Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Lott Limbach A. Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityinflamfibroushyperplasia.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Reactive inflammatory fibrous hyperplastic lesion that can be the result of chronic irritation, most frequently due to ill fitting dentures
Essential features
- Benign reactive inflammatory hyperplastic lesion that is the result of chronic irritation
- Histologically is composed of squamous mucosa overlying a dense collagen proliferation with focal chronic inflammation
- It is most commonly associated with ill fitting dentures
Terminology
- Epulis fissuratum, denture epulis, fibroepithelial hyperplasia, fibrous hyperplasia, fibroepithelial polyp, fibroma, fibrous epulis (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103, Tex Dent J 2009;126:172)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K13.6 - irritative hyperplasia of oral mucosa
Epidemiology
- Middle aged and older adults, female predominance (Acta Histochem 2016;118:451, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401, Quintessence Int Dent Dig 1984;15:699)
- Denture wearers (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401, Quintessence Int Dent Dig 1984;15:699)
Sites
- Oral cavity: gingiva, alveolar ridge (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2014;18:S86, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401)
Pathophysiology
- Chronic trauma / irritation leading to exaggerated tissue repair with accumulation of collagen in the submucosal connective tissue (Acta Biomed 2022;93:e2022219, Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2019;24:e305)
Etiology
- Chronic trauma (Tex Dent J 2009;126:172)
