Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Marques-Piubelli ML, Torres-Cabala CA, Miranda RN. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonBsubcutaneouspan.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Primary cutaneous cytotoxic T cell lymphoma, which typically involves subcutaneous adipose tissue (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:17, JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Blood 2020;135:1058, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919)
- First described by Gonzalez and colleagues in 1991
- Defined as a distinct entity by the 2001 World Health Organization Classification of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tumors
- Initially included cases of both α / β and γ / δ phenotypes
Essential features
- Primary cutaneous cytotoxic T cell lymphoma, which typically involves subcutaneous adipose tissue (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:17, JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Blood 2020;135:1058, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919)
- Rare (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:740)
- < 1% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- Homozygous germline HAVCR2 (TIM-3) mutation in ~60% of patients (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Blood 2020;135:1058, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, Nat Genet 2018;50:1650)
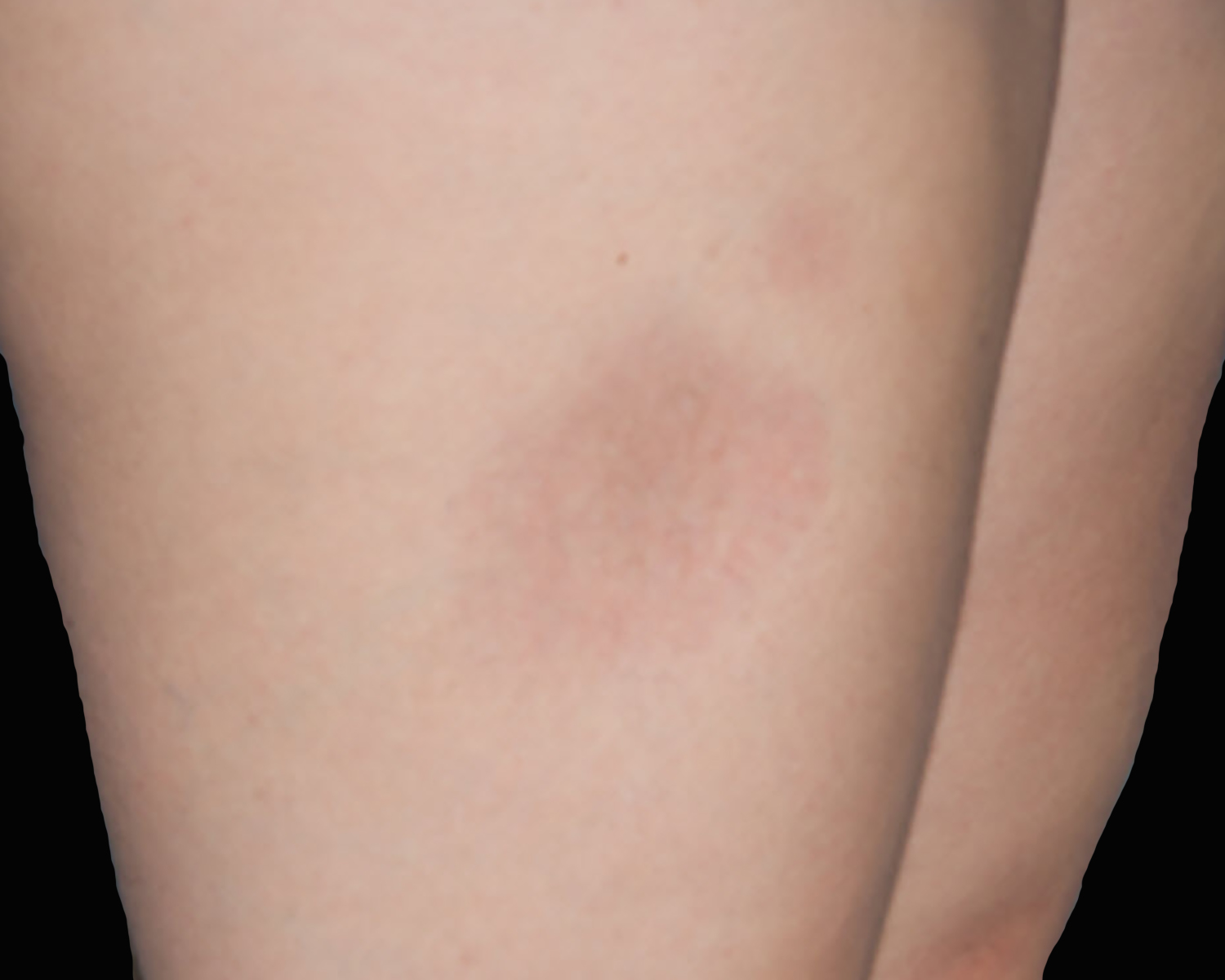
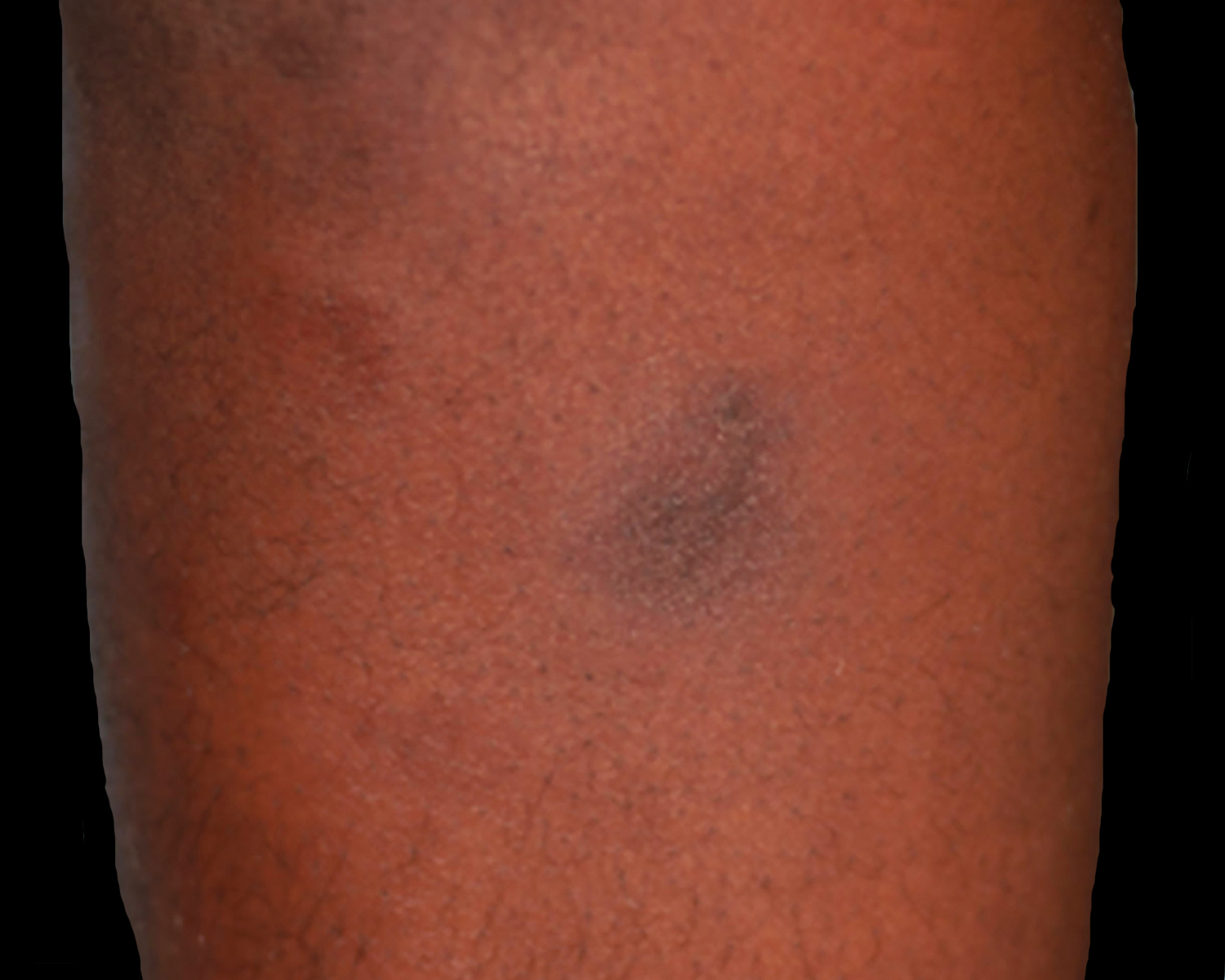
- Solitary or multiple erythematous subcutaneous tender and deep nodules or plaques (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
Terminology
- T cell lymphoma involving subcutaneous tissue
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C86.3 - subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Epidemiology
- Rare (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:740)
- < 1% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas
- Median age: ~25 - 35 years (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2022;17:432)
- < 20% of cases occur in adolescents or children
- Similar clinical course
- < 20% of cases occur in adolescents or children
- F > M (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Nat Genet 2018;50:1650)
- F:M = ~2:1
Etiology
- Homozygous germline HAVCR2 (TIM-3) mutation (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Blood 2020;135:1058, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, Nat Genet 2018;50:1650)
