Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Magliocca K. Nasopalatine duct cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillanasopalatine.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nasopalatine duct cyst is a nonodontogenic developmental cyst that arises in maxillary bone within the incisive canal (Clin Oral Investig 2015;19:1611)
Essential features
- Developmental cyst, nonodontogenic
- Epicenter within the incisive canal; can involve the right or left maxilla as it enlarges
- Cyst lining is nonkeratinized squamous or respiratory epithelium
- Neurovascular bundle may or may not be identified within the cyst wall
Terminology
- Incisive canal cyst
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K09.1 - developmental (nonodontogenic) cysts of oral region
Epidemiology
- Is the most common nonodontogenic cyst within the jaws (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1994;77:276, J Oral Pathol Med 2006;35:392)
- Occurs most frequently in patients aged 30 - 60 years (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2018;46:264)
- M:F = ~3:1 (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2018;46:264)
Sites
- Exclusively in maxilla
- Most commonly located in anterior hard palate, usually midline (Clin Oral Investig 2015;19:1611)
Pathophysiology
- Trauma, inflammation and infection may stimulate proliferation of the epithelial remnants in the nasopalatine canal and may represent etiologic factors in a subset of cases (Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2008;13:E438, Clin Oral Investig 2015;19:1611)
Etiology
- Developmental cyst, nonodontogenic
- Arises from respiratory and squamous epithelial vestigial remnants of an embryonic nasopalatine duct (Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2017;300:1093)
Clinical features
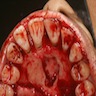
- Presents as sessile swelling posterior to the maxillary incisors or entirely asymptomatic
- May present as a swelling on the labial alveolus or bulging into the nasal floor (Oral Implantol (Rome) 2012;5:47, J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2018;46:264)
- Lesion is often 1 - 2 cm in size but may reach several centimeters (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49:268, Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2008;13:E438)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is dependent on clinical, radiologic and pathologic correlation including
- Epicenter within the incisive canal
- Cyst lining of nonkeratinized squamous or respiratory epithelium
- Neurovascular elements or benign cartilage may or may not be identified within the cyst wall
Radiology description
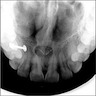
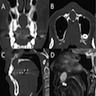
- Well circumscribed, corticated, symmetrical rounded or heart shaped radiolucency within the anterior maxilla
- Radiographic superimposition of the anterior nasal spine often produces a characteristic heart or pear shaped radiolucency
- Cyst is often located between the roots of central incisors and may cause displacement
- Adjacent teeth are vital with intact lamina dura
- In general, the cyst is typically > 6 mm (i.e., larger than the generally accepted diameter of the normal incisive canal) (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49:268)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence is unexpected after complete treatment (Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2013;65:385)
Case reports
- 31 year old man with small nasopalatine duct cyst (J Dent Sci 2021;16:1047)
- 43 year old man with nasopalatine duct cyst masquerading as a periapical cyst (Int J Appl Basic Med Res 2024;14:60)
- 45 year old man with nasopalatine duct cyst in association with dental implant (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:319)
Treatment
- Surgical excision (open or endoscopically) is most common but marsupialization may also been performed (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49:268)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Sectioning reveals cystic and fibrous areas
Frozen section description
Frozen section images
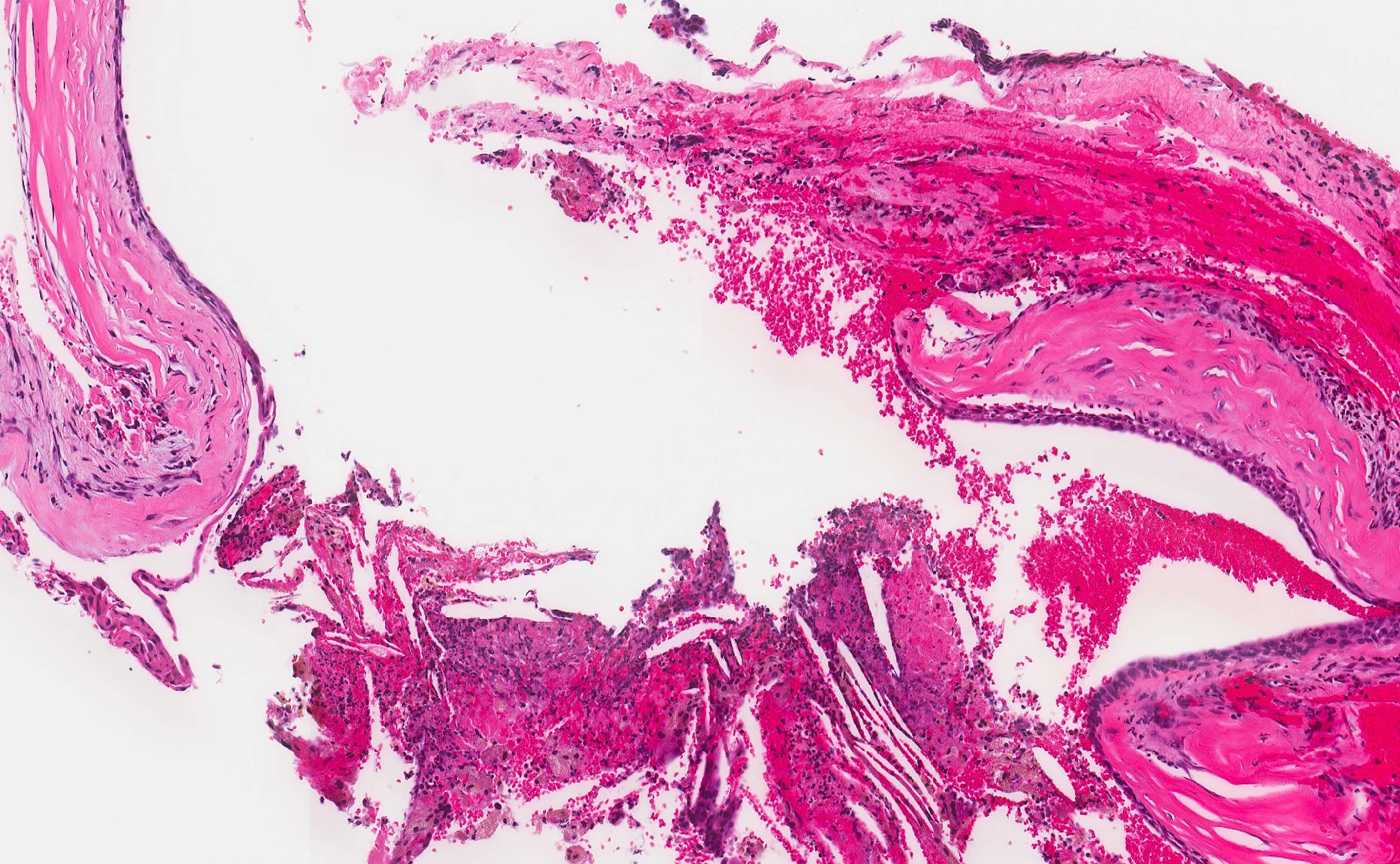
Microscopic (histologic) description
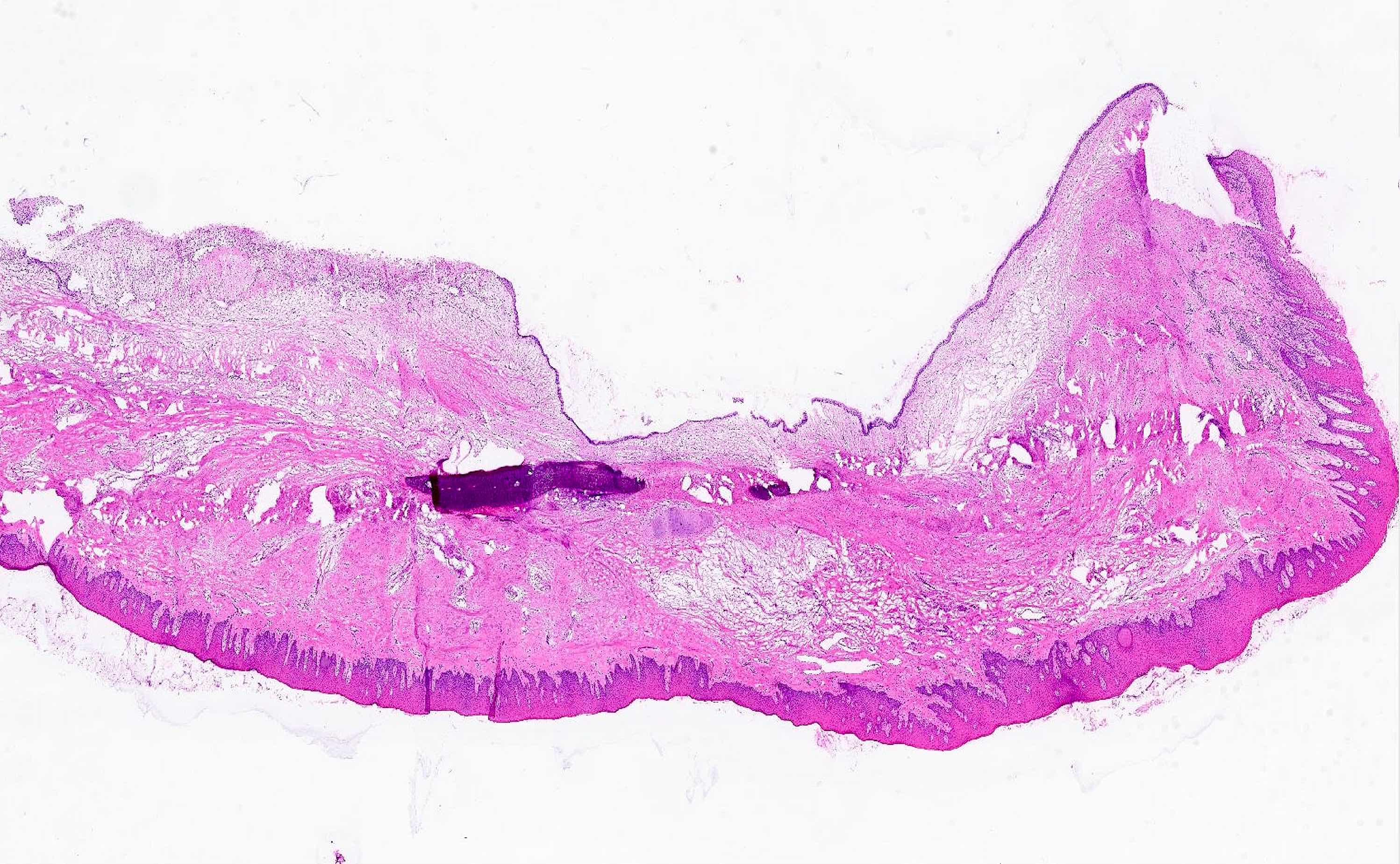
- Cyst epithelium
- Often lined by > 1 type of epithelium and intermediate appearances are often seen (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49:268, J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2018;46:264)
- Nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (variable cilia and goblet cells)
- Bilaminar cuboidal epithelium
- Subepithelial hyalinization may occur
- Cyst wall may feature
- Dense fibrous tissue with nerves, cartilaginous rests, vascular channels
- Lobules of mucous or seromucinous glands
- Inflammation and cholesterol clefts may be present
- Incidental trabeculae of bone (incorporated during surgical excision)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Videos
Cysts of the jaws part 4: miscellaneous cysts
Sample pathology report
- Anterior maxilla, excision:
- Nasopalatine duct cyst
Differential diagnosis
- Glandular odontogenic cyst:
- Intraosseous developmental odontogenic cyst; may have ciliated or mucous cells within cystic lining
- Nasolabial (nasoalveolar) cyst:
- Soft tissue (nonintraosseous) cyst with histologic features that can resemble nasopalatine duct cyst
- Occurs in soft tissues of upper lip lateral to midline
- Should not have contents of incisive foramen (peripheral nerve, cartilaginous rests, muscular vascular channels)
- Periapical (radicular) cyst:
- Most common inflammatory odontogenic cyst
- Lined by stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness, often with scattered ciliated cells
- Derived from rests of Malassez
- Surgical ciliated cyst:
- Cyst occurring many years after a surgical procedure involving maxillary sinus or nasal cavity
- Cystic expansion of respiratory epithelium within maxilla; may have ciliated or mucous cells within cystic lining
- Usually located in posterior maxilla and lacks contents of incisive foramen
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Benign cyst arising from remnants of the nasopalatine duct is the correct answer because the cyst is a developmental nonodontogenic cyst that arises from the remnants of the nasopalatine duct. Answer B is incorrect because nasopalatine duct is not a neoplasm. Answer C is incorrect because nasopalatine duct cyst exclusively occurs in the maxilla. Answer D is incorrect because nasopalatine duct cyst is not typically associated with acute inflammation.
Comment Here
Reference: Nasopalatine duct cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Nasopalatine duct cyst
Board review style question #2
What is the most common clinical presentation of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
- Asymptomatic swelling of the anterior palate
- Numbness and tingling of the lower lip
- Painful swelling in the mandibular region
- Ulceration and bleeding of the gingiva
Board review style answer #2
A. Asymptomatic swelling of the anterior palate is the correct answer because nasopalatine duct cyst tends to slowly expand the region of the anterior palate as the cyst enlarges. Answer C is incorrect because nasopalatine duct cyst does not occur in the mandible. Answer B is incorrect because nasopalatine duct cyst does not occur near nerves that would lead to numbness and tingling in the lower lip. Answer D is incorrect because nasopalatine duct cyst tends to enlarge slowly over time with little resulting ulceration or bleeding of surrounding structures.
Comment Here
Reference: Nasopalatine duct cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Nasopalatine duct cyst