Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Glass SH. Amalgam tattoo. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavityamalgamtattoo.html. Accessed December 27th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Iatrogenic implantation of exogenous foreign material, specifically dental amalgam, into the tissues of the oral cavity
Essential features
- Deposition often occurs during oral procedures involving amalgam
- Gray, blue or black macule on clinical exam in the oral cavity
- Large black deposits or fine black granules in the connective tissue with affinity for reticulin fibers
Terminology
- Foreign body tattoo
ICD coding
- ICD-10: M79.5 - residual foreign body in soft tissue
Epidemiology
- Person with history of amalgam tooth restorations (dental fillings)
- Affects 3.3% of the U.S. adult population (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
Sites
- Any location in the oral cavity, with gingiva and alveolar mucosa being the most common location due to proximity to the teeth
Pathophysiology
- Implantation of dental amalgam into oral mucosa
Etiology
- Implantation of dental amalgam can occur several ways, including contaminated mucosal abrasion during dental procedure, broken amalgam pieces in an extraction site and endodontic retrofill procedure (Neville: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, 4th Edition, 2015)
Clinical features
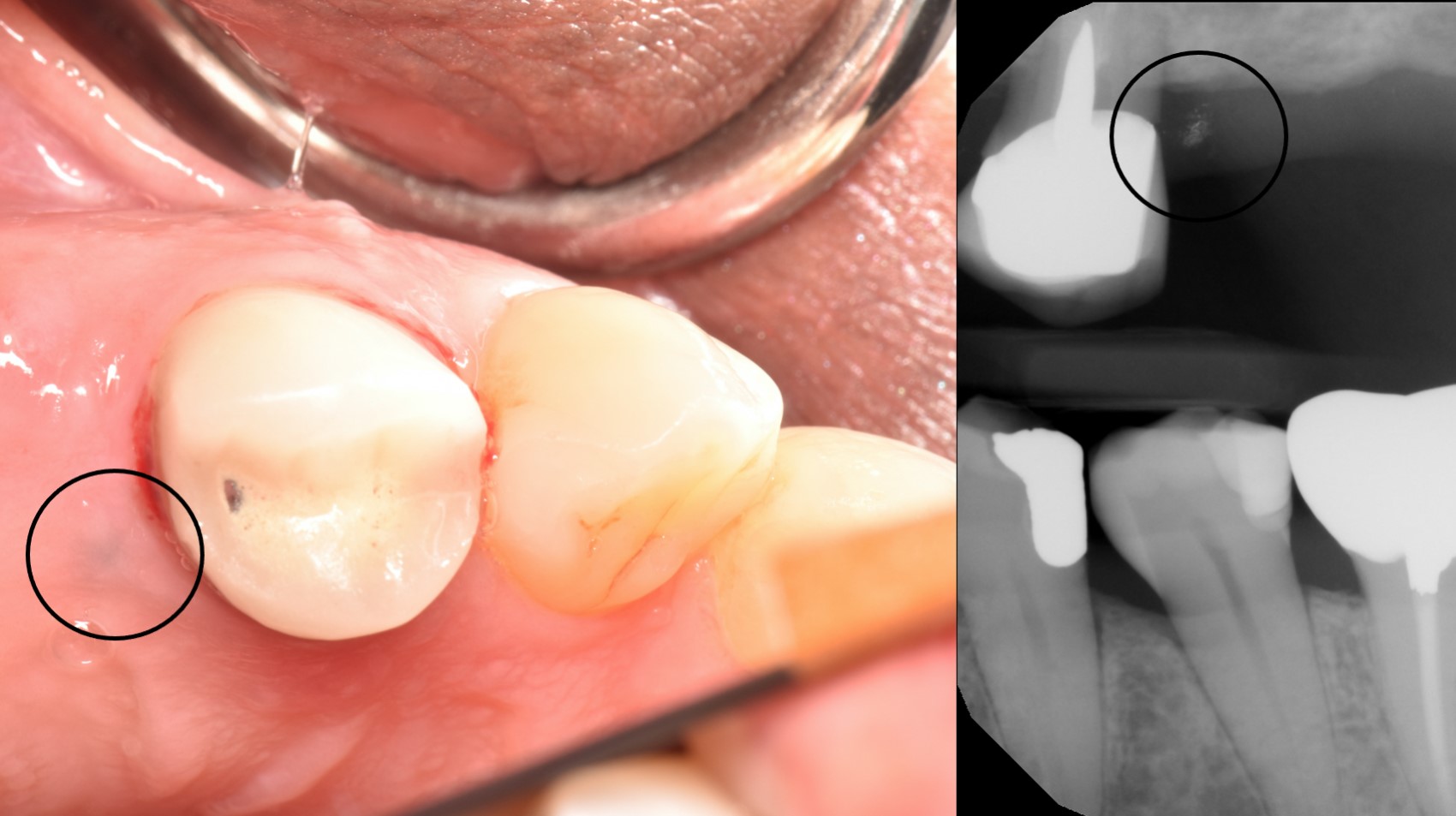
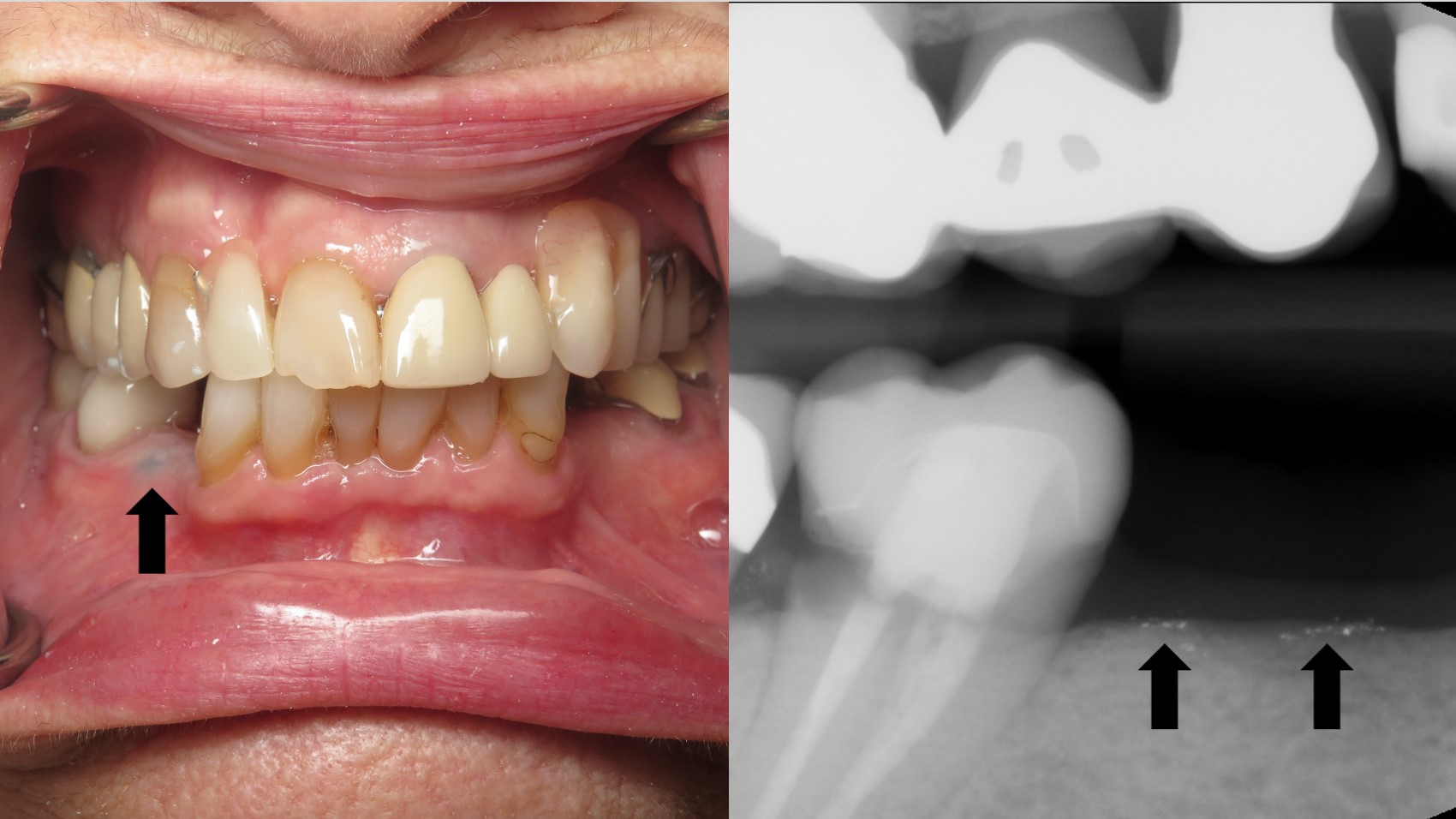
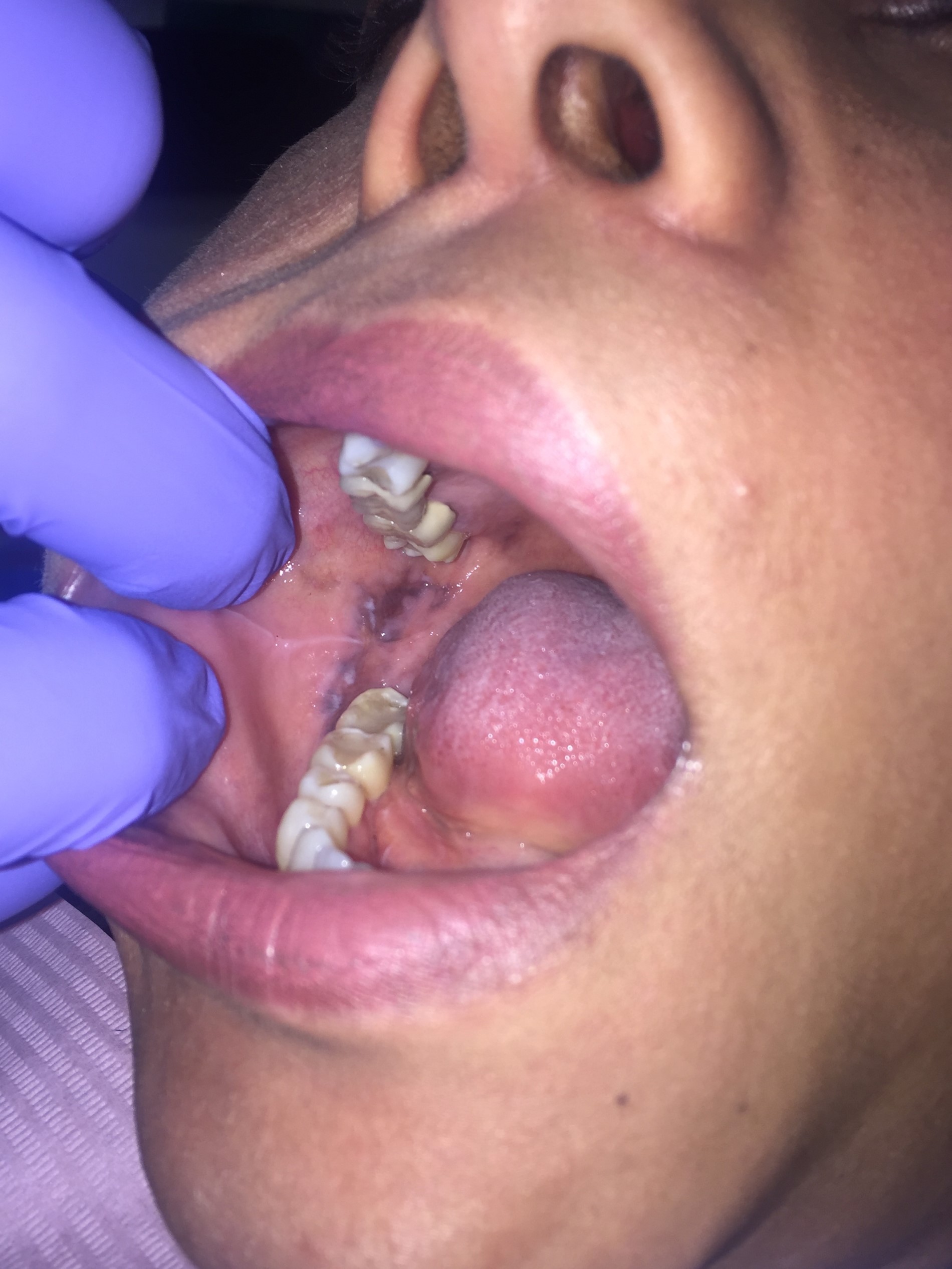
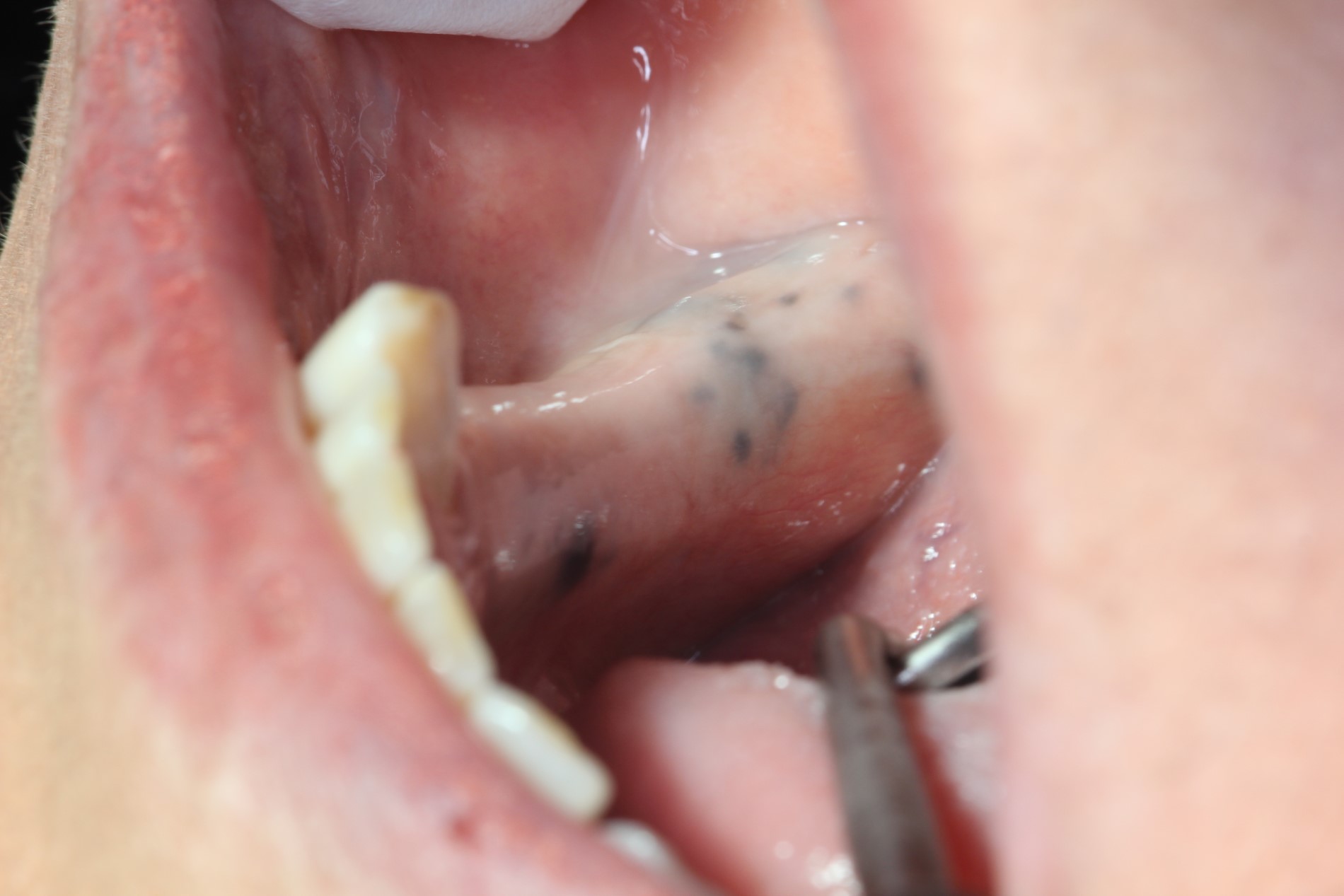
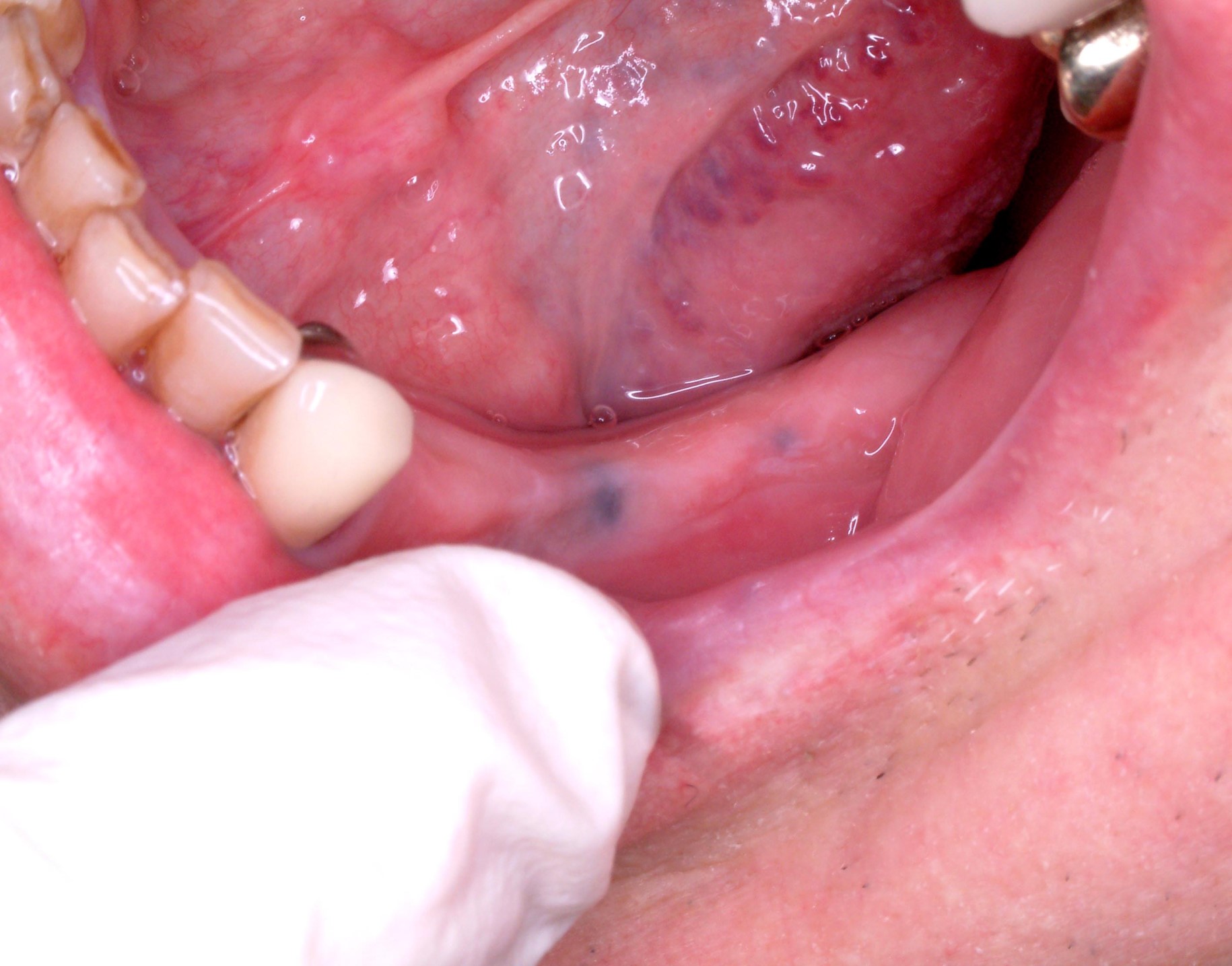
- Gray, blue or black macule that is rarely raised
- Multiple macules may occur
- Borders may be well defined, irregular or diffuse
- Enlargement can occur (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
- May be useful as a means for person identifications (J Forensic Odontostomatol 1991;9:17)
Diagnosis
- In some cases, the diagnosis may be presumed on clinical exam with corresponding historical information and radiographic features
