Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Rohr BR, Hossler EW. Demodex. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumordemodex.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Demodex mites are commensal organisms that are occasionally implicated in inflammatory skin disease
Essential features
- Commensal mite found in folliculosebaceous units
- Increased incidence with age
- Pathogenic with overgrowth or immune reaction causing rosacea or folliculitis
Terminology
- Demodex mites, demodicosis, demodicidosis, Demodex folliculorum, Demodex brevis, face mite, follicle mite
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Acquired after birth (Clin Dermatol 2014;32:739)
- Prevalence increases with age (Cutis 2005;76:294)
- M > F (Cutis 2005;76:294)
- Worsened with immunosuppression
- Worsened with topical or systemic corticosteroids
- Demodectic mange well established in dogs
Sites
- D. folliculorum
- Follicular infundibulum (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- D. brevis
- Sebaceous duct and meibomian glands (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Face (most common)
- Eyelids
- Scalp
- Upper aspect of chest
- Neck
- Trunk
Pathophysiology
- Unclear
- 4 proposed mechanisms for how Demodex cause disease (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453):
- Blockage of hair follicle and sebaceous ducts
- Humoral or cell mediated immune reaction to mite components
- Foreign body granulomatous reaction to mite’s exoskeleton
- Vector role for bacteria
- Wolbachia within Demodex may incite inflammation (Cutis 2005;76:294)
- Upregulation of TNF alpha and IL1β in papulopustular rosacea (Clin Dermatol 2014;32:739)
- Papulopustular reaction associated with HLA type (Cutis 2005;76:294, Clin Dermatol 2014;32:739)
- Lack of HLA-A2 phenotype
- HLA-Cw2 phenotype
Etiology
- Unclear why it is pathogenic in some (Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:589)
