Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Marques-Piubelli ML, Torres-Cabala CA, Miranda RN. Primary cutaneous gamma delta. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonBcutangammadelta.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Primary cutaneous lymphoma with a mature phenotype, expressing the T cell receptor gamma delta and usually characterized by aggressive clinical behavior (J Invest Dermatol 1991;96:718, Leukemia 2022;36:1720, J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Br J Dermatol 2019;181:848, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- Used to be lumped together with cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma rare subtypes but it is now a distinct entity in the 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Hematolymphoid Tumors
- Prior to 2005, the cases were grouped as subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
- First described in 1991
- Used to be lumped together with cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma rare subtypes but it is now a distinct entity in the 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Hematolymphoid Tumors
Essential features
- Primary cutaneous lymphoma with a mature T cell phenotype and expression of the T cell receptor gamma delta; it is usually characterized by an aggressive clinical behavior (J Invest Dermatol 1991;96:718, Leukemia 2022;36:1720, J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Br J Dermatol 2019;181:848, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- Rare (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Br J Dermatol 2019;181:848, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36, Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206)
- < 1% of all primary cutaneous lymphomas
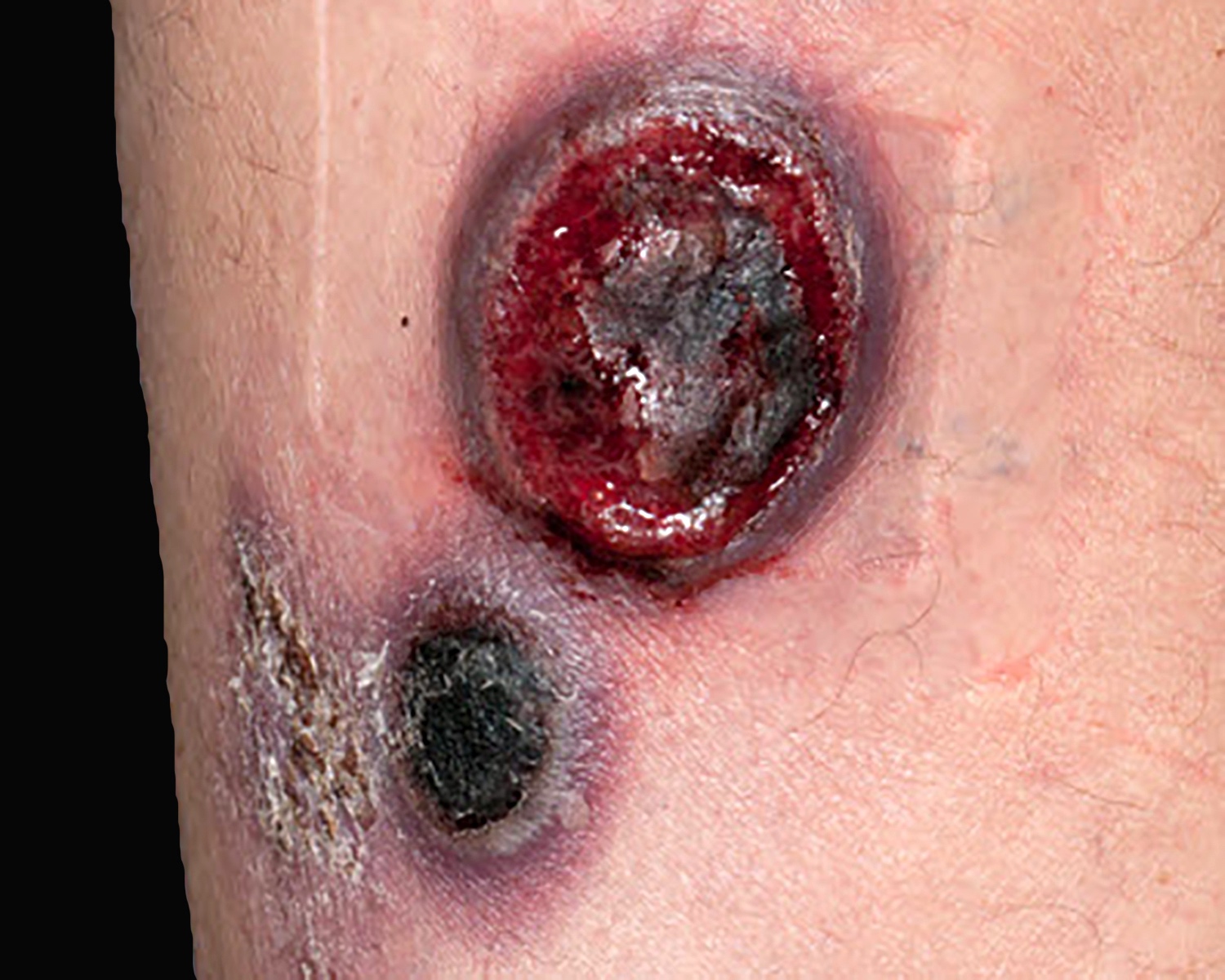
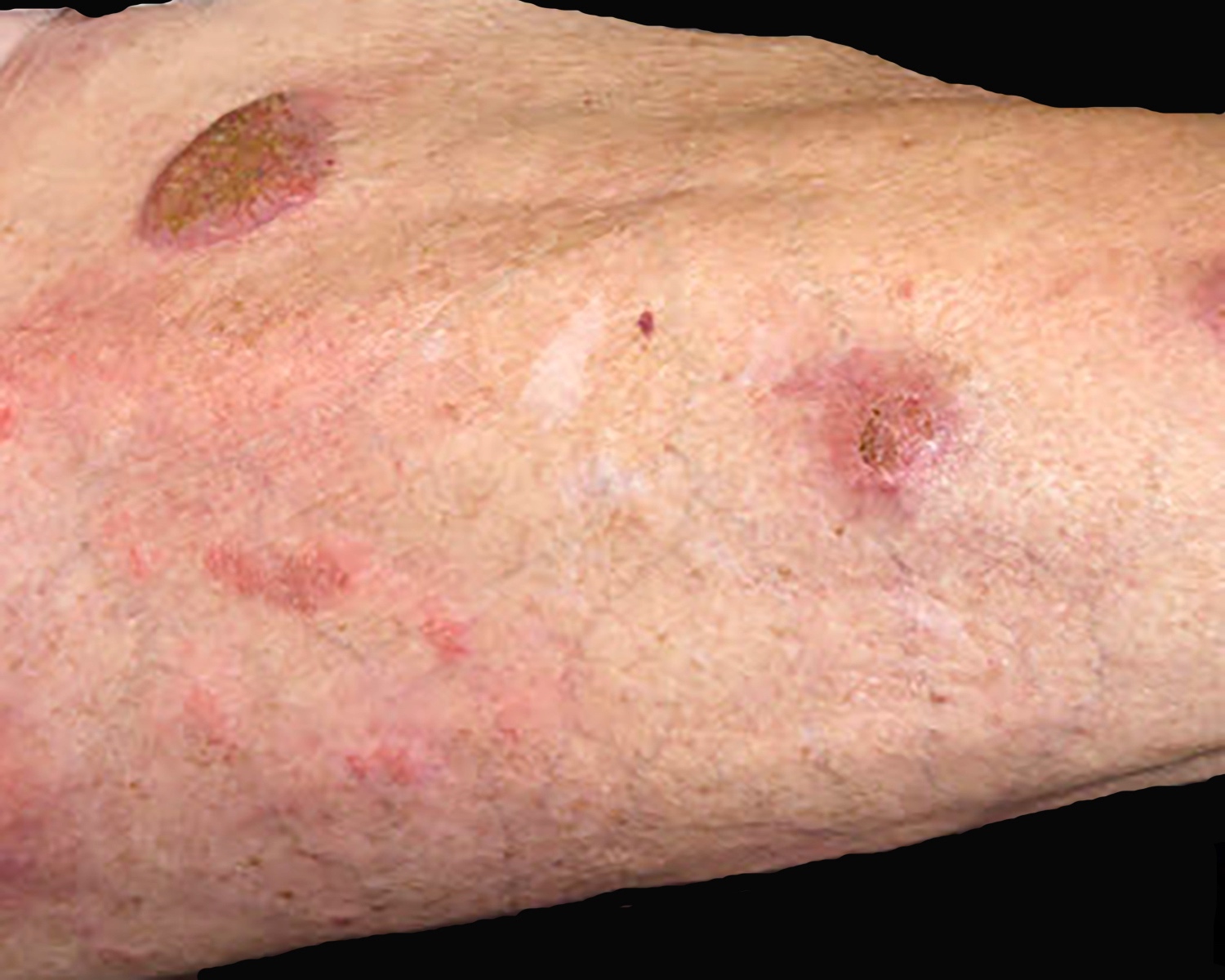
- Multifocal deeply seated plaques, nodules and tumors in extremities and trunk that usually present as tumoral ulcers (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- Rapid progression
Terminology
- Obsolete terms:
- Histiocytic cytophagic panniculitis
- Weber-Christian disease
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Br J Dermatol 2019;181:848, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36, Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206)
- < 1% of all primary cutaneous lymphomas
- Incidence: 0.4 cases per 10 million people
- Sixth and seventh decade (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Br J Dermatol 2019;181:848, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- Median age is 62 years
- M = F or slightly M > F (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Blood 2003;101:3407, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- More common in Caucasians (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515)
Sites
- Multifocal lesions in extremities and trunk (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407)
Pathophysiology
- Chronic antigen stimulation / antigen modulation or immunosuppression may be involved in gamma delta T cell proliferation (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
Etiology
- T cell receptors (TCR) are responsible for antigen recognition (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Front Immunol 2021;12:627139, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407)
- TCRs are usually classified in 2 groups (alpha beta and gamma delta chains) based on the type of antigen binding site
- Linked with CD3 subunits; crucial for TCR insertion and signaling
- TCR alpha and TCR gamma: chromosome 14
- TCR beta and TCR delta: chromosome 7
- Double negative 3 (DN3) stage (CD4- / CD8- / CD44- / CD25+) is determinant for the differentiation of alpha beta or gamma delta subsets
- Gamma delta T cells are < 5% of circulating T cells
- More abundant in spleen (red pulp)
- Less dependent on thymic maturation
- Strong plasticity and regulation of macrophage homeostasis
- Role in B cell maturation
- Possible role in the initial phase of infection: innate and adaptive immunity
- Nonprocessed major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins, lipid and direct bacterial antigens
- Memory-like characteristics
- TCR diversity
- Rearrangement of several segments: C (constant), D (diversity), J (joining) and V (variable)
- V1δ and V2δ: > 97% of gamma delta T cells
- V1δ
- Thymus, intestine and spleen
- More common in cases arising in superficial layers of skin
- Cytokines: IL10, IL2, IL4, IL17, IFN gamma and TNF alpha
- V2δ
- Peripheral blood and lymph node
- More common in panniculitic cases
- Cytokines: IL21, IL17, IL24, IFN gamma and TNF alpha
- V3δ
- Peripheral blood and liver
- Cytokines: IL4, IL10, IL17, IFN gamma and TNF alpha
- V1δ
- V1δ and V2δ: > 97% of gamma delta T cells
- Addition of nucleotides to the rearranged genes
- Rearrangement of several segments: C (constant), D (diversity), J (joining) and V (variable)
- TCRs are usually classified in 2 groups (alpha beta and gamma delta chains) based on the type of antigen binding site
Clinical features
- Multifocal, deeply seated plaques, nodules and ulcerated tumors in extremities and trunk (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- More superficial and predominantly epidermotropic presentation also occurs (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- Rapid progression
- Plaques are more common
- Ulceration in ~50% of cases
- Rare cases of indolent clinical course or following a diagnosis of mycosis fungoides (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:570, Int J Dermatol 2014;53:e82, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:350, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:50, J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:1063)
- Indolent cases usually present with localized disease
- May transform to aggressive clinical course
- Predominantly epidermotropic variant also occurs (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- B symptoms (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- Extracutaneous disease and hemophagocytic syndrome (HLH): variable, as high as 50% of cases (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707)
- Lung, thyroid, breast and testis are the most frequently involved
- Mucosal involvement is described (Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- Rare involvement of bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- History of autoimmune disease: ~25%
Diagnosis
- Association of clinicopathologic features and correct interpretation of histologic findings (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
- Bone marrow and PET / CT are required for complete staging (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1)
Laboratory
- No specific laboratory findings (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1)
- Elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): up to 30%
- Cytopenias
- Isolated or associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognosis (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Blood 2003;101:3407, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:375)
- Complete response: 20 - 30%
- Median overall survival is ~15 - 30 months
- 5 year overall survival is 10 - 20%
- Cases with predominantly epidermotropic distribution have a better prognosis than those with dermal / subcutaneous involvement
- Staging is according to the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) / European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) for cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides / Sézary syndrome (Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206)
Case reports
- 45 year old woman with an indolent primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma mimicking lupus erythematous profundus (Front Oncol 2020;10:133)
- 54 year old man with primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma mimicking leukemia cutis by chronic lymphocytic leukemia (J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:1015)
- 60 year old man with primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma in complete remission after bendamustine monotherapy (JAMA Dermatol 2020;156:1029)
- 60 year old man with predominantly epidermotropic primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma with aggressive clinical behavior albeit bland histopathological findings (Am J Dermatopathol 2016;38:e147)
- 64 year old woman with primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma and dermatomyositis initially diagnosed as subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2022;9:143)
- 67 year old man with a previous history of rheumatoid arthritis in treatment with etarnercept and a diagnosis of primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma (Acta Derm Venereol 2009;89:653)
Treatment
- No standard treatment and poor response to treatment (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1093, Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
- Localized disease
- Radiation therapy
- Disseminated disease
- Immunotherapy
- Brentuximab (for CD30 positive cases)
- Mogamulizumab
- Alemtuzumab
- Multiagent chemotherapy with or without allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine and prednisone (CHOP)
- Etoposide and CHOP (EPOCH)
- Ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide (ICE)
- Hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and dexamethasone (hyper CVAD)
- Immunotherapy
- Localized disease
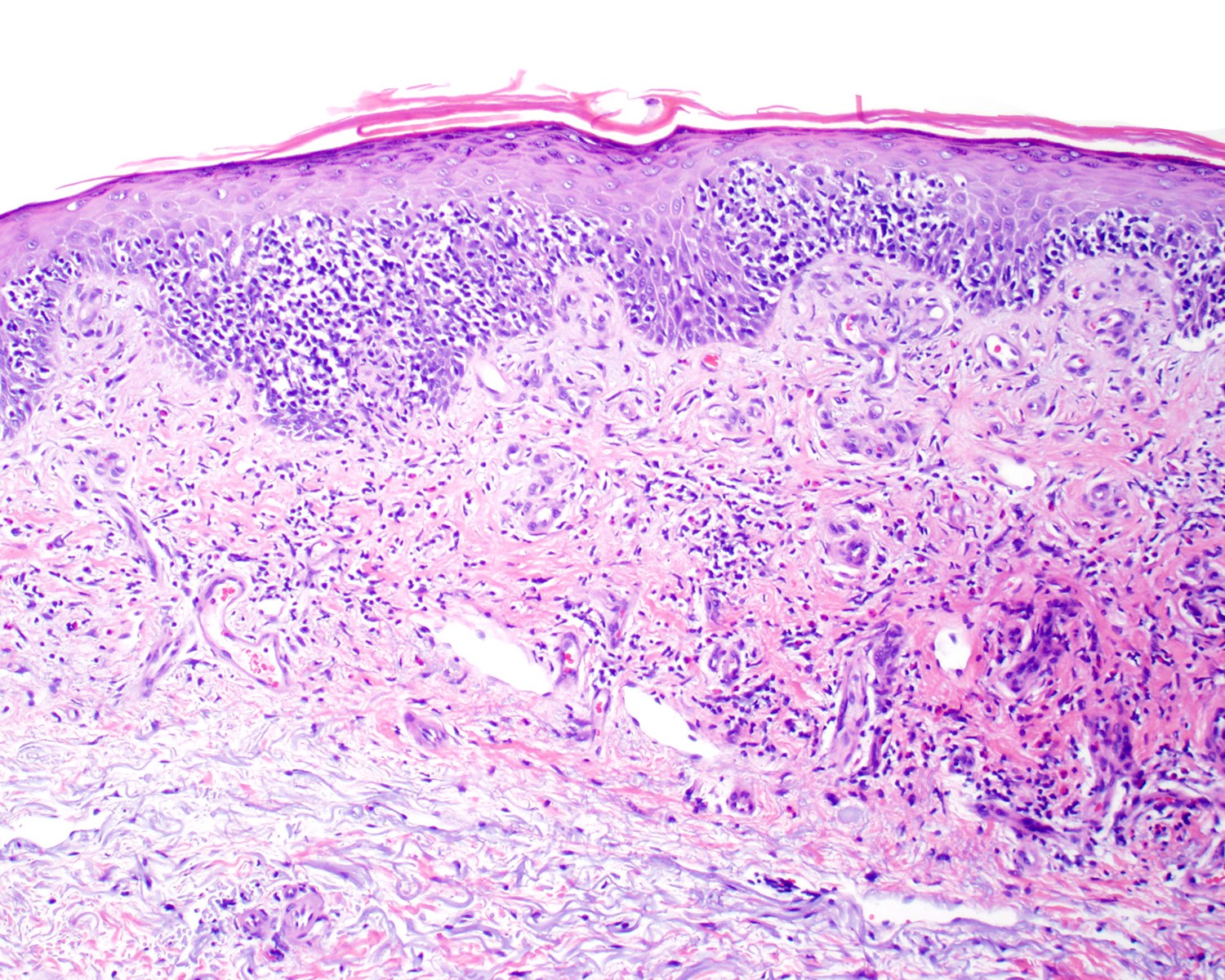
