Table of Contents
Adenocarcinoma | Basaloid | Clear cell | Mucoepidermoid | Sarcomatoid | UndifferentiatedCite this page: Gulwani H. Thymic carcinoma-other variants. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mediastinumthymiccarcinomaother.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Adenocarcinoma
Definition / general
Epidemiology
Clinical features
Case reports
- Rare, < 10 cases reported
- Most common type is papillary, mucinous subtype also reported
Epidemiology
- Mean age 50 years but wide range
Clinical features
- Must rule out metastatic tumor
- More likely to be thymic primary if CD5+ and transition from thymoma or thymic cyst to adenocarcinoma is present
- Outcome is highly variable
Case reports
- 15 year old with mucinous adenocarcinoma and 39 year old with papillary adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:124)
- 41 year old man with primary mucinous adenocarcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:201)
- 59 year old man with tumor demonstrating papillary, acinar and cribriform structure and which produced abundant extracellular mucin (Hum Pathol 2005;36:219)
- 61 year old woman with tumor with numerous psammoma bodies and 82 year old woman with case arising from thymic cyst with areas of transition from benign to dysplastic epithelium (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1330)
- Tubular adenocarcinoma (Int J Surg Pathol 2006;14:243)
Basaloid
Definition / general
Clinical features
Prognostic factors
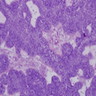
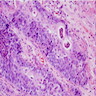
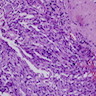
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Primary thymic tumor or metastatic tumor to mediastinum from oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx, esophagus, lung, anorectum
Clinical features
- Present with intrathoracic mass
- Primary tumors are associated with multilocular thymic cysts
- Capable of aggressive behavior and significant mortality (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1113)
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis with few fatalities if well differentiated
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nests, cords and sheets of small polygonal cells with minimal cytoplasm, hyperchromatic round nuclei, abundant mitotic figures
- No nuclear molding
- Separated by myxoid or eosinophilic stroma
- May have peripheral pallisading of nuclei
- May have areas of squamous differentiation with keratin pearls or stromal mucin containing gland-like profiles
- May have cystic structures
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Neuroendocrine markers
Electron microscopy description
- Poorly differentiated squamous proliferation with limited cytoplasmic tonofilaments, well formed desmosomes, redundant basal lamina
- No neurosecretory granules
Clear cell
Definition / general
Case reports
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Rare; clear cytoplasm due to either glycogen or degenerative changes
- Almost always fatal
Case reports
- 42 year old man with a rare thymic clear cell carcinoma (Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;58:98)
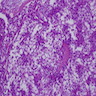
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Lobular or occasionally sheet-like growth pattern of polygonal cells with clear cytoplasm, rather bland nuclear features, round vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli; delicate fibrovascular stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:835)
- No blood lakes, no mucin
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
Mucoepidermoid
Clinical features
Case reports
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
- Usually low grade, may be associated with multilocular thymic cysts (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1526)
- Poor behavior if poorly differentiated with marked cytologic atypia or high stage (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:826)
- Good prognosis with few fatalities if well differentiated
Case reports
- 31 year old man with thymic mucoepidermoid carcinoma with massive calcification (Kyobu Geka 2010;63:919)
- 53 year old man with asymptomatic hilar mass (Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;12:273)
- 53 year old man with chest discomfort, dyspnea and weakness (Pathol Res Pract 2004;200:567)
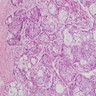
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sheets, lobules and nests of squamous, mucinous and intermediate cells in densely fibrotic stroma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Sarcomatoid
Definition / general
Terminology
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Differential diagnosis
- Very rare; usually presents as rapidly growing, anterior mediastinal mass
- Must exclude metastases before making this diagnosis
- May arise from malignant transformation of preexisting spindle cell thymoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:691)
- Aggressive: recurrence, metastasis and death are common
Terminology
- Also called spindle cell thymic carcinoma
Case reports
- 43 year old man with tumor arising in metaplastic thymoma (Histopathology 2008;52:409)
- 63 year old woman with tumor arising in metaplastic thymoma (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:677)
Gross description
- Large (mean 15 cm), well circumscribed, locally infiltrative
- Firm cut surface, focal hemorrhage, necrosis, cystic changes
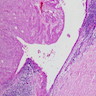
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Irregular fascicles of fusiform and pleomorphic cells with amphophilic or eosinophilic cytoplasm, hyperchromatic nuclei, prominent nucleoli (at least focally), brisk mitotic activity, often atypical mitotic figures
- May have epithelioid foci
- Usually transitional areas with spindle cell thymoma
- May also have lymphoepithelioma-like or anaplastic areas
- Rarely rhabdomyogenic foci with cross striations
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- EMA (may be focal), keratin (including CAM5.2), vimentin, muscle markers in areas of myogenic differentiation
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Focal junctional complexes between spindle cells, tonofibrils
Differential diagnosis
- Germ cell tumor
- Malignant schwannoma: triton tumor
Undifferentiated
Definition / general
- Undifferentiated large cell thymic carcinoma accompanied by inflammatory reaction resembling hyaline vascular Castleman disease (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:490)
- May be asymptomatic with incidental detection
- Tumor cells are cytokeratin+ / CD5-
- May have neuroendocrine features
- Indolent behavior