Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Nayman E, Tariq H. Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomasdrpl.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, low grade splenic B cell lymphoma characterized by prominent splenomegaly, circulating villous lymphocytes, sinusoidal bone marrow infiltration and diffuse involvement of the splenic red pulp (Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
Essential features
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma (SDRPL) is a rare, indolent, low grade B cell lymphoma that belongs to the family of splenic B cell lymphomas and presents with splenomegaly, peripheral blood lymphocytosis, diffuse splenic red pulp infiltration and sinusoidal bone marrow infiltration
- SDRPL shows considerable overlap with other splenic B cell lymphomas (i.e., splenic marginal zone lymphoma [SMZL], hairy cell leukemia [HCL] and splenic B cell lymphoma with prominent nucleoli [SBLPN])
- SDRPL shows atypical lymphocytes with polarized cytoplasmic projections and inconspicuous nucleoli in the peripheral blood, diffuse infiltration of the red pulp cords and sinuses, an atrophic to absent white pulp in the spleen and a characteristic prominent sinusoidal infiltration pattern in the bone marrow
- SDRPL is more frequently positive for cyclin D3 and DBA-44 than other splenic B cell lymphomas and consistently negative for cyclin D1, ANXA1 and CD123
- SDRPL shows a higher frequency of CCND3 and BCOR mutations and a lower frequency of KLF2, NOTCH2 and NFκB pathway gene alterations compared to other splenic B cell lymphomas; the lack of BRAF mutation helps exclude HCL
- References: Discov Med 2012;13:253, Histopathology 2002;40:22, Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Int J Lab Hematol 2018;40:e59
Terminology
- Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia, unclassifiable or not further classified (not recommended)
- Splenic diffuse red pulp lymphoma
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma, diffuse variant
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9591/3 - splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
- ICD-10: C83.07 - small B cell lymphoma, spleen
- ICD-11: 2A82.Y & XH99V9 - other specified mature B cell neoplasm with leukemic behavior & splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Epidemiology
- < 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- ~10% of B cell lymphomas diagnosed in splenectomy specimens
- 0.5% of chronic lymphoid malignancies involving peripheral blood (Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666, Discov Med 2012;13:253)
- Sex: M > F (ratio varies between 1.6 and 2.4)
- Median age: 66 - 79 years old; 70 - 90% of patients are > 60 years old (Haematologica 2010;95:1122)
Sites
- Always involves the spleen
- Bone marrow and peripheral blood are involved in most cases
- Splenic hilar lymph nodes are usually involved but involvement of other lymph node sites is extremely rare
- Rarely presents with liver lesions (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Rare reports describe involvement of testicles, lymph nodes outside of the splenic hilar nodes or skin (erythematous and pruritic skin papules seen in up to 10% of cases) (Haematologica 2010;95:1122)
Pathophysiology
- Aberrant antigenic stimulation may contribute to uncontrolled B cell proliferation as evidenced by almost universal expression of B cell receptor immunoglobulins with a biased and somatically hypermutated IGHV repertoire (Blood 2008;111:2253, Leukemia 2012;26:1638, Haematologica 2017;102:1758)
- Most common recurrent genomic abnormalities involve CCND3 and BCOR
- CCND3 encodes for cyclin D3, which promotes pre-B cell and B cell proliferation in germinal centers
- BCOR encodes for the BCL6 corepressor whose effects in germinal centers include transient repression of response to DNA damage, cell cycle inhibition and plasma cell differentiation among others