- If the diagnosis cannot be made confidently on clinical exam, a biopsy is recommended for definitive diagnosis (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
Radiology description
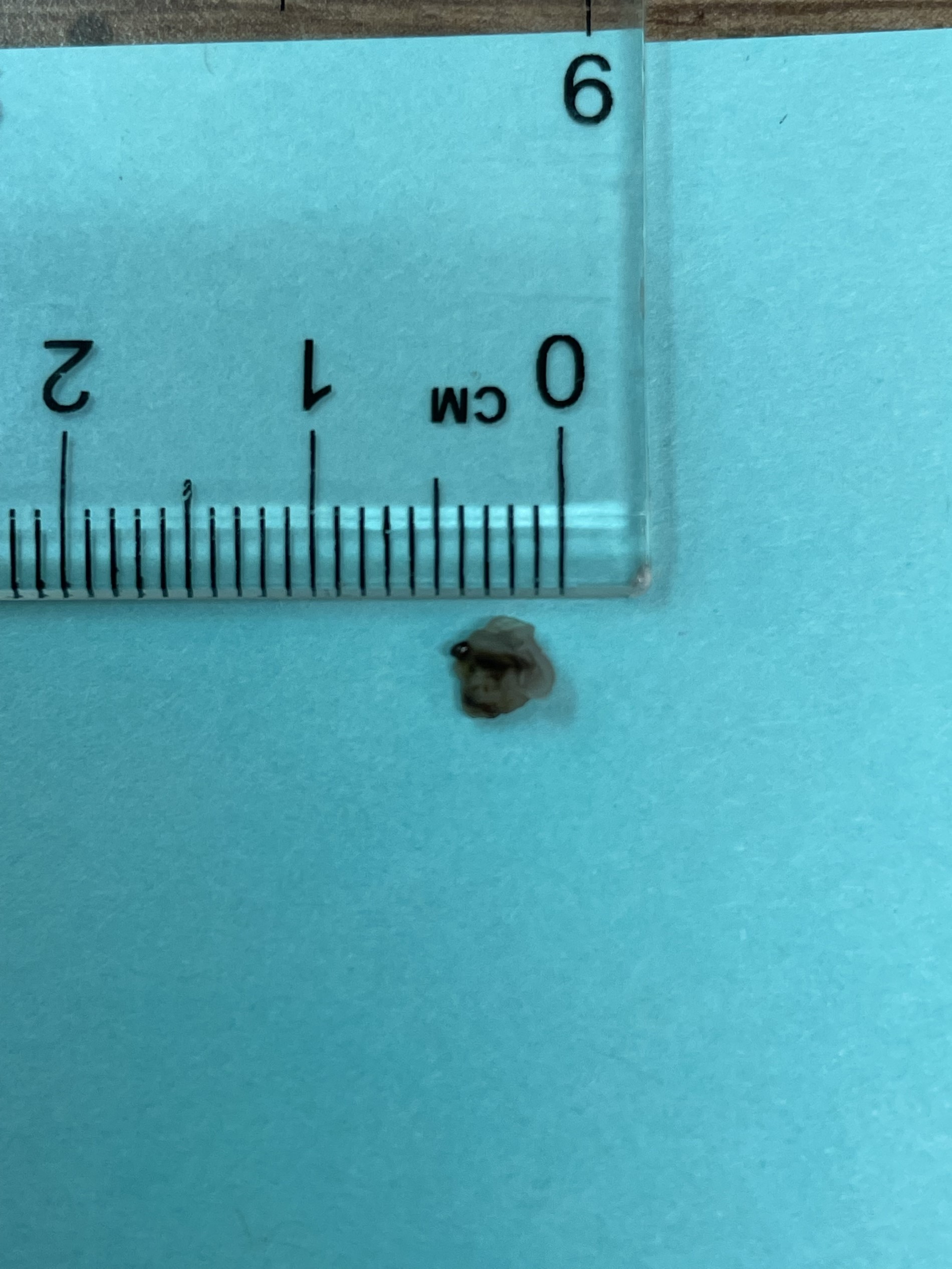
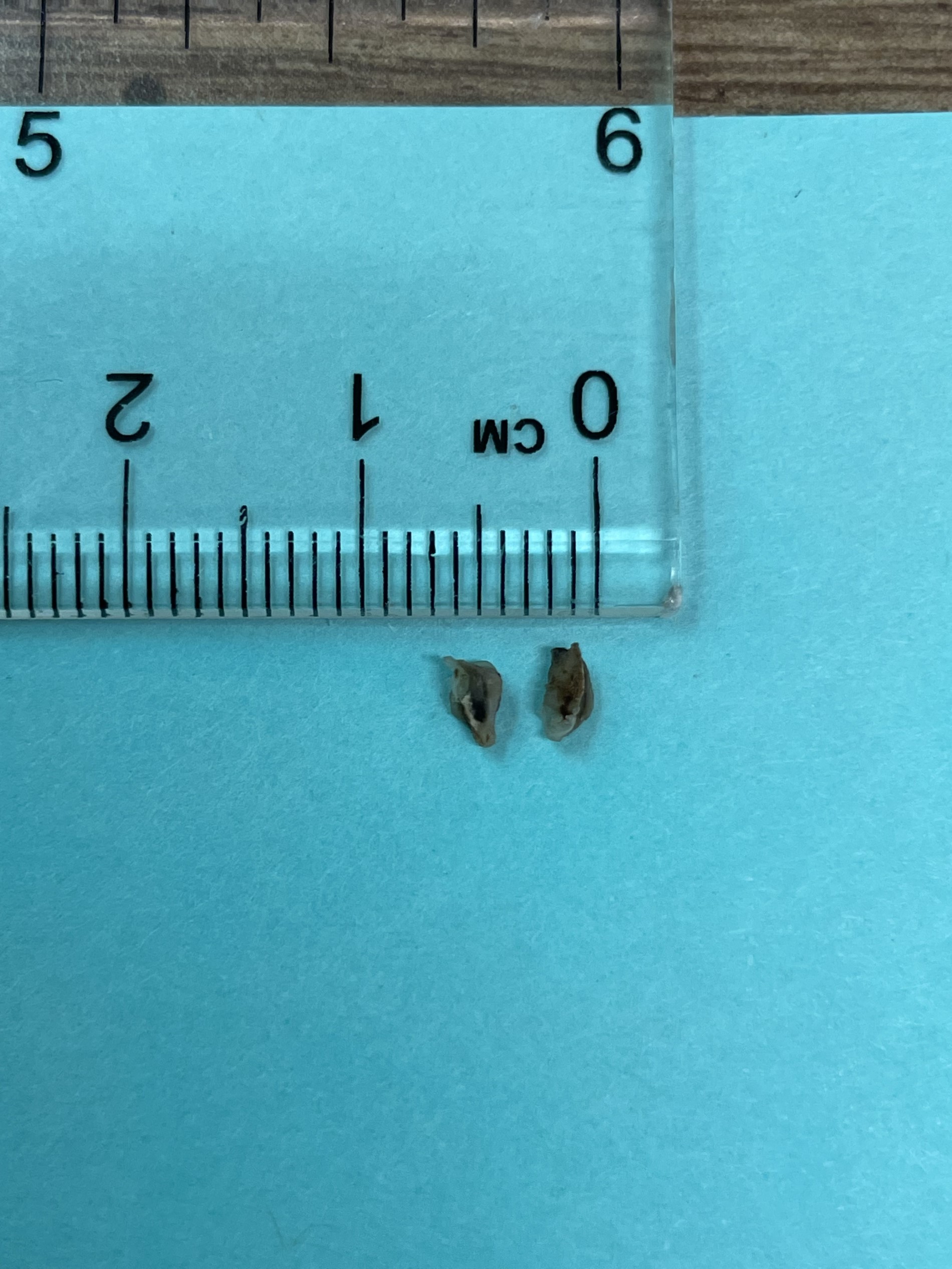
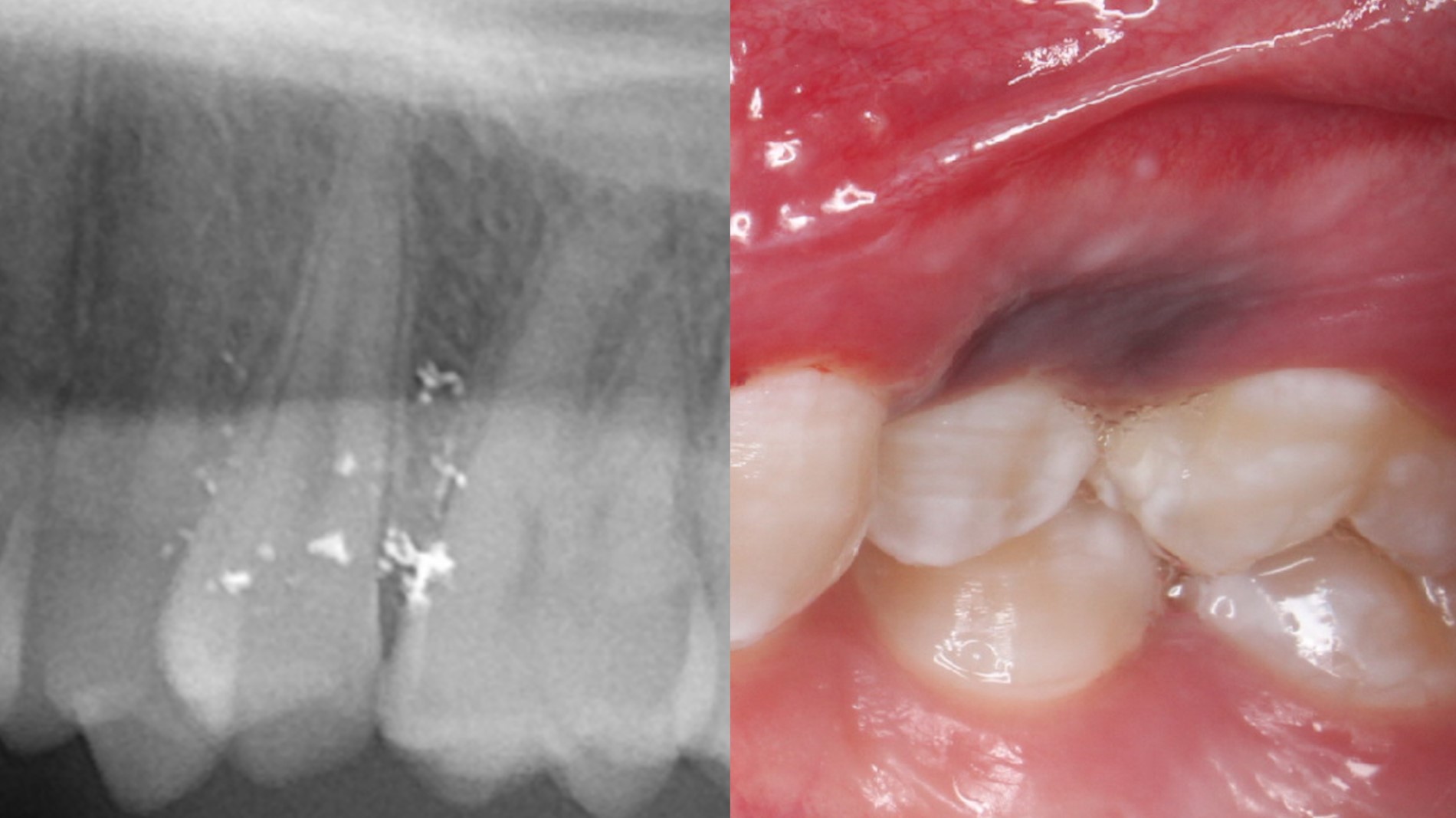
- Radiopaque fragments may be noted on radiographic exam if amalgam particles are large; however, this is not common
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
Case reports
- 38 year old woman with amalgam in mucoperiosteal flap from endodontic surgery (J Conserv Dent 2016;19:280)
- 49 year old woman with a brown-gray macule on the ventral tongue noted after dental restoration (N Engl J Med 2016;374:e21)
