Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Sites | Laboratory | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Hale C. Staph aureus. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/microbiologystaphaureus.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
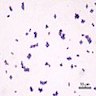
Definition / general
- Gram stain: positive
- Morphology: cocci in clusters
- Facultative anaerobe
- Part of normal flora of skin, mucus membranes, nasal passages
Terminology
- Greek "Staphyle" (grape) + coccus, referring to grape cluster-like morphology on Gram stain
Sites
- Staphylococcal food poisoning
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Septic arthritis
- Endocarditis
- Bacteremia
- Any body site may be infected
Laboratory
- Culture conditions:
- BAP (non-contaminated sites), colistin nalidixic acid agar (contaminated sites) or mannitol-salt agar
- Chromogenic agars (J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:5695)
- 34 - 37°C
- Gram positive
- Catalase positive
- Coagulase positive (slide or tube test)
- Mannitol fermenter
- Novobiocin sensitive (S. saprophyticus is novobiocin resistant)
Treatment
- Penicillin resistance widespread, treatment depends on local susceptibility patterns, infection site, clinical context
- MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics
- Community acquired MRSA: use macrolides, clindamycin, cotrimoxazole
- Multiresistant MRSA: use vancomycin (Intern Med J 2005;35:S97)
- Infectious Disease Society of America MRSA treatment recommendations
Gross description
- Cream yellow to orange on BAP, smooth, beta-hemolytic
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PCR methods now available (PLoS One 2012;7:e43935)
Differential diagnosis
- Aerococcus
- Micrococcus
- Other Staphylococcal species
- Streptococci
Additional references