Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Smith MH. Fordyce granules. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityfordyce.html. Accessed December 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Ectopic sebaceous glands within oral cavity or on vermillion border of lips
Essential features
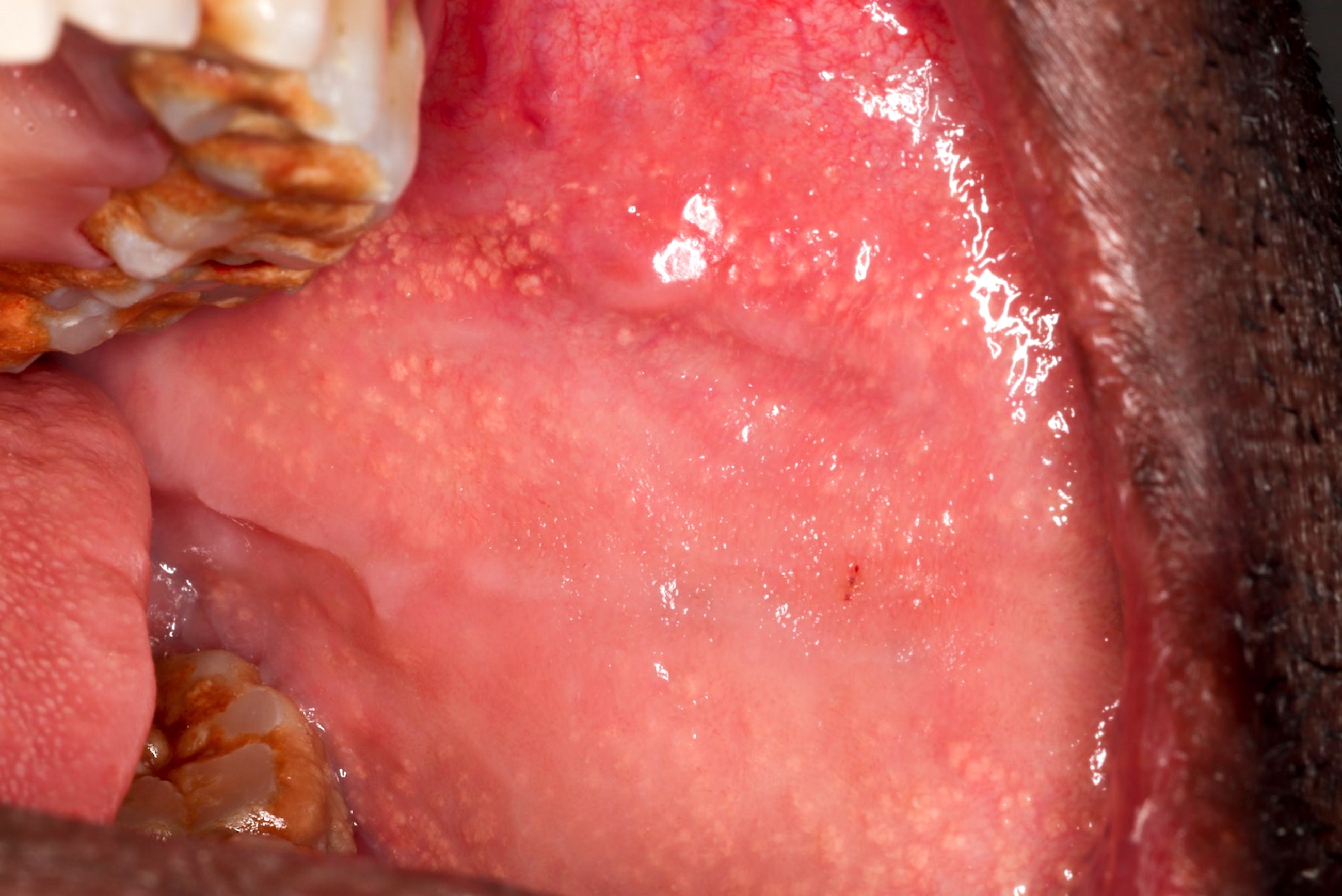
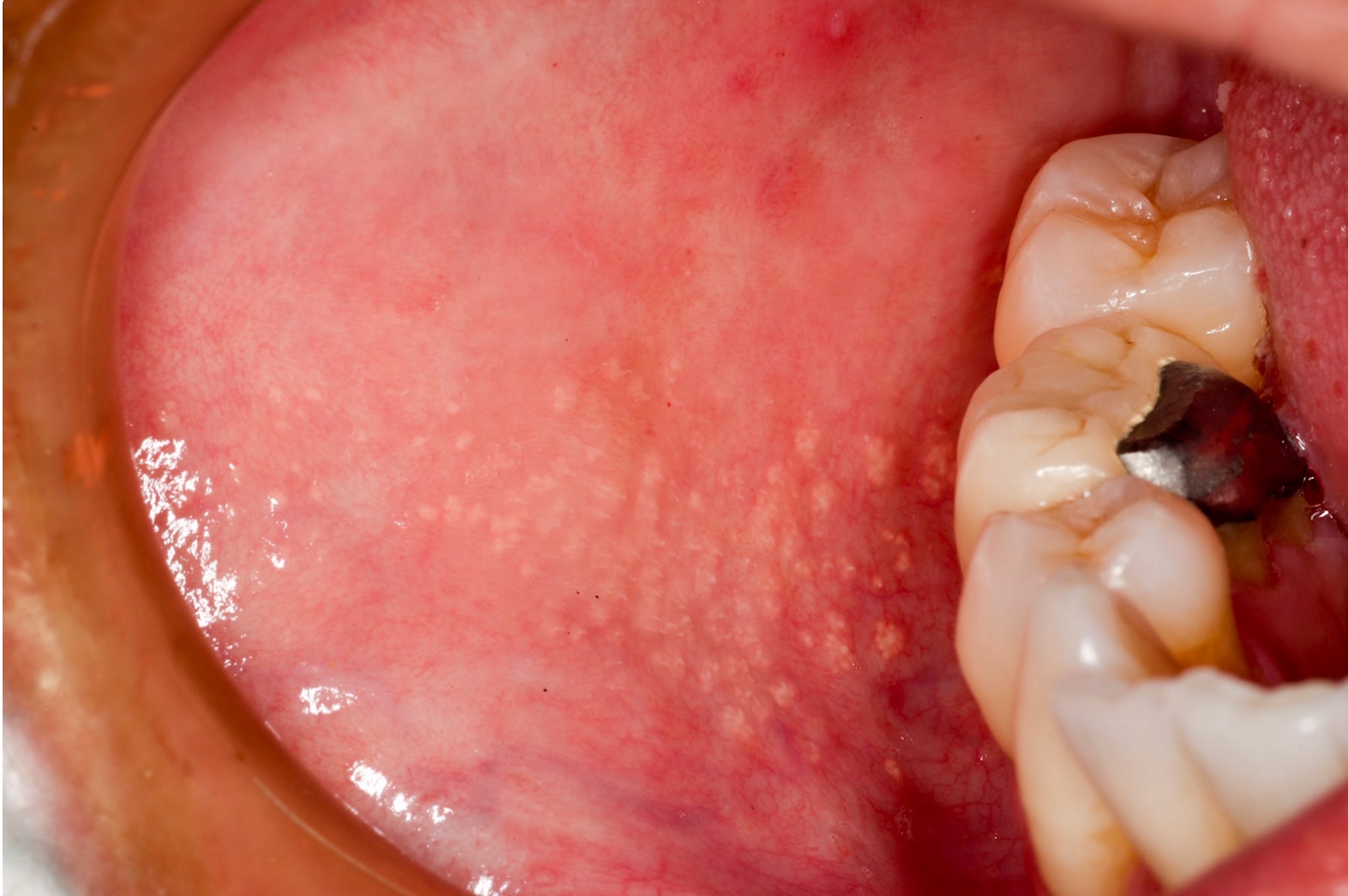
- Appear as yellow-white, asymptomatic 1 - 3 mm papules in the oral cavity or lip vermillion
- May be hyperplastic and nodular
- Neoplastic transformation very rare but reported (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1991;72:709, Head Neck 2016;38:E20, Case Rep Dent 2018;2018:3054931)
- Have been associated with Lynch and Muir-Torre syndromes (Gut 2005;54:1279, J Oral Pathol Med 2015;44:552)
- Present in ~80 - 90% of the population (Med Clin North Am 2014;98:1281)
Terminology
- Fordyce granules
- Fordyce spots
ICD coding
- ICD-10: Q38.6 - other congenital malformations of the mouth
Epidemiology
- No sex or racial predilection
- Often most prominent after puberty (Med Clin North Am 2014;98:1281)
- Hyperplastic examples have been associated with Lynch and Muir-Torre syndromes (Gut 2005;54:1279, J Oral Pathol Med 2015;44:552)
- Patients with high densities of Fordyce granules may have higher lipid profiles (Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2014;11:553)
Sites
- Buccal mucosa (often bilateral), upper lip vermilion border, mandibular retromolar pad and tonsillar areas
- Similar anomalies affect the areolae, glans penis and labia minora
Etiology
- Congenital
- Considered benign sebaceous hamartomas
Clinical features
- Yellow-white, asymptomatic, floral appearing 1 - 3 mm papules that remain constant throughout life
- May be hyperplastic and nodular
Diagnosis
- Diagnosed clinically
- Rarely may require biopsy for identification when hyperplastic or nodular
Treatment
- No treatment necessary unless for cosmetic reasons
Clinical images
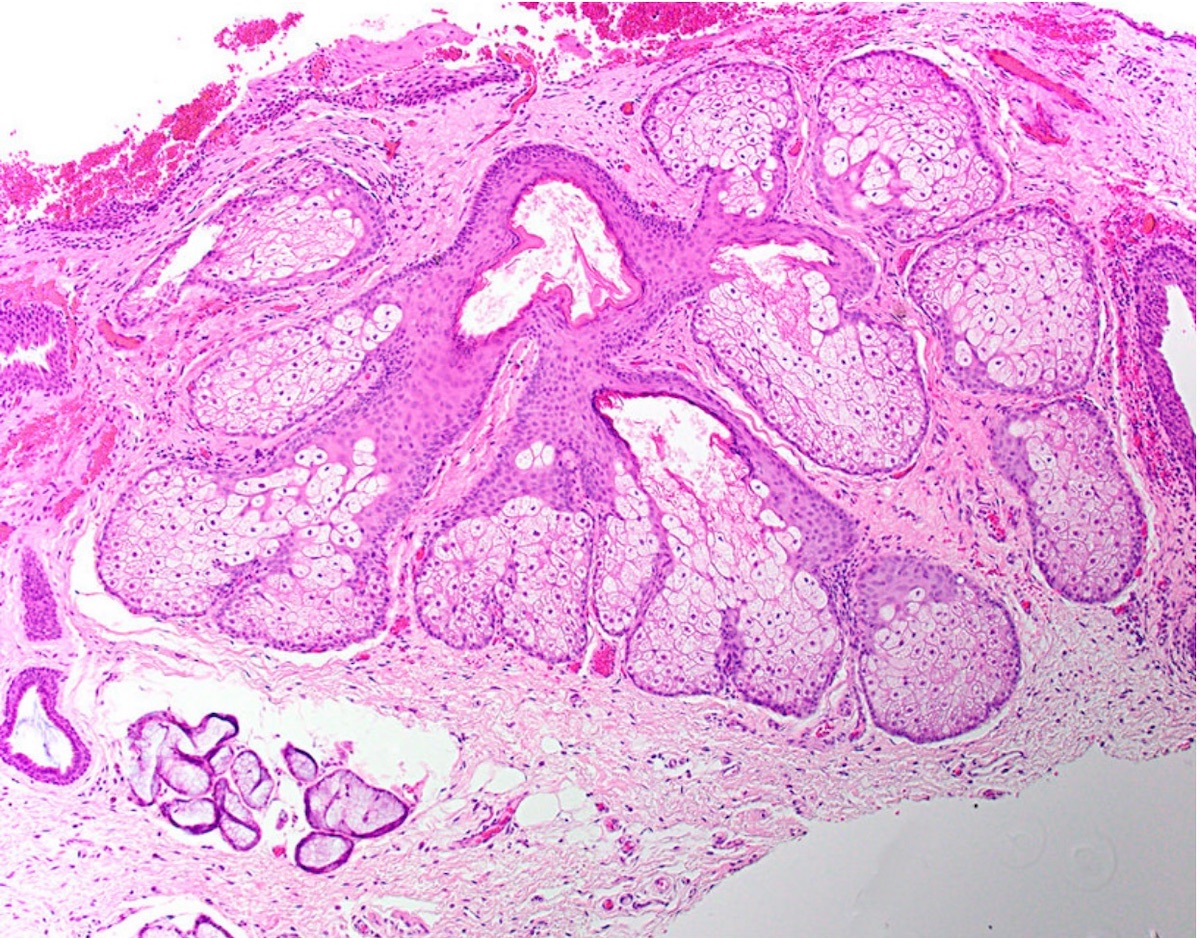
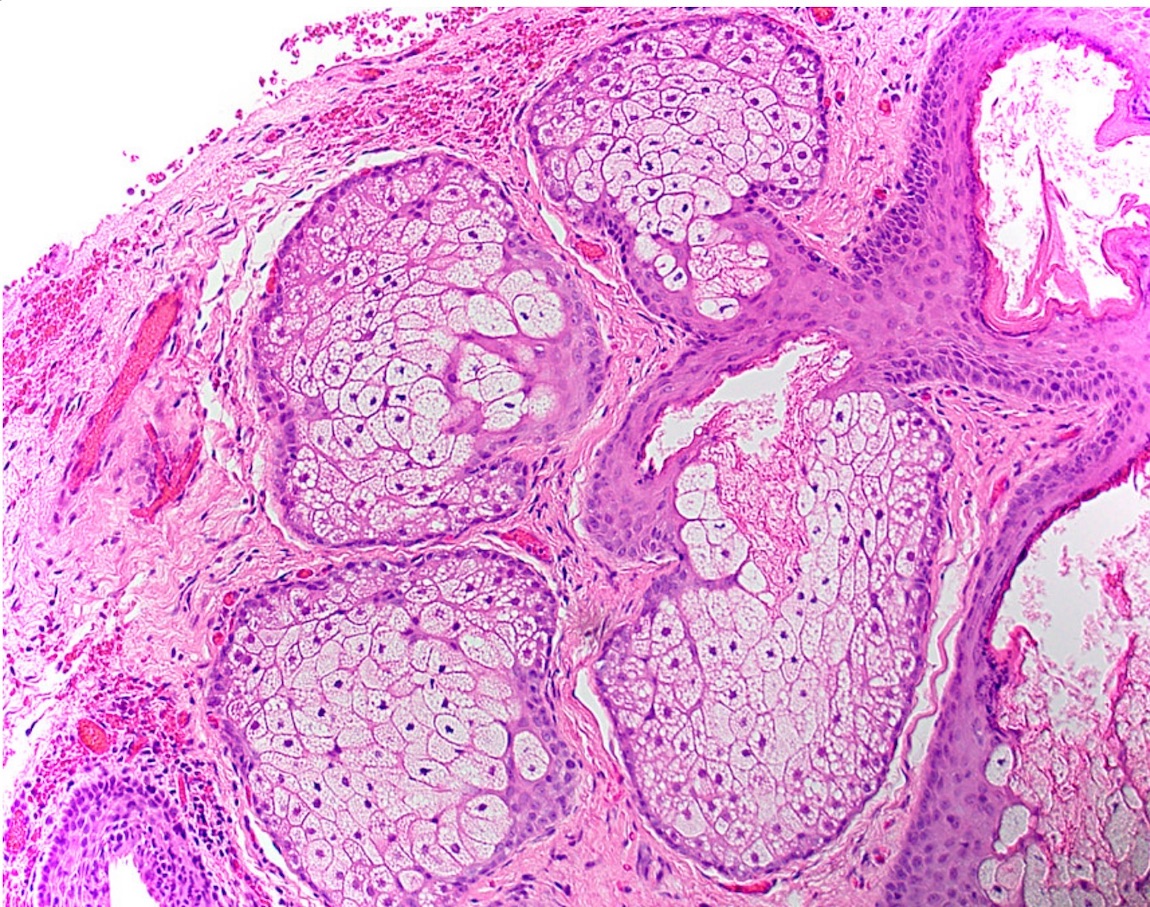
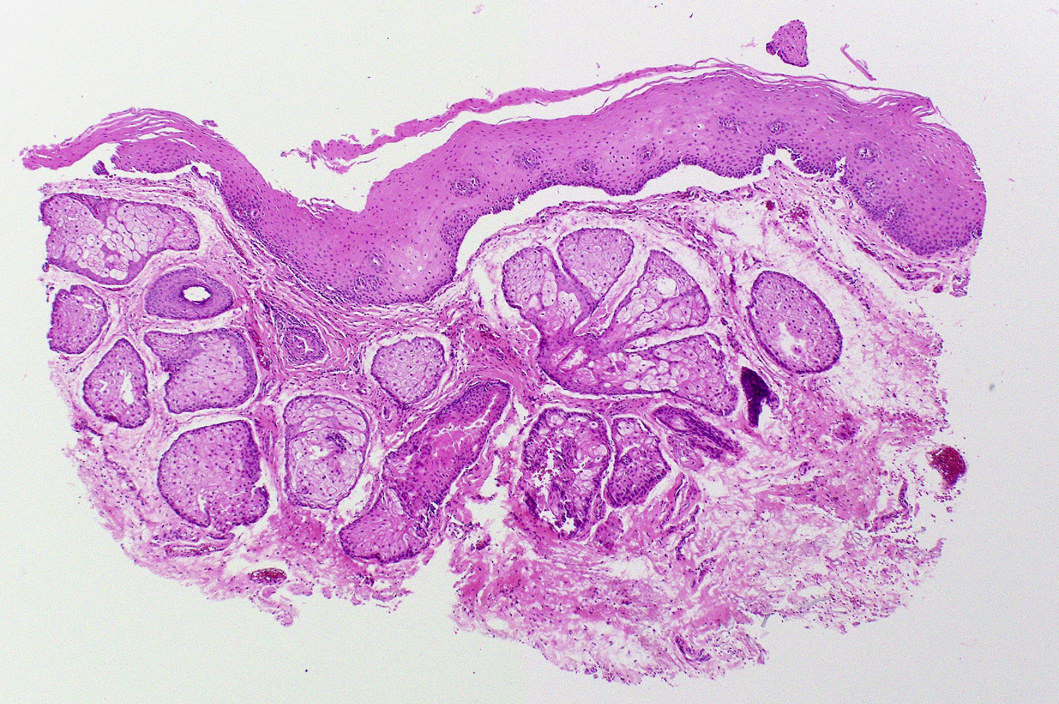
Microscopic (histologic) description
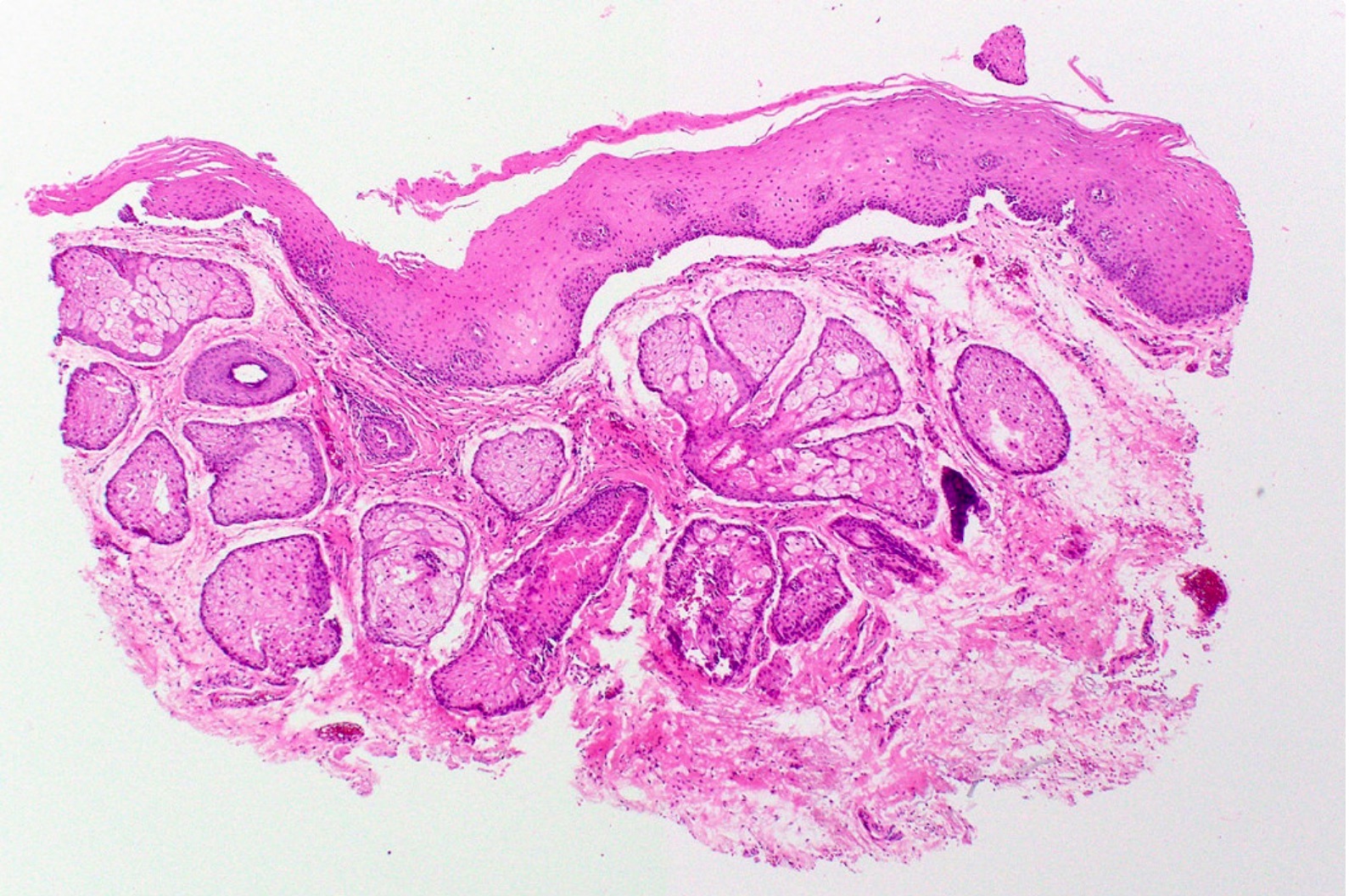
- Similar to normal sebaceous glands of skin but lack hair follicles and almost always lack ductal communication with surface
- Parakeratotic stratified squamous epithelium overlies the sebaceous lobules
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Although associated with Lynch and Muir-Torre syndromes, which demonstrate defects in DNA mismatch repair (MMR) proteins leading to microsatellite instability, preservation of MMR proteins is noted upon immunostaining of Fordyce granules (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2017;25:209)
Sample pathology report
- Left buccal mucosa, incision:
- Fordyce granules (see comment)
- Comment: Microscopic examination reveals parakeratotic stratified squamous epithelium overlying mesenchymal tissue. Within the mesenchymal stroma are numerous sebaceous gland lobules. Hair follicles are not appreciated.
Differential diagnosis
- Clinically diagnostic and doesn't have a differential diagnosis; often are not even biopsied but found only incidentally on pathology
- Usually noted on routine examination
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about this oral mucosal entity?
- Immunohistochemistry is necessary to define this process
- It is found in higher frequency in those who have Lynch and Muir-Torre syndromes
- Neoplastic transformation occurs in the majority of cases
- This entity is most frequently found on the tongue
Board review style answer #1
B. It is found in higher frequency in those who have Lynch and Muir-Torre syndromes
Comment here
Reference: Fordyce granules
Comment here
Reference: Fordyce granules
Board review style question #2
A 43 year old female patient presents to the clinic for a routine head and neck cancer screening.
Upon examination, numerous yellow-white papules (approximately 1 - 3 mm in diameter) are present
along the upper lip vermillion border and on the right and left buccal mucosa. The patient states that
the spots are asymptomatic and thinks that they have always been there. Which is the most likely
diagnosis?
- Actinic cheilitis
- Fordyce granules
- Morsicatio buccarum
- Salivary gland hyperplasia
Board review style answer #2