- Demodex mites in 42% of 388 follicles with inflammation
- Demodex mites in 10% of noninflamed follicles
- 83% of follicles with Demodex with inflammation
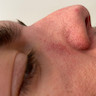
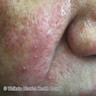
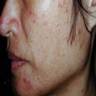
Clinical features
- 2 species on humans: D. folliculorum and D. brevis (WebMD: What are Demodex Mites? [Accessed 25 February 2022])
- Folliculocentric erythematous papules and pustules:
- Pityriasis folliculorum (spinulate demodicosis)
- Papulopustular rosacea
- Acne rosacea-like demodicosis
- Granulomatous rosacea-like (demodicosis gravis)
- Perioral dermatitis-like
- Blepharitis
- Otitis externa / pruritus (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Mimics acute graft versus host disease (GVHD) (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2020;26:S342)
- Pigmented demodicosis (Int J Dermatol 2021 Dec 13 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Brown-gray facial pigmentation
- Dark skinned individuals
- Demodectic frost of the ear (JAMA Dermatol 2017;153:356):
- Sandpaper-like follicular based scale on ear
- Vulvar demodicosis (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:1063):
- Erythematous pruritic papules
- Fordyce spots colonized with mites
- Possible association with neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:315):
- Erythematous annular facial plaques
Diagnosis
- Skin scraping:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) examination
- Density > 5 mites/follicle or 5 mites/cm2 (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Skin biopsy
Case reports
- 12 and 15 year old boys with acneiform eruption following dupilumab (Pediatrics 2021;147:e2020029520)
- 36 year old woman with vulvar demodicosis (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:1063)
- 46 year old woman with demodex folliculitis mimicking acute GVHD (JAMA Dermatol 2013;149:1407)
- 48 year old woman with pruritic face and neck eruption (Dermatol Online J 2007;13:9)
- 61 year old white man with neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis colonized by demodex mites (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:315)
Treatment
- Topical sulfur compounds (Cutis 2005;76:294, J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Permethrin
- Ivermectin
- Topical metronidazole (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Topical dilute camphor oil with oral metronidazole (Cutis 2005;76:294, JAMA Dermatol 2017;153:356)
- Benzyl benzoate (not available in US)
- Lindane, crotamiton
- Demodectic frost treatment (JAMA Dermatol 2017;153:356):
- Selenium sulfide wash and low potency topical corticosteroid with or without salicylic acid
Clinical images
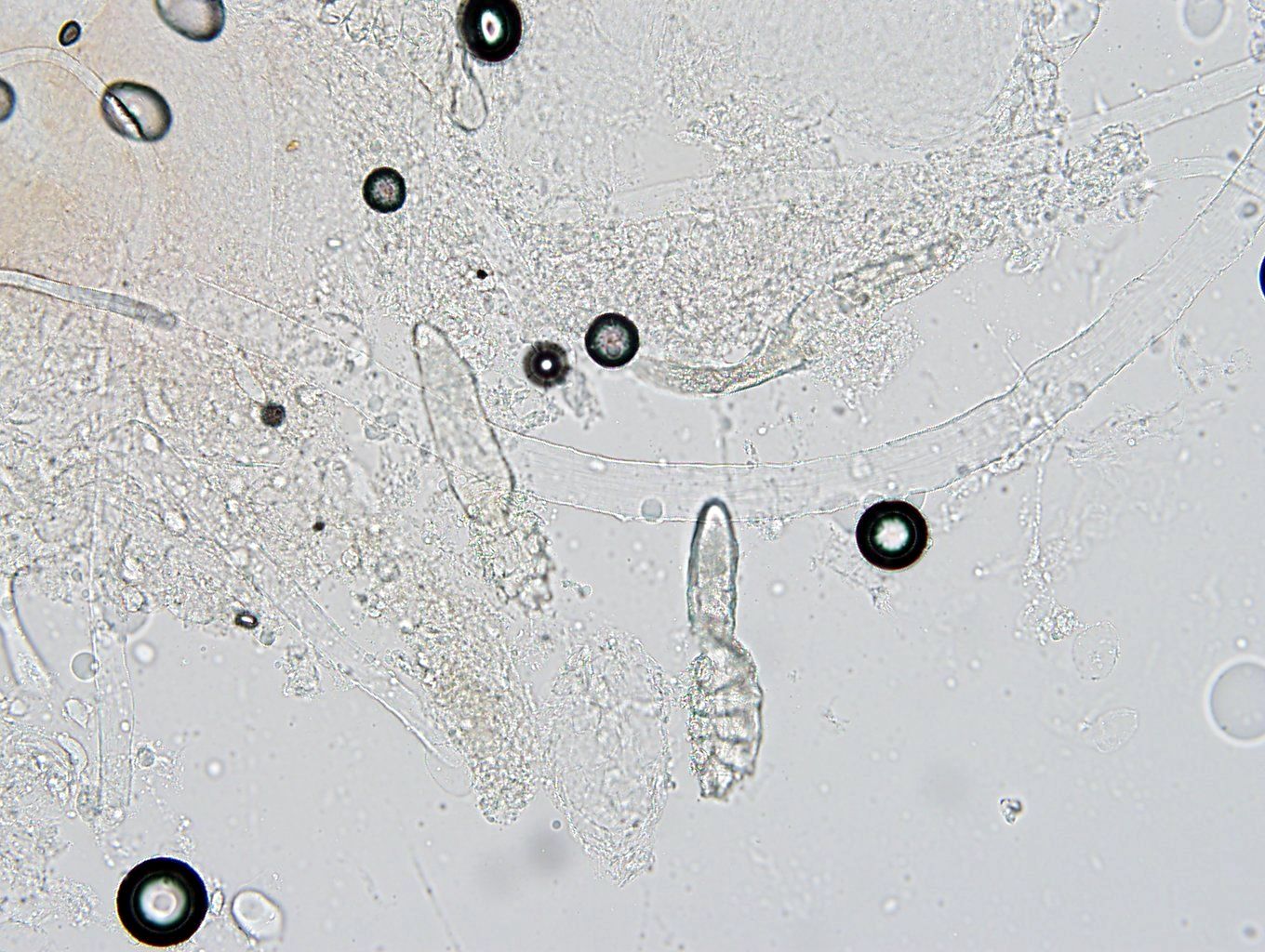
Microscopic (histologic) description
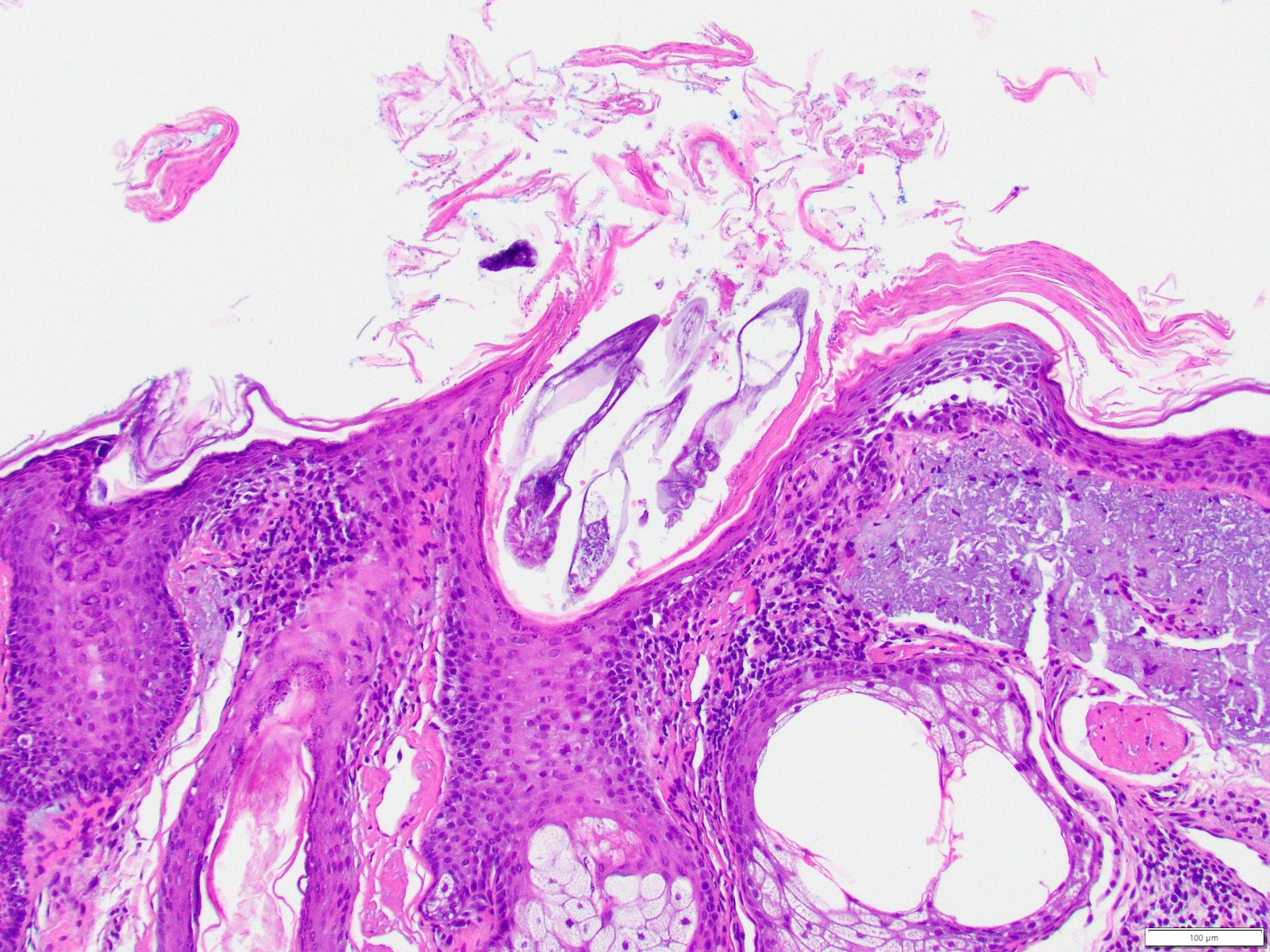
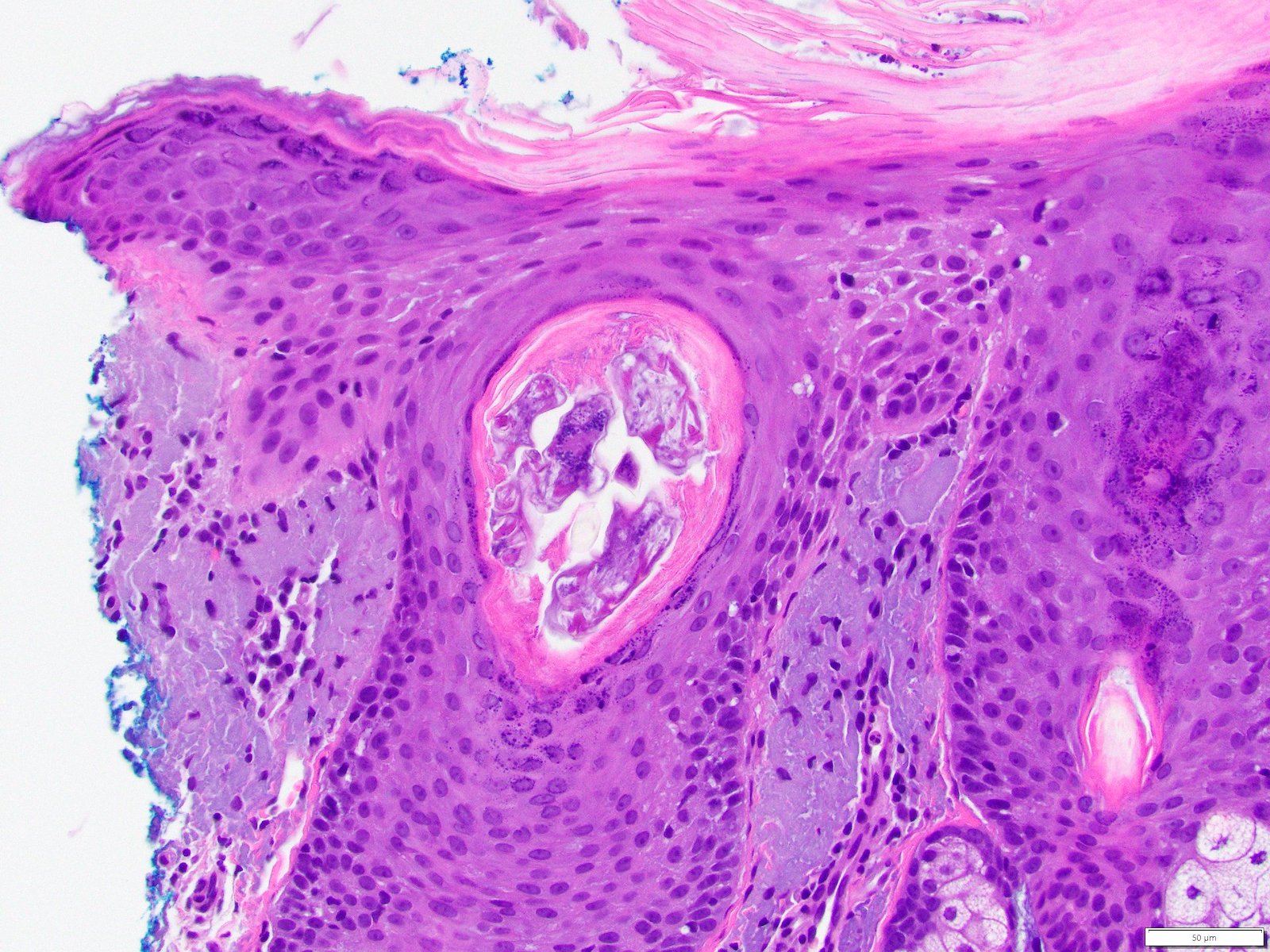
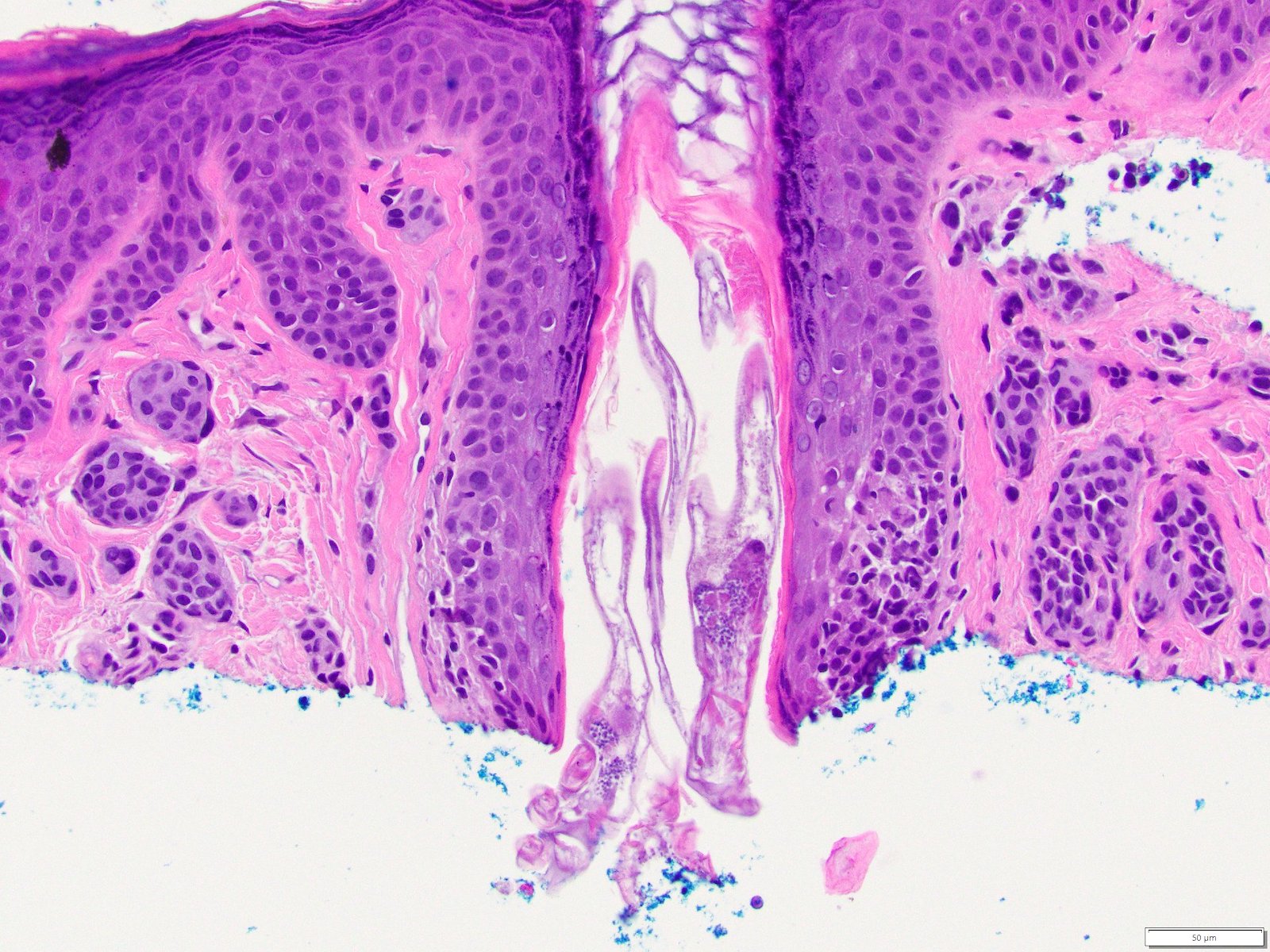
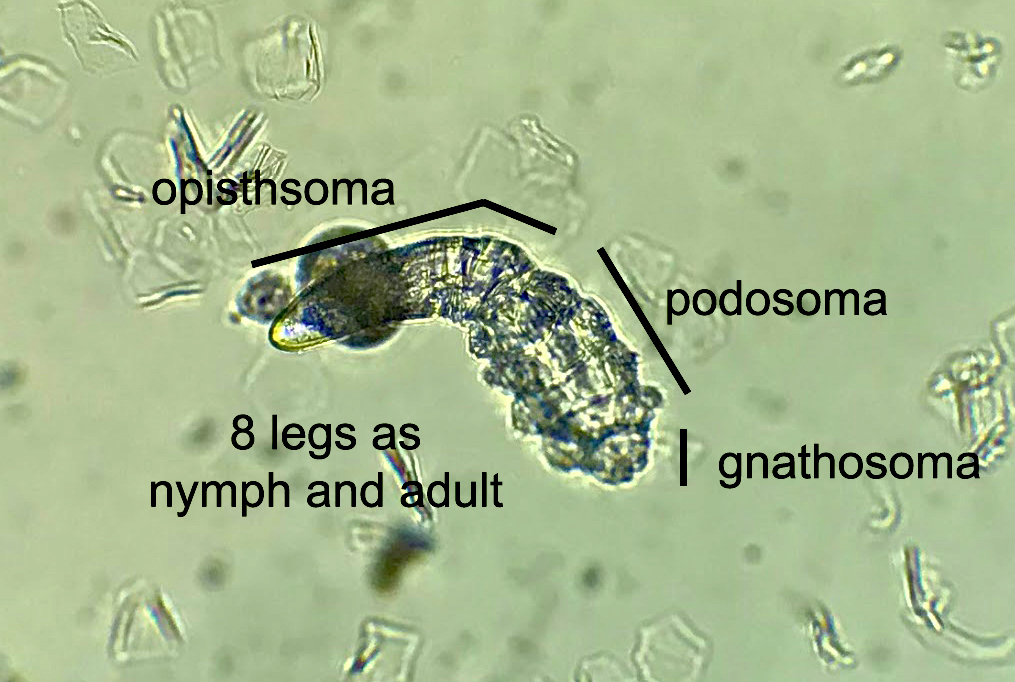
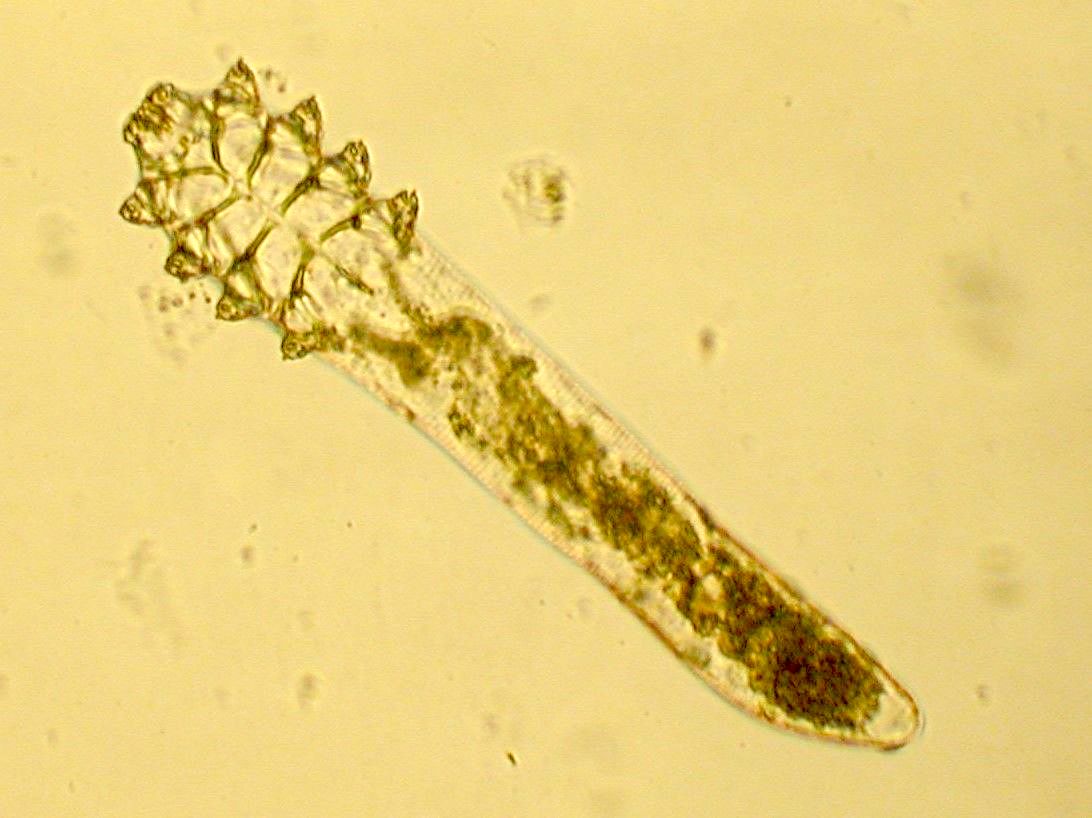
- 8 legged mites in folliculosebaceous units
- Incidental identification in 10% of skin specimens (Clin Dermatol 2014;32:739)
- D. folliculorum: 0.3 - 0.4 mm, head and neck (WebMD: What are Demodex Mites? [Accessed 25 February 2022])
- D. brevis: 0.15 - 0.2 mm, upper trunk (WebMD: What are Demodex Mites? [Accessed 25 February 2022])
- If pathogenic:
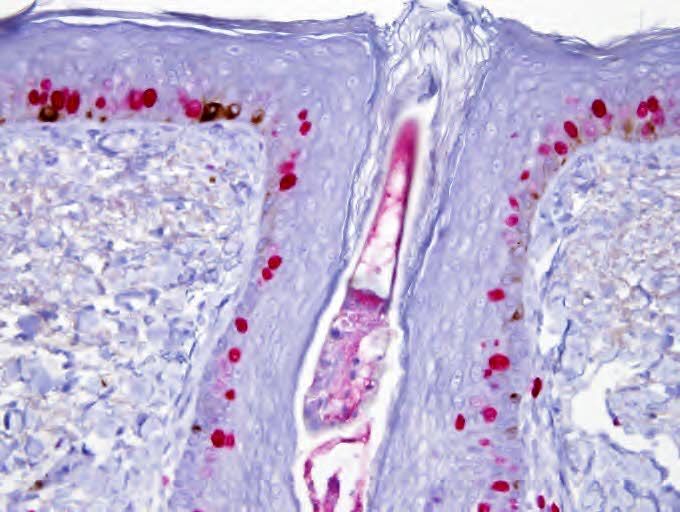
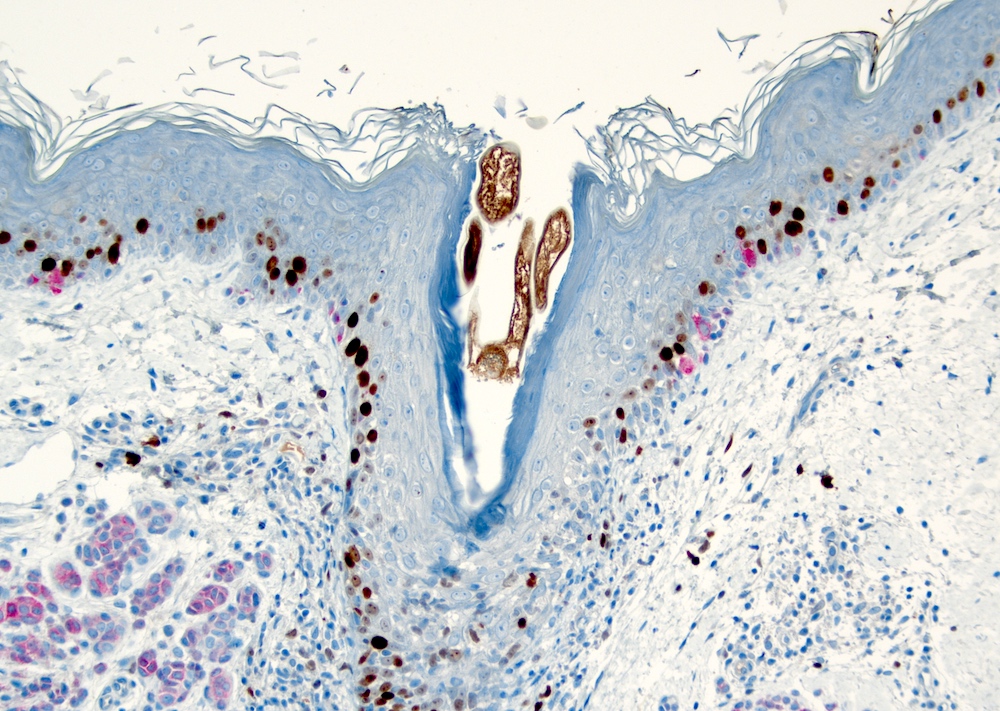
- Demodex mites in spongiotic follicular infundibulum or sebaceous gland with perifollicular and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- With or without neutrophils and multinucleated histiocytes
- Infundibular pustules containing mites
- Demodicosis gravis:
- Dermal granulomas with central caseation necrosis and phagocytized mite fragments in foreign body giant cells (J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;60:453)
- Pigmented demodicosis (Int J Dermatol 2021 Dec 13 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Numerous mites in a follicular infundibulum with interface dermatitis involving the follicle
- Numerous melanophages
- Vulvar demodicosis (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:1063):
- Demodex mites in Fordyce spots with surrounding neutrophilic and histiocytic infiltrate
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Videos
These face mites really grow on you
Demodex mite
Sample pathology report
- Skin, face:
- Suppurative folliculitis with Demodex (see comment)
- Comment: In the correct clinical setting, these findings are consistent with Demodex folliculitis. Similar findings can be seen in rosacea or other acneiform process.
Differential diagnosis
- Acne:
- Usually teens
- Comedones
- Pustules, cysts, nodules
- Bacterial folliculitis:
- Swab or tissue culture
- Fungal folliculitis:
- Often in setting of tinea corporis
- Fungal hyphae and spores within involved hair follicle
- Tissue culture
- Pityrosporum folliculitis (Cutis 2021;107:E40):
- Caused by Malassezia furfur
- Pruritic monomorphic folliculocentric pustules
- KOH shows short hyphae and spores
- Biopsy shows hyphae and spores in inflamed follicular infundibula
- Eosinophilic folliculitis (Cutis 2021;107:E40):
- Pruritic facial papules and pustules
- 3 variants: Ofuji disease, immunosuppression associated and infancy associated
- Peripheral eosinophilia
- Histopathology shows follicular spongiosis with exocytosis of eosinophils
- Miliaria (Cutis 2021;107:E40):
- Due to occlusion of eccrine glands
- 2 - 4 mm erythematous vesicular papules or pustules in area of occlusion
- Not folliculocentric
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Demodex mites have been implicated in which of the following conditions?
- Atopic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Vitiligo
Board review style answer #2
Board review style question #3
Board review style answer #3