- Ultimately, the functional effects of these are unknown (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:697)
Etiology
- Unknown (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:697)
Clinical features
- Most patients present with pronounced splenomegaly and lymphocytosis
- Bone marrow (95 - 100%) and peripheral blood (92 - 100%) are involved in nearly all cases (Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666, Discov Med 2012;13:253, Blood 2022;140:3632)
- 96 - 100% of patients are diagnosed with stage IV disease (blood and bone marrow involvement) but pancytopenia is rare (Histopathology 2013;62:876)
- Minority of patients present with poor performance status (i.e., ECOG ≥ 2)
- B symptoms observed in up to ~33% of cases (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
Diagnosis
- Splenic biopsy or splenectomy is required for diagnostic confirmation (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1295)
- Since spleen specimens are exceedingly rare in the diagnostic practice of lymphoma, confirmatory diagnosis is not possible in many cases
- Shows overlapping clinical, morphologic, immunophenotypic and genetic features with SMZL and SBLPN but can be differentiated from HCL in nearly all cases
- Essential diagnostic criteria
- Characteristic diffuse infiltration of the splenic red pulp by monomorphic small B cells accompanied by an atrophic white pulp
- Peripheral blood circulating small to intermediate sized lymphocytes with easily visible, broad based, unevenly distributed (polarized) cytoplasmic villous projections and inconspicuous nucleoli
- Compatible immunophenotype (most importantly CD200:CD180 mean fluorescence intensity [MFI] < 0.5)
- Desirable diagnostic criteria
- Absence of BRAF p.v600E mutation
- No lymphadenopathy outside of the splenic hilar lymph nodes (Mod Pathol 2024;37:100466)
Laboratory
- Low to moderate level lymphocytosis, in contrast to HCL (which rarely presents with lymphocytosis) and SBLPN (which often presents with severe lymphocytosis) (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Thrombocytopenia or anemia in a minority of cases
- Pancytopenia is rare unlike the significant pancytopenia commonly seen in HCL (Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666)
- Few cases with monoclonal IgM or IgG spike on serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) (Discov Med 2012;13:253)
Radiology description
- Abdominal ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) may show a diffusely enlarged spleen without discrete lesions
- Positron emission tomography (PET) / CT may show mildly increased homogenous fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake (Pathol Int 2012;62:577)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Indolent but difficult to fully eradicate disease (incurable) with similar median overall survival (OS) to SMZL and SBLPN
- 5 year overall survival (OS) of 93% (Haematologica 2010;95:1122)
- 2 year overall survival and progression free survival of 92% and 62%, respectively, following splenectomy (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:192)
- Mutations in NOTCH1, NAP2K1 and TP53 associated with shorter progression free survival (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:192)
- Hemoglobin < 10 mg/dL and age > 60 years old associated with inferior survival (Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Blood 2022;140:3632)
Case reports
- 29 year old woman with splenomegaly and 62 year old woman with weight loss (Sao Paulo Med J 2016;134:359)
- 45 year old man with abdominal swelling and generalized weakness (Blood Res 2018;53:74)
- 57 year old woman with B symptoms, abdominal pain and splenomegaly (J Hematol 2023;12:118)
- 62 year old man with chronic lymphocytosis and splenomegaly (Int J Hematol 2023;118:394)
- 72 year old woman with IgA deficiency and chronic sporadic pancytopenia (Leuk Res 2012;36:e103)
Treatment
- Lack of clinical studies comparing various therapeutic regimens due to disease rarity
- First line treatment includes splenectomy or rituximab (Discov Med 2012;13:253)
- Splenectomy may provide more durable remission though it is not curative as the bone marrow can harbor residual disease (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:192)
- Rituximab monotherapy is preferred for older patients because it is better tolerated than splenectomy (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
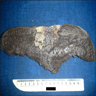
Gross description
- Diffusely enlarged spleen with a homogenous, beefy, red-brown cut surface without discrete lesions (J Hematol 2023;12:118)
- Possible wedge shaped subcapsular infarcts (Blood Res 2018;53:74)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Spleen
- Diffuse involvement of the red pulp with infiltration of cords and sinuses by monomorphic lymphocytes with clumped chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and pale cytoplasm
- Neoplastic cells may appear plasmacytoid
- Effacement of the white pulp with residual lymphoid follicles typically only identifiable by immunohistochemistry (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:192)
- Blood lakes / pseudosinuses lined by neoplastic cells may be seen
- Rare prominent nucleoli and clusters of large cells (Histopathology 2002;40:22, Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Discov Med 2012;13:253, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Diffuse involvement of the red pulp with infiltration of cords and sinuses by monomorphic lymphocytes with clumped chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and pale cytoplasm
- Peripheral blood
- Small to medium sized lymphocytes with easily visible, broad based and polarized cytoplasmic villi
- Clumped chromatin
- Nucleolus is small or not visible in most of the cells (Blood 2008;111:2253)
- Bone marrow
- Sinusoidal infiltration is the rule
- Can also show a variable degree of nodular and interstitial involvement in addition to sinusoidal infiltration (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1609)
- Mild fibrosis in some cases
Microscopic (histologic) images
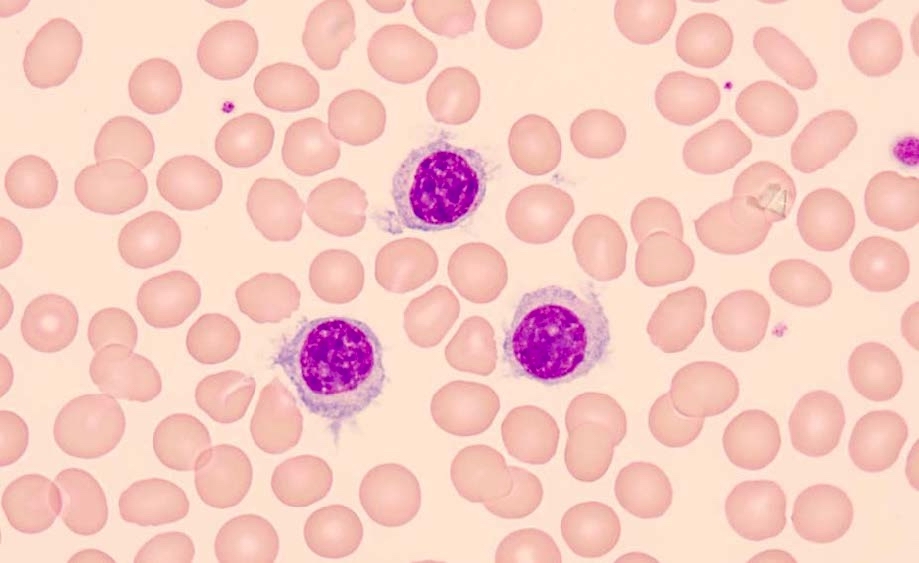
Peripheral smear description
- Lymphocytosis consisting of intermediate sized lymphocytes with round nuclei, clumped chromatin and abundant cytoplasm with polarized, unevenly distributed, broad based villous projections; no prominent nucleoli are seen
- These are differentiated from the typical HCL cells that have an oval / indented nucleus and abundant fine circumferential projections
- Absence of a readily identifiable single prominent nucleolus helps distinguish it from SDRPL
- Distinction between SDRPL and SMZL is often not possible based on peripheral blood smear morphology alone
Peripheral smear images
Positive stains
- Pan-B cell markers (CD20, CD19, PAX5, CD79a)
- Cyclin D3 in ~70% and DBA-44 in ~80% of cases (Blood 2017;129:1042, Haematologica 2010;95:1122)
- IgG (66.7%), kappa restricted (33.3%), lambda restricted (66.7%), Ki67 (< 10%) (Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666, Blood Res 2018;53:74, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
Negative stains
- CD5, CD10, CD23, CD43, ANXA1, BCL6, cyclin D1, SOX11, CD25, CD123, TRAP, IgD (Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
Flow cytometry description
- Positive
- CD19, CD20 and CD22 positive (moderate to strong)
- CD180 (strong in nearly all cases) (Leukemia 2013;27:1748, Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666)
- CD11c (moderate in ~67% of cases)
- CD200 (dim positive in ~40% of cases) (Int J Lab Hematol 2018;40:e59)
- CD103 (moderate expression in 16.7% of cases)