- Poorly fitting dental prosthesis (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401, Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2019;24:e305)
Clinical features
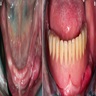
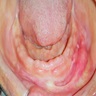
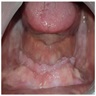
- Either single or multiple folds of flesh colored tissue (Tex Dent J 2009;126:172, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401)
- May be ulcerated (Tex Dent J 2009;126:172, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis based on clinical features (folds of tissue) and the presence of a poorly fitting denture (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401, Quintessence Int Dent Dig 1984;15:699)
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion; does not recur if the irritation is resolved (Tex Dent J 2009;126:172)
Case reports
- 58 year old man with epulis fissuratum (SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2021;9:2050313X211063135)
- 70 year old woman with epulis fissuratum (Pan Afr Med J 2022;41:49)
- 81 year old man with epulis fissuratum (Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e04440)
- Case series of histopathologic findings of epulis fissuratum (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974;37:401)
Treatment
- Surgical excision of tissue and remake or reline of ill fitting denture
- Submission of excised tissue is recommended, as malignancies (e.g., metastatic or primary) rarely may clinically mimic denture epulides
Clinical images
Gross description
- Mucosal covered tissue with tan-white cut surface
Microscopic (histologic) description
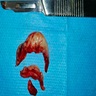
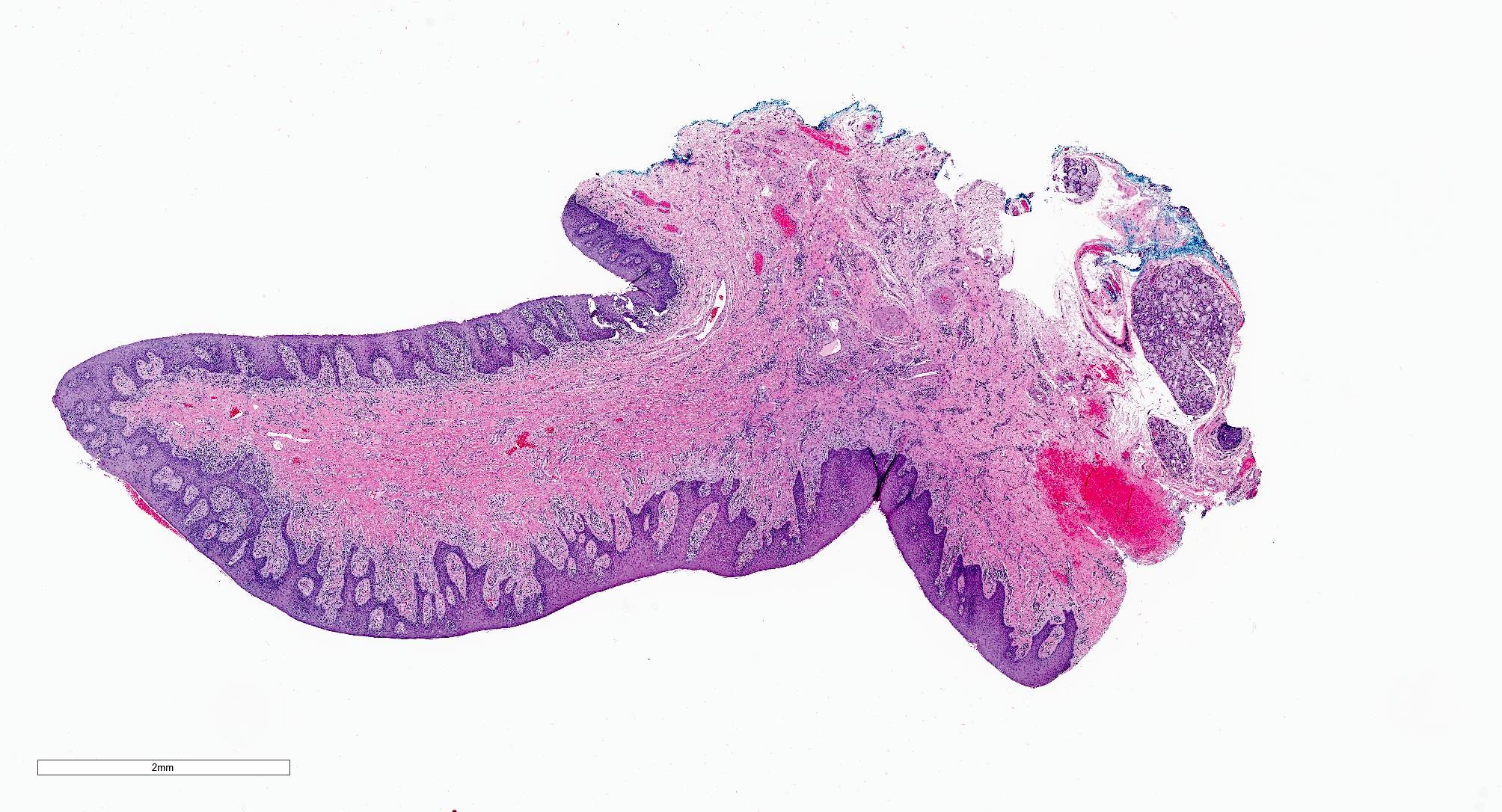
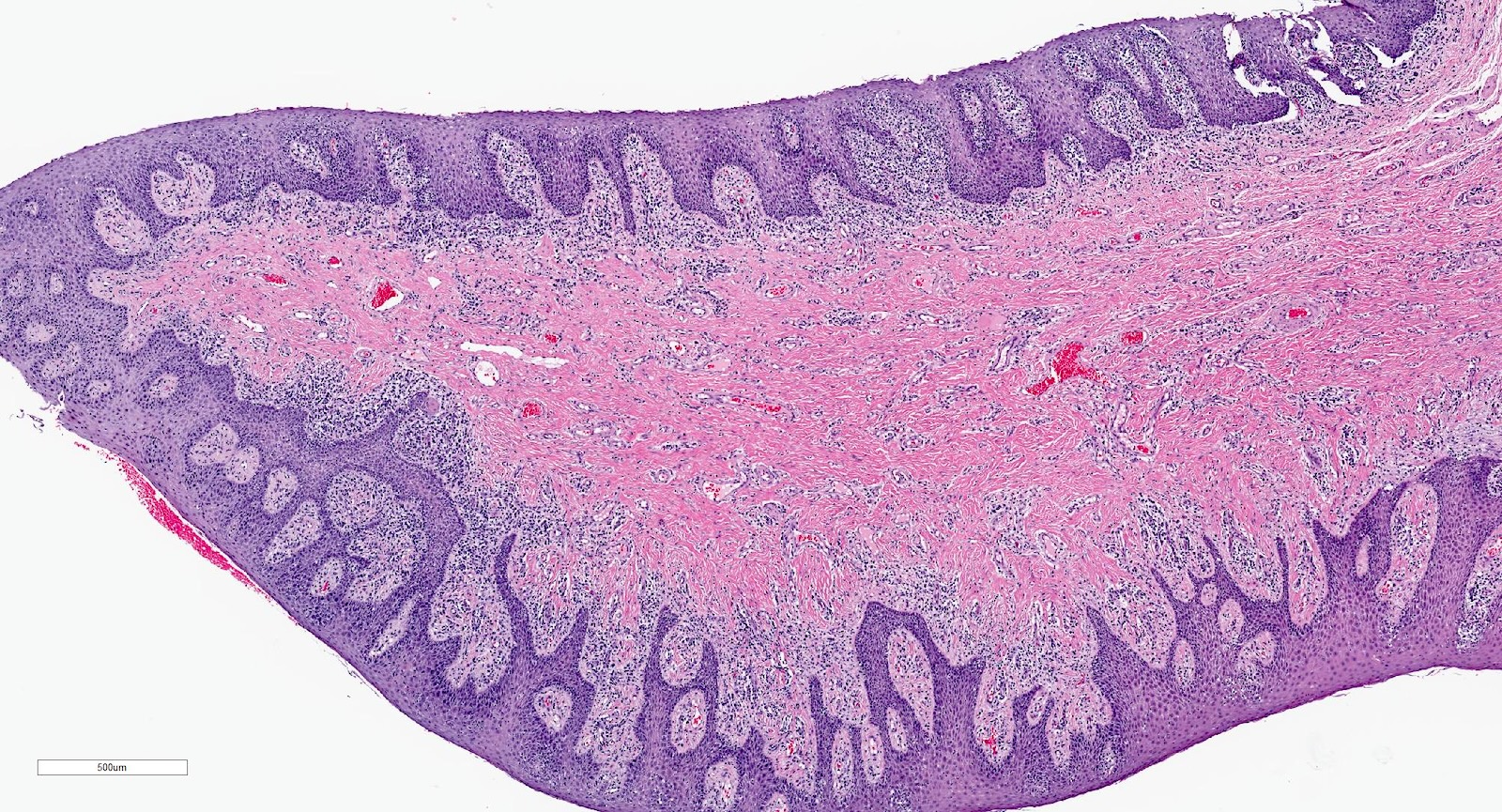
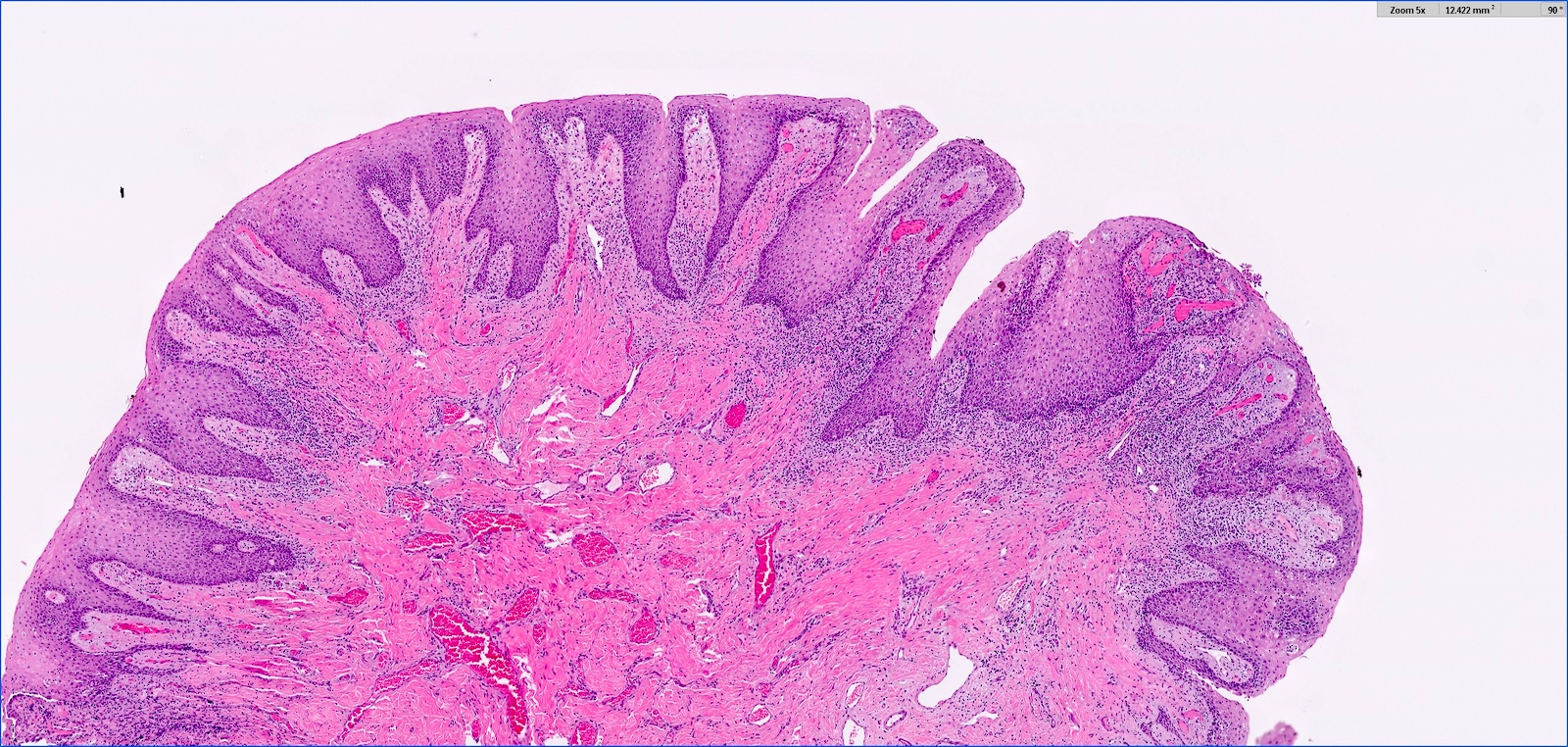
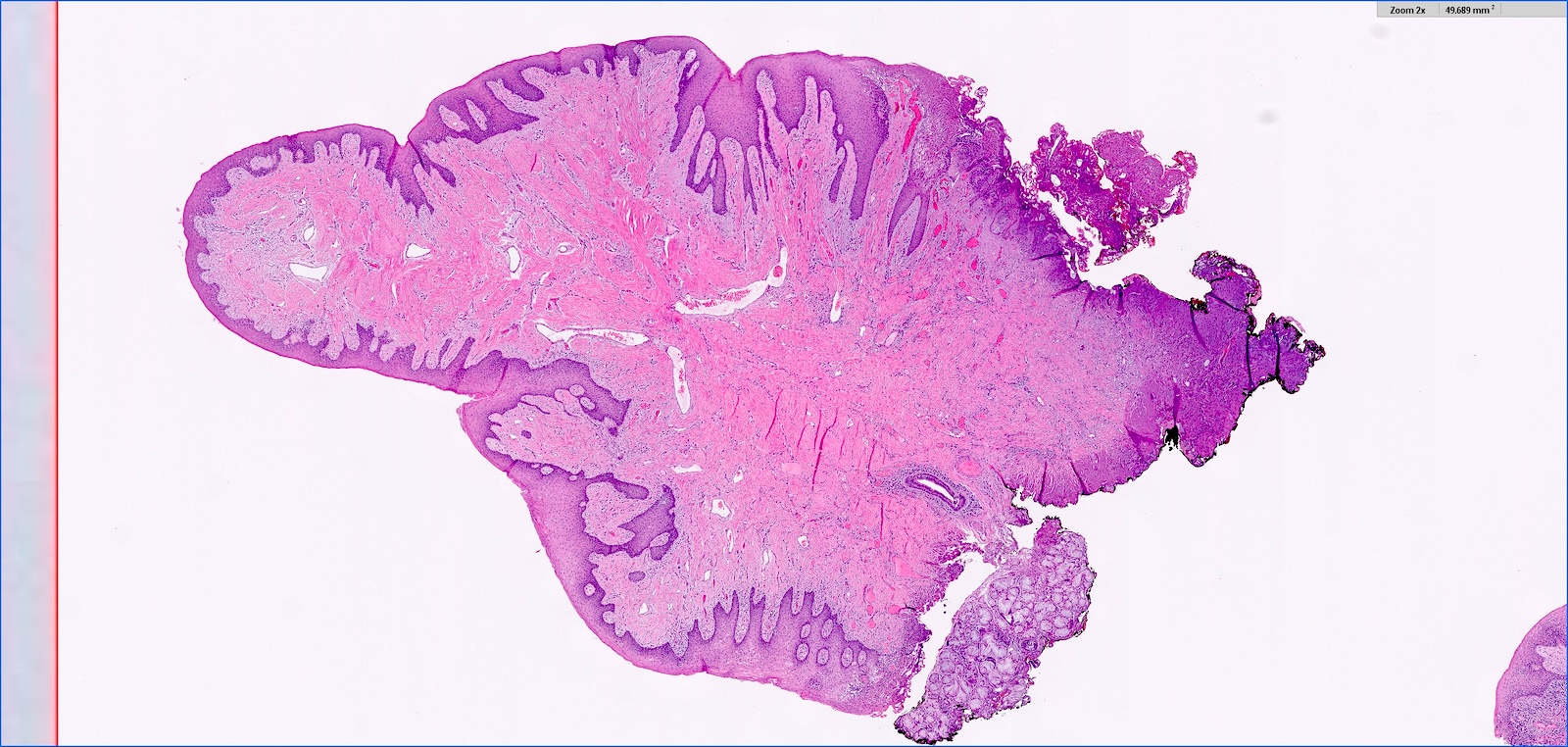
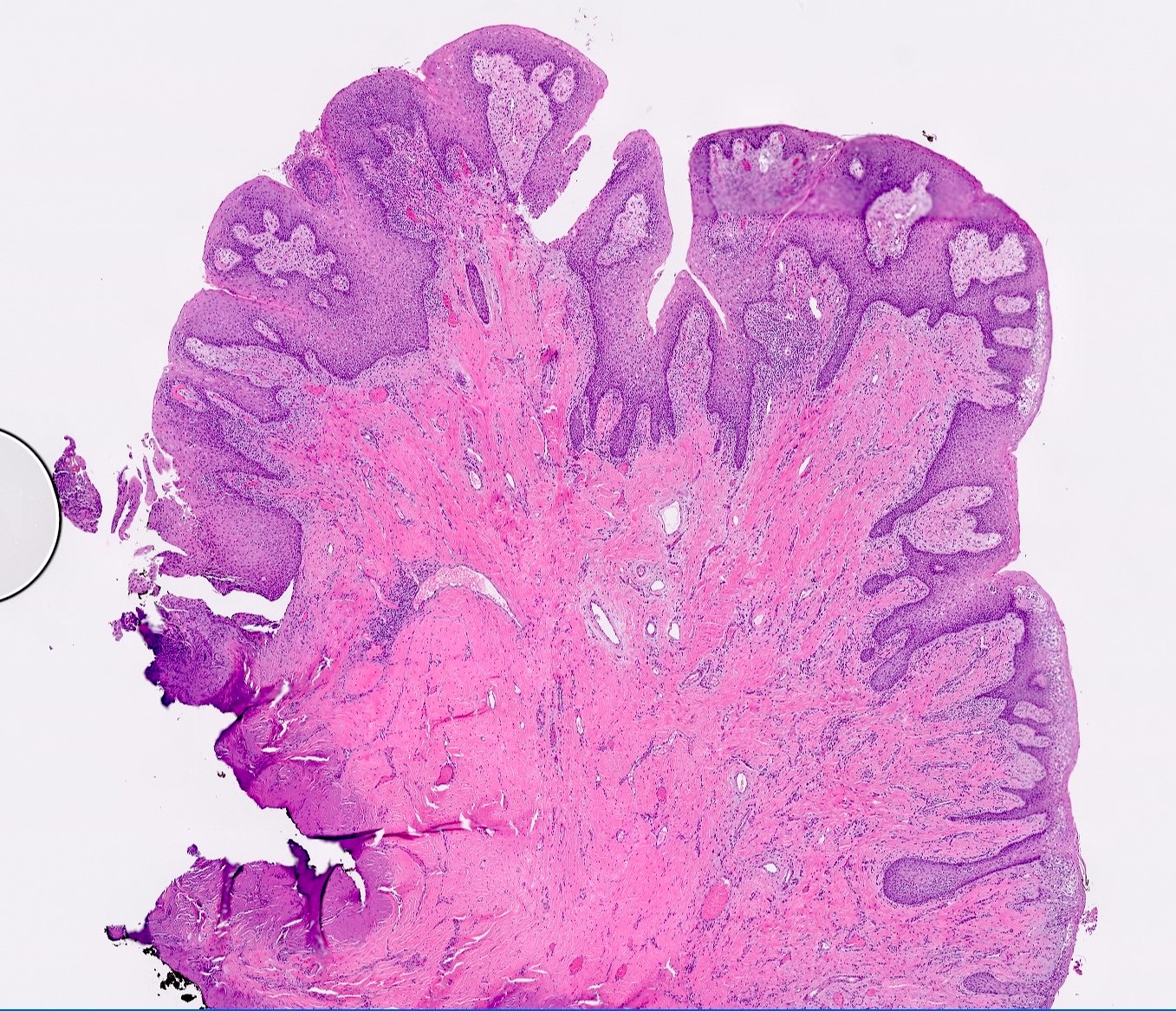
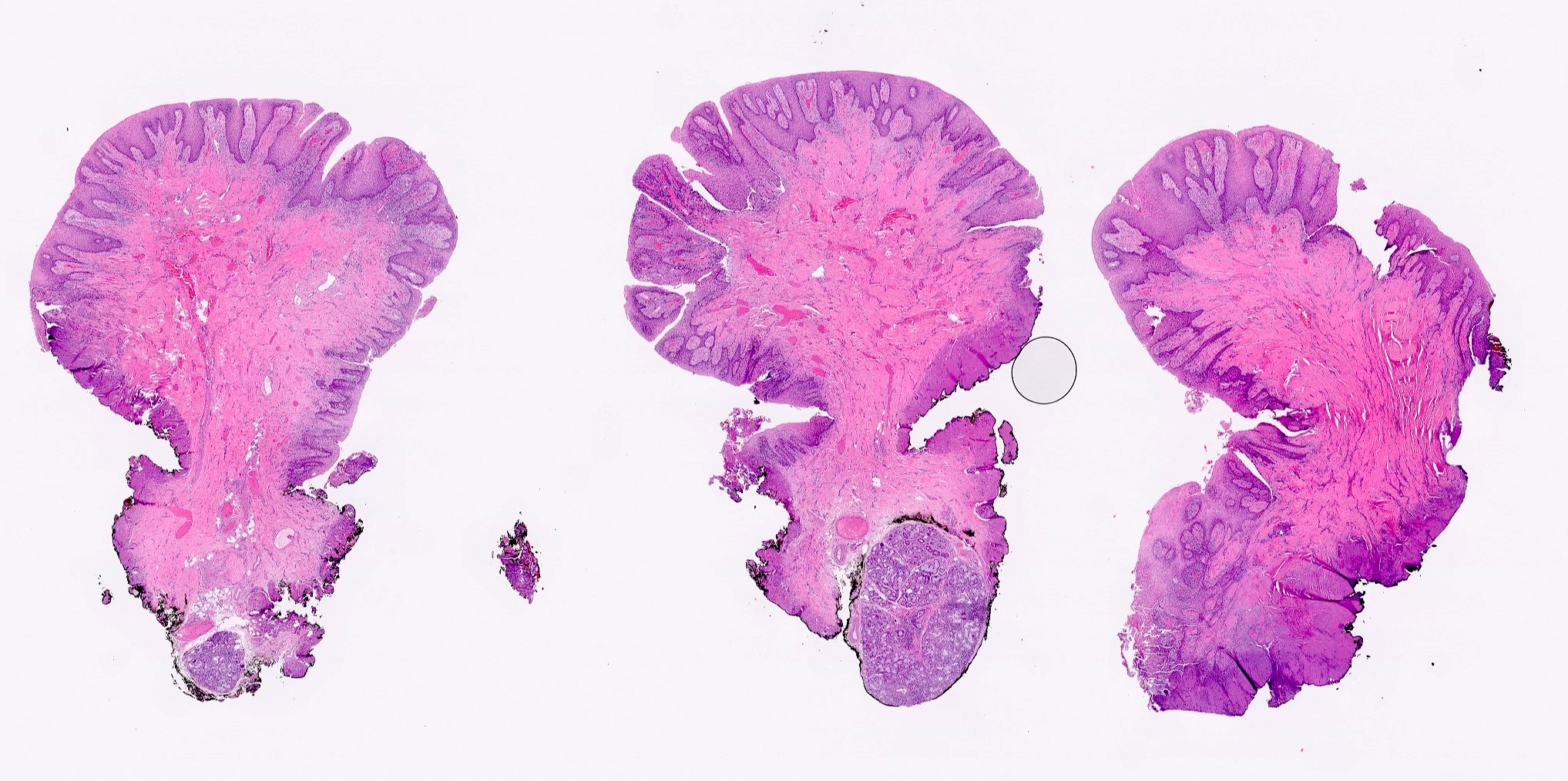
- Hyperplastic keratinized squamous mucosa overlying dense nodular connective tissue and variable inflammatory infiltrate (Acta Histochem 2016;118:451, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103)
- Underlying connective tissue is variably collagenized with scant bland spindled fibroblasts (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:103)
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia or secondary candidal colonization may be present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Mandibular alveolar ridge, excision:
- Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia (epulis fissuratum)
Differential diagnosis
- Pyogenic granuloma:
- Also known as lobular capillary hemangioma
- Pedunculated ulcerated gingival mass that bleeds easily
- Histologically a vascular proliferation resembling granulation tissue with surface ulceration
- Peripheral giant cell granuloma:
- Reactive lesion caused by irritation or trauma
- Histologically numerous multinucleated giant cells
- Background of ovoid to spindle shaped cells with extensive hemorrhage
- Drug induced gingival hyperplasia:
- Can be caused by calcium channel blockers, antiseizure meds or cyclosporine
- Can look identical to a denture epulis
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Surgery followed by revision of denture. This is inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia caused by trauma from the ill fitting denture. Answer C is incorrect because her hyperplasia is not related to medication. Answers A and B are incorrect because immunotherapy and radiation therapy are inappropriate for a benign condition.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia. The image shows squamous mucosa overlying a dense collagenous proliferation with focal chronic inflammation. Answer A is incorrect because amyloidosis is an accumulation of an acellular eosinophilic amorphous material in the submucosa. Answer B is incorrect because giant cell fibroma is not related to a history of chronic irritation. Morphologically the submucosa contains numerous stellate fibroblasts that can be multinucleated. Answer D is incorrect because solitary fibrous tumor is a cellular and vascular neoplastic proliferation; it does not have abundant reactive collagen.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia