Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Lott Limbach A. Lymphoepithelial cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillalymphoepithelial.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Lymphoepithelial cysts are uncommon benign oral cavity cysts
Essential features
- Oral lymphoepithelial cysts are most common in the lateral tongue and floor of mouth
- Histologic features include a squamous epithelial lined cyst filled with keratin debris and stromal lymphoid tissue
- Treatment is conservative surgical excision with no recurrence
Terminology
- Oral lymphoepithelial cyst
- Intraoral lymphoepithelial cyst
- Benign lymphoepithelial cyst
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- < 1% of all lesions in oral cavity
- Occurs in adults
- Most common in fifth to sixth decade
- F > M (Head Neck Pathol 2021 Jun 29 [Epub ahead of print])
Sites
- Oral cavity (Head Neck Pathol 2021 Jun 29 [Epub ahead of print], J Oral Pathol Med 2020;49:219)
- Most common site: ventral and posterolateral tongue
- Second most common site: floor of mouth
- Other sites in the oral cavity: buccal mucosa, palate, tonsillar pillar, lip
Etiology
- Unknown:
- Leading theory: pseudocysts develop from obstruction of tonsil crypt of oral tonsil tissue (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1970;29:295)
- Another theory postulates traumatic implantation of epithelium into deeper tissues, forming cyst (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1963;16:1214)
- A third theory postulates lymphoid tissue with ectopic foci of entrapped glandular epithelium (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1966;21:120)
- Oral lymphoepithelial cyst is not associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), unlike a subset of lymphoepithelial cysts of the major salivary glands
Clinical features
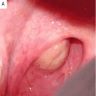
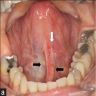
- Small, white-yellow submucosal nodule
- < 1 cm
- Often painless and asymptomatic
- References: Head Neck Pathol 2021 Jun 29 [Epub ahead of print], J Oral Pathol Med 2020;49:219
Diagnosis
- Combination of clinical and histologic findings
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis
- No recurrence after excision
Case reports
- 21 year old man with lymphoepithelial cyst in the palatine tonsil (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:4264)
- 42 year old woman with multiple lymphoepithelial cysts (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2013;56:473)
- 55 and 57 year old women with oral lymphoepithelial cysts (Bull Tokyo Dent Coll 2012;53:17)
Treatment
- Conservative surgical excision
Clinical images
Gross description
- Cystic structure, well demarcated, filled with yellowish keratin-like material
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed cyst lined by parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium with lymphoid stroma
- May have connection to overlying epithelium but not always identified
- Other cyst linings: nonkeratinized squamous epithelium, respiratory metaplasia or ciliated pseudostratified epithelium (or any combination)
- Cyst contents: predominantly keratin debris, amorphous eosinophilic material and inflammatory cells
- Lymphoid stroma may or may not have germinal centers
- Rarely subgemmal neurogenous plaques have been reported near the cyst (Head Neck Pathol 2021 Jun 29 [Epub ahead of print], J Oral Pathol Med 2020;49:219)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Cyst lining: p40+
- Lymphoid stroma: CD20+ cells predominant, rare CD3+ (J Oral Pathol Med 2020;49:219)
Sample pathology report
- Floor of mouth, biopsy:
- Oral lymphoepithelial cyst
Differential diagnosis
- Epidermal inclusion cyst (epidermoid cyst):
- Squamous lined cyst without lymphoid stroma
- Sebaceous cyst:
- Squamous lined cyst with adnexal structures, lacking lymphoid stroma
- Fordyce granules:
- Clusters of sebaceous glands
- Sialolith:
- Calcified material with surrounding ductal epithelium (with squamous metaplasia)
- Mucocele:
- Pseudocyst filled with mucin, lined by histiocytes and lymphocytes
- Foreign body reaction:
- Numerous multinucleated giant cells with poorly formed granulomas with foreign material
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Invasive proliferation of squamous nests
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is seen in the stroma surrounding the cyst lining of a lymphoepithelial cyst?
- Collagen
- Lymphoid tissue
- Mucin
- Sebaceous glands
- Seromucinous glands
Board review style answer #2