- Immune checkpoint gene frequently mutated in sporadic cases
- Encodes T cell immunoglobulin mucin 3 (TIM-3)
- Modulation of T cell function
- Impairs TIM-3 protein folding, cellular expression and function
- Induces a persistent inflammatory response and potentially causes hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
- Impairs TIM-3 protein folding, cellular expression and function
- Regulates monocyte / macrophage activation
- Modulation of T cell function
- Recurrent mutations in phosphoinosiditide 3 kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and JAK / STAT pathways (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:740, Br J Haematol 2018;181:406, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919)
- Chemokine dysregulation (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27)
- Expression of CCR5 by neoplastic T cells
- CCR5 ligands (CCL3, CCL4, CCL5) on the adipocyte membrane
- Expression of CCR5 by neoplastic T cells
- Rare cases associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27)
- Inhibition of SAP / SH2D1A gene by EBV latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
- Increased cytokine secretion
- Delay in the apoptosis of T cells through TNFα / TNF receptor 1 via nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) pathway
- Inhibition of SAP / SH2D1A gene by EBV latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
- Association with autoimmunity (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Nat Genet 2018;50:1650)
- Personal or family history of autoimmune diseases
- ~20% of cases
- Lupus erythematous is the most common
- Multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis have also been described
- Rare cases associated with COVID vaccine association (JAAD Case Rep 2022;28:18)
Clinical features
- Solitary or multiple erythematous subcutaneous tender and deep nodules or plaques (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- Lower / upper extremities, trunk, head and neck
- ~75% are multifocal
- Extent of involvement and size of lesions are variable
- Ulceration is rare, lipoatrophy may be seen
- Indolent clinical course
- Wax and wane
- Median clinical onset: ~18 months
- Lower / upper extremities, trunk, head and neck
- B symptoms in ~70% of patients (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167)
- Hemophagocytic syndrome in ~20% of patients (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27)
- Usually associated with more extensive disease
- Rare cases with hepatosplenomegaly, lymph node or bone marrow involvement (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
Diagnosis
- Association of clinicopathologic features and correct interpretation of histologic findings (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, J Clin Oncol 2015;33:1216)
- Unrelated malignant and nonmalignant confounding histopathology can masquerade as subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma (SPTCL)
Laboratory
- Elevated rates of ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), erythrocyte sedimentation rate / C reactive protein, beta 2 microglobulin and aspartate transaminase (AST) may be presented (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093)
- Cytopenias (anemia, neutropenia or lymphopenia) may be present (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160)
Radiology description
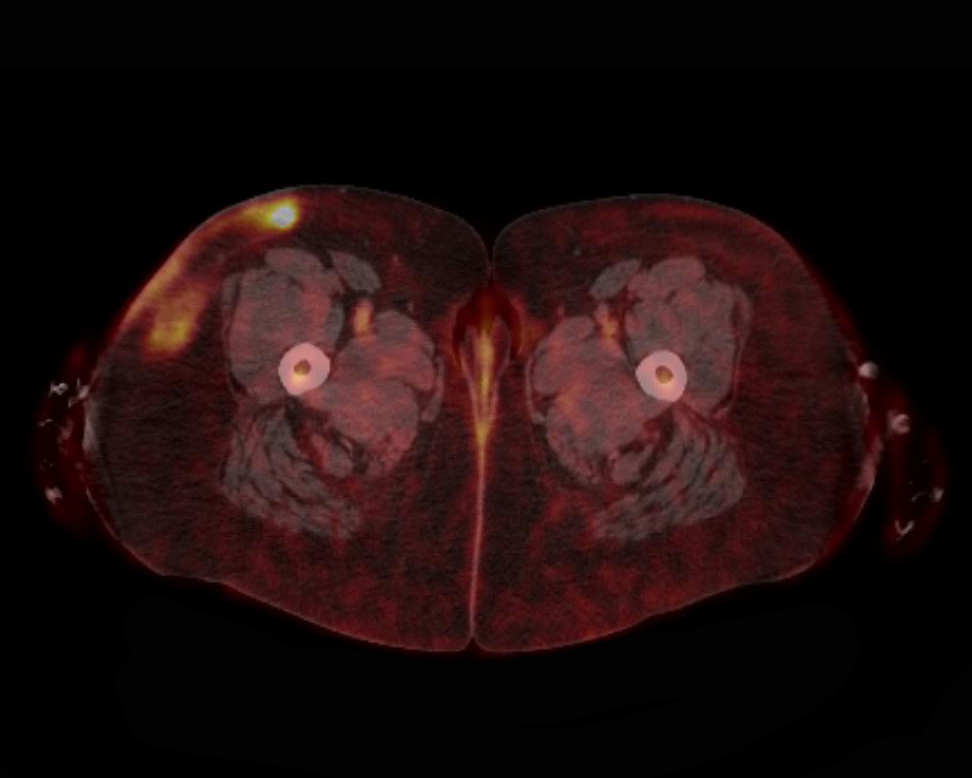
- Fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography / computed tomography (18F-FDG PET / CT) usually shows moderate to intense uptake of subcutaneous lesions (J Clin Oncol 2015;33:1216, J Radiol Case Rep 2022;16:1, Front Oncol 2021;11:650822)
- Used for disease activity (cutaneous or extracutaneous), staging and treatment response
Prognostic factors
- Overall good prognosis (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919)
- 5 year overall survival (OS): 85 - 91%
- Factors associated with worse prognosis
- Involvement of upper extremities
- Hemophagocytic syndrome
- 5 year overall survival: ~50%
Case reports
- 26 year old man with a diagnosis of panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma with HAVCR2 mutation and previous history of lupus panniculitis (Intern Med 2023;62:1537)
- 34 year old woman with liver failure and skin lesions as main manifestation of subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma (Ann Transl Med 2022;10:1408)
- 39 year old man with a diagnosis of panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma presenting as an abscess following arthropod bite (Dermatol Online J 2022;28:3)
- 42 year old man diagnosed with panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma in complete remission after 2 cycles of romidepsin (Case Rep Oncol 2022;15:1088)
- 47 year old woman with a diagnosis of panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma with inverted FDG uptake pattern in 18F-FDG PET (Clin Nucl Med 2023;48:186)
