Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Smith MH. Hairy tongue. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityhairytongue.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign condition of the dorsal tongue characterized by elongation and often staining of the filiform papilla, imparting a hairy appearance
Essential features
- Marked elongation of the lingual filiform papillae
- Hairy appearance of the dorsal tongue
- Associated with cigarette use, electronic cigarette use, xerostomia, oxidizing mouthwashes, hyposalivation, radiation, older age, general debilitation, medication use, lack of coarse foods in diet and poor oral hygiene
Terminology
- Oral hairy tongue
- Black hairy tongue
- Foliate papillae hypertrophy
- Lingua villosa nigra
- Melanoglossia
- Similar to coated tongue
- Not to be confused with oral hairy leukoplakia, an unrelated entity
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K14.3 - hypertrophy of tongue papillae
Epidemiology
- Slight male predominance
- Prevalence varies from 0.6 - 11.3% of the general population (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:10845)
Sites
- Dorsal tongue, often posterior midline area
Pathophysiology
- Elongation of filiform papillae due to decreased sloughing or increased production of keratin
Etiology
- Associated with cigarette use, electronic cigarette use, xerostomia, oxidizing mouthwashes, hyposalivation, radiation, older age, general debilitation, medication use, lack of coarse / crunchy foods in diet and poor oral hygiene (J Evid Based Dent Pract 2019;19:101318, World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:10845)
- Associated medications include bismuth, penicillin, chlorpromazine, ranitidine, tetracycline, linezolid, olanzapine, interferon, prednisolone (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
- Pigment often is caused by pigment producing bacteria or exogenous substances, such as food, medicines or tobacco
Clinical features
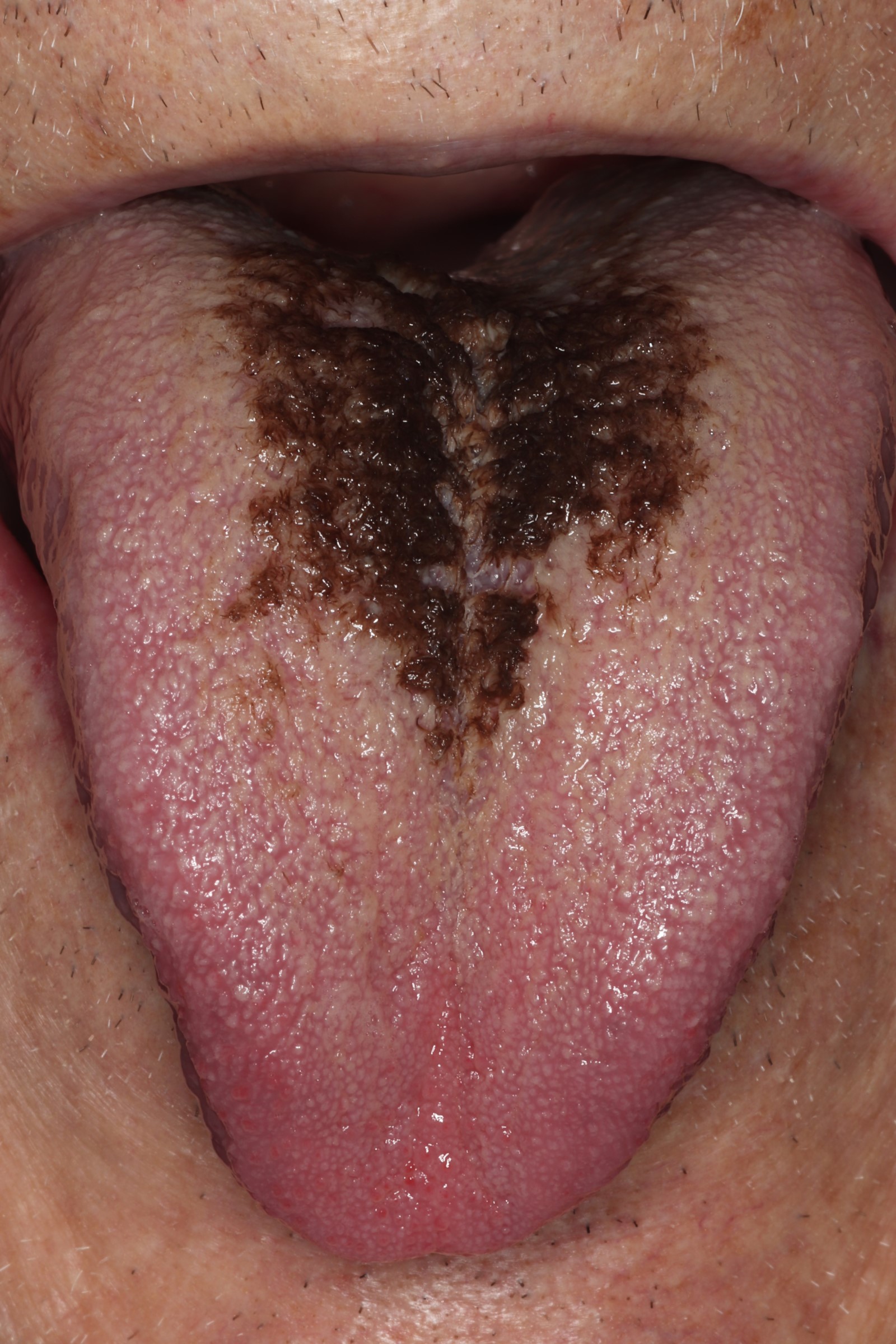
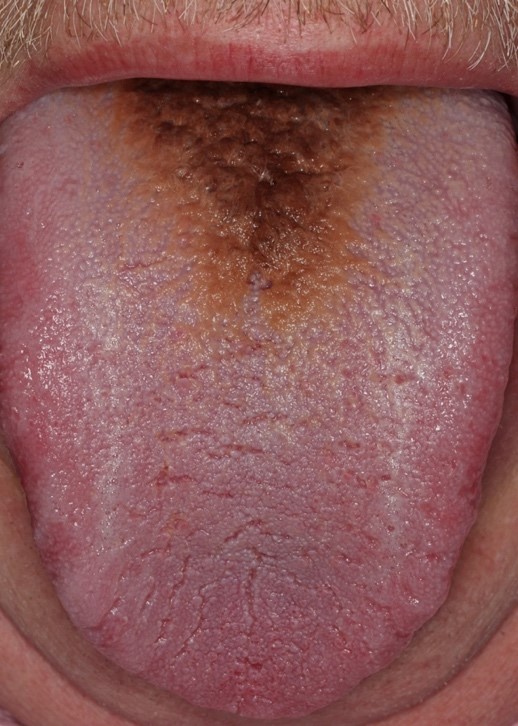
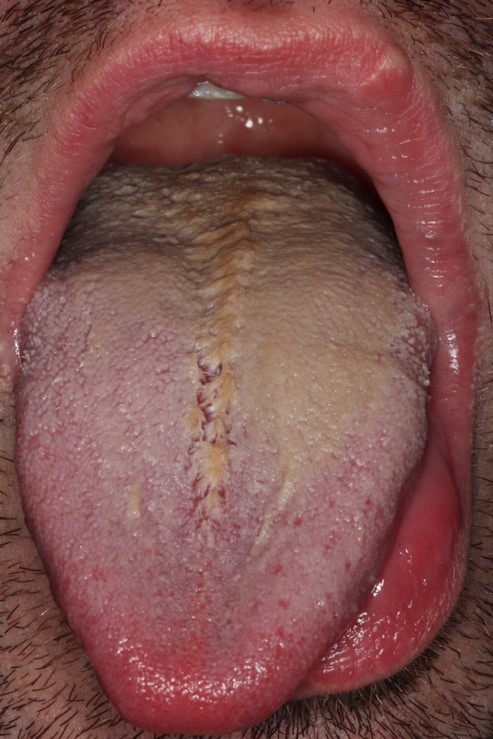
- Hair-like projections of the dorsal tongue (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
- Brown, black, green or yellow discoloration may be present
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is made clinically; biopsy is not necessary
Prognostic factors
- Asymptomatic, although some patients may experience gagging sensation, malodor or foul taste
Case reports
- 54 year old woman smoker with hairy tongue occurring concurrently with respiratory infection (Cleve Clin J Med 2017;84:434)
- 56 year old white man with black hairy tongue associated with linezolid (J Med Case Rep 2013;7:46)
- 60 year old woman with hairy tongue after prednisolone use (Arch Rheumatol 2019;34:348)
- 63 year old man with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and hairy tongue (J Int Soc Prev Community Dent 2016;6:80)
- 64 year old woman with hairy tongue associated with interferon therapy for hepatitis C (Ann Hepatol 2015;14:414)
Treatment
- Treatment is not urgent or immediately necessary
- Patients may seek treatment for foul breath, abnormal sensation
- Includes tongue scraping / brushing, elimination of offending / contributing agents (e.g. tobacco, medications), addition of crunchy / coarse foods to diet and oral hygiene improvement (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
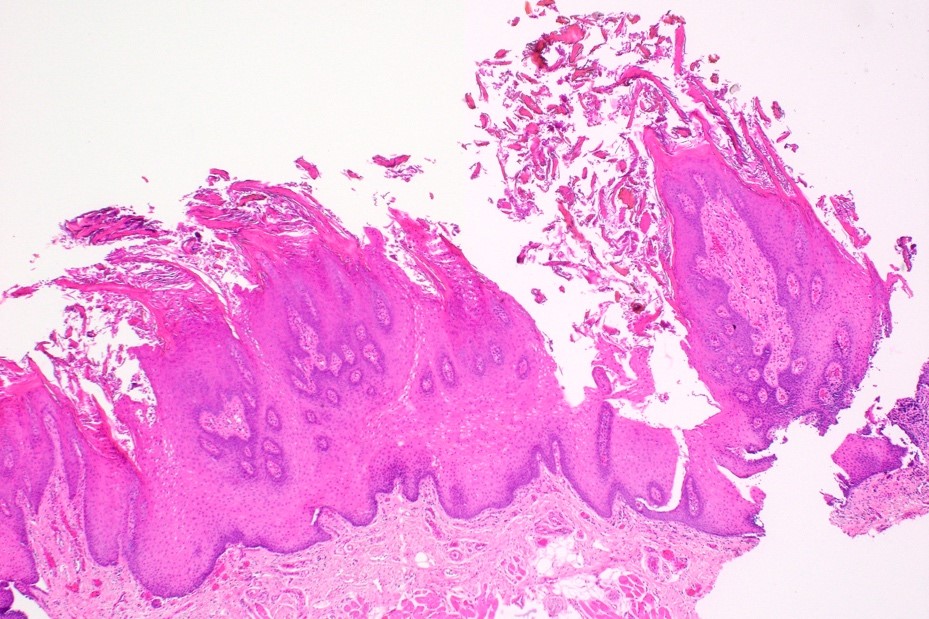
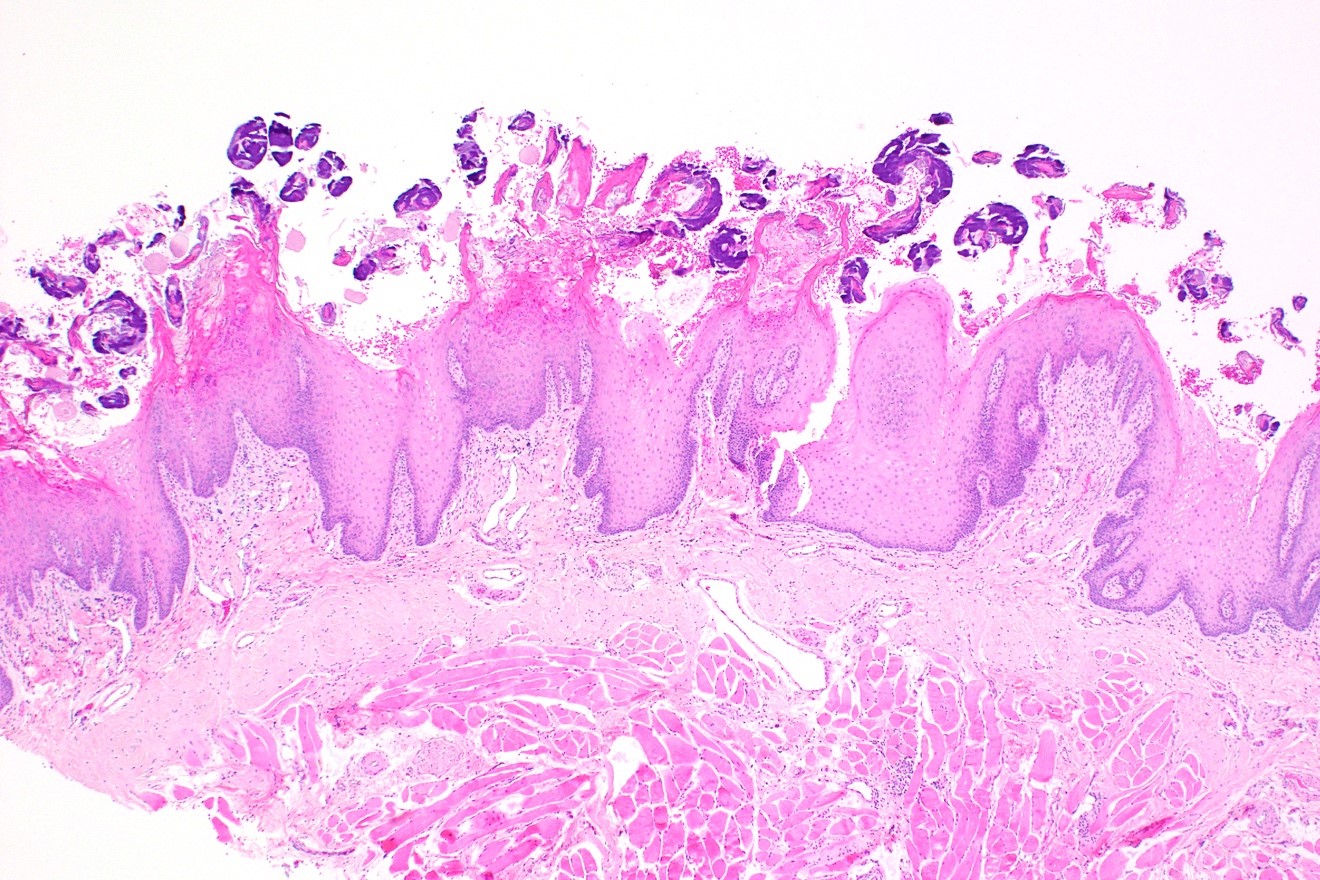
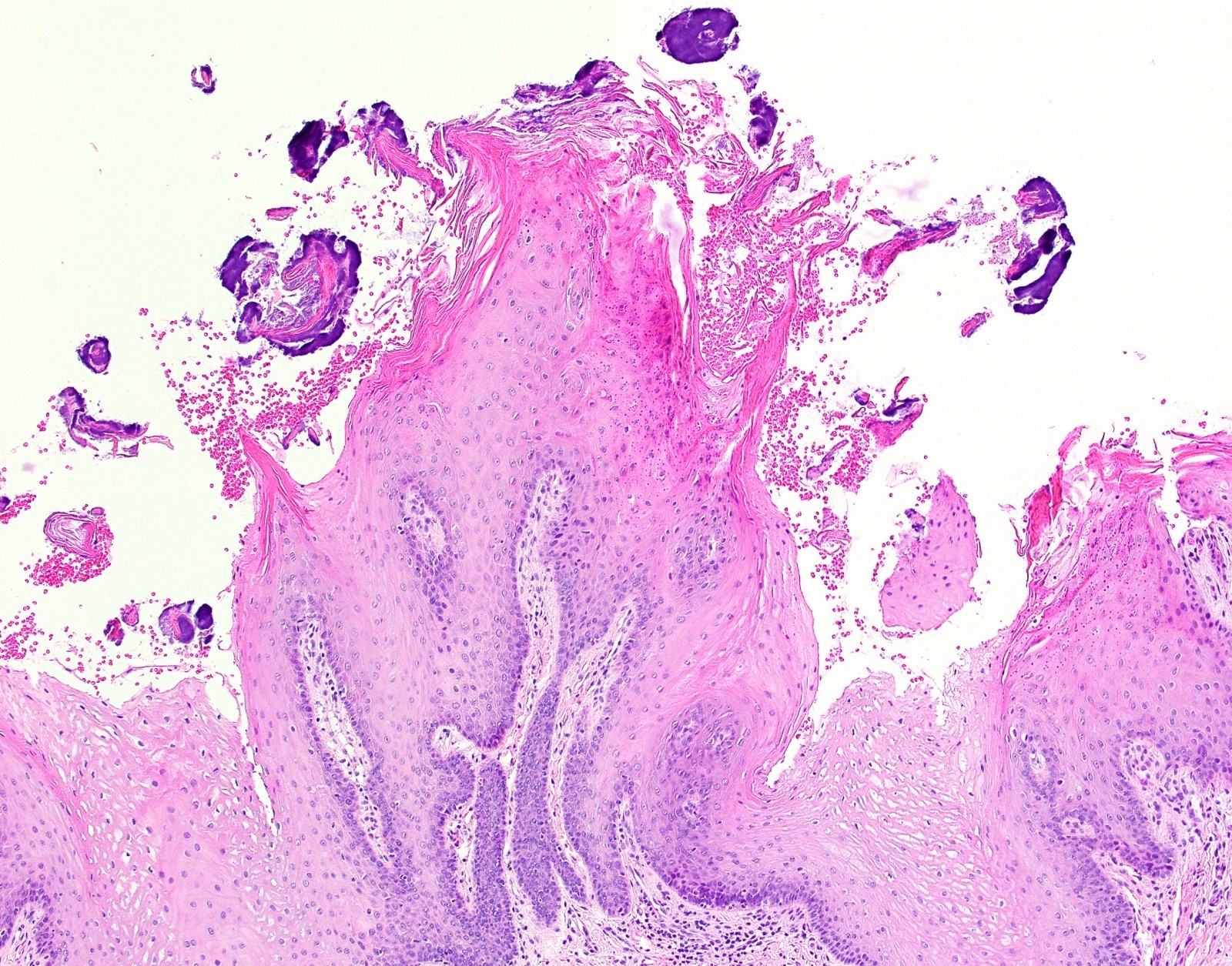
- Markedly elongated filiform papillae with hair-like spires of keratin (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:10845)
- Basophilic bacterial colonies often adhered to keratin surface
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Negative in situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus (EBER); there is no association with EBV
Sample pathology report
- Dorsal tongue, incisional biopsy:
- Hyperkeratosis and elongation of filiform papillae (see comment)
- Comment: The histologic findings are compatible with hairy tongue.
Differential diagnosis
- Coated tongue:
- White, brown, black, yellow discoloration of the dorsal tongue without prominent elongation of the filiform papillae
- Oral hairy leukoplakia:
- Only included in differential diagnosis due to similarity of terminology
- Most often presents as furrowed white plaques on lateral tongue
- Associated with Epstein-Barr virus
- Positive upon in situ hybridization with EBER
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about hairy tongue, shown in the image?
- Hairy tongue is positive upon in situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus (EBER)
- Hairy tongue is strongly correlated with smoking and medication use
- Microscopic examination reveals eosinophilic condensation in a perinuclear arrangement in the superficial aspects of the epithelium
- Treatment varies based on the histologic grade
Board review style answer #1
B. Hairy tongue is strongly correlated with smoking and medication use
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy tongue
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy tongue
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2