Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Goldfaden JS, Vargo RJ. Oral focal mucinosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityoralfocalmucinosis.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign pathologic process that is the oral counterpart of cutaneous focal mucinosis or cutaneous myxoid cyst (Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1990;19:337)
Essential features
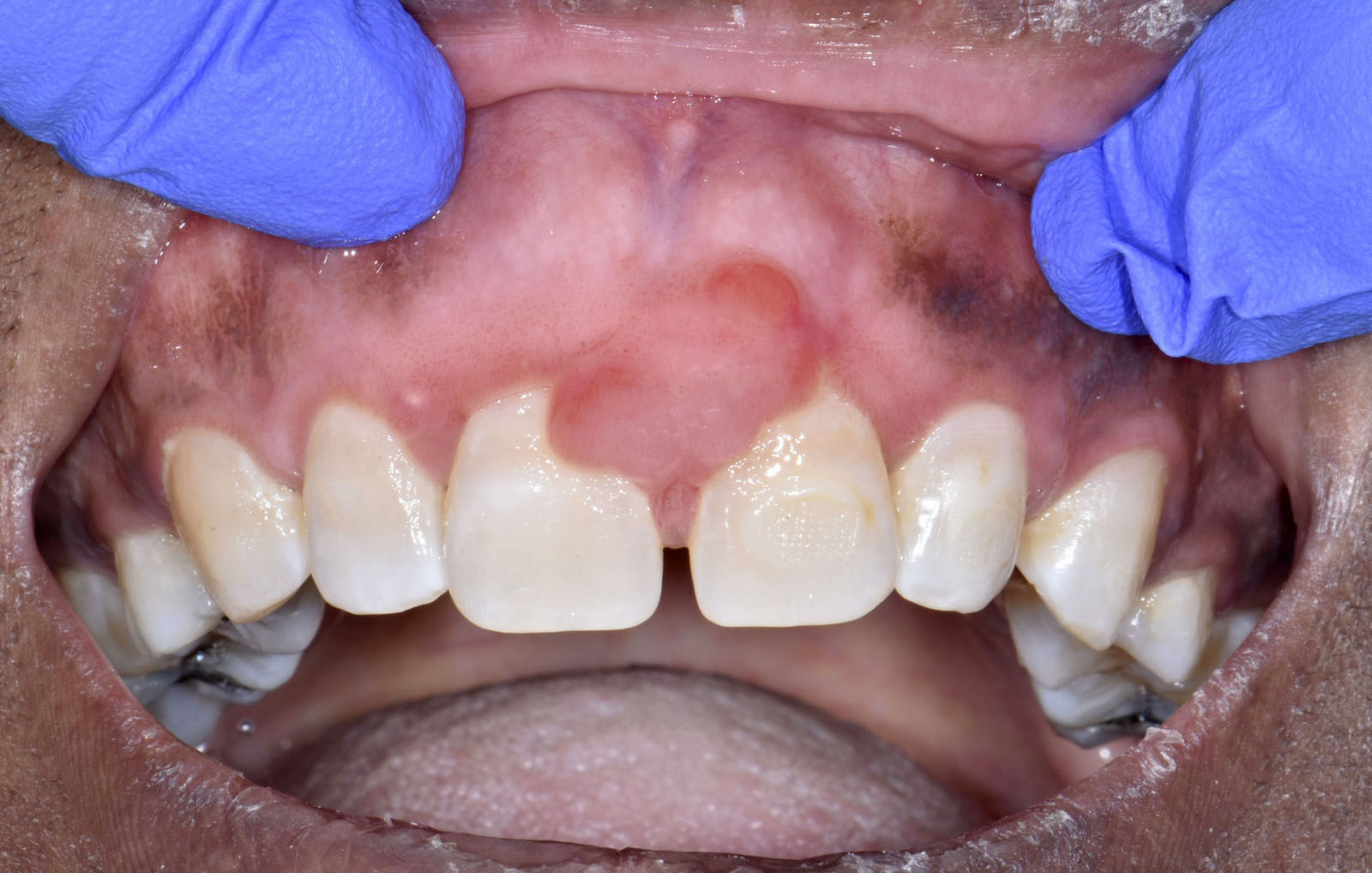
- Clinically manifests as a nodular mass with a predilection for gingiva and hard palatal mucosa (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:24)
- Oral focal mucinosis has a predilection for women in the fourth or fifth decade of life (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:24)
- Cause of oral focal mucinosis is unknown but it is thought to result from the overproduction of hyaluronic acid by mucosal fibroblasts (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2017;21:273)
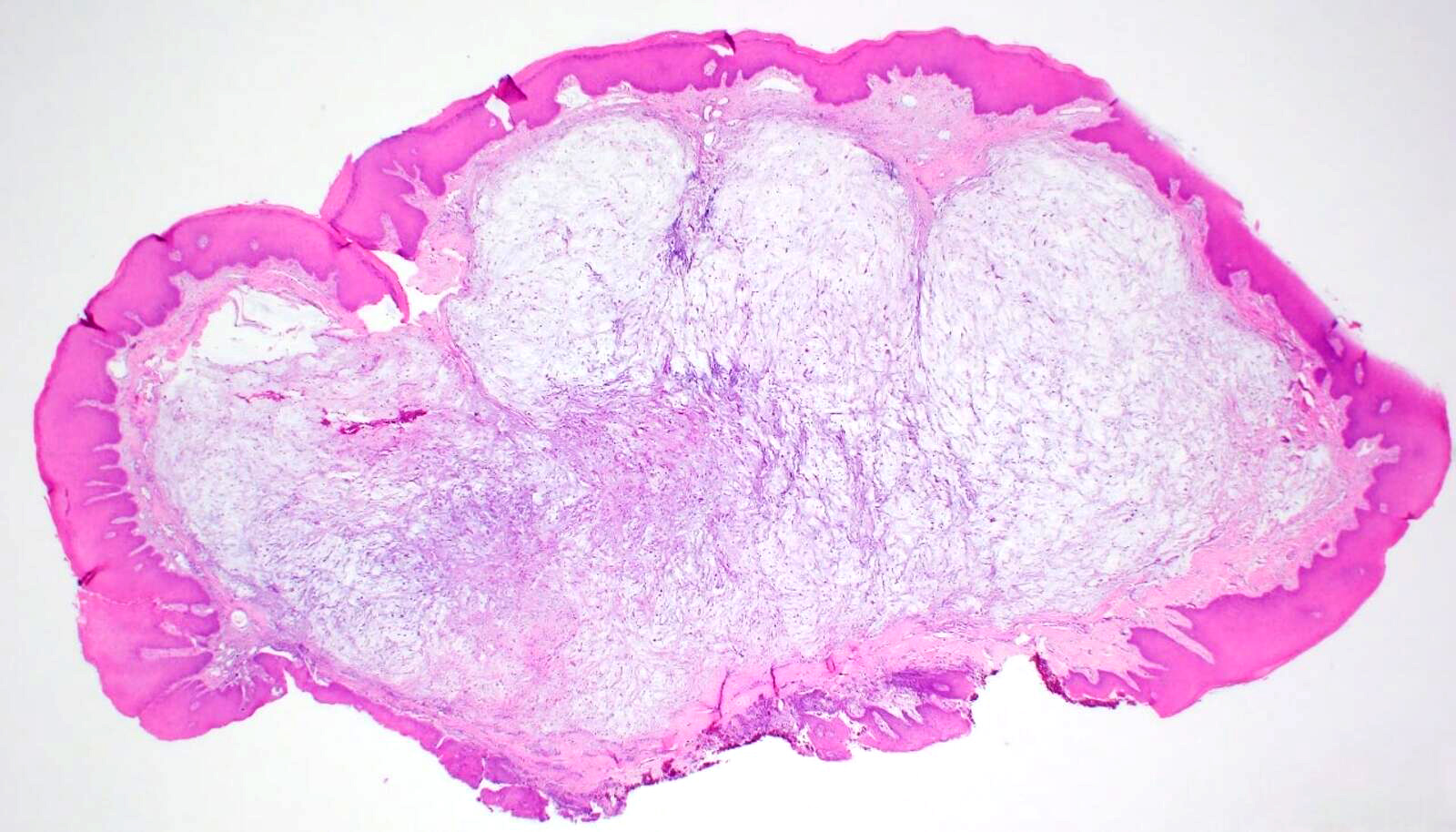
- Histologically, the lesion presents as a submucosal lesion with an area of nonencapsulated mucinous / myxoid connective tissue containing widely separated collagen fibers and scattered ovoid, spindled or stellate fibroblasts
Terminology
- Oral focal mucinosis was first described in 1974 by Tomich, who suggested that these lesions are the oral counterpart of cutaneous focal mucinosis or cutaneous myxoid cyst (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;38:714)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Predominantly affects women and commonly occurs in the fourth or fifth decade of life (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:24)
Sites
- Gingiva and hard palatal mucosa are the most affected sites (58.2% and 15.3%, respectively) (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:24)
Pathophysiology
- Oral focal mucinosis is thought to result from the overproduction of hyaluronic acid by oral mucosal fibroblasts
- Excessive amounts of hyaluronic acid cause myxoid degeneration of the connective tissue (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2017;21:273)
Etiology
- Cause of oral focal mucinosis is unknown
Clinical features
- Usually presents as a nonspecific, asymptomatic, sessile or pedunculated, nodular mass with a fibrous appearance (unless secondarily infected)
Diagnosis
- Biopsy
- Nodular mass that may be detected as an incidental finding
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis excellent; rare recurrence
Case reports
- 13 year old girl with hyperplastic gingiva between the left mandibular first and second molar (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e232671)
- 15 year old girl with a swelling posterior to the left mandibular second molar that is slowly enlarging (J Exp Ther Oncol 2019;13:49)
- 17 year old girl with pedunculated, exophytic nodule of the right anterior palatal gingiva (Clin Case Rep 2022;10:e6594)
- 41 year old woman with 8 month history of growing palatal mass (Autops Case Rep 2018;8:e2018044)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
Microscopic (histologic) description
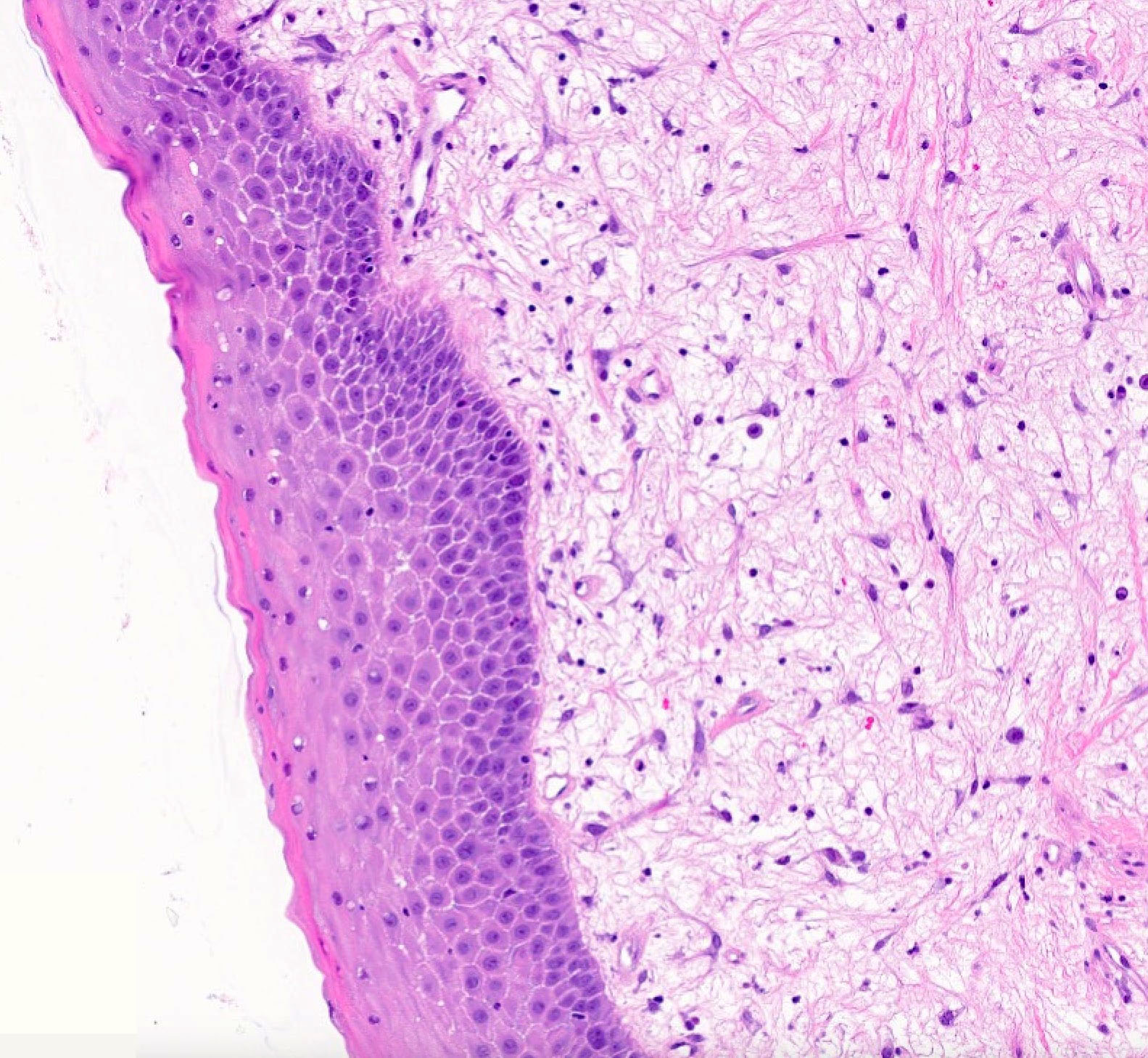
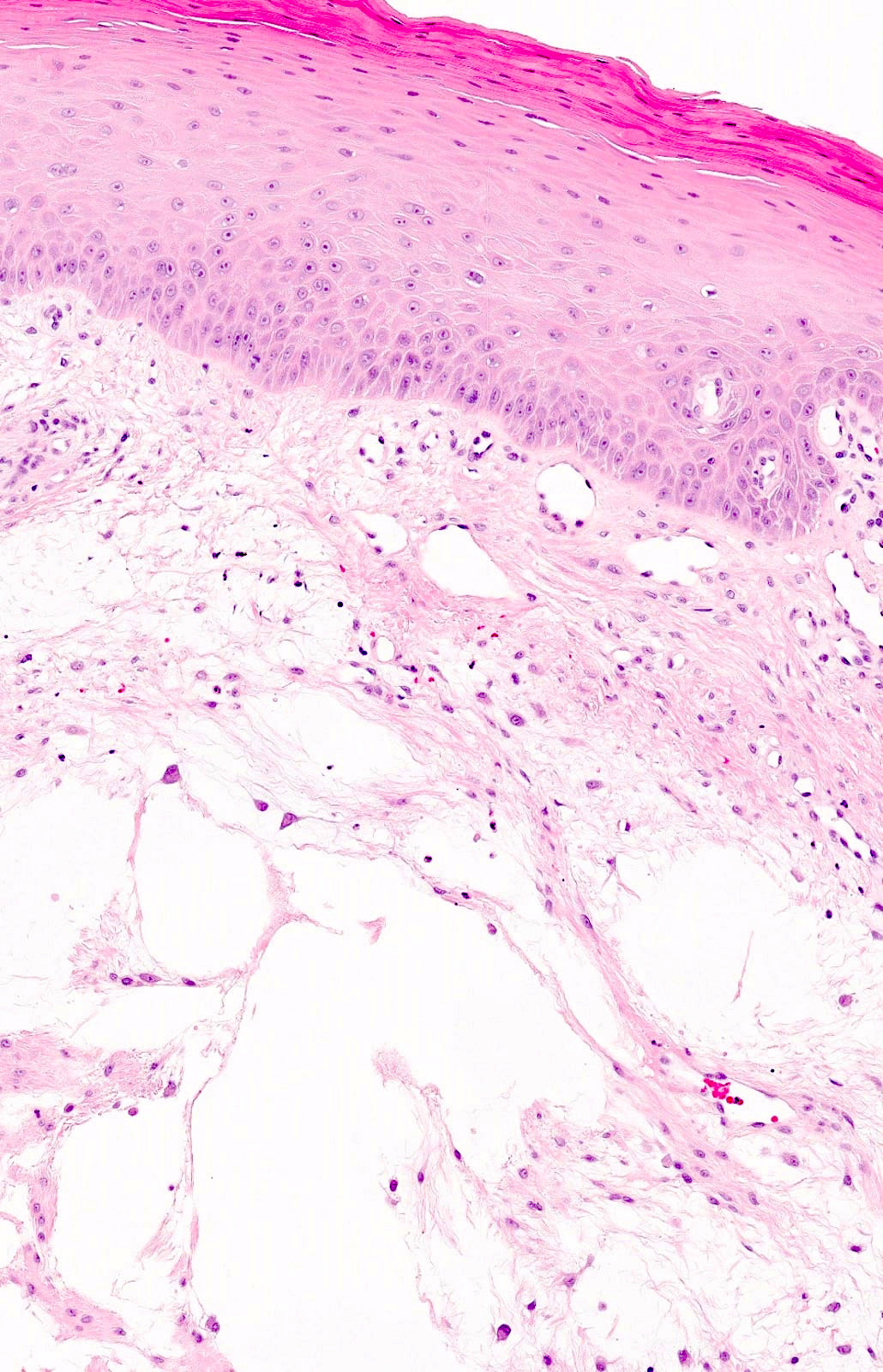
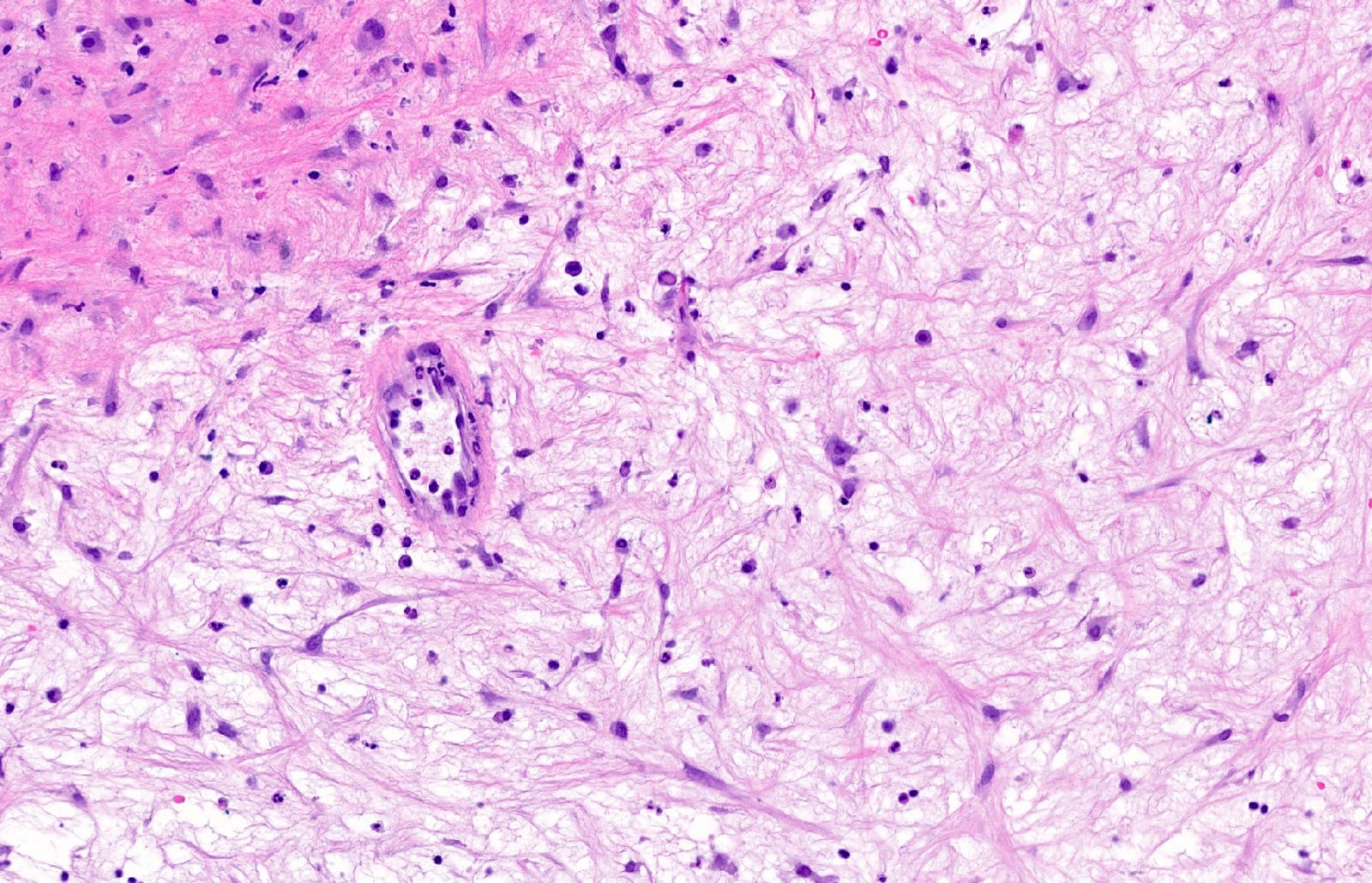
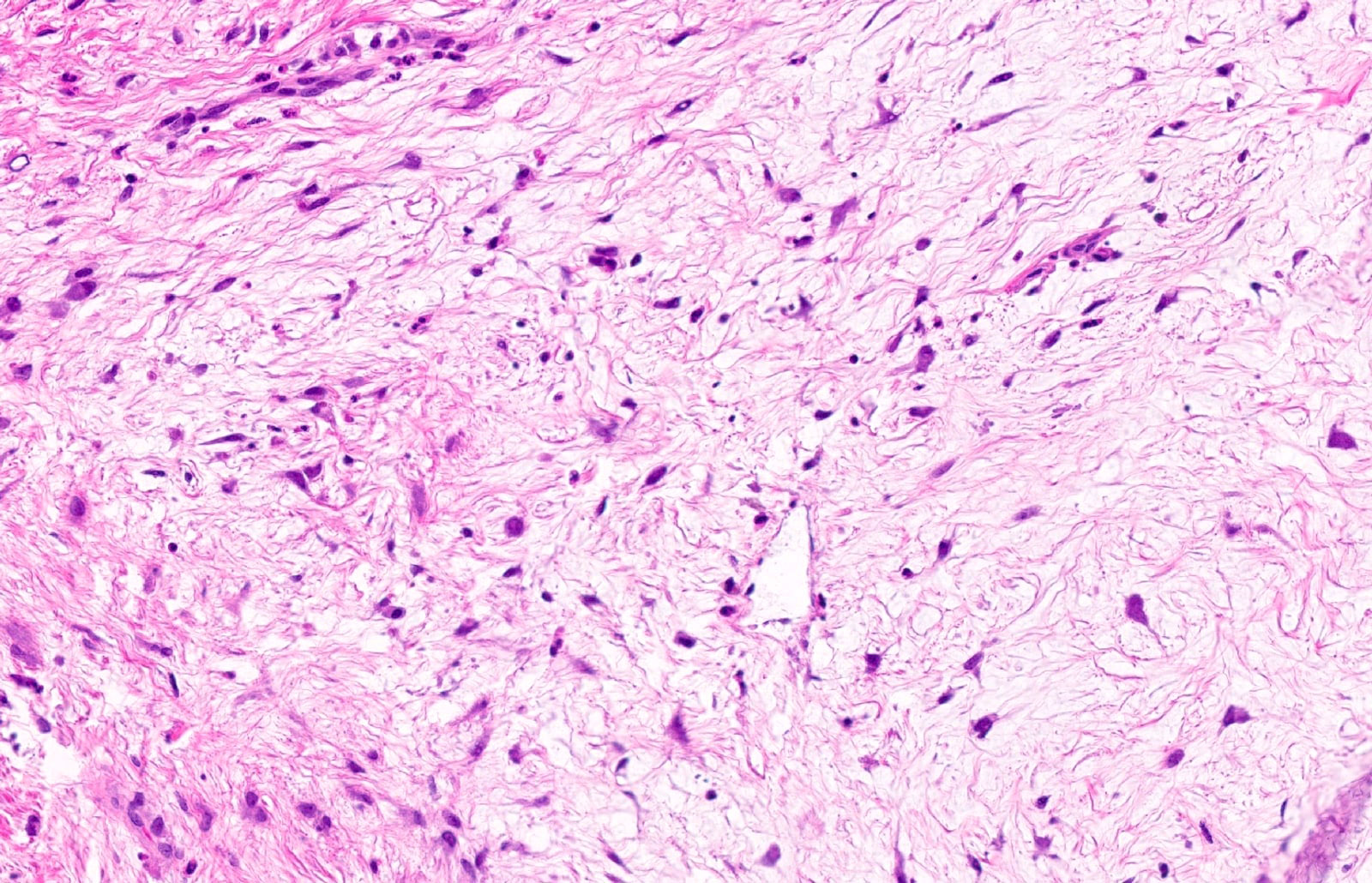
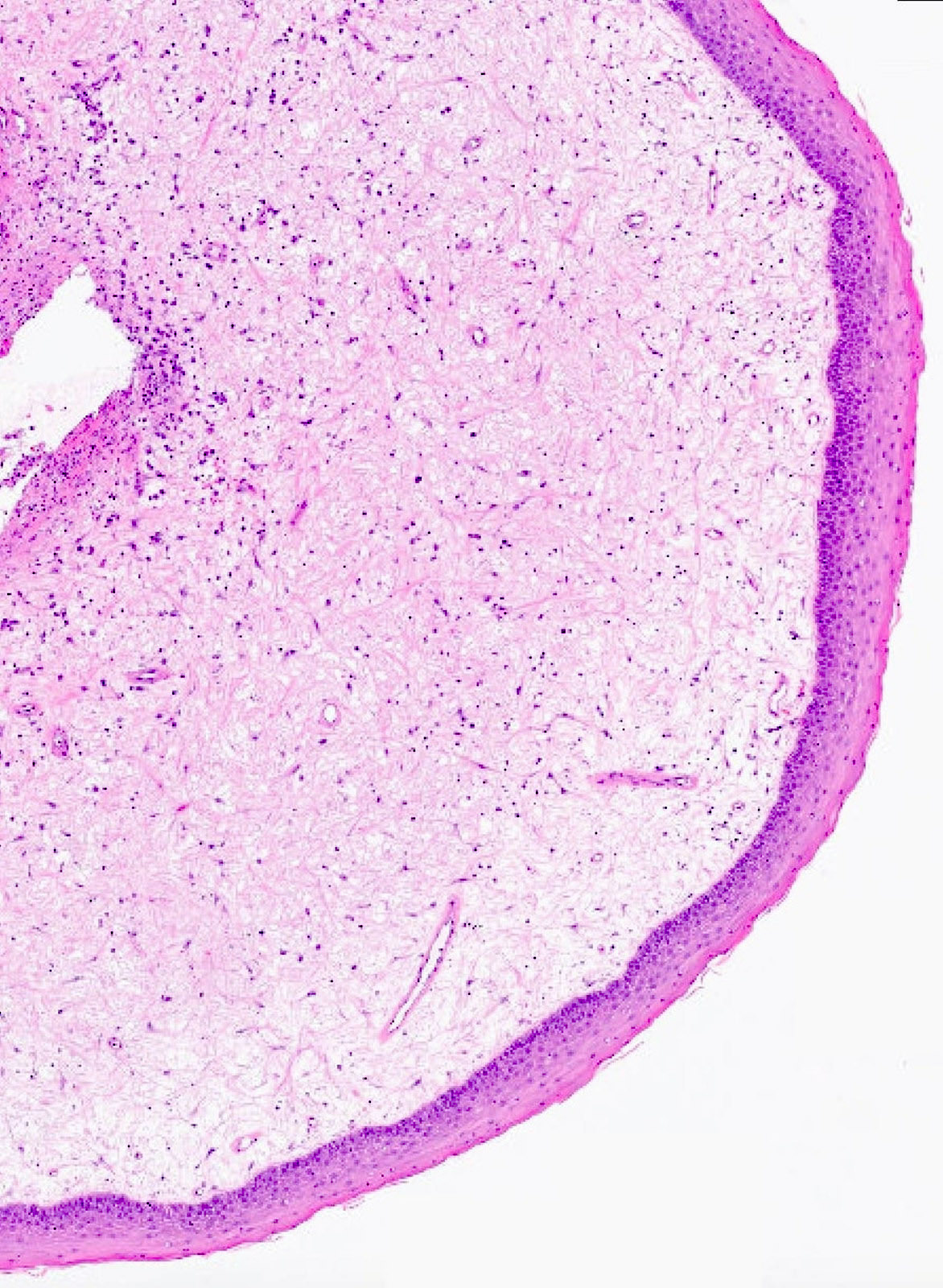
- Localized, nonencapsulated area of mucinous / myxoid connective tissue surrounded by normal, fibrocollagenous tissue
- Typically presents beneath the surface epithelium and often compresses rete ridges
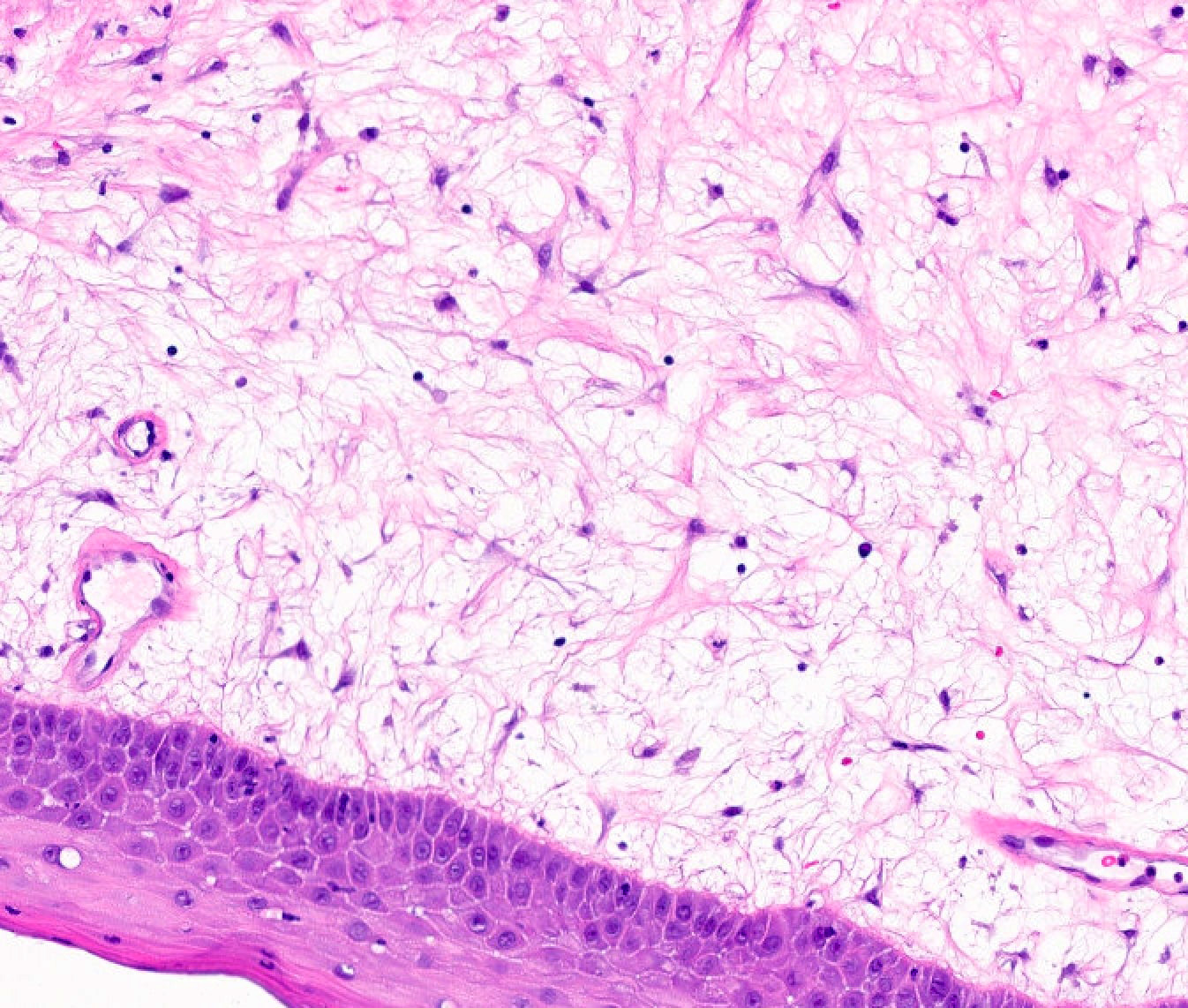
- Mucinous / myxoid areas exhibit scant capillaries, particularly compared to surrounding dense connective tissue
- Mucinous / myxoid zones are not especially inflamed but a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate is frequently seen within surrounding connective tissue
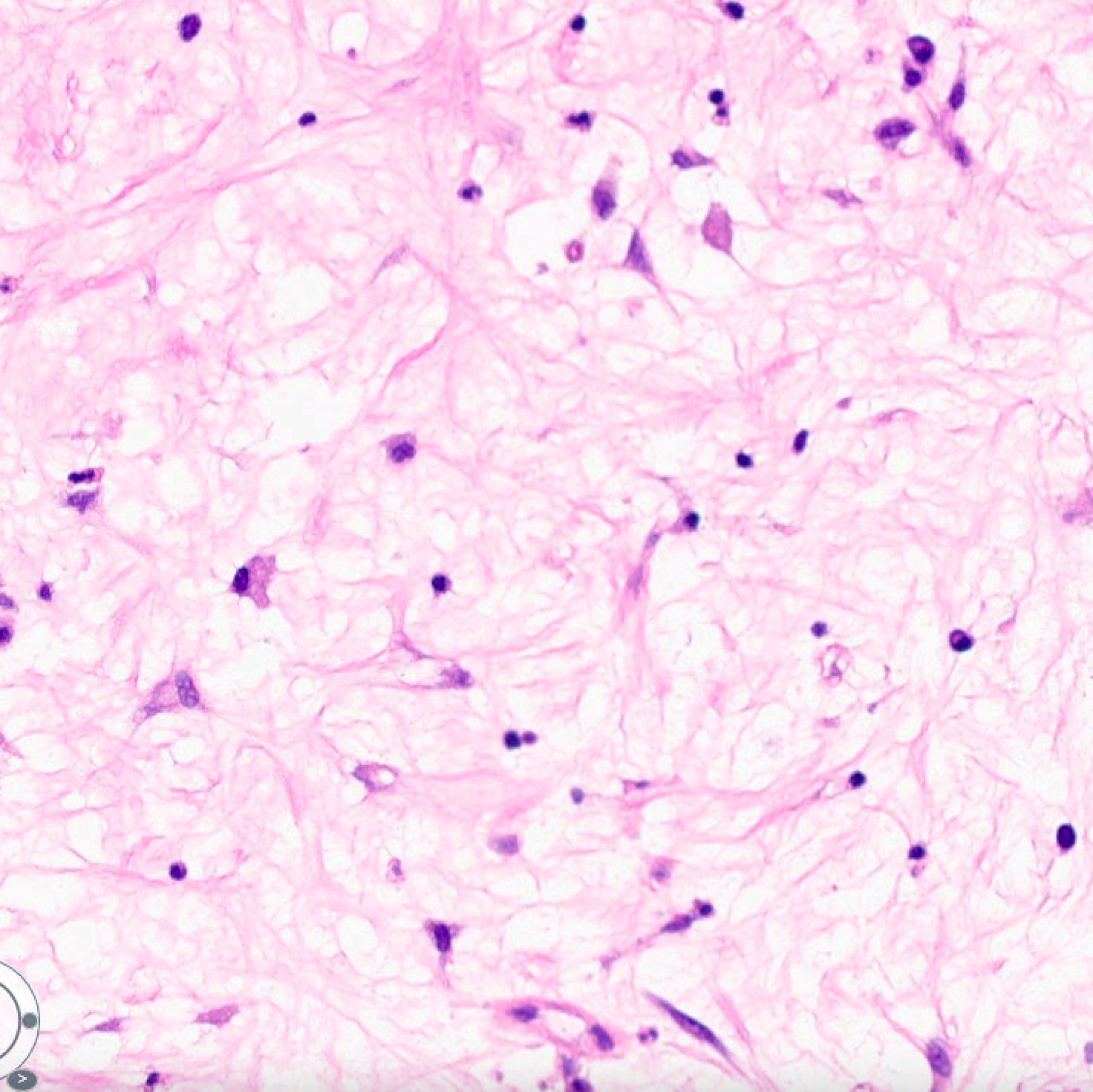
- Fibroblasts within mucinous / myxoid regions can have an ovoid, spindled or stellate morphology
- Cells may demonstrate fine fibrillar processes
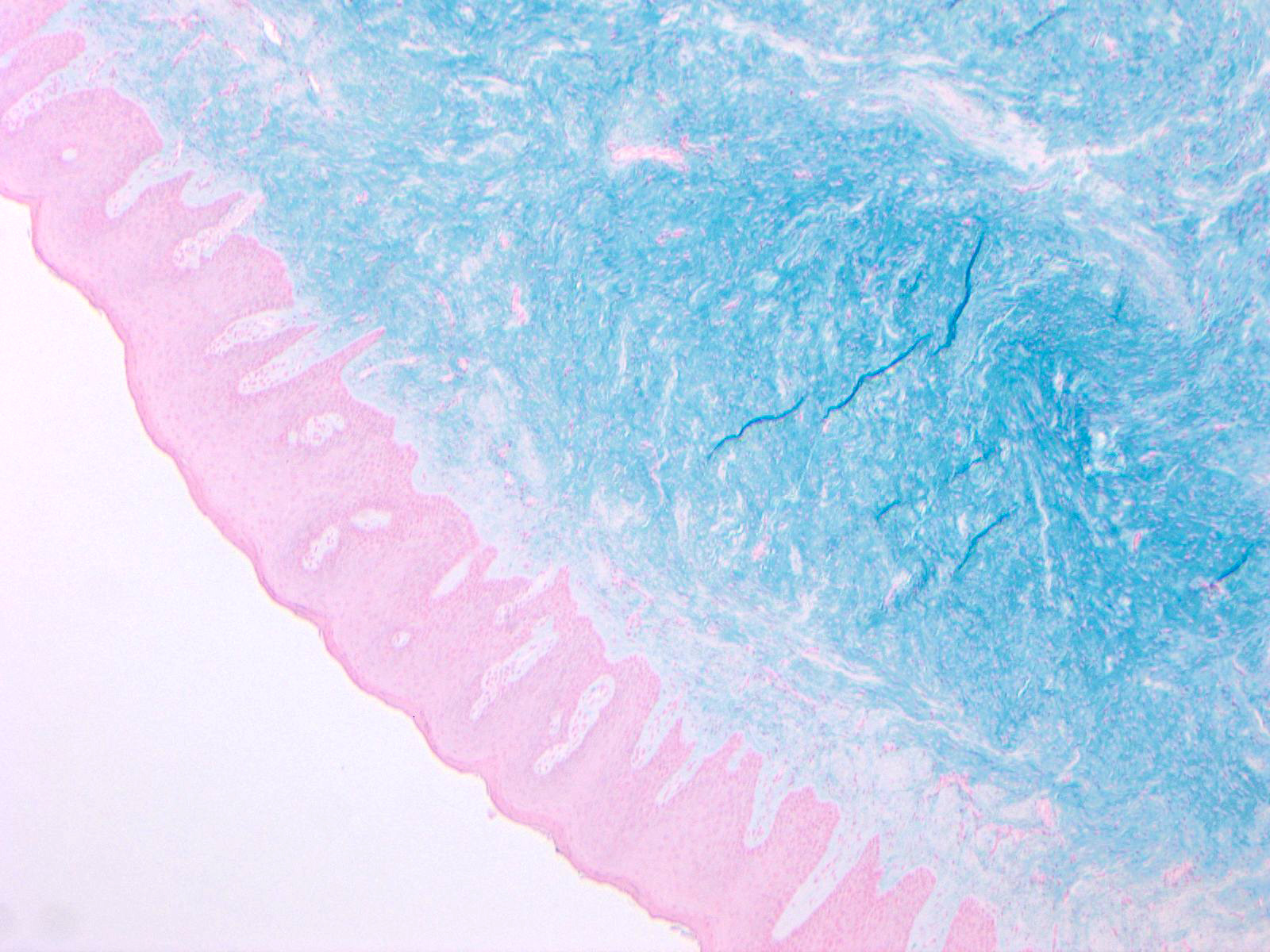
- No reticulin is evident within the lesion and Alcian blue (pH 2.5) routine stain indicates that the mucinous / myxoid component is hyaluronic acid (Pathology 2003;35:393)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Joshua Seth Goldfaden, D.D.S.
Positive stains
- Alcian blue (pH 2.5) exhibits strong, diffuse positivity in mucinous / myxoid stromal regions (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2018;126:e42)
Negative stains
- Spindle cells are negative for PAS, S100, vimentin and CD34 (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2018;126:e42)
Sample pathology report
- Anterior hard palatal mucosa, left, excisional biopsy:
- Oral focal mucinosis
Differential diagnosis
- Myxoid neurofibroma:
- May be hypocellular with myxoid changes
- Consists of Schwann cells, mast cells and fibroblasts; nuclear atypia may be noted
- Stromal spindle cells exhibit S100 positivity
- Superficial angiomyxoma:
- Myxoid stroma with dispersed collagen fibers
- Numerous blood vessels
- Spindle cells exhibit CD34 positivity
- Intramuscular myxoma:
- Hypocellular stroma with scattered, bland cells that exhibit no mitotic activity; minimal blood vessels and focal histiocytes may be noted
- There may be hypercellular areas or areas with increased vasculature
- Slightly more cellular at periphery with a distinct collagen capsule
- May infiltrate skeletal muscle at periphery; the involved skeletal muscle may be atrophic
- Spindle cells exhibit CD34 positivity (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151409)
- Odontogenic myxoma:
- Erratically arranged stellate, spindle shaped and round cells in profuse fibrillary myxoid stroma
- Small islands of inactive odontogenic epithelium may be present
- Radiographic findings should be correlated with histopathologic diagnosis
- Mucocele:
- Pseudocystic cavity filled with extravasated mucin
- Numerous foamy histiocytes in addition to neutrophils and granulation tissue
- Adjacent minor salivary gland lobules may be present
- Mucoceles are only present in anatomic sites with salivary glands (i.e., these lesions cannot be found on attached gingiva)
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presents with an asymptomatic, nodular mass of the posterior mandibular gingiva with no evidence of radiographic change. A biopsy reveals a lesion with scattered stellate cells in a mucinous / myxoid background that is Alcian blue (pH 2.5) positive as well as S100 and CD34 negative spindle cells and rare capillaries. Based on these findings, what is the most appropriate diagnosis?
- Intramuscular myxoma
- Mucocele
- Myxoid neurofibroma
- Oral focal mucinosis
- Superficial angiomyxoma
Board review style answer #1
D. Oral focal mucinosis. A gingival lesion with an Alcian blue (pH 2.5) positive mucinous / myxoid stroma and scattered stellate fibroblasts is consistent with oral focal mucinosis. Answer A is incorrect because intramuscular myxomas often exhibit a distinct collagen capsule at the periphery, may infiltrate skeletal muscle and are CD34 positive. Answer B is incorrect because mucoceles often exhibit foamy histiocytes and accompanying inflammation with occasional minor salivary gland lobules; additionally, mucoceles cannot be found on the attached gingiva. Answer C is incorrect because myxoid neurofibroma has stromal spindle cells that are S100 positive. Answer E is incorrect because superficial angiomyxomas have numerous blood vessels and stromal spindle cells that are CD34 positive.
Comment Here
Reference: Oral focal mucinosis
Comment Here
Reference: Oral focal mucinosis