- Surface light chain restricted (moderate to bright); more frequently lambda than kappa
- Negative
- CD123
- CD25 (90%)
- CD5 and CD23
- CD38, CD24 and CD27 mostly negative (Haematologica 2010;95:1122, Hematol Oncol 2011;29:47, Discov Med 2012;13:253)
- SDRPL shows considerable immunophenotypic overlap with other splenic B cell lymphomas; however, the weak to negative expression for CD200 and bright CD180 expression strongly favors SDRPL (CD200:CD180 MFI < 0.5) (Int J Lab Hematol 2018;40:e59)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Absence of BRAF p.V600E mutation (desirable diagnostic criterion)
- Recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities
- 7q deletion, trisomy 18 or partial trisomy 3q (~33% of cases)
- Complex karyotype and TP53 alterations (~10% of cases) (Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Recurrent genomic abnormalities
- Missense mutations in CCND3 (20 - 24% of cases)
- BCOR mutations (16% of cases)
- Hypermutated IGVH3-23 or IGHV4-34 (79 - 89% of cases) (Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:697)
- Mutations in NOTCH1, MAP2K1 and TP53 associated with shorter progression free survival (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:192)
- Infrequent mutations in NOTCH2 and KLF2 (Leuk Lymphoma 2017;58:666)
Sample pathology report
- Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and bone marrow core biopsy:
- Splenic B cell lymphoma, most compatible with splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma, involving 30 - 40% of hypercellular bone marrow (~60 - 70% cellular) (see comment)
- Comment: The patient's history of lymphocytosis and worsening splenomegaly is noted. The peripheral blood and bone marrow aspirate show frequent small to intermediate sized atypical lymphocytes with round to slightly irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and a moderate amount of pale cytoplasm with projections. The bone marrow core shows an atypical prominent intrasinusoidal B cell infiltrate that is positive for CD20, DBA-44 and cyclin D3, while negative for CD5, CD10, LEF1, cyclin D1, CD25, ANXA1 and BRAF. Next generation sequencing detected a BCOR mutation while negative for all other mutations tested, including BRAF V600E and NFκB pathway gene alterations. The findings are most consistent with splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma.
- Peripheral blood, flow cytometric immunophenotyping:
- Flow cytometric immunophenotyping performed on the peripheral blood reveals a monotypic lambda surface light chain restricted B cell population (~15% of total cellular events) that is CD19+, CD20+ (moderate to bright), CD5-, CD10-, CD23-, CD180+ (strong and uniform) CD200-, CD38-, CD22+, CD52+, CD25-, CD11c+, CD103+, FMC7+, dim CD79b+ and CD123-. This population shows moderately increased side scatter.
- Comment: The patient's history of lymphocytosis and worsening splenomegaly is noted. Flow cytometric analysis reveals peripheral blood involvement by a mature B cell lymphoma / leukemia. The concurrent peripheral blood smear shows frequent small to intermediate sized atypical lymphocytes with round to slightly irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and a moderate amount of pale cytoplasm with projections. Next generation sequencing detected a CCND3 mutation while negative for all other mutations tested, including BRAF V600E. The overall findings are consistent with a splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia. The main diagnostic considerations are splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma and splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Distinguishing between these entities is challenging without splenic evaluation; however, the strong expression of CD180, lack of CD200 and presence of CCND3 mutation all favor splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma.
- Spleen, splenectomy:
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: The spleen shows diffuse infiltration of the red pulp by monomorphic small lymphocytes with clumped chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli. By immunohistochemistry, these cells are positive for CD20 and PAX5, while negative for CD5, CD10, CD23, LEF1, SOX11, cyclin D1, ANXA1, BRAF and CD123. Next generation sequencing performed on the splenic tissue is positive for a CCND3 mutation and negative for all other variants tested, including MYD88 and BRAF. The findings are most consistent with splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma:
- Commonly presents with anemia or thrombocytopenia
- Peripheral blood smear morphology is indistinguishable from SDRPL in most cases
- Histologic findings
- Spleen: nodular pattern with expansion of the white pulp
- Bone marrow: nodular B cell aggregates with focal intrasinusoidal infiltration
- Immunohistochemistry: cyclin D3 negative, CD21 positive meshworks within nodular aggregates
- Flow cytometry: CD200:CD180 MFI > 0.5
- Molecular: KLF2, NOTCH2 and NFκB pathway gene alterations are relatively more frequent
- Hairy cell leukemia:
- Commonly presents with anemia or thrombocytopenia and characteristically monocytopenia
- Peripheral blood smear: monomorphic, ovoid cells with indented nuclei, circumferential fine projections and inconspicuous nucleoli
- Histologic findings
- Spleen: diffuse infiltrate with effacement of white pulp
- Bone marrow: diffuse infiltrate often with fried egg appearance
- Immunohistochemistry: ANXA1+, CD25+, CD123+, cyclin D1+, cyclin D3-
- Cytochemistry: TRAP+
- Flow cytometry: CD25+, CD103+, CD123+, CD200+
- Molecular: presence of BRAF p.V600E mutation
- Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia with prominent nucleoli (formerly hairy cell leukemia variant):
- Commonly presents with anemia or thrombocytopenia
- Peripheral blood smear: monomorphic medium to large sized cells with large prominent single nucleolus and variably defined projections
- Histologic findings
- Spleen: diffuse infiltrate with effacement of white pulp
- Bone marrow: interstitial and intrasinusoidal infiltration
- Immunohistochemistry: cyclin D3-
- Flow cytometry: CD200:CD180 MFI > 0.5, CD103+
- Molecular: TP53 mutations / deletions and MAP2K1 mutations are more common
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 65 year old man presents with abdominal fullness. An abdominopelvic CT shows massive splenomegaly. A peripheral blood smear reveals monomorphic lymphocytes with polarized, broad based cytoplasmic villi. Flow cytometry performed on the peripheral blood reveals a lambda restricted B cell population that is strongly positive for CD19, CD20 and CD180, partial positive for CD11c and negative for CD200, CD25, CD103 and CD123. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ratio between CD180 and CD200 is < 0.5. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia with prominent nucleoli
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma. The presence of splenomegaly and abnormal lymphocytes with cytoplasmic projections is consistent with a splenic B cell lymphoma, a category that includes all 4 listed entities. The immunophenotype (CD180+, CD200-, CD25-, CD103-, CD123-) and a CD180:CD200 MFI ratio of < 0.5 is most compatible with splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma. Answer A is incorrect because hairy cell leukemia is defined by circumferential hairy projections and a CD25+, CD11c+, CD103+, CD123+ and CD200+ phenotype. Answer D is incorrect because SMZL shows a CD180:CD200 MFI ratio of > 0.5 by flow cytometric immunophenotyping. Answer B is incorrect because the lymphocytes on peripheral blood smear would show prominent nucleoli and a CD180:CD200 MFI ratio of > 0.5.
Comment Here
Reference: Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Board review style question #2
A 58 year old man with a history of metabolic syndrome presents for evaluation of low level but persistent lymphocytosis that was discovered on routine CBC. Peripheral blood smear is remarkable for lymphocytes with cytoplasmic villous projections. Nucleoli are not readily identified. PET / CT shows an enlarged spleen with moderately increased uptake and no lymphadenopathy. The patient undergoes a bone marrow biopsy which reveals an abnormal intrasinusoidal B cell infiltrate that is CD20+, DBA-44+, cyclin D1-, cyclin D3+ and ANXA1-. A CD20 IHC is shown above. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia with prominent nucleoli
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Board review style answer #2
C. Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma. The presence of splenomegaly and abnormal lymphocytes with cytoplasmic projections is consistent with a splenic B cell lymphoma, a category that includes all 4 listed entities. The prominent intrasinusoidal infiltration pattern in the bone marrow and the immunohistochemical profile is most consistent with splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma. Answer D is incorrect because splenic marginal zone lymphoma mostly shows nodular bone marrow infiltration with focal intrasinusoidal infiltration. A predominant intrasinusoidal pattern and cyclin D3 positivity are not typical. Answer A is incorrect because hairy cell leukemia presents with a diffuse interstitial bone marrow infiltrate and stains positive for cyclin D1 and ANXA1. Answer B is incorrect because there were no prominent nucleoli described.
Comment Here
Reference: Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma