Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Proliferating multilocular thymic cystCite this page: Gulwani H. Thymic cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mediastinumthymiccyst.html. Accessed November 27th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Thymus derived from third and fourth branchial pouch, as is parathyroid gland
- Usually presents as incidental mass in anterosuperior mediastinum
- Congenital (unilocular) or acquired (multilocular)
- Rarely occur postoperatively
- Mixed multilocular thymic cyst: has parathyroid or salivary gland tissue
Epidemiology
- Usually ages 20 - 50 years
Clinical features
- May be associated with thymic carcinoma, mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma but not non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1074)
Radiology description
- Xray: rounded, circumscribed masses in anterior mediastinum, may have peripheral rim of calcification
Case reports
- 6 year old boy with right neck swelling (Case of the Week #333)
- 6 year old boy with huge cervicothoracic thymic cyst (Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2003;2:339)
- 23 year old man with epithelioid granulomas within cyst (Ann Diagn Pathol 2012;16:38)
Gross description
- ≤ 18 cm
- Unilocular with thin wall and serous fluid or multilocular with turbid, cheesy or hemorrhagic material, thick wall and fibrous adhesions
- Either centered in thymus or connected to it by a small pedicle
Gross images
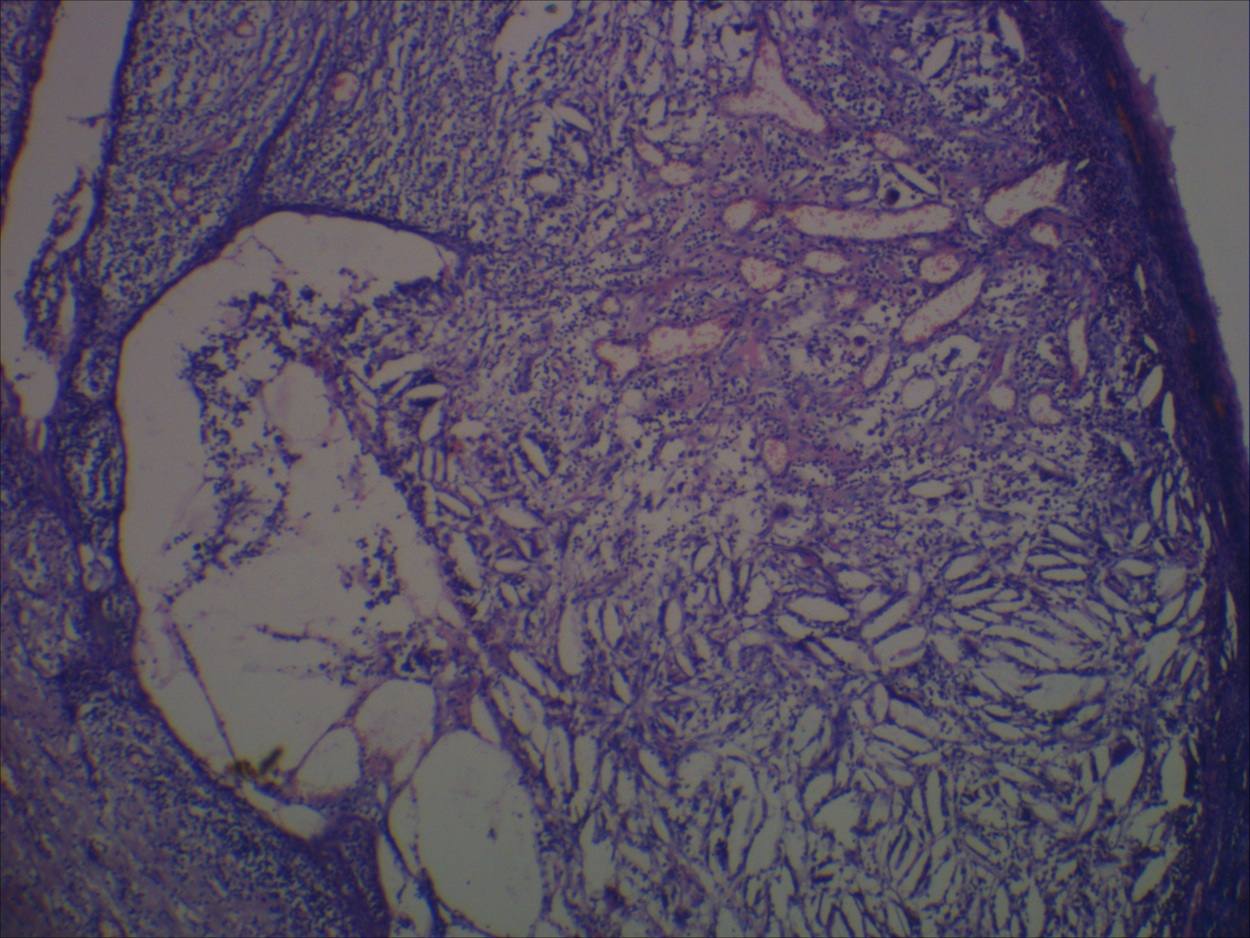
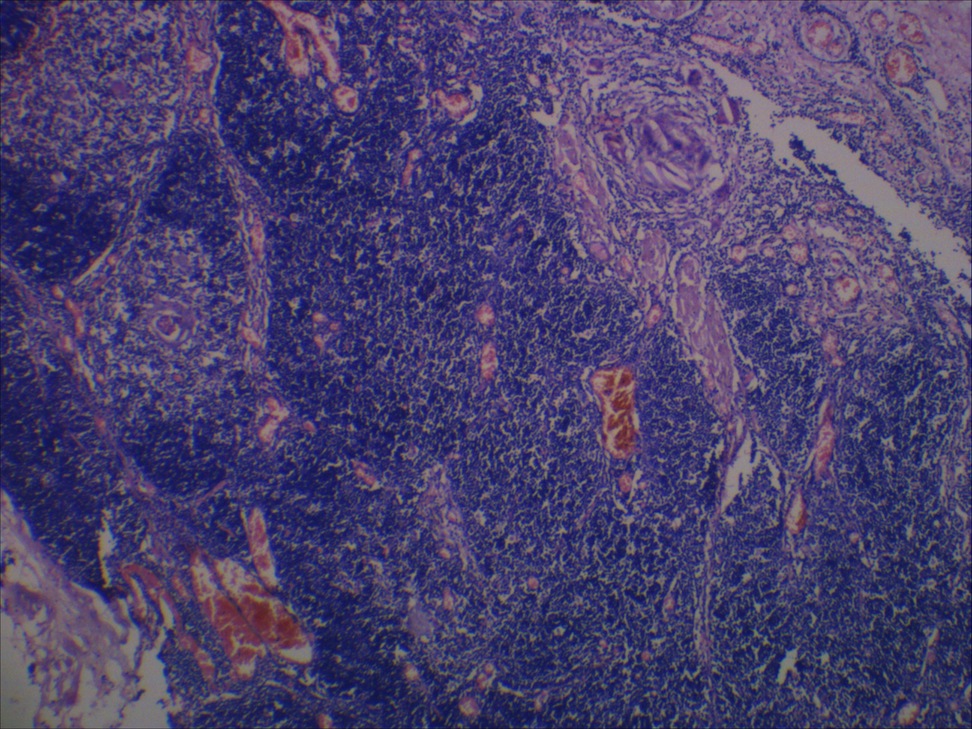
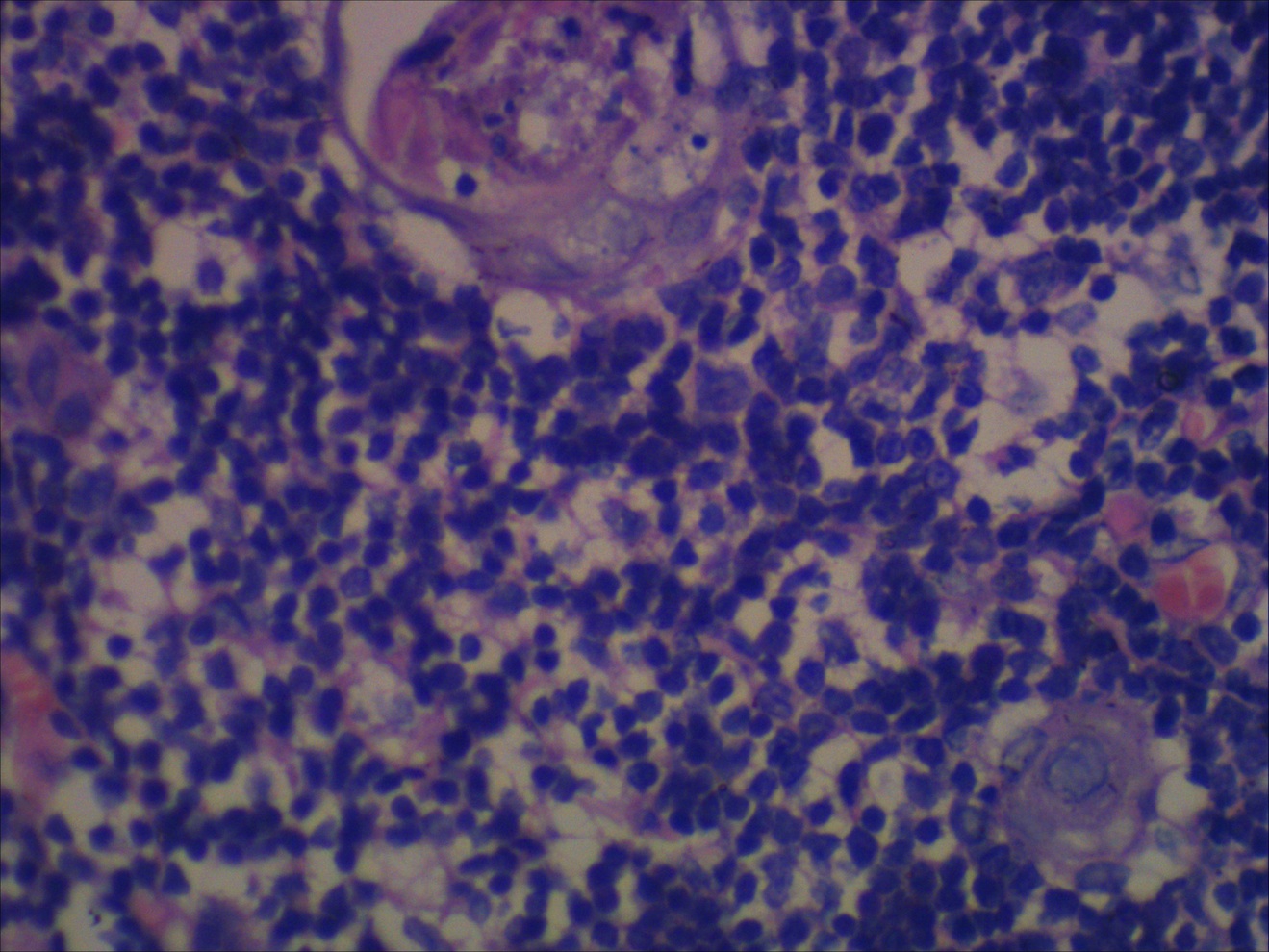
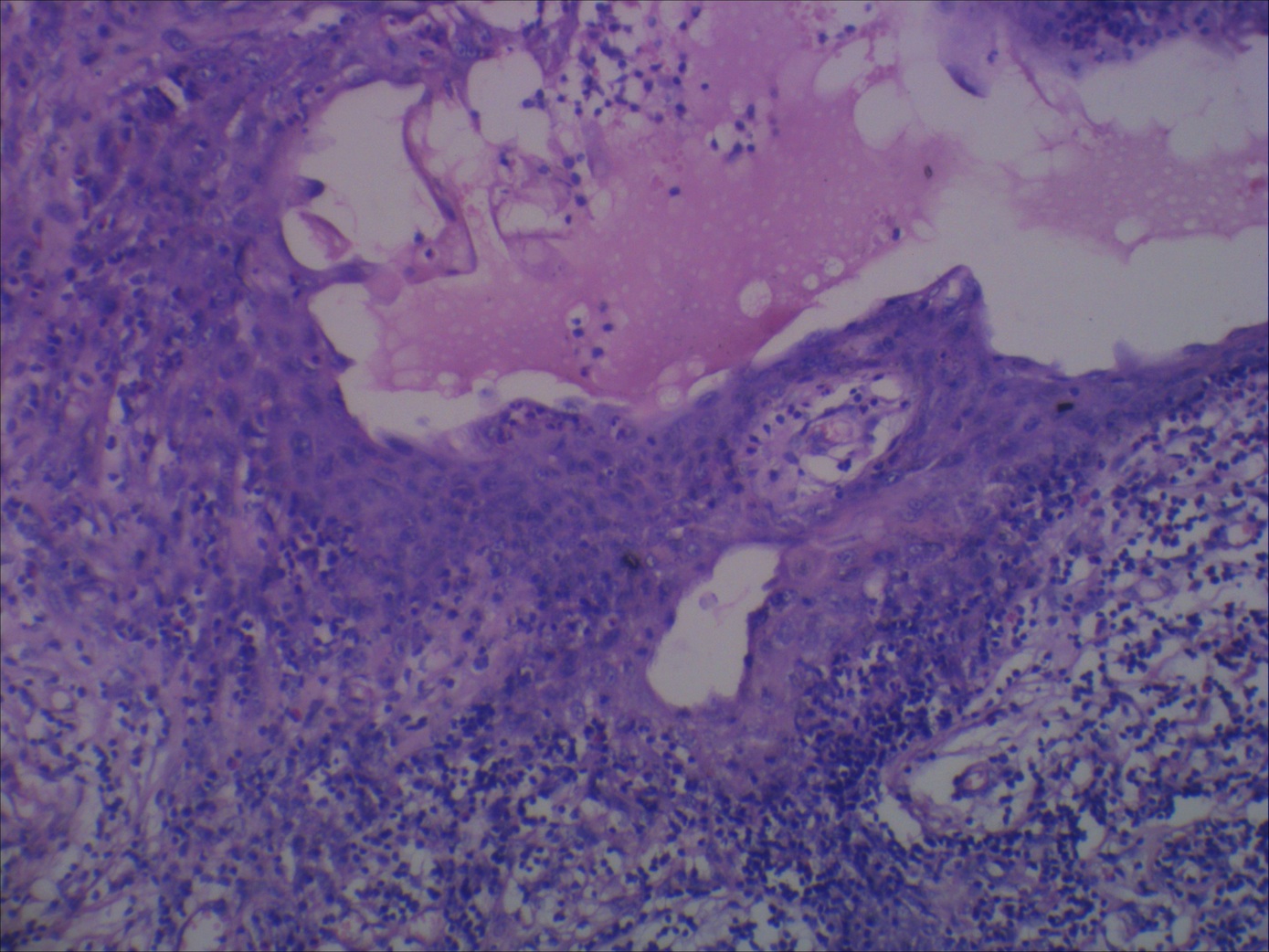
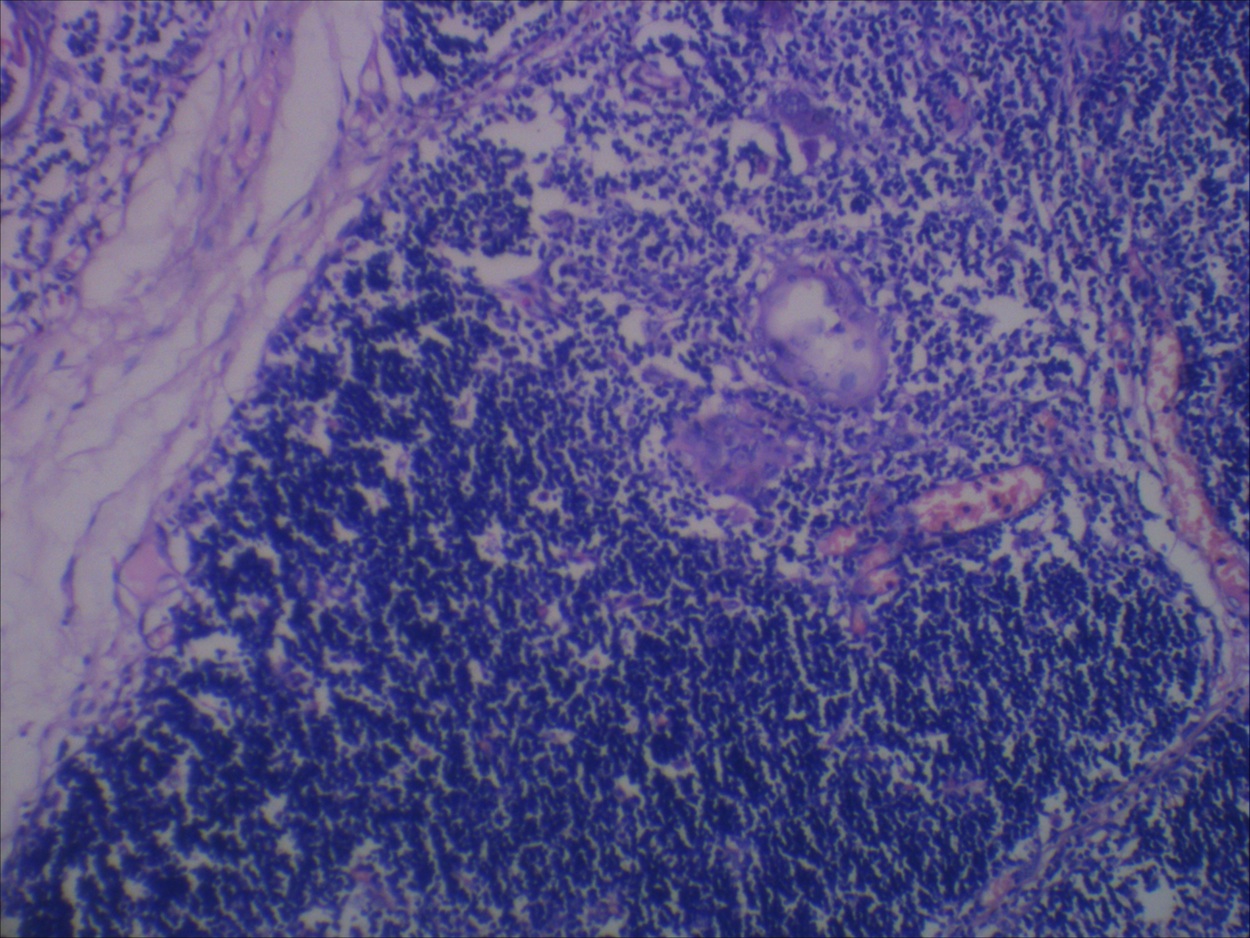
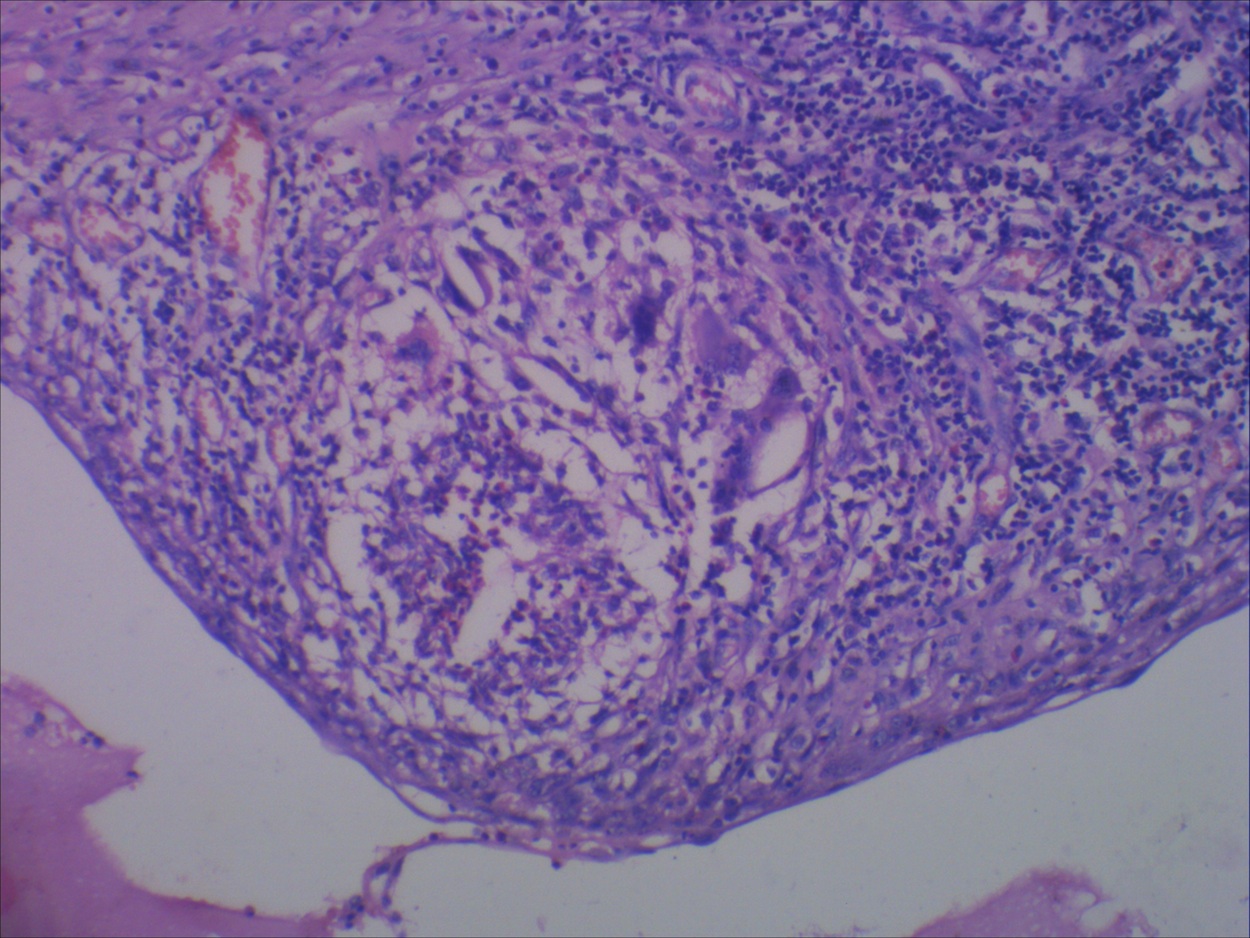
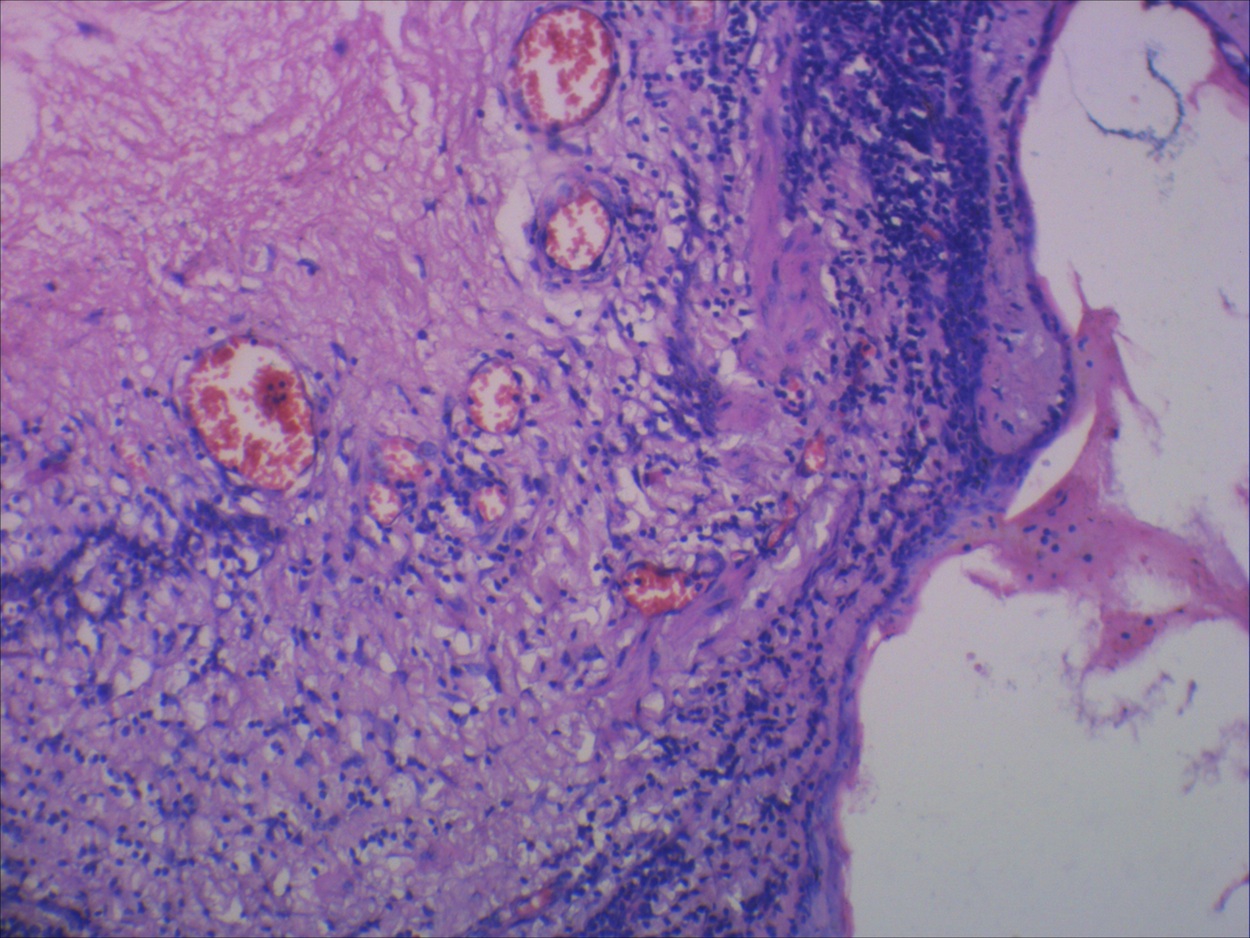
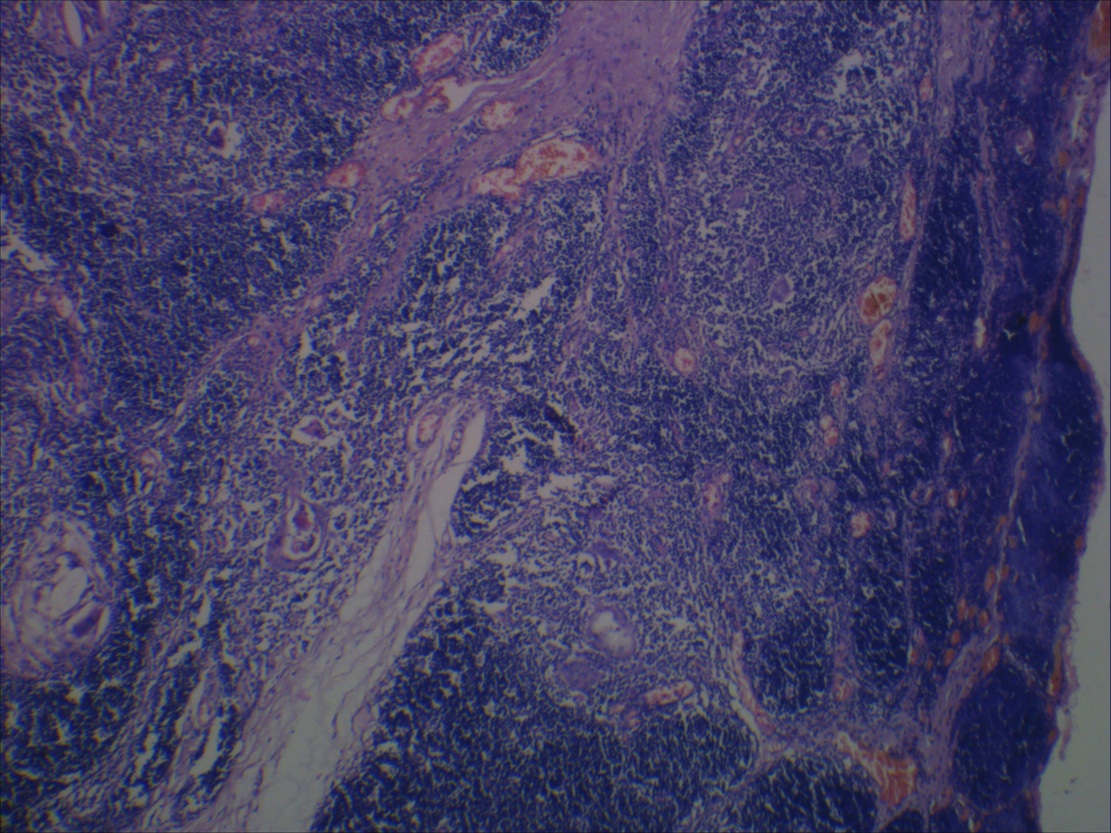
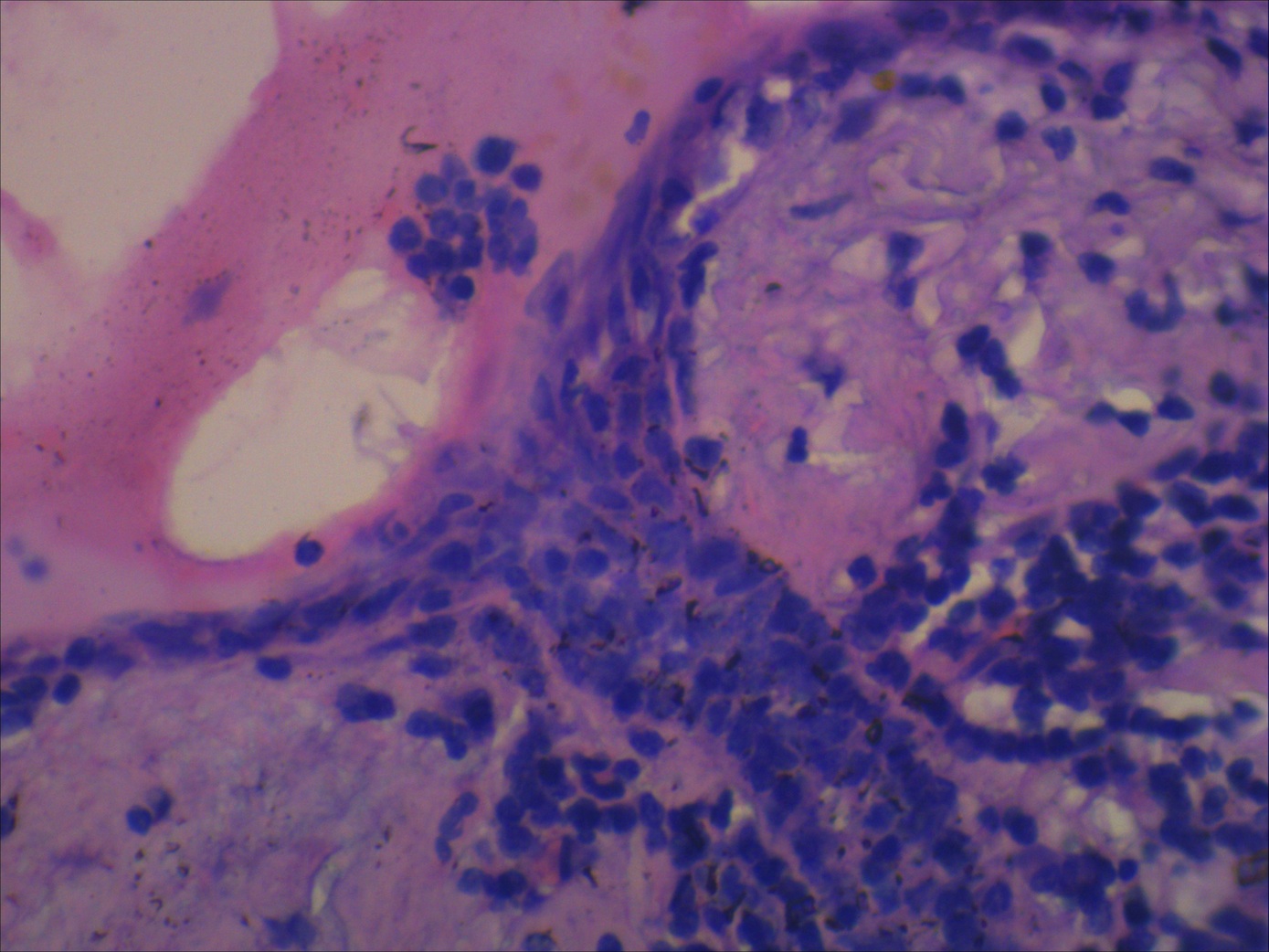
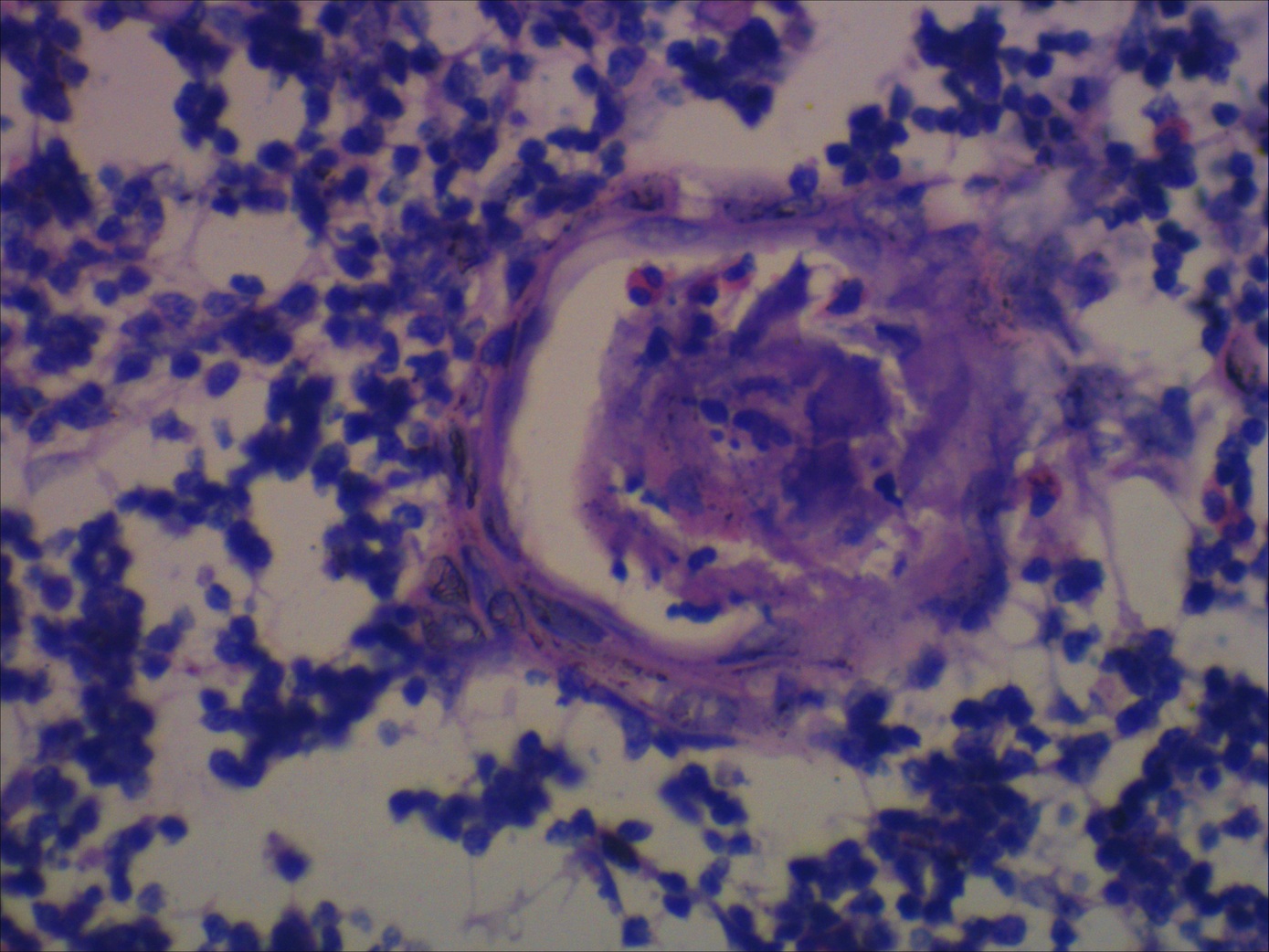
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Unilocular cysts:
- Have thin wall with a few layers of bland squamoid cells and thymic tissue in wall, no inflammation, no cholesterol granulomas, no hemorrhage
- Multilocular cysts:
- May have more layers of squamoid, cuboidal, columnar, micropapillary or mixed glandular epithelium
- May have pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
- Usually cholesterol granulomas
- Commonly lymphocytes, granulation tissue, hemorrhage
- Cysts separated by thick fibrous septae
- 50% have Hassall corpuscles or other thymic tissue but not in cyst wall
- No cartilage or smooth muscle is present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
Proliferating multilocular thymic cyst
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
Differential diagnosis
- Resembles cutaneous proliferating epidermoid cyst and proliferating trichilemmal cyst
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of cyst lining cells (narrow tongues of squamoid epithelium extending deeply into fibrous cyst wall) with reactive changes but no dysplasia
- Typical mitotic figures present
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Extremely rare in thymic cysts