- 53 year old man with black macule on alveolar ridge and remote history of tooth extraction (Indian J Med Res 2018;148:240)
Treatment
- No treatment is needed once diagnosis is established
- Conservative surgical excision can be recommended for esthetic concerns, especially for the anterior maxilla (J Esthet Restor Dent 2020;32:770)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Well defined or diffuse black, gray or blue pigmentation in connective tissue on cross section
Microscopic (histologic) description
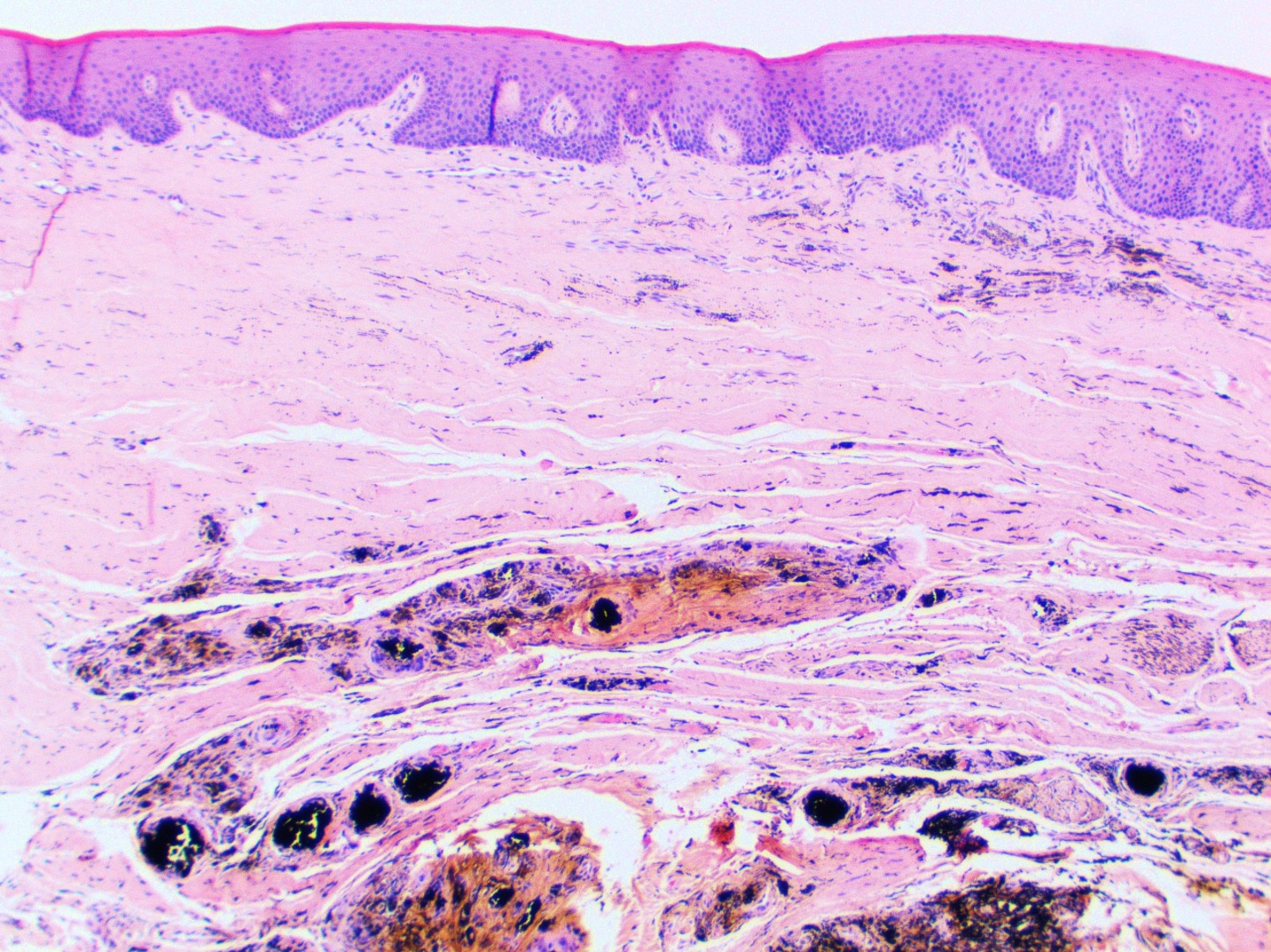
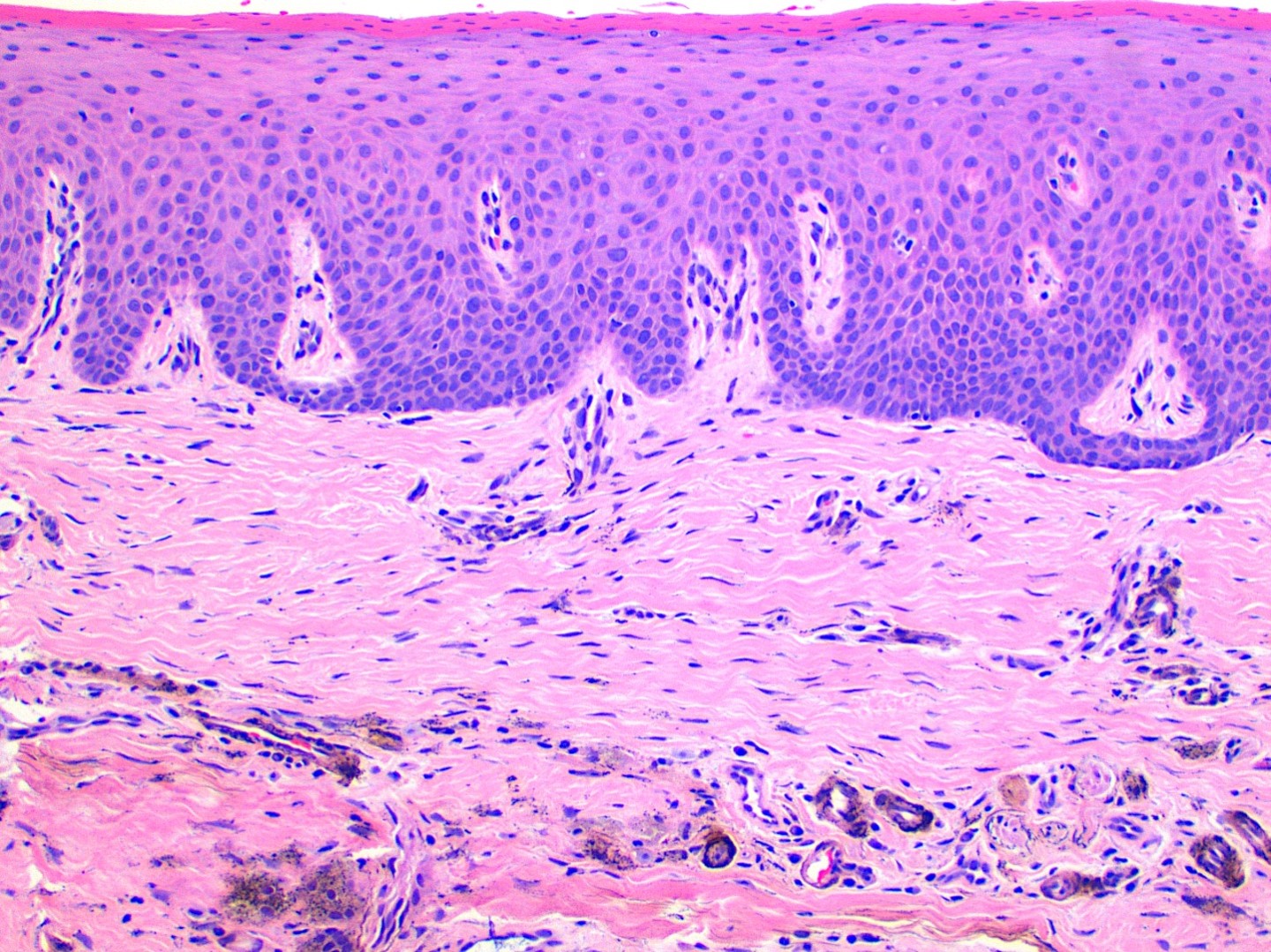
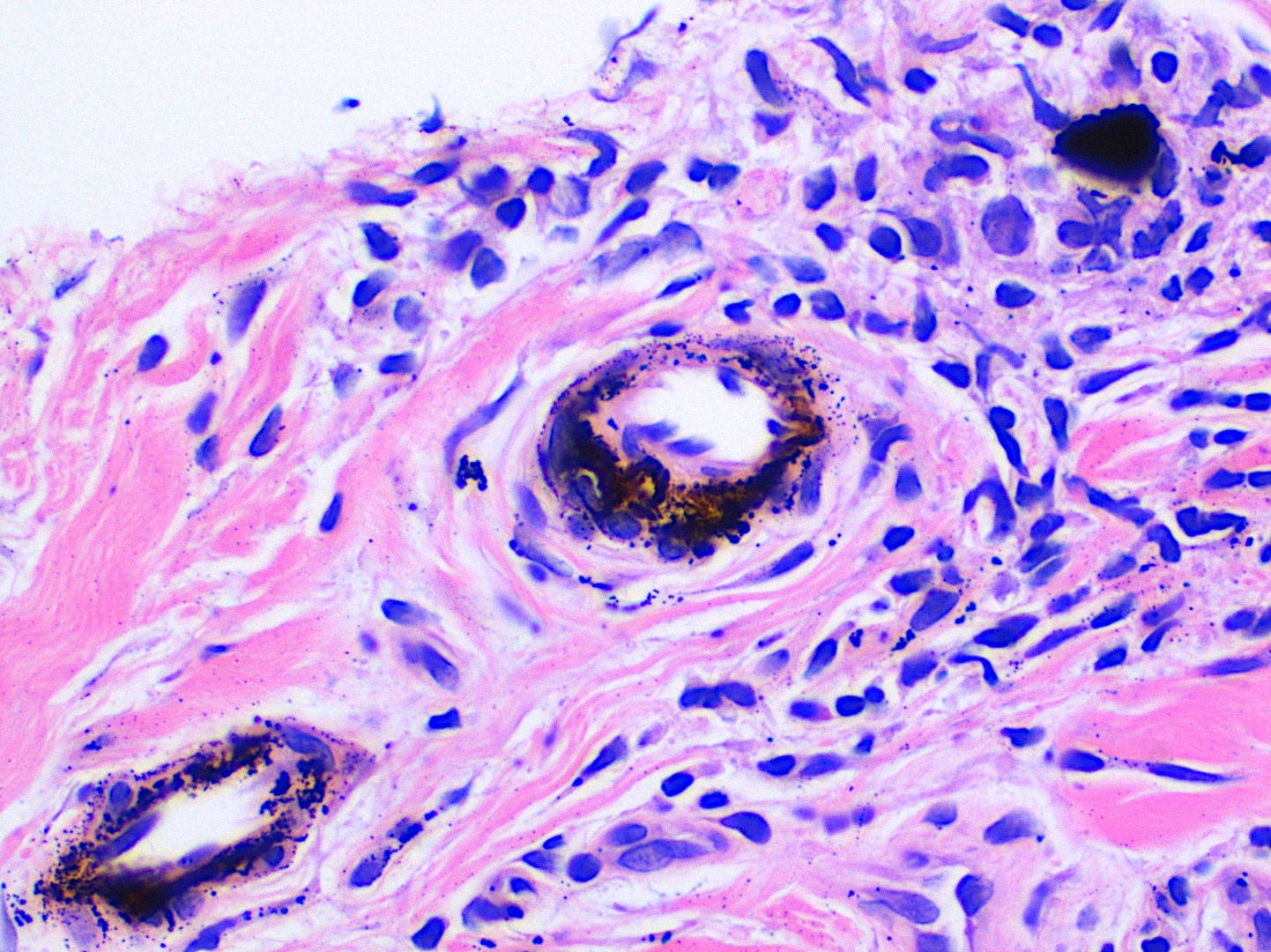
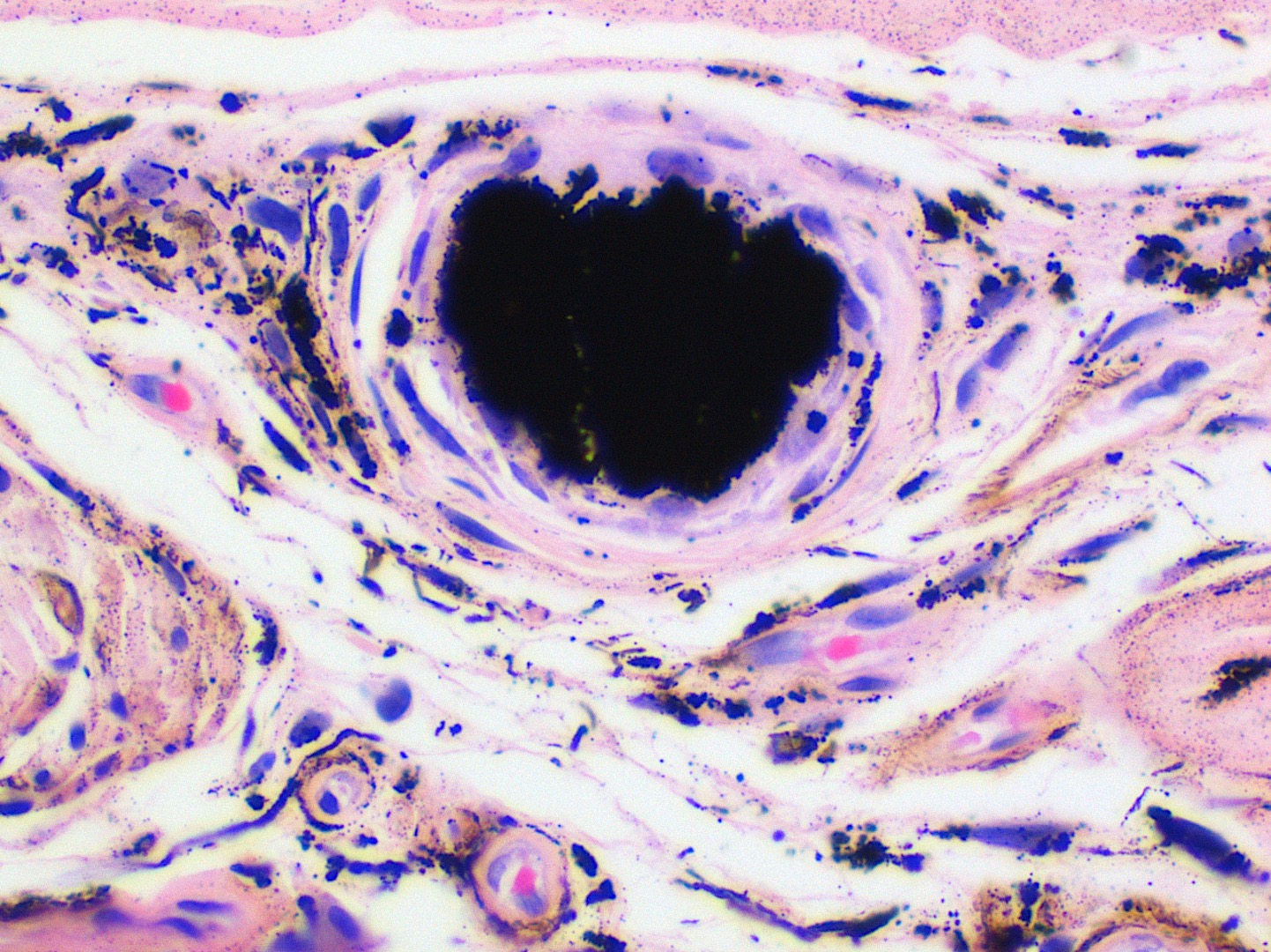
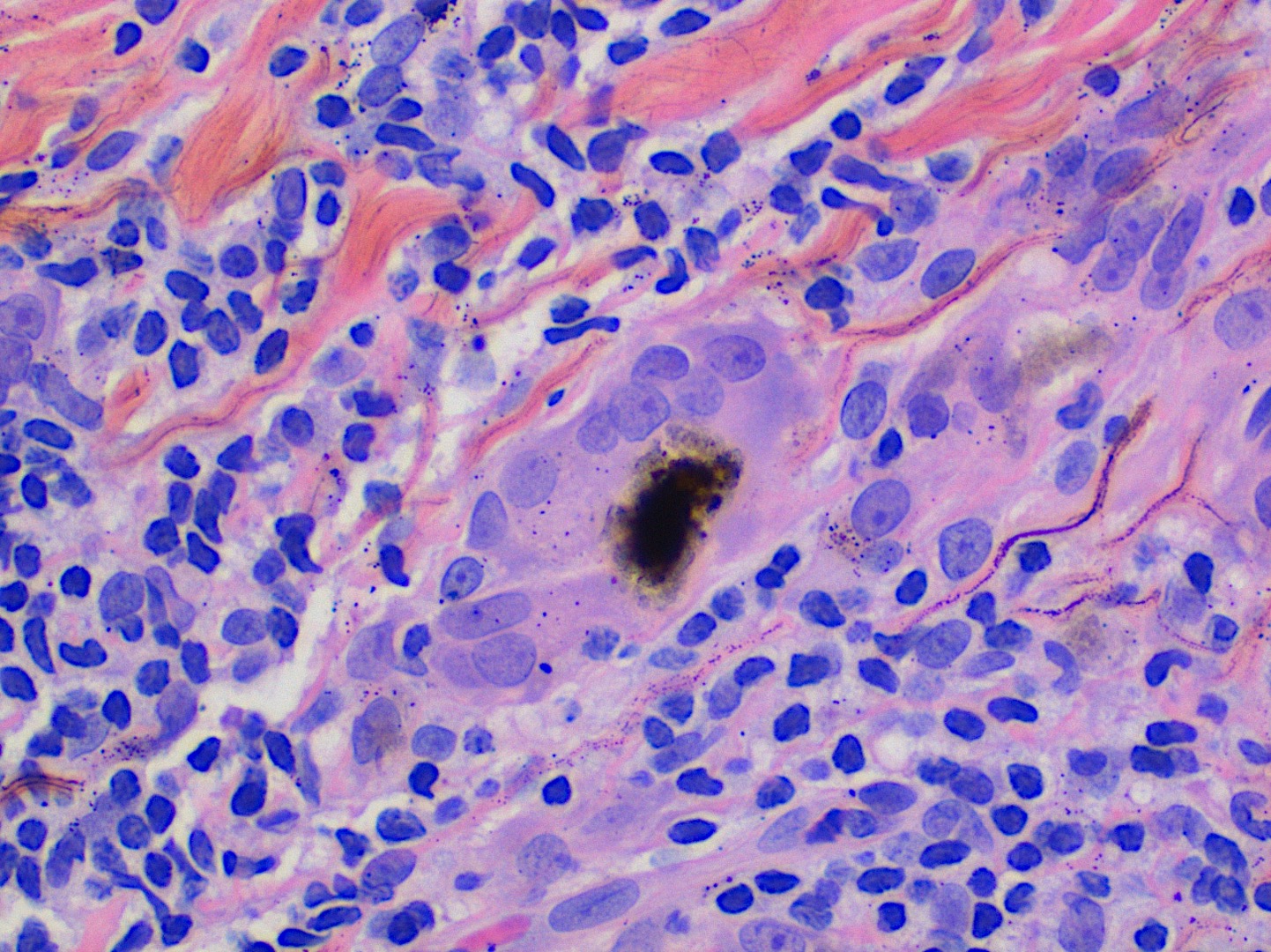
- Large black deposits of foreign material with or without a chronic inflammatory response in the connective tissue
- Fine black granules in the connective tissue; may demonstrate affinity for reticulin fibers (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Oral cavity, excisional biopsy:
- Foreign body tattoo (see comment)
- Comment: The histopathology and clinical information are consistent with an amalgam tattoo.
Differential diagnosis
- Oral melanotic macule:
- Increased melanin in basal cell layer of the epithelium with melanin incontinence in the superficial connective tissue
- Multifocal presentation may be seen in a systemic disease, such as Addison disease or Peutz-Jegher syndrome (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
- Foreign body tattoo or other exogenous material:
- Intentional tattoo pigment (shown above)
- Graphite from pencil (Dermatol Online J 2015;21:13030)
- Drug related discolorations:
- Depending on the drug, histopathology features mimic those of melanotic macule or brown-yellow granules in connective tissue (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:47)
- Submucosal hemorrhage:
- Hemosiderin in the connective tissue from trauma
- Positive Prussian blue
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Amalgam tattoo. Although all answer choices can result in pigmented macules in the oral cavity, amalgam is the only exogenous material. This foreign material has a particular affinity for reticulin fibers and can be seen around blood vessels.
Comment Here
Reference: Amalgam tattoo
Comment Here
Reference: Amalgam tattoo
Board review style question #2
What is the etiology of an amalgam tattoo from the oral cavity?
- Drug related discoloration
- Iatrogenic implantation of dental filling material
- Increased melanin production
- Trauma induced hemosiderin deposition
Board review style answer #2
B. Iatrogenic implantation of dental filling material. A dental professional may inadvertently implant amalgam, an exogenous foreign material, into the oral mucosa during a dental procedure.
Comment Here
Reference: Amalgam tattoo
Comment Here
Reference: Amalgam tattoo