Treatment
- No standard treatment
- Immune modulatory treatments as single agents or combined (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
- Cyclosporine A, systemic steroids, bexarotene, low dose methotrexate, chlorambucil, azathioprine
- Overall response rate (ORR): ~50%
- Chemotherapy
- CHOP: cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone
- CHOP-like regimens
- Radiation
- Localized disease
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27)
- Refractory / relapsed or disseminated cases
- Immune modulatory treatments as single agents or combined (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
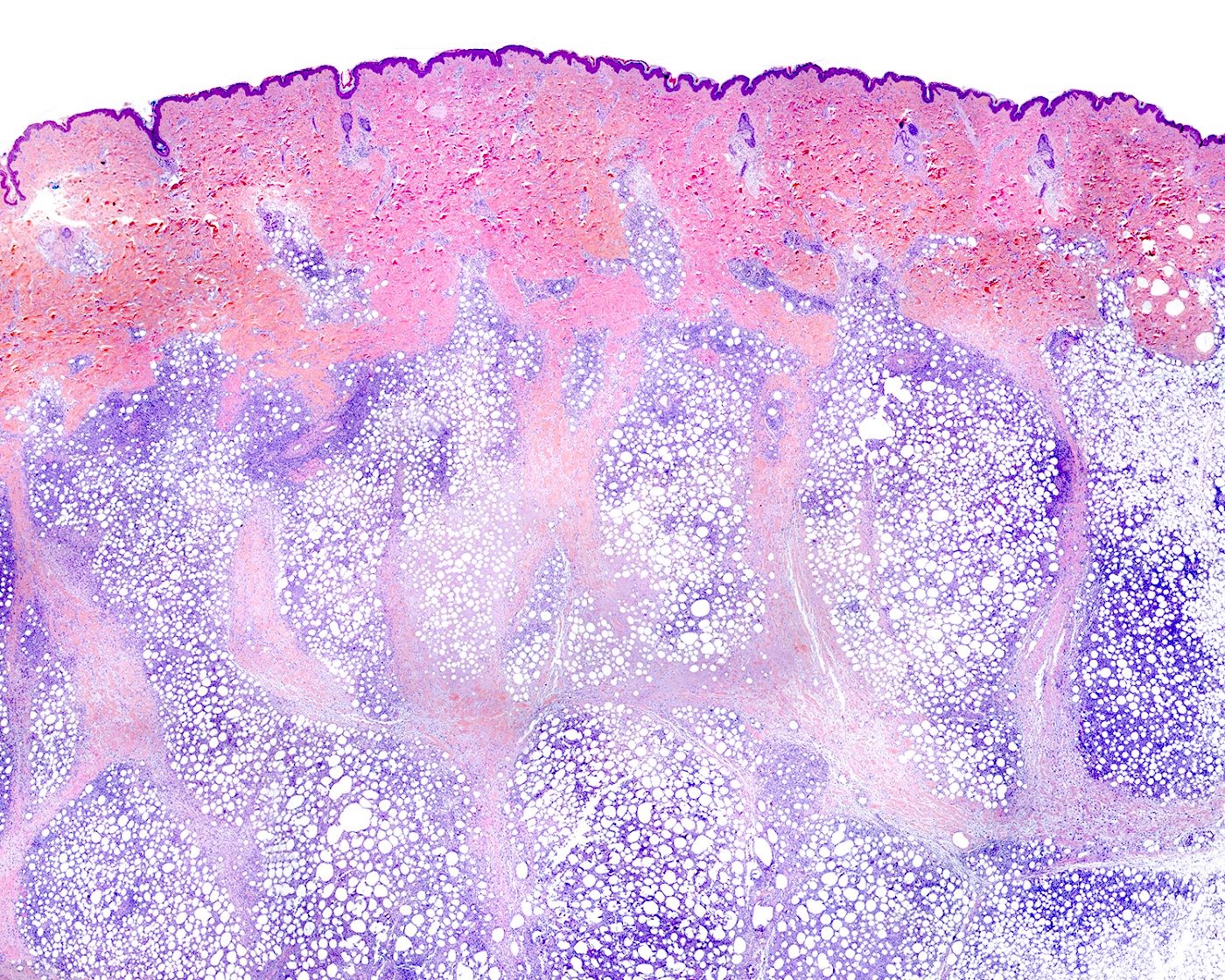
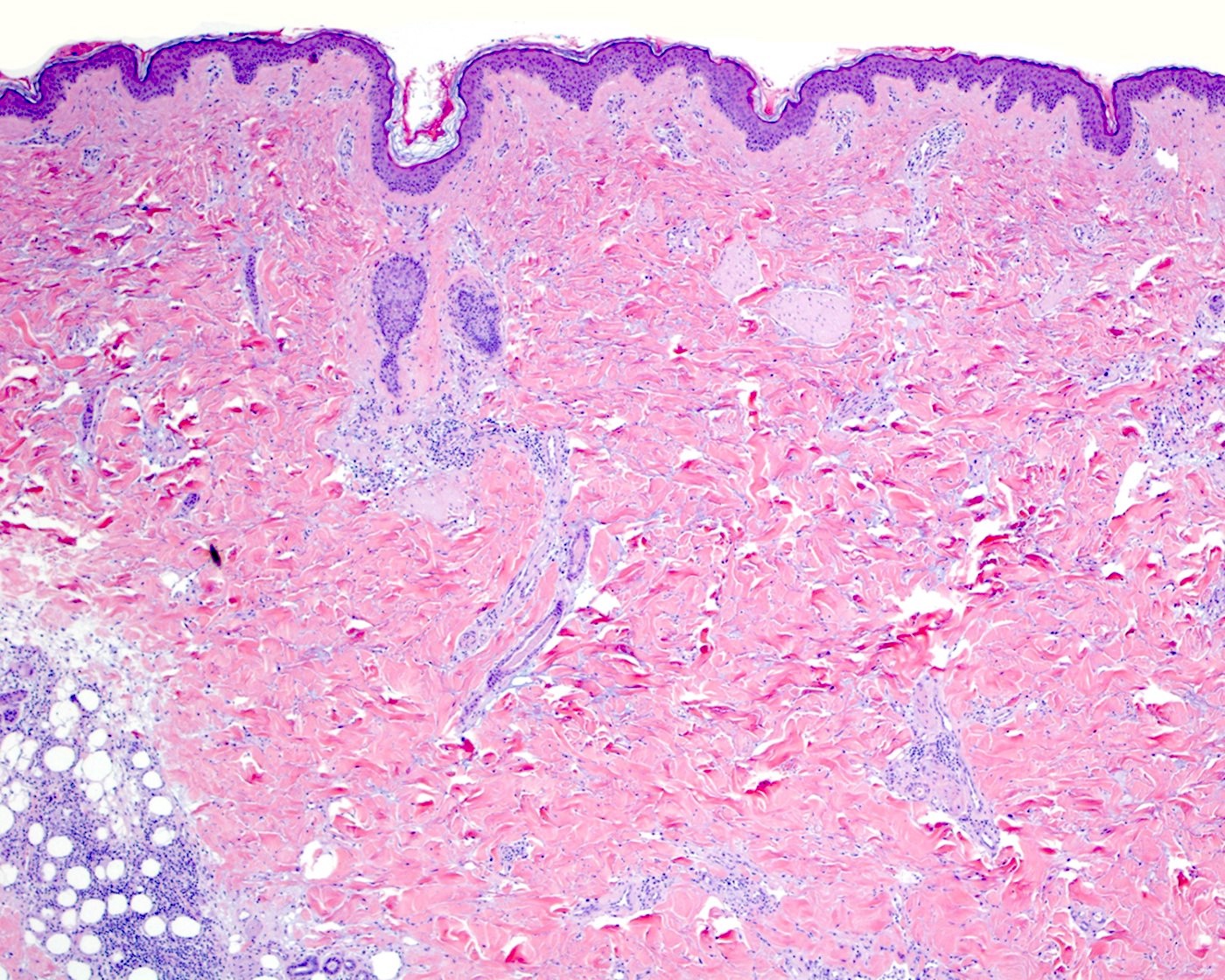
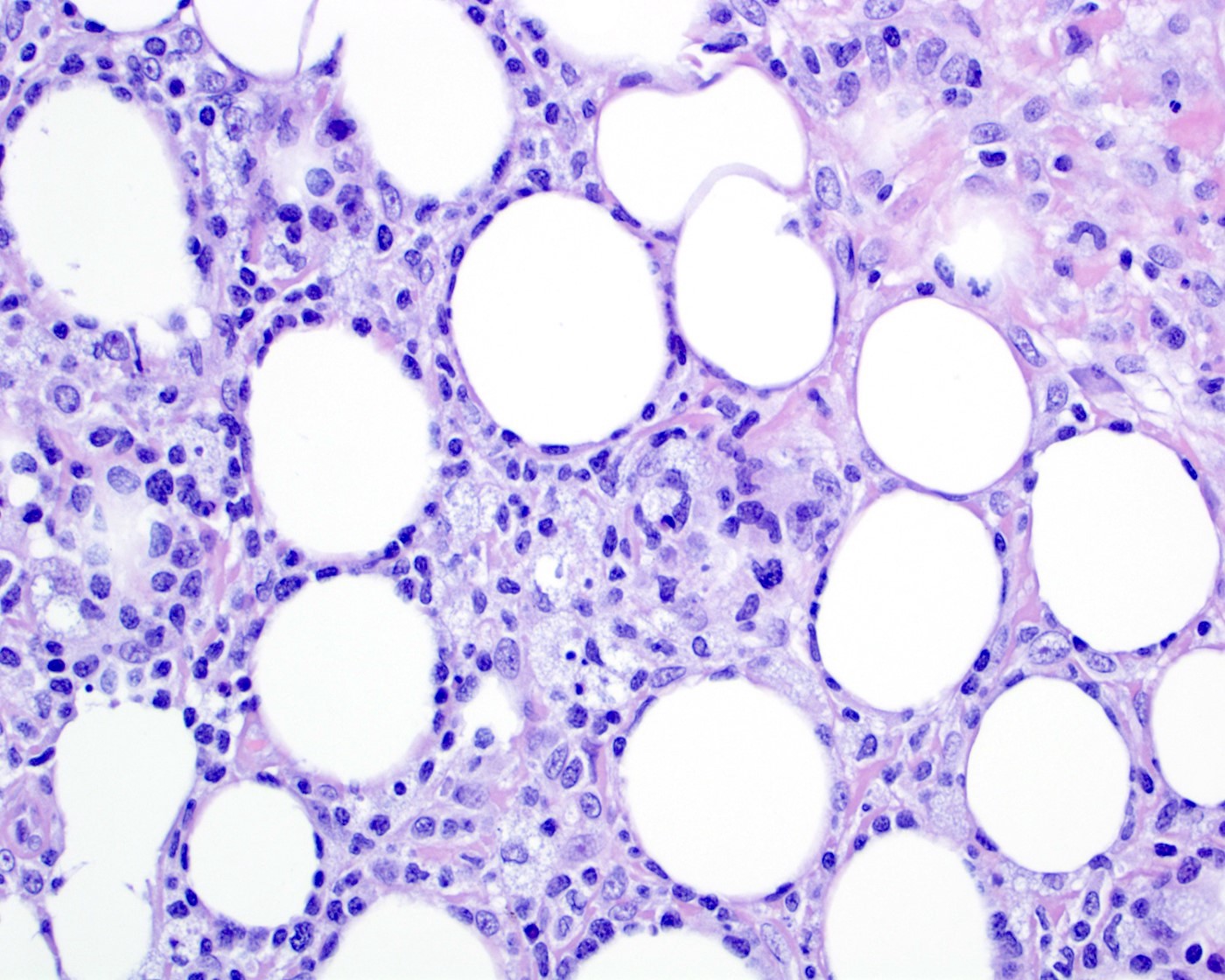
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Skin involvement (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Histopathology 2013;62:1057, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- Epidermis and dermis are usually spared
- Interface dermatitis, plasma cell aggregates, follicular plugging or mucin deposits may occur
- Minimal involvement by lymphoma cells of deep dermis can be observed
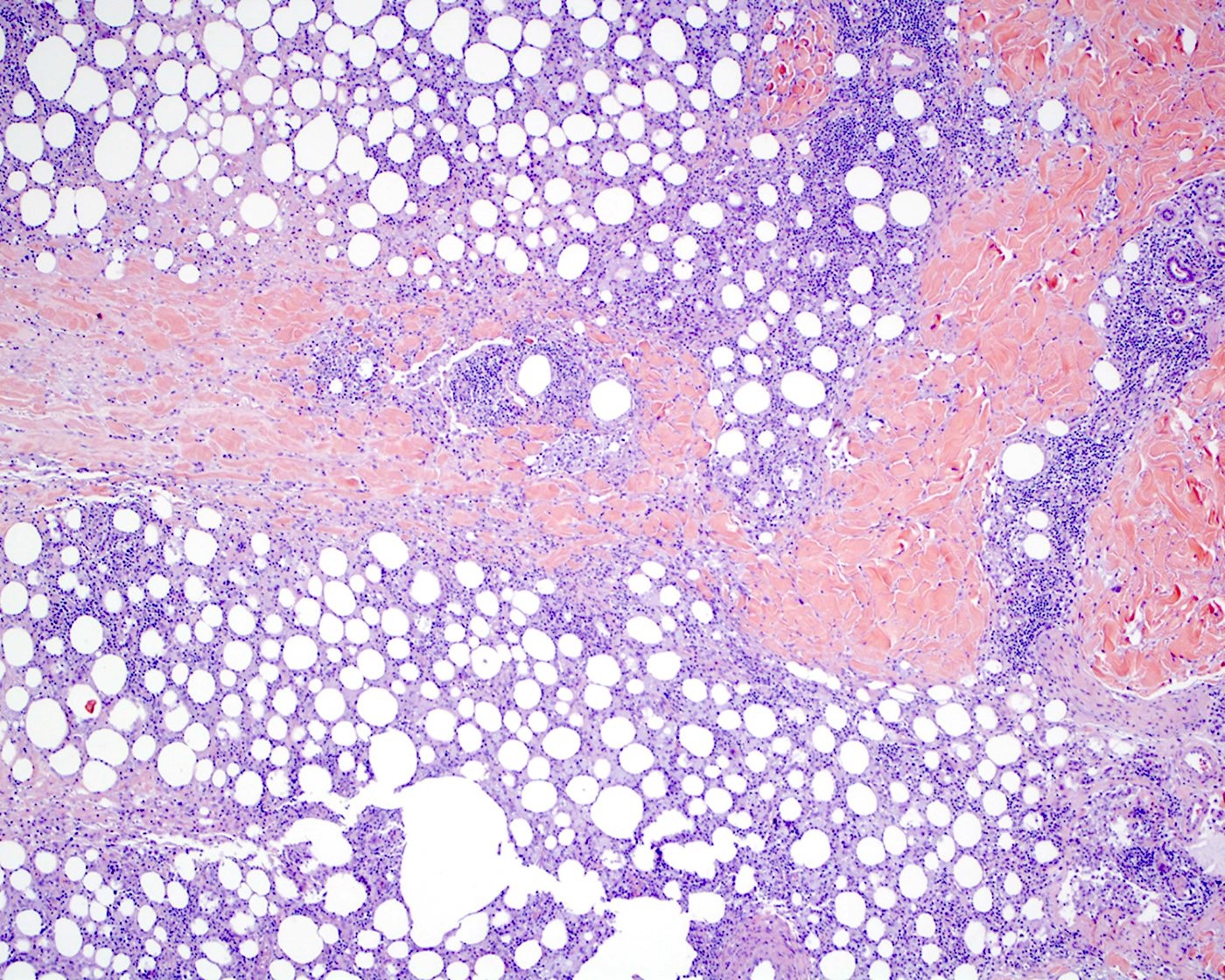
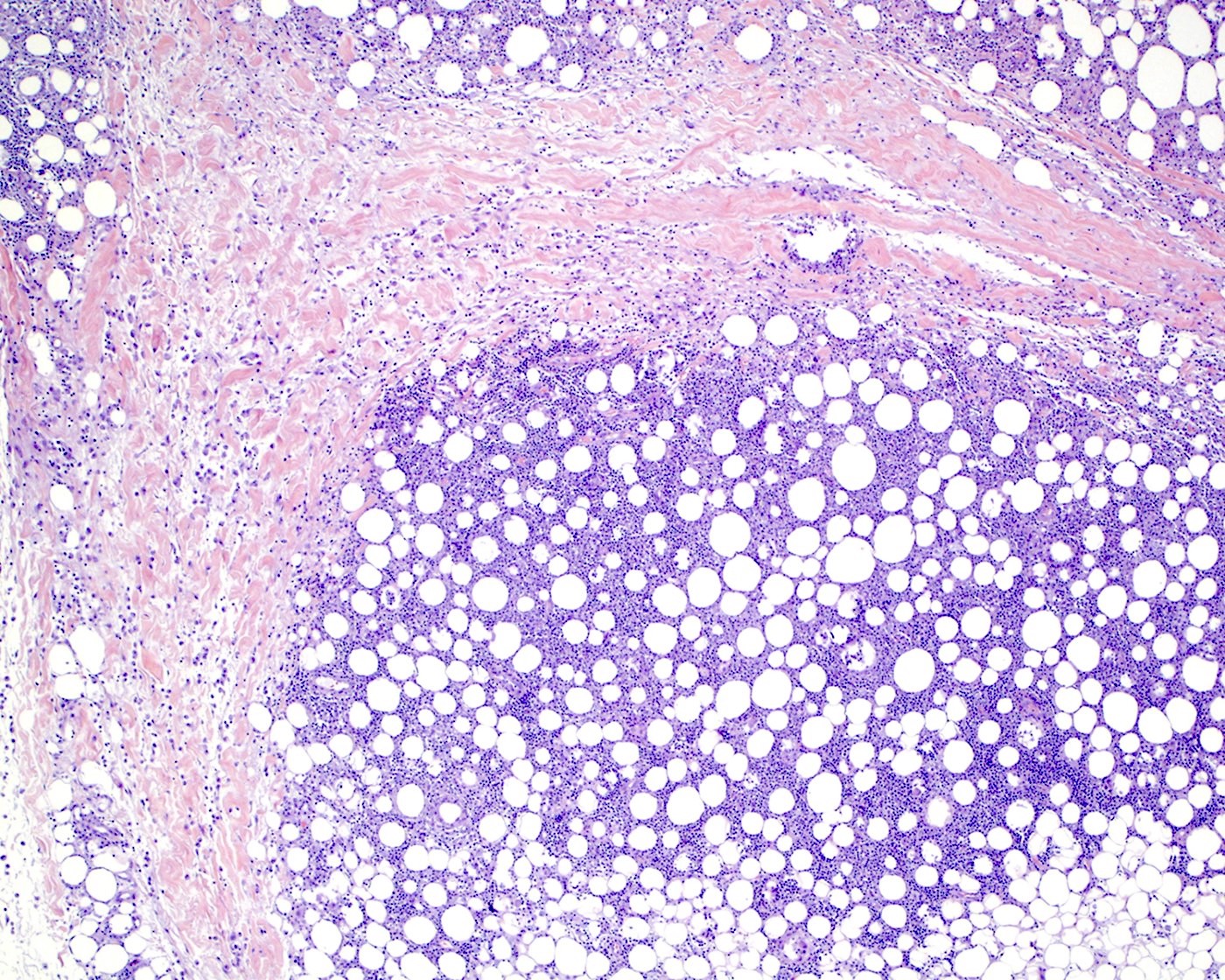
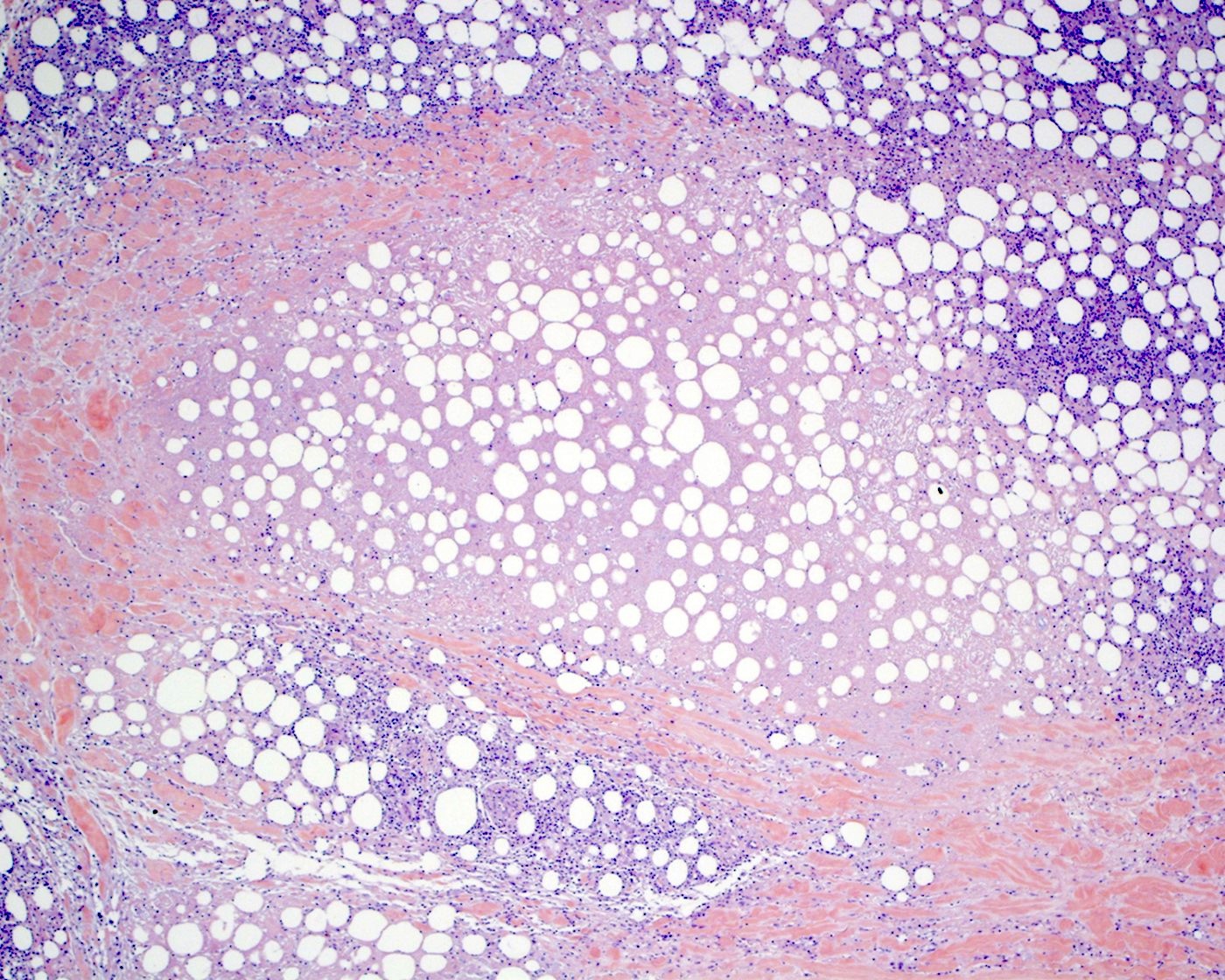
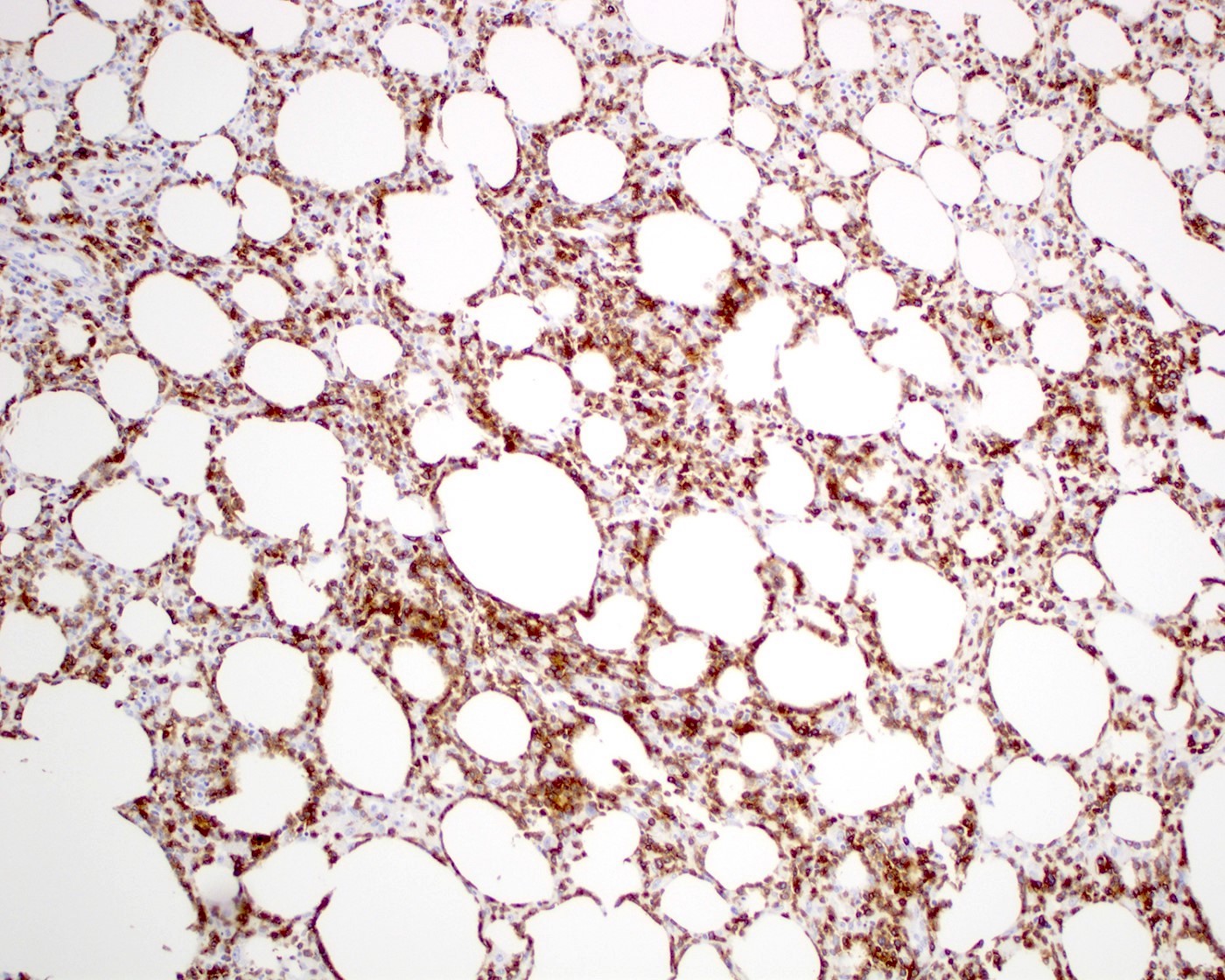
- Lobular infiltrate
- Variable size (small to intermediate) lymphocytes with hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei and scant pale / clear cytoplasm
- Subset of cases with large cell or pleomorphic morphology
- Variable density of atypical lymphocytes involving lobules and sparing septa
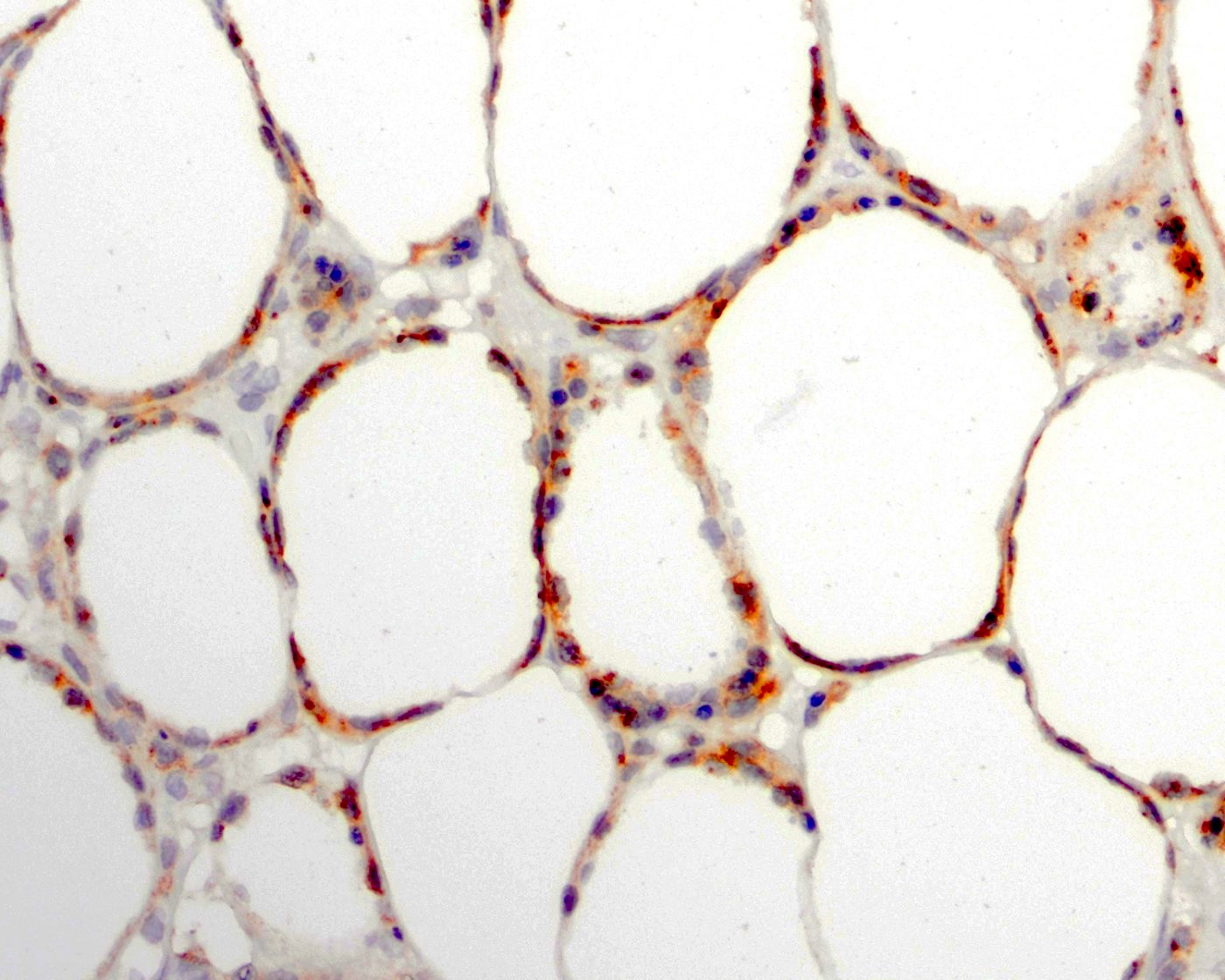
- Rimming adipocytes or lipid vacuoles
- Background
- Scattered reactive plasma cells and neutrophils
- Absence of plasmacytoid dendritic cells aggregates (> 10 cells)
- Reactive histiocytes, sometimes dense and forming granulomas or lipogranulomas
- Variable size (small to intermediate) lymphocytes with hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei and scant pale / clear cytoplasm
- Necrosis may vary from mild to extensive
- Karyorrhexis, mitotic figures and hemorrhage can be present
- Hemophagocytosis may be detected in skin or other tissues (e.g., bone marrow)
- Epidermis and dermis are usually spared
- Bone marrow is not involved by overt lymphoma cells but aggregates of small lymphocytes can be detected around adipocytes
Microscopic (histologic) images
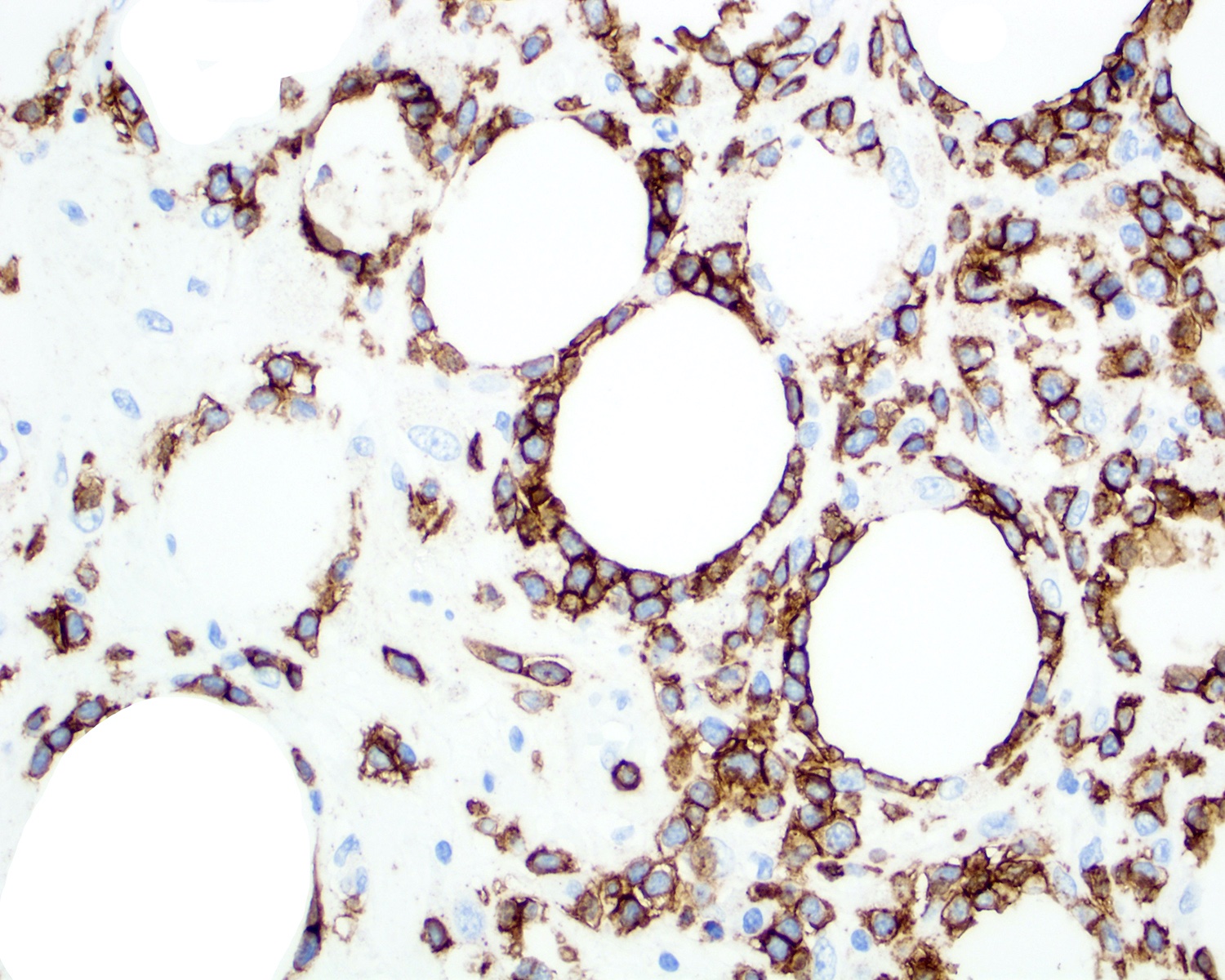
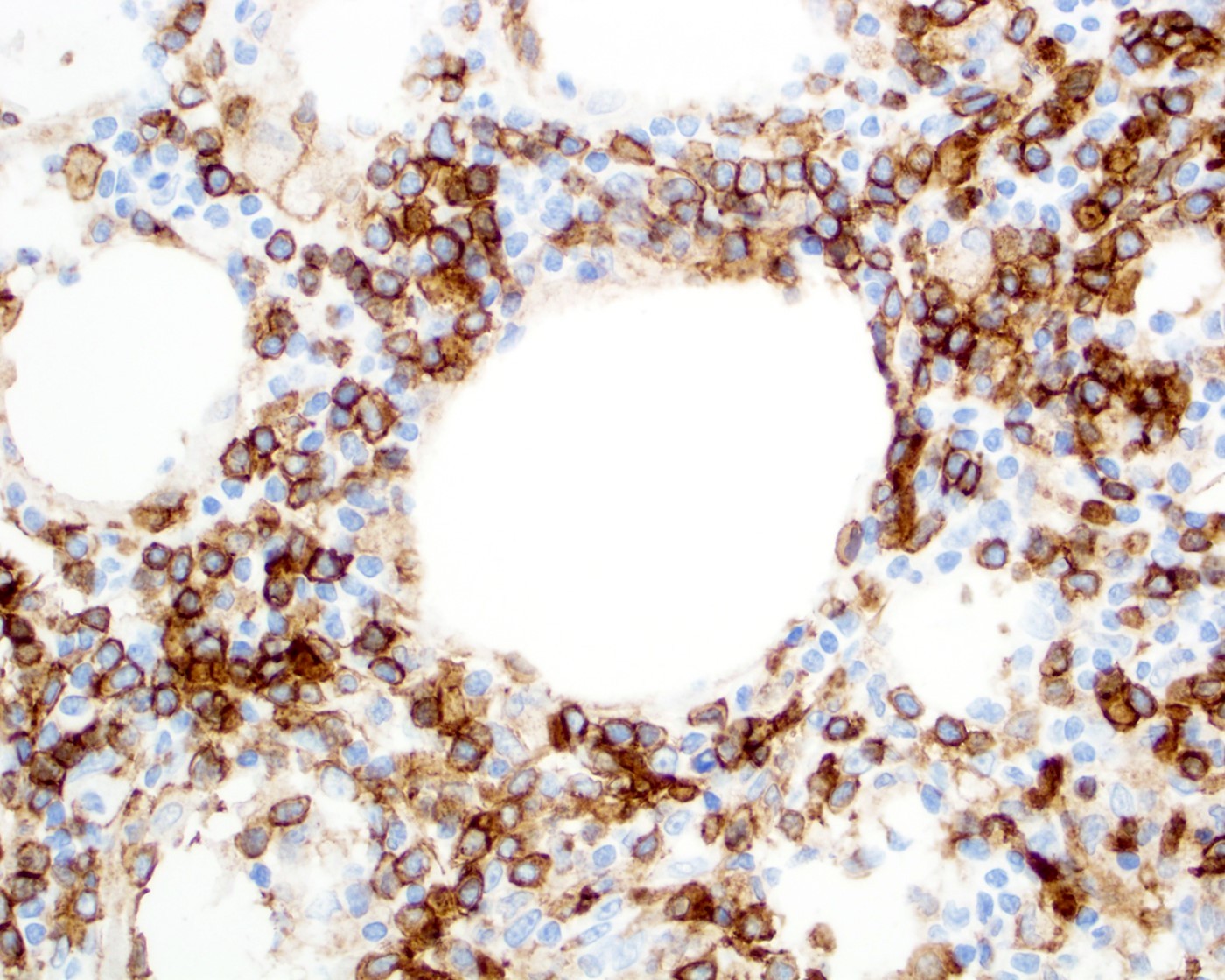
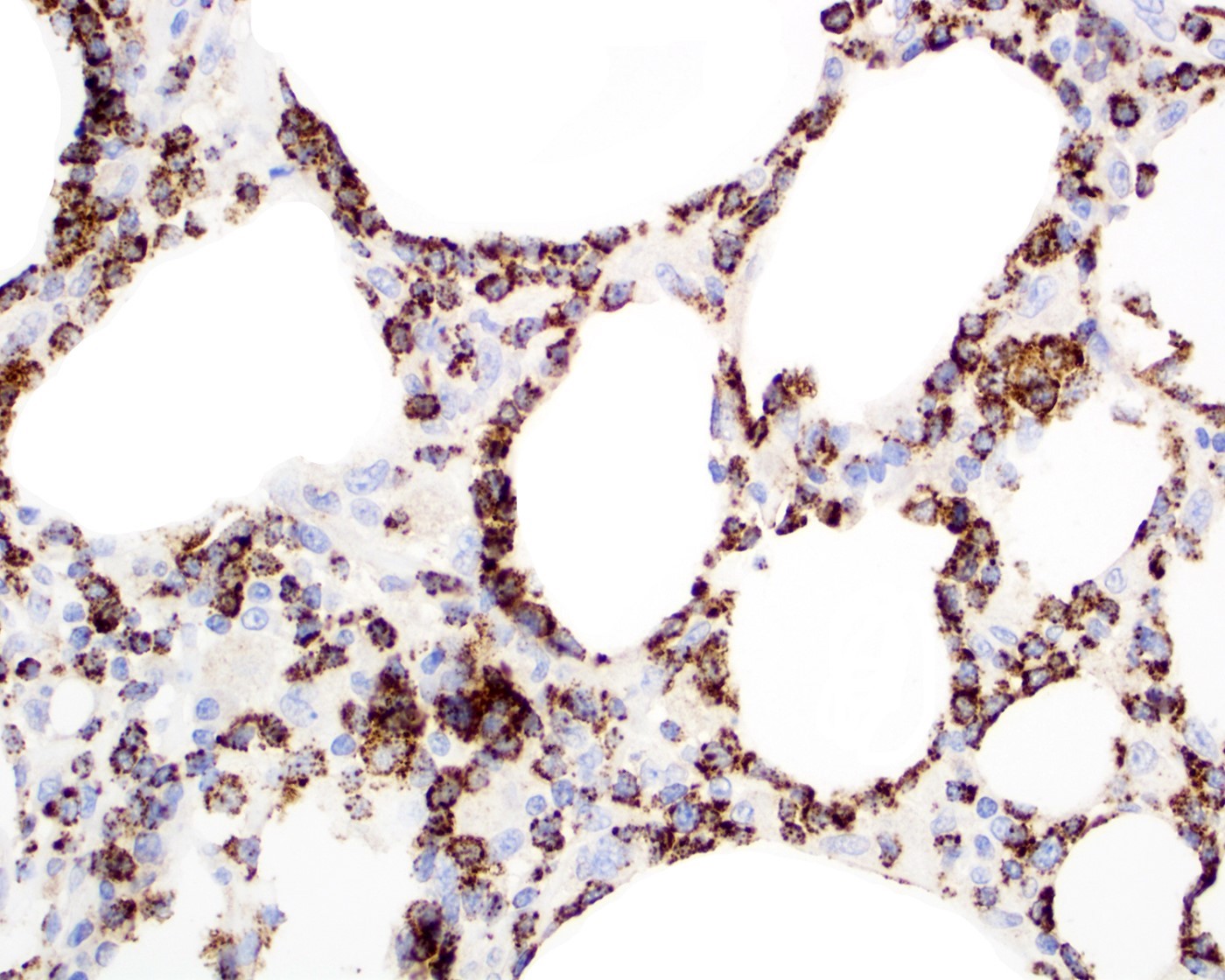
Positive stains
- CD3, CD8 (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Front Oncol 2021;11:650822, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160)
- Cytotoxic immunophenotype (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, Front Oncol 2021;11:650822)
- TIA1, granzyme B and perforin
- CD43 (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167)
- TCRα / β (βF1) (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- BAX and p53 (Mod Pathol 2002;15:625)
- Associated with large cell morphology
- CCR5, pSTAT3 and CXCR3 (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2016;30:1413, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160)
- TIM-3 (Blood 2020;135:1058)
- Ki67 proliferation index (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167)
- Present in hotspots (> 30%)
- Overall ~50%
Negative stains
- Aberrant loss of T cell markers (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167)
- B cell markers: CD20, CD79a, PAX5 (Front Oncol 2021;11:650822)
- CD30 (Front Oncol 2021;11:650822, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- CD45RA (JAMA Dermatol 2022;158:1167)
- CD56 (Front Oncol 2022;12:779230, Front Oncol 2021;11:650822, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160)
- BCL2 (Mod Pathol 2002;15:625)
- TCRγ (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- Epstein-Barr virus encoded small RNAs (EBER) (Front Oncol 2021;11:650822)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Monoclonal rearrangement of TCR (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160, J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954)
- Homozygous germline mutations of HAVCR2 (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Blood 2020;135:1058, Blood Adv 2021;5:3919, Nat Genet 2018;50:1650)
- HAVCR2Y82C is the most common mutation (hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2)
- Y82C, I97M and T101I are the most common recurrent germline mutations
- Y82C variants are more common in Polynesian and East Asian populations
- Associated with younger age, systemic illness, HLH or HLH-like syndrome, inflammatory microenvironment and shorter relapse free survival (RFS) when compared to wild type cases
- Enriched in genes involving IL6-JAK-STAT3, TNFα and NKκB signaling
- Y82C, I97M and T101I are the most common recurrent germline mutations
- Wild type cases
- Mutations in ASXL1, UNC13D, PIAS3 and KMT2D are more frequent
- Enrichment in CCR4
- HAVCR2Y82C is the most common mutation (hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2)
- Exome sequencing (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:740)
- Missense mutations in ARID1B
- Gene expression profiling (Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2130, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:160)
- Upregulation
- Cytotoxic genes: PRF1, NKG7, GZMB, GZMH and GZMA
- CD8 exhaustion: IL10, LAG3 and EOMES
- Th1 type cytokines
- KIR2DL3 and IDO1
- Downregulation
- Mast cell genes: HDC, CPA3 and MTA3
- B cell genes: KDR
- Apoptosis genes: MIB1 and EFHC1
- Dendritic cell genes: SP1, CCL3 and CD209
- Upregulation
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right thigh lesion, punch:
- Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: According to clinical notes, this is a 37 year old woman with a history of a solitary, tender and painless lesion in distal thigh (3 cm in the greater axis) that the patient noted wax and wane for several months.
- Histologic sections of the specimen designated right thigh lesion demonstrate a punch skin biopsy that includes epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue. Epidermis is unremarkable. Deep dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue show dense small to medium sized lymphoid cells, neutrophils and histiocytes. The lymphocytes show irregular nuclear contours, hyperchromatic chromatin and scant pale cytoplasm. The distribution is mainly involving the lobules with fat rimming and sparing the septa. Mitotic figures are frequent and karyorrhectic debris is present.
- Immunohistochemical studies showed the atypical lymphocytes are positive for CD2, CD3, CD8, CD43, TIA1, perforin and TCRα-β (βF1). The abnormal lymphocytes are negative for CD4, CD7, CD30, CD56 and TCRγ / δ. Ki67 index is ~70% (variable, ranging from 40 - 100%). Epstein-Barr virus encoded small RNAs (EBER) in situ hybridization is negative.
- Polymerase chain reaction to assess for clonality of T cell receptors gamma and delta chains clonal TCRβ (TRB) and polyclonal TCRγ (TRG) and TCRδ (TRD).
Differential diagnosis
- Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:24, Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2023;19:27, Histopathology 2013;62:1057, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:745):
- F > M
- Multiple or single lipoatrophy, erythema or subcutaneous nodules
- Extremities (upper arms) > face > trunk
- Epidermal and dermal changes
- Lymphocytic lobular / septal panniculitis with mild or no cytological atypia
- Intradermal mucin, hyaline lipomembranous changes, mild vasculitis, reactive germinal centers and plasma cells
- Aggregates of CD123+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- Absence of atypical T cells
- Low Ki67 proliferation index (~< 10%)
- Usually polyclonal TCRγ gene rearrangement
- Rare cases with monoclonal peak
- Cytophagic histiocytic panniculitis (Ital J Pediatr 2014;40:17):
- Infiltration of subcutaneous by T cells and phagocytic histiocytes
- Isolated in skin or associated with other malignancies
- Skin lesions may remain
- No evidence of monoclonal rearrangements of TRB or TRG gene
- Cold panniculitis (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954):
- Physical panniculitis
- Appropriate clinical history
- More common in pediatric patients
- Face (chin and cheeks)
- Different chemical composition of the adipose tissue
- Face (chin and cheeks)
- Adults: usually after chronic use of ice pack or environmental exposure
- Lymphoid infiltrate of lobular distribution
- Increased density along the dermal - subcutaneous transition, dermal perivascular and periadnexial regions
- Dermal mucin and interface dermatitis may be present
- No evidence of monoclonal TCB or TRG gene rearrangements
- Lyme disease (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:954):
- Rare cases presenting as lobular panniculitis
- Dense lymphocytic infiltrate in subcutaneous tissue with scattered plasma cells
- Small to medium size and moderate atypia
- No extension to overlying dermis or epidermis
- Dense lymphocytic infiltrate in subcutaneous tissue with scattered plasma cells
- Predominance of CD8+ cells
- Identification of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by PCR or positive serology
- Rare cases presenting as lobular panniculitis
- Atypical lymphocytic lobular panniculitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:206):
- Indolent condition with spontaneous regression
- Controversial entity
- Lobular infiltration of clonal, small to intermediate sized T cells and mild nuclear atypia
- Usually less dense infiltrate
- Adipocyte rimming is less frequent
- Hemorrhage and karyorrhexis are usually absent
- Good prognosis
- Indolent condition with spontaneous regression
- Primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177):
- Plaques, nodules and tumors with rapid progression and ulceration
- Involvement of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue
- Medium to large size lymphocytes with irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin and eosinophilic cytoplasm
- CD3+, CD7+, CD5-, CD4-, CD8-
- TIA1+, granzyme B+, perforin+
- TCRδ+, TCRγ+, TCRβ (βF1)-
- Poor prognosis
- Primary cutaneous CD30+ T cell lymphoproliferative disorders (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177):
- Primary cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021;35:658):
- Solitary or disseminated papulonodular or tumor lesions with rapid growth and necrosis
- Nodular or diffuse infiltrate in dermis and subcutaneous tissue
- Variable morphology, usually large, pleomorphic cells
- Epidermotropism absent or focal
- CD3+ / CD4- / CD8- or CD3+ / CD4+ / CD8-
- CD8+ may also occur
- Poor prognosis
- 3 year overall survival: ~60%
- 5 year overall survival: ~50%
- Acute myeloid leukemia involving skin (An Bras Dermatol 2018;93:216):
- Variable clinical presentation
- Diffuse infiltration of dermis and hypodermis
- Neoplastic cells can rim adipocytes
- Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma involving skin (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177):
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma?
- Frequently presents with an aggressive clinical behavior
- Localized or multiple subcutaneous nodules are the most common clinical presentation
- Lymph nodes are usually involved at initial diagnosis
- Somatic mutations of HAVCR2 are common
Board review style answer #1
B. Localized or multiple subcutaneous nodules are the most common clinical presentation. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma usually presents as localized or multiple subcutaneous nodules, usually in the legs, arms or trunk and rarely with lymph node involvement. Germline mutations of HAVCR2 are classically described as a predisposing factor in up to 85% of patients.
Comment Here
Reference: Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. CD3+, CD4-, CD8+, TIA1+, granzyme B+, TCRαβ+. The typical immunophenotype is CD3+, CD4-, CD8+, TIA1+, granzyme B+ and TCRαβ+. The picture shows positivity in the neoplastic cells and highlights rimming of adipocytes.
Comment Here
Reference: Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma