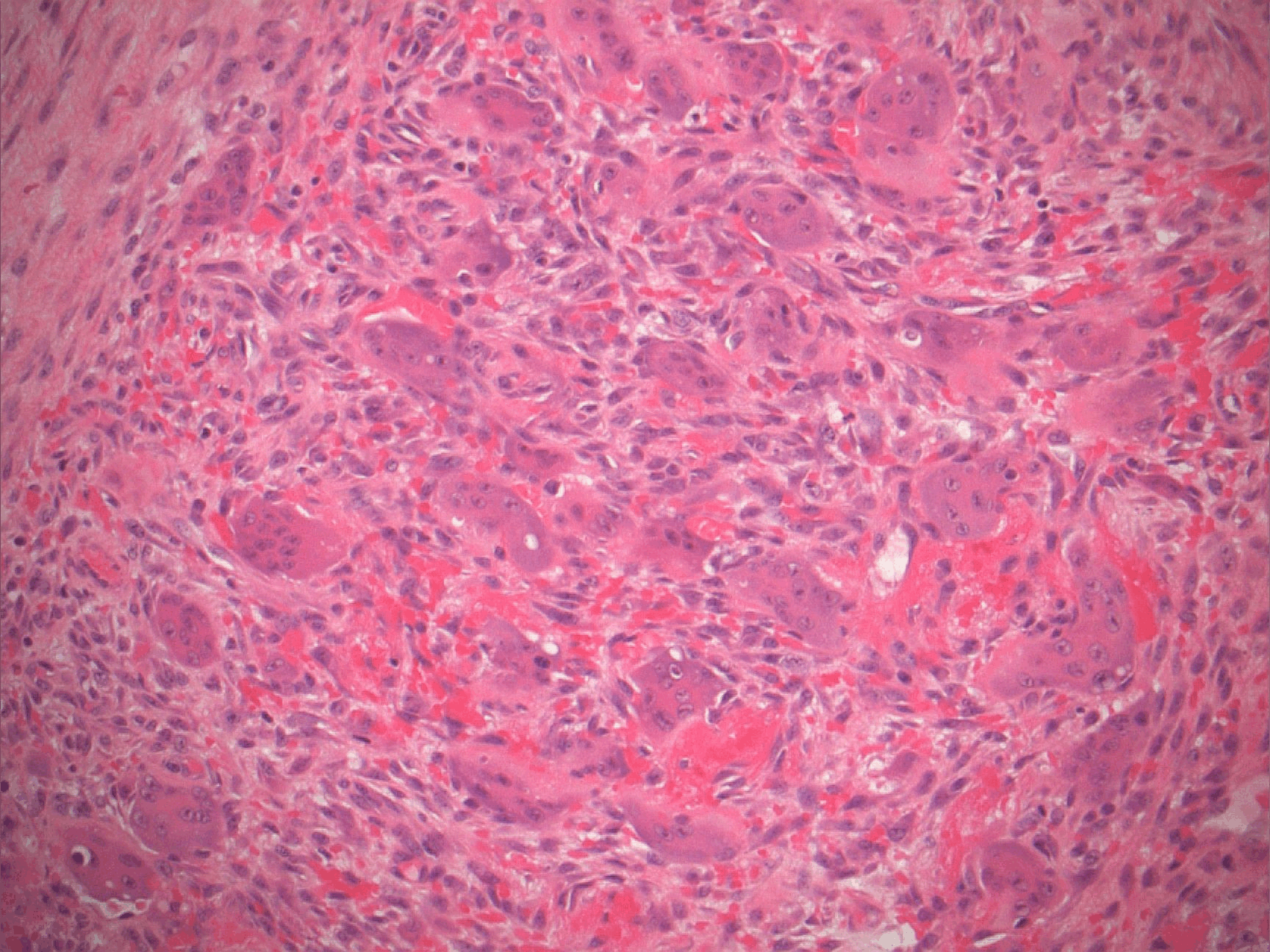
Microscopic (histologic) description
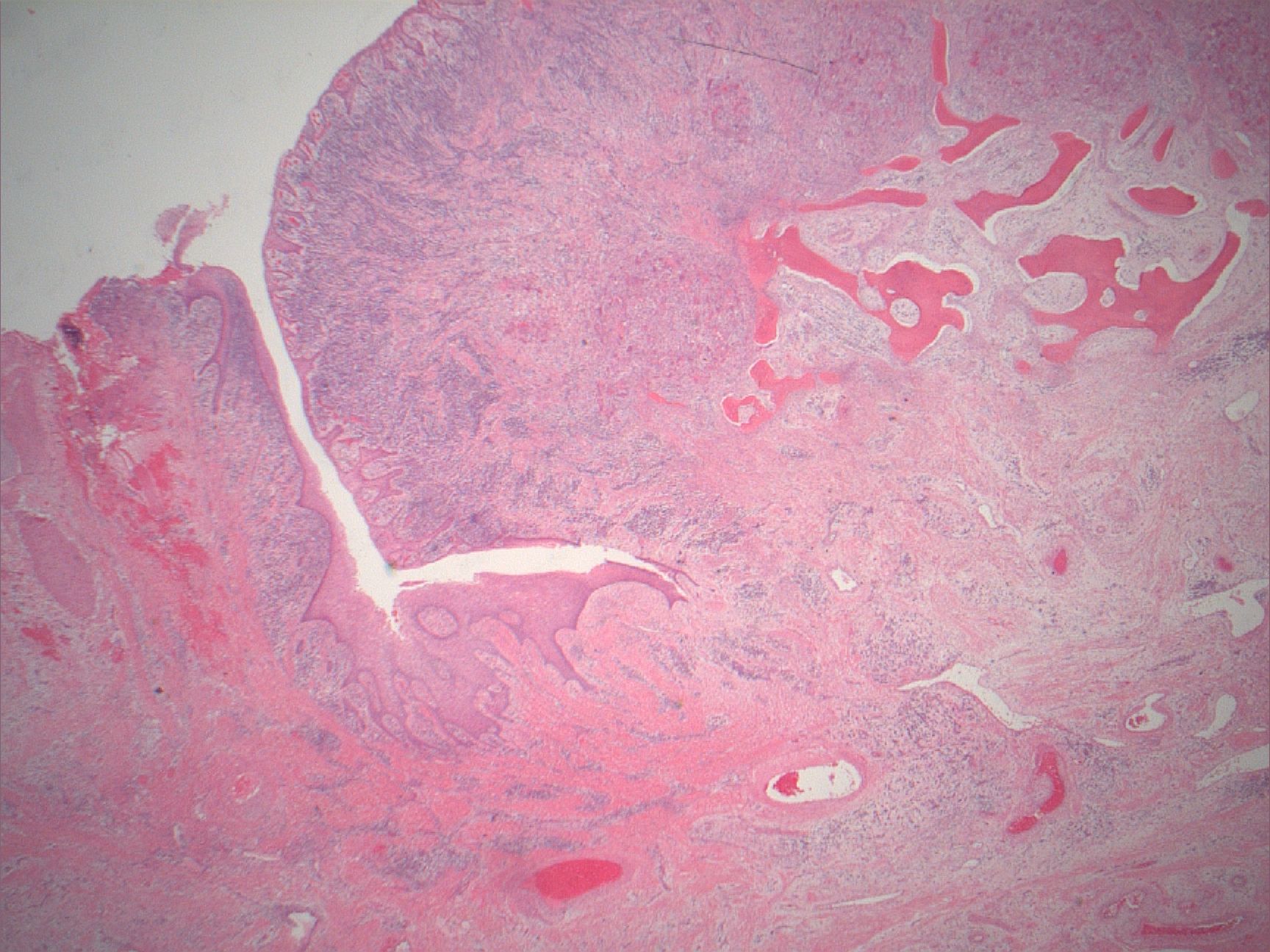
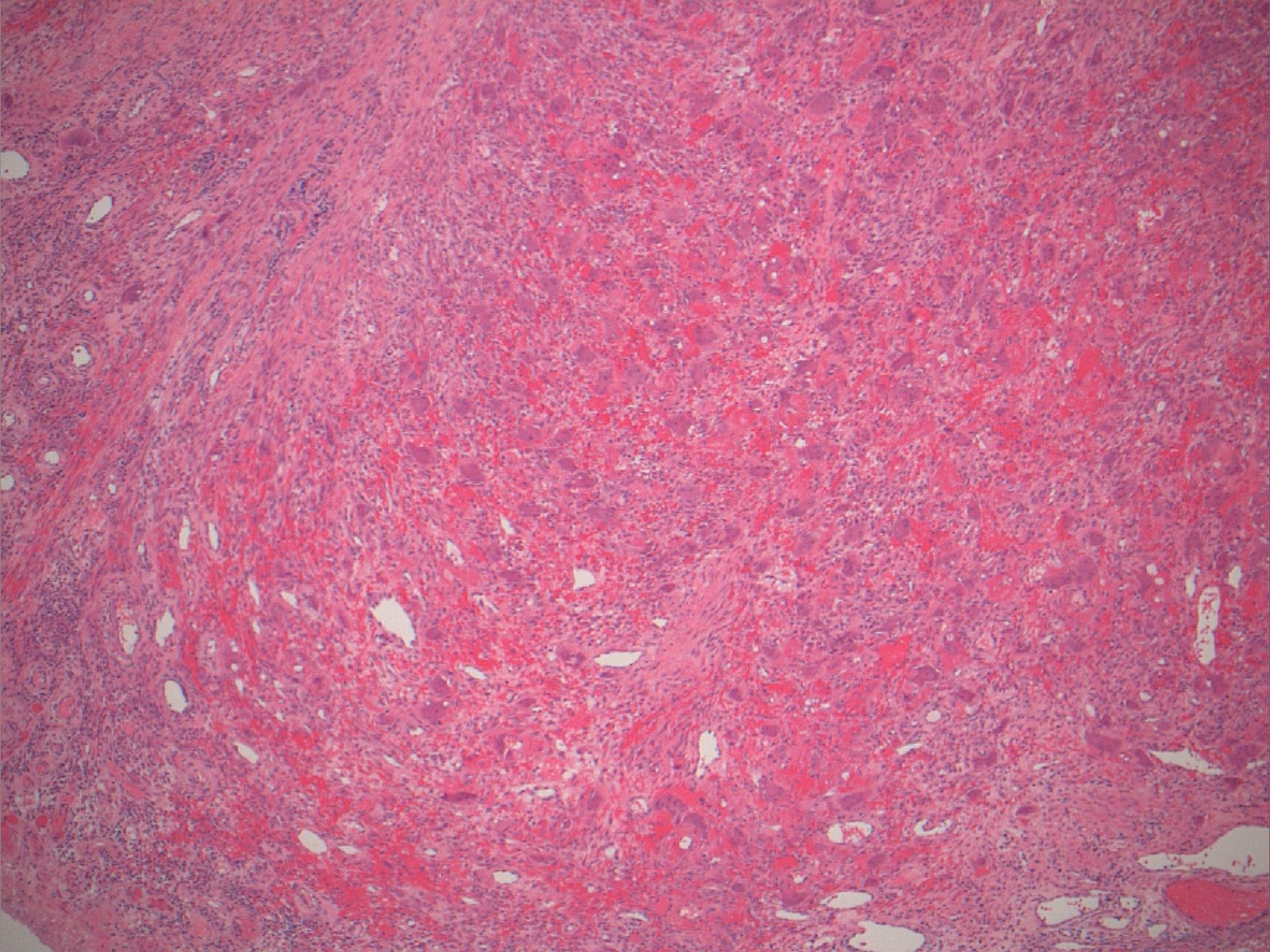
- Nonencapsulated aggregates of foreign body giant cells and fibroangiomatous stroma with hemorrhage, hemosiderin, acute and chronic inflammatory cells
- Alveolar bone often expanded in edentulous patients, leading to superficial bone loss with peripheral cuffing
- Variable mitotic activity
Microscopic (histologic) images