Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Sun J, Brandwein-Weber M. Chronic rhinosinusitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/nasalchronicrhinitis.html. Accessed November 28th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Chronic inflammation of the nasal cavity (rhinitis) or the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis), symptoms lasting more than 6 weeks
- Sequel to acute rhinitis (symptoms lasting 6 weeks or less), with development of secondary bacterial infection
- Associated with deviated septum or nasal polyps; also ulceration and infection extending into sinuses
Essential features
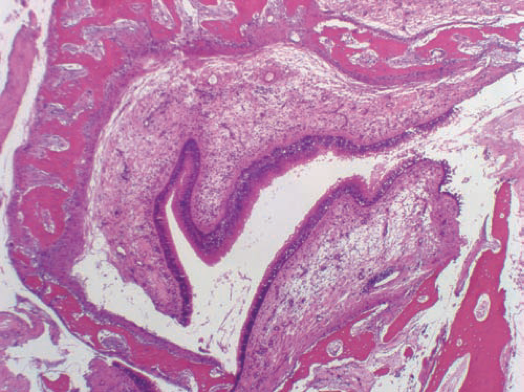
- Thickened, hyalinized basement membrane (minimal criteria) directly beneath respiratory epithelium and around seromucinous glandular tubuli
Terminology
- Rhinosinusitis, sinusitis
Epidemiology
- Most common health problem in the United States
Sites
- Unilateral or bilateral, nasal cavity or paranasal sinus
Pathophysiology
- Associated with deviated septum or nasal polyps
- Ostial obstruction in osteomeatal compex causes anaerobic overgrowth
Etiology
- Allergy, vasomotor (constricted or dilated vessels), infection, diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis, Kartagener syndrome, aspirin intolerance, Churg-Strauss disease, nickel exposure
Clinical features
- Facial pain, pressure, congestion or fullness; nasal obstruction, blockage, discharge or purulence
Treatment
- Aeration or drainage, ensuring ostial patency
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Thickened basement membrane (minimal criteria) directly beneath respiratory mucosa and around seromucinous glandular tubuli
- Increased lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
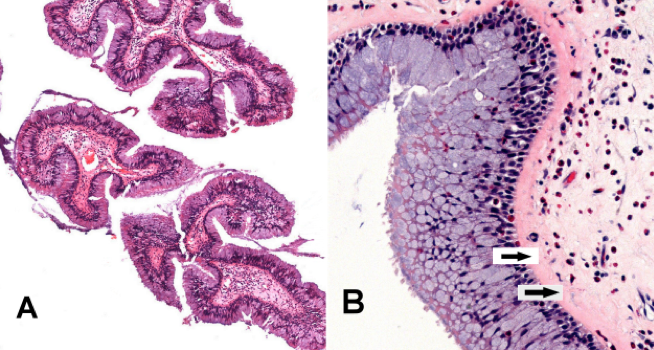
- Goblet cell hyperplasia and papillary hyperplasia
- Squamous metaplasia can be seen and is associated with cigarette exposure
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Chronic allergic sinusitis
- Chronic infectious sinusitis