Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology: normal cells / structures | Terminology: cysts | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Morrison A. Eruption cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaeruptioncyst.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Develops in soft tissues overlying alveolar bone due to separation of dental follicle from crown of erupting tooth
Terminology: normal cells / structures
- Ameloblasts:
- Specialized epithelial cells that form tooth enamel
- Deciduous tooth:
- Also called baby tooth or primary tooth
- Falls out during childhood
- Succedaneous tooth:
- Also called permanent tooth or adult tooth
- Replaces deciduous teeth
- Ideally lasts throughout life under most normal circumstances
- Natal tooth:
- Tooth or teeth present at birth
- Neonatal tooth:
- Tooth or teeth present during the first 30 days of life
Terminology: cysts
- Dentigerous cyst:
- Developmental odontogenic cyst occurring within the jawbone, originates by separation of dental follicle from around the crown of an unerupted tooth
- Follicular cyst:
- Synonym for dentigerous cyst
- Eruption cyst:
- Soft tissue counterpart to dentigerous cyst involving an erupting tooth
- Whereas dentigerous cyst develops around crown of an unerupted tooth lying in the bone, eruption cyst occurs when a tooth is impeded in its eruption within the soft tissues
- The epithelium lining the dilated cystic space is reduced enamel epithelium
- Eruption hematoma:
- Surface trauma may result in a considerable amount of blood in the fluid of the eruption cyst, which imparts a blue to purple-brown color
- Reduced enamel epithelium:
- Tooth enamel is normally composed of two cell layers: inner layer of reduced or atrophied ameloblasts and external layer, probably stratum intermedium cells
- Reduced enamel epithelium is normally found overlying an unerupted, otherwise developed tooth
Epidemiology
- 1 - 10% of submitted jaw cysts, but may be underrepresented since cysts that rupture spontaneously are not submitted for examination
- Age: usually < age of 10, occasionally older patients with delayed tooth eruption, rarely congenital
- Gender: male to female ratio 2:1
Sites
- Mandibular central incisors and permanent first molars most common sites affected
Pathophysiology
- Accumulation of fluid or hemorrhage between crown of erupting tooth and the reduced enamel epithelium of the surrounding dental follicle
- In eruption cyst, tooth is within oral soft tissues, not bone, as occurs in dentigerous cyst
- Factors actually impeding eruption through soft tissues are unknown, possibly dense fibrous tissue
Etiology
- Develops secondary to accumulation of blood or fluid between tooth crown and an erupting primary or permanent tooth and the overlying mucosa
Clinical features
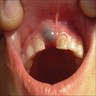
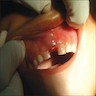
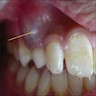
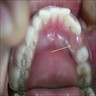
- Raised, bluish or mucosal colored dome shaped gingival mass on alveolar ridge
- Variable size, dependent on size and number of associated teeth, but usually < 1.5 cm
- Usually asymptomatic but, if inflamed, may be painful and tender
- Occasionally multiple cysts
Diagnosis
- Radiographic findings, in combination with clinical information, can support a histomorphologic diagnosis
Radiology description
- Usually no bone involvement except the dilated erupting tooth crypt
- Soft tissue "shadow" of cyst may be seen on radiograph
Case reports
- 8 year old boy with bilateral mandibular cysts associated with cyclosporine use (Pediatr Nephrol 2001;16:993)
- Boy with eruption cyst associated with cyclosporin A (J Clin Periodontol 2003;30:462)
- Child with hepatoblastoma and oral eruption cysts (J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2009;31:509)
- Child with Lowe syndrome and multiple eruption cysts and hematomas (J Clin Pediatr Dent 1999;23:357)
- Kinky hair disease with multiple eruption cysts (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1996;82:537)
Treatment
- None:
- Treatment not likely required if the cyst ruptures spontaneously, permitting the tooth to erupt
- Marsupialization:
- If tooth eruption appears to be impeded by the lesion, the cyst can be unroofed, which usually allows the tooth to erupt
- The dome of the cyst is excised, exposing the crown of the tooth, which is allowed to erupt
- Submission of the cyst roof is recommended to confirm the clinical impression and exclude other pathology
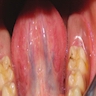
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
Epithelial surface facing oral cavity:
- Keratinized squamous oral epithelium on superior / external or oral aspect of specimen corresponding to gingiva or alveolar ridge tissue
- Lamina propria underlying the oral epithelium and overlying the roof of the cyst shows a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate
- May be possible to distinguish a line of demarcation between gingival and follicular connective tissues: the gingival connective tissue is relatively acellular and densely collagenous and so has an eosinophilic hue; the follicular connective tissue is more densely cellular, less collagenous and has a more basophilic hue, presumably because of a higher content of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in the ground substance
- Odontogenic epithelial cell rests may be present in the connective tissue
- The deep portion of the specimen, which represents the roof of the cyst, shows a thin layer of nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium
- In non-inflamed areas, the epithelial lining of the cyst is characteristically of reduced enamel epithelial origin, consisting of 2 - 3 cell layers of squamous epithelium with a few foci where may be thicker
- If the epithelial lining is inflamed, acute inflammatory cells are found in the epithelium which proliferates and shows reactive spongiosis
Differential diagnosis
- Correlation with patient age, specific anatomic location at tooth bearing area of jaws, and radiographic findings is essential
- Congenital, neonates, infants:
- Epstein pearls
- Bohn nodules
- Gingival cyst of newborn
- Children (less than 14 - 16 years of age):
- Buccal bifurcation cyst
- Dentigerous cyst
- Dental follicle
- Unicystic ameloblastoma
- Soft tissue keratocystic odontogenic tumor
- Adults:
- Gingival cyst
- Dentigerous cyst
- Dental follicle
- Paradental cyst
- Unicystic ameloblastoma
- Soft tissue keratocystic odontogenic tumor