Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonedesmoplasticfibroma.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign / borderline behavior; bony counterpart of soft tissue fibromatosis
- Intraosseous component of soft tissue fibromatosis
- May be due to local trauma; may be part of Gardner syndrome
- Benign but up to 35% recur, does not metastasize
Epidemiology
- Mean 23 years, range 1 - 75 years
- 75% younger than age 30 years, may be more common in males
Sites
- Metaphysis of long bones (56%), mandible (26%), pelvis (14%)
Radiology description
- Lytic and honeycombed (“soap bubble” appearance) metaphyseal lesions, cortical thinning with soft tissue extension
Case reports
- 3 year old boy with swelling of the right mandbile (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:107)
- 19 year old man with rib lesion (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:721)
Treatment
- Wide local excision to prevent otherwise frequent recurrences
- Causes local destruction, no metastases
Gross description
- White-gray, nonencapsulated, fibrous rubbery mass with variable bony spicules and cysts
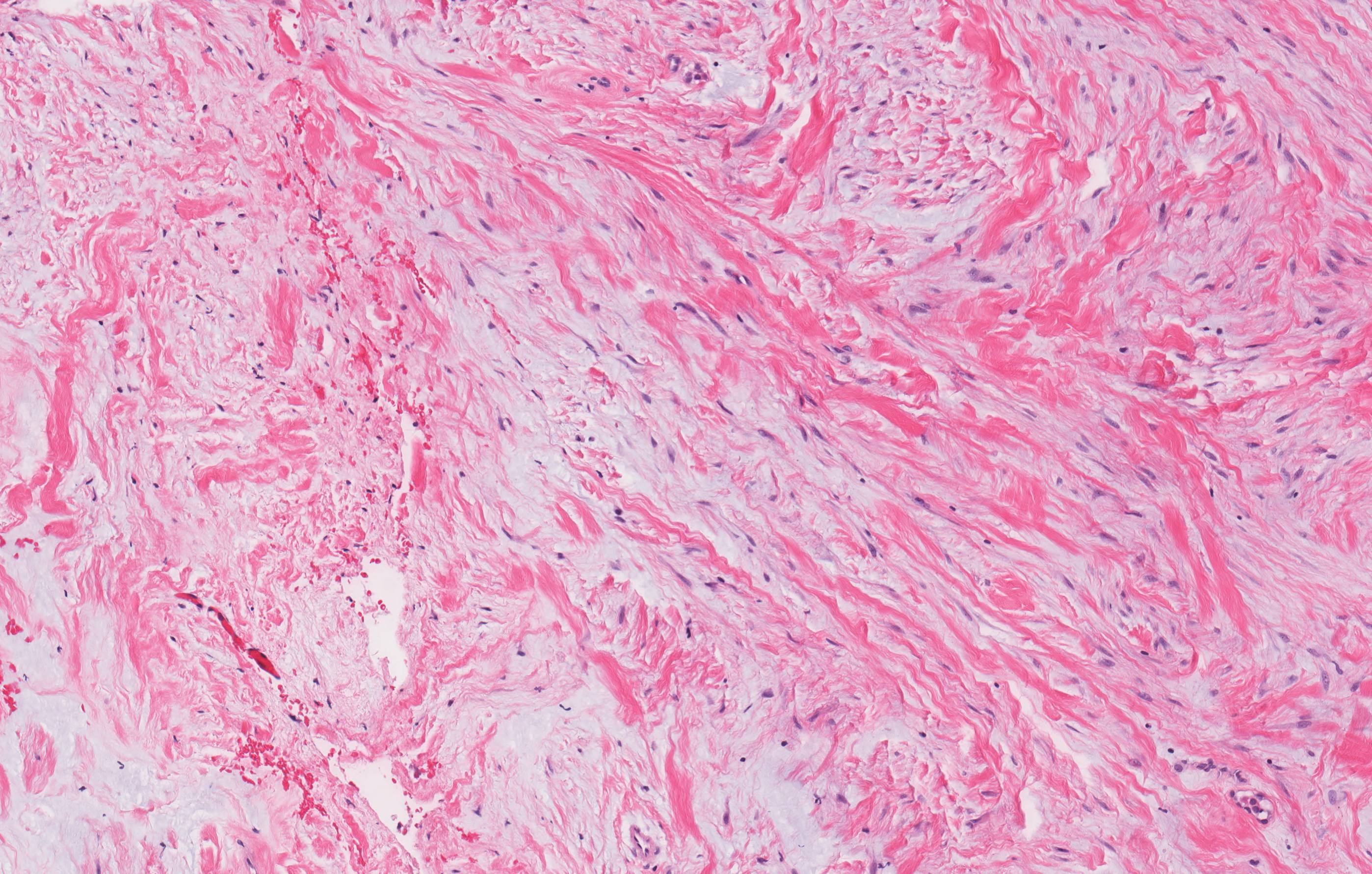
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Poorly demarcated lesion with interlacing or fascicular pattern of mature fibrous tissue composed of small fibroblasts with no / minimal mitotic activity and abundant collagenous stroma
- Mature, bland fibroblasts separated by abundant collagen with thin walled, dilated vascular channels
- May infiltrate into soft tissue
- No necrosis, no pleomorphism or atypia
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Trisomy 8, trisomy 20
Positive stains
Electron microscopy description
- Predominantly myofibroblasts, also fibroblasts and primitive mesenchymal cells
Differential diagnosis
Additional references