Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Nowacki N. MCL-leukemic nonnodal. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonnodalmantlecell.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mantle cell lymphoma involving the peripheral blood, bone marrow, occasionally spleen and gastrointestinal tract but not lymph nodes
Essential features
- Must lack significant lymphadenopathy (< 1 cm on physical exam and not detected via imaging / CT scans)
- t(11;14)(q13;q32) = fusion of CCND1 and IGH genes
- Positive for Cyclin D1 (also known as BCL1) and negative for SOX11
Terminology
- Leukemic mantle cell lymphoma
- Nonnodal leukemic mantle cell lymphoma (NN-L-MCL)
- Monoclonal asymptomatic lymphocytosis, cyclin D1 positive (MALD1)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C83.10 - mantle cell lymphoma, unspecified site
Epidemiology
- M > F = ~2:1
- Mean age = ~60 years old
Sites
- Peripheral blood, bone marrow and occasionally spleen or gastrointestinal tract
- Circulating cells may reversibly infiltrate extranodal sites and typically remain in the mantle zones of follicles, overlapping with in situ mantle cell lymphoma
Pathophysiology
- t(11;14)(q13;q32), fusion of CCND1 gene and IGH promoter increases production of the Cyclin D1 protein, regulator of cyclin dependent kinase (CDK4) and CDK6 which controls the G1 / S cell cycle transition (J Clin Invest 2012;122:3416)
Etiology
- Cell of etiology thought to be peripheral B cell of inner mantle zone
Clinical features
- Typically asymptomatic at presentation
Laboratory
- Mild leukocytosis and mild absolute lymphocytosis
- 10 - 20% patients will have a monoclonal protein
Prognostic factors
- Better prognosis than classic mantle cell lymphoma (mean survival of leukemic nonnodal = 79 months) (Blood 2003;101:4975)
- TP53 gene mutations = more aggressive course (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:e93, Leukemia 2012;26:1895)
- Deletions of TP53, ATM or 13q14 = worse prognosis (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:214)
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with disease progression 20 years after splenectomy (Clin Case Rep 2017;5:477)
- 53 year old man with TP53 loss and response to rituximab / ibrutinib therapy (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:e93)
- 84 year old woman with associated pure red blood cell aplasia (Int J Hematol 2014;99:777)
Treatment
- May be observed until progression, then treated as typical mantle cell lymphoma with combination chemotherapy, rituximab and subsequent stem cell transplant depending on age and performance status (Curr Oncol Rep 2018;20:79)
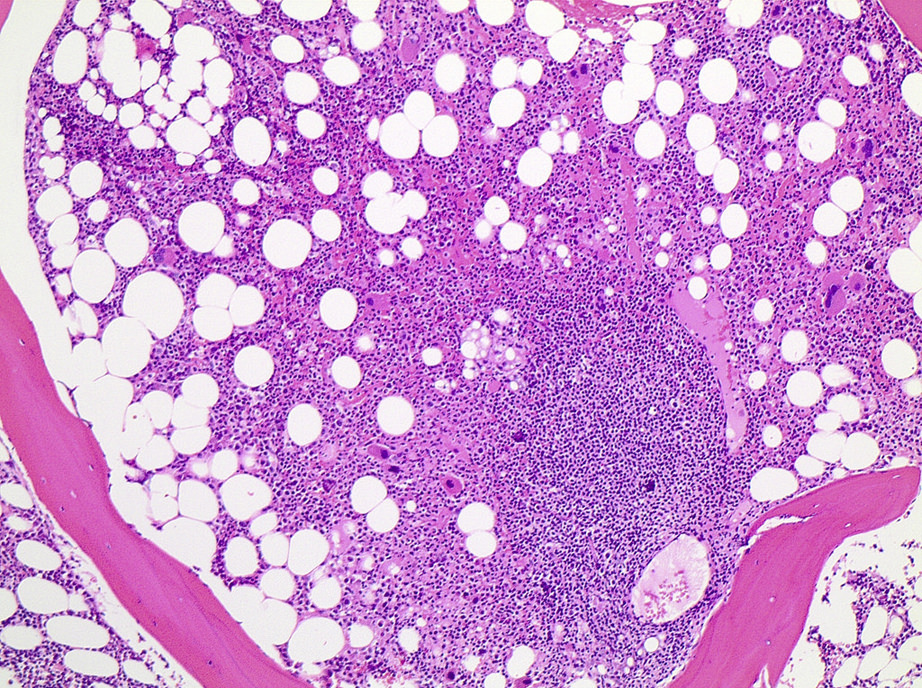
Microscopic (histologic) description
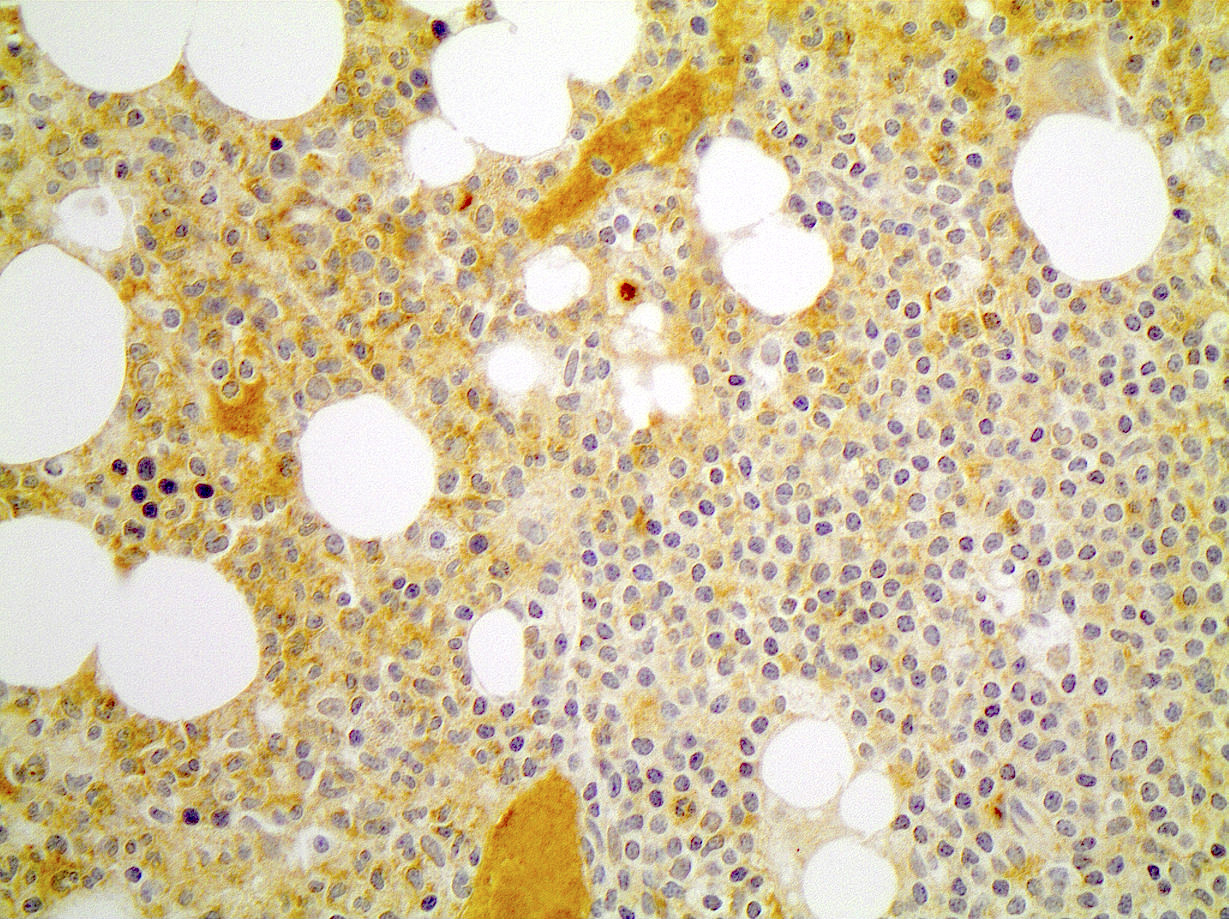
- Diffuse interstitial infiltrate or small scattered nonparatrabecular lymphoid aggregates
- Small to intermediate size lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm, round to slightly irregular nuclear contours and mature chromatin
- Some cases will show dispersed chromatin and indistinct nucleoli
Microscopic (histologic) images
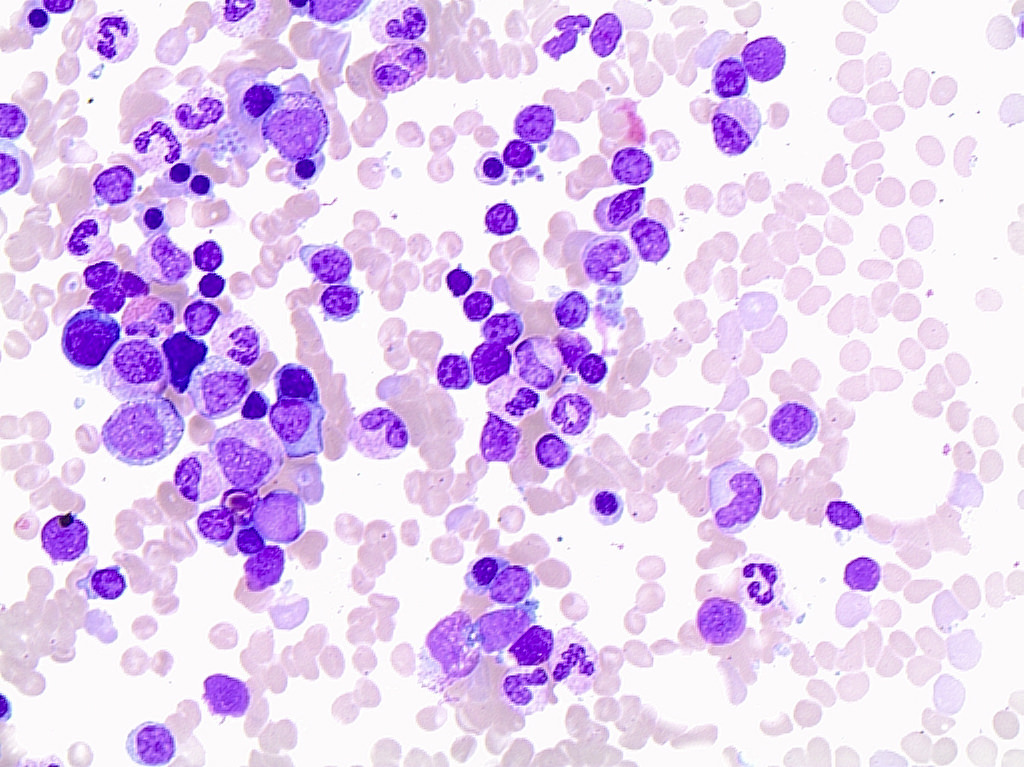
Cytology description
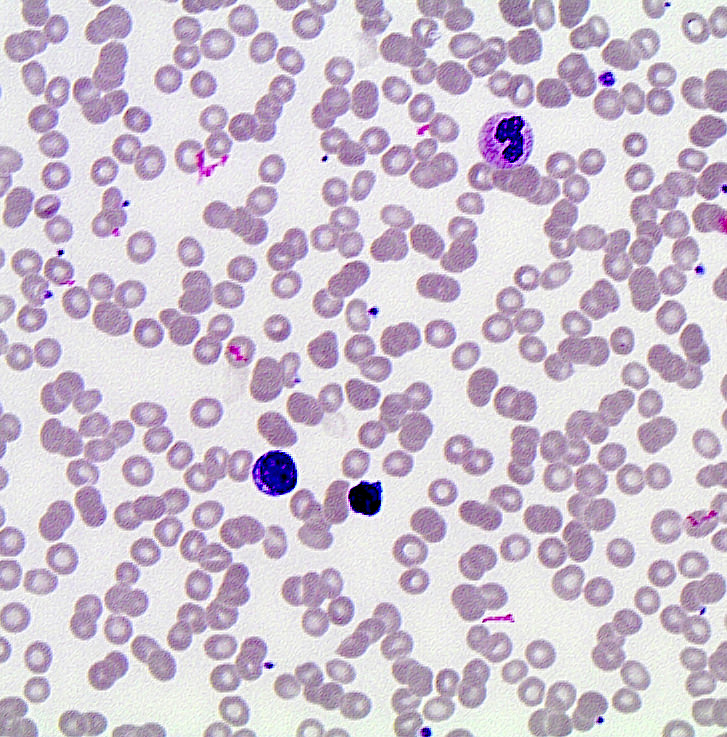
- Variable morphologic appearance
- Majority (~70%) show chronic lymphocytic leukemia-like morphology = small with scant cytoplasm, round nuclear contours and condensed chromatin (Cancer Res 2010;70:1408)
- Fewer (~30%) with typical mantle cell lymphoma, centrocyte-like morphology = small to medium sized lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contours, dispersed chromatin and indistinct nucleoli
Peripheral smear description
- Same as cytology description
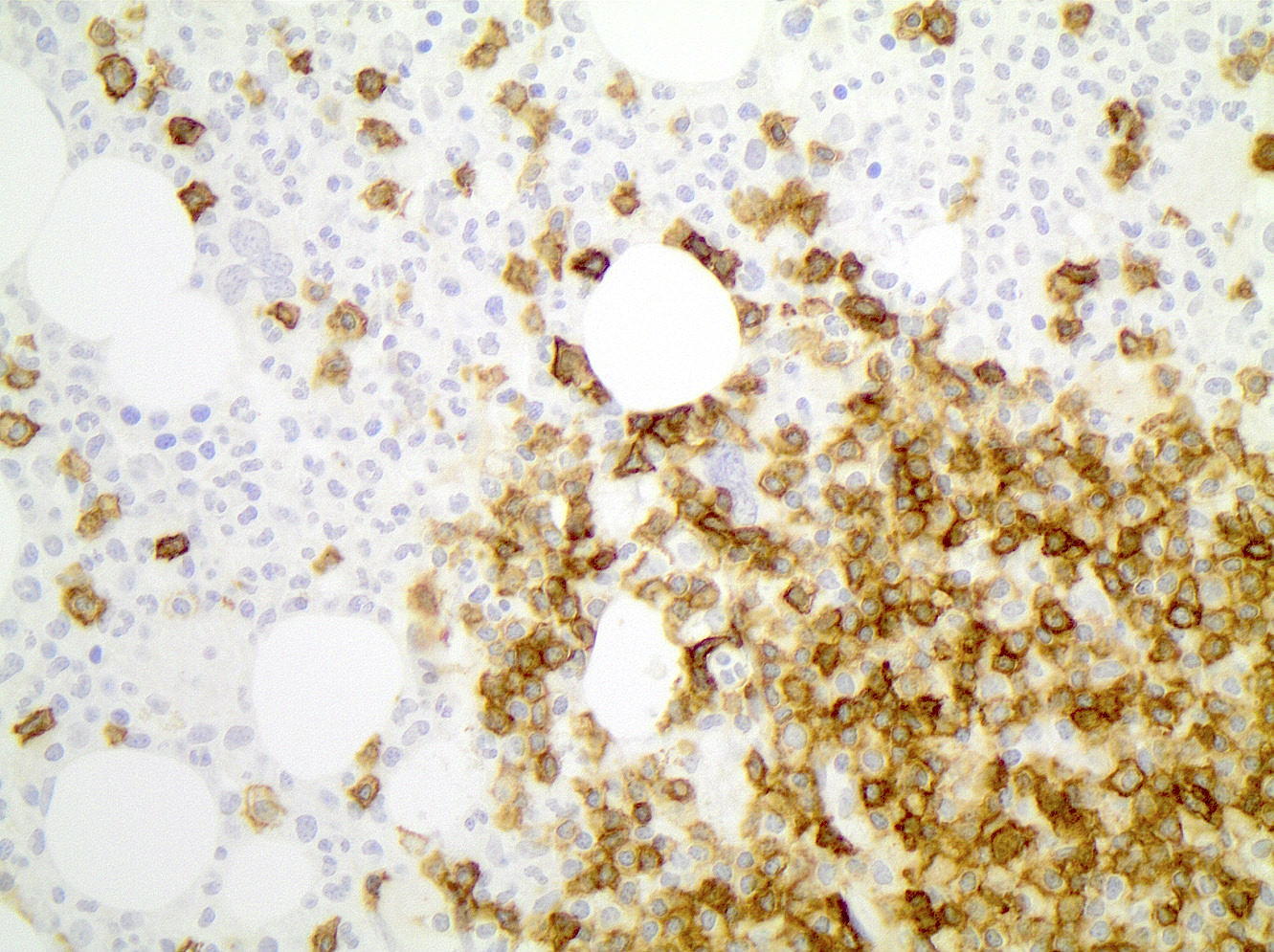
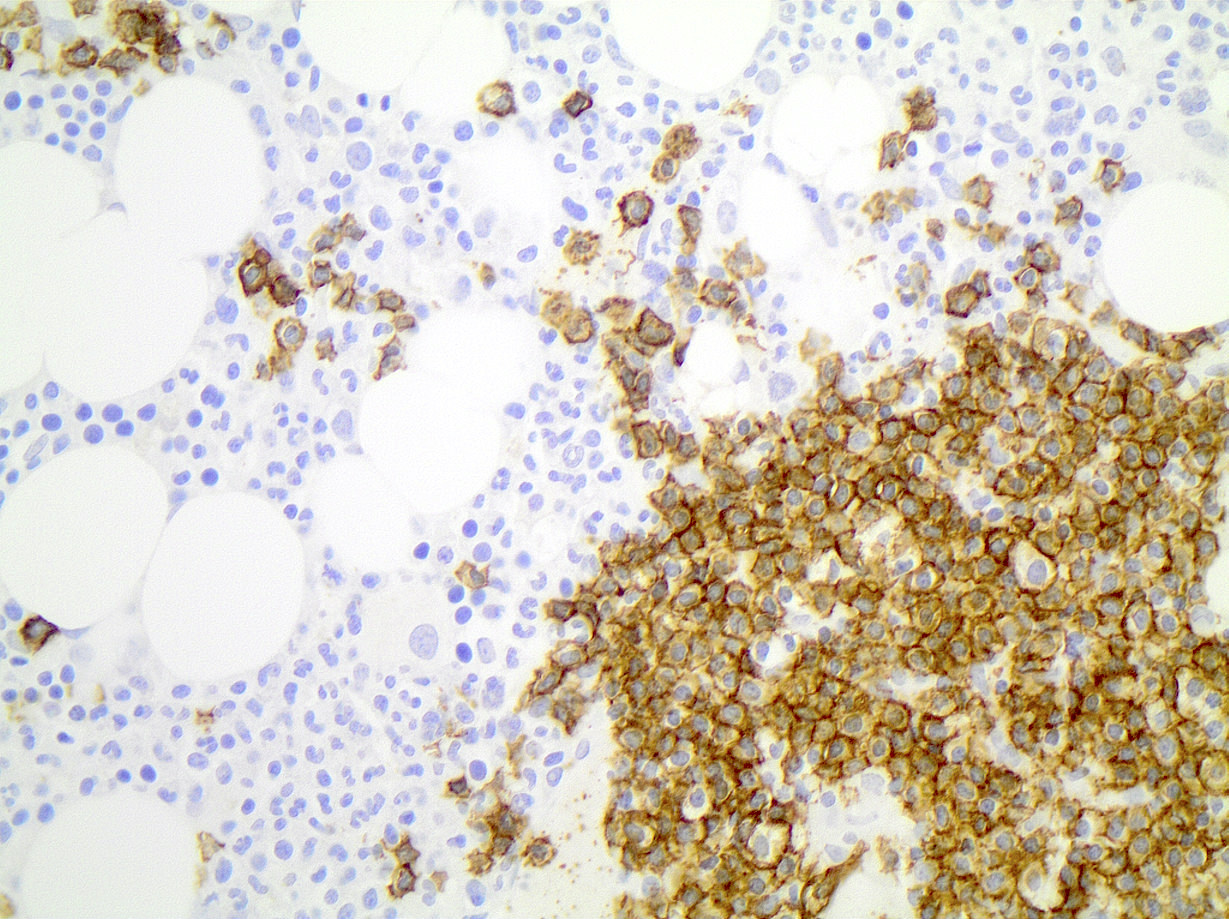
Positive stains
Flow cytometry description
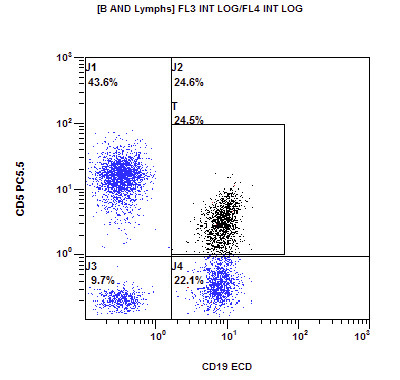
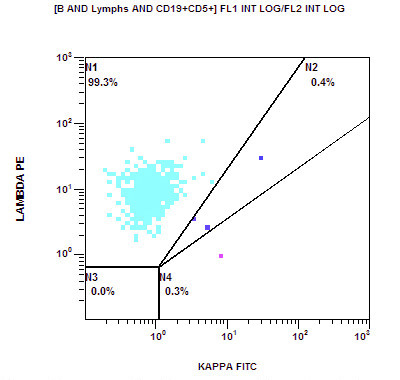
- Typical immunophenotype:
- Positive: CD20 (moderate to bright), surface light chain restriction (moderate to bright), CD5 (subset), CD79b, FMC7
- Negative: CD10, CD103, CD123, CD11c
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- t(11;14)(q13;q32), fusion of CCND1 and IGH genes
- Most cases have somatic hypermutation / IgVH gene hypermutated (Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:1007)
- Typically few additional cytogenetic abnormalities and much less likely to have a complex karyotype than classic mantle cell (Leukemia 2012;26:1895)
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, biopsy, aspirate and peripheral blood smear:
- Mantle cell lymphoma involving a normocellular marrow with preserved trilineage hematopoiesis (see comment)
- Comment: The overall findings are consistent with marrow involvement by mantle cell lymphoma. Given the lack of SOX11 staining, the possibility of the leukemic nonnodal mantle cell lymphoma variant should be considered. By definition, patients with this variant must lack significant lymphadenopathy (< 1 cm). The presence of lymphadenopathy would argue for the classic variant of mantle cell lymphoma. Clinical correlation and correlation with cytogenetic / FISH studies, including t(11;14)(q13;q32) IGH-CCND1, is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Classical mantle cell lymphoma: often lymphadenopathy (> 1 cm) is present and typically SOX11+
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia with variant immunophenotype: negative for cyclin D1 and t(11;14)(q13;q32) IGH-CCND1
- Hairy cell leukemia (HCL): frequent cyclin D1 positivity with t(11;14) translocation in hairy cell leukemia can mimic mantle cell lymphoma but hairy cell leukemia typically shows unique morphology and immunophenotype CD103+, CD123+, CD11c+ and CD5-
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What is the most likely immunophenotype for leukemic nonnodal mantle cell lymphoma?
- CD20+, CD5+, CD10+, CD103-, CD123-, Cyclin D1+, SOX11+
- CD20+, CD5+, CD10-, CD103+, CD123+, Cyclin D1+, SOX11-
- CD20+, CD5+, CD10-, CD103-, CD123-, Cyclin D1+, SOX11+
- CD20+, CD5+, CD10-, CD103-, CD123-, Cyclin D1+, SOX11-
- CD20+, CD5-, CD10-, CD103-, CD123-, Cyclin D1-, SOX11+
Board review style answer #1
D. CD20+, CD5+, CD10-, CD103-, CD123-, Cyclin D1+, SOX11-
Comment here
Reference: Nonnodal mantle cell lymphoma
Comment here
Reference: Nonnodal mantle cell lymphoma
Board review style question #2
A 60 year old woman was noted to have a mild absolute lymphocytosis on routine labs. A bone marrow biopsy was performed and based on the morphologic and immunophenotypic features a diagnosis of leukemic nonnodal mantle cell lymphomais is suspected. If this is correct, which cytogenetic abnormality should be detected on cytogenetic / FISH
analysis?
- deletion 17p and t(8;14)(q24;q32) IGH-MYC
- t(8;14)(q24;q32) IGH-MYC
- t(11;14)(q13;q32) IGH-CCND1
- t(14;18)(q32;q231) IGH-BCL2
- trisomy 12
Board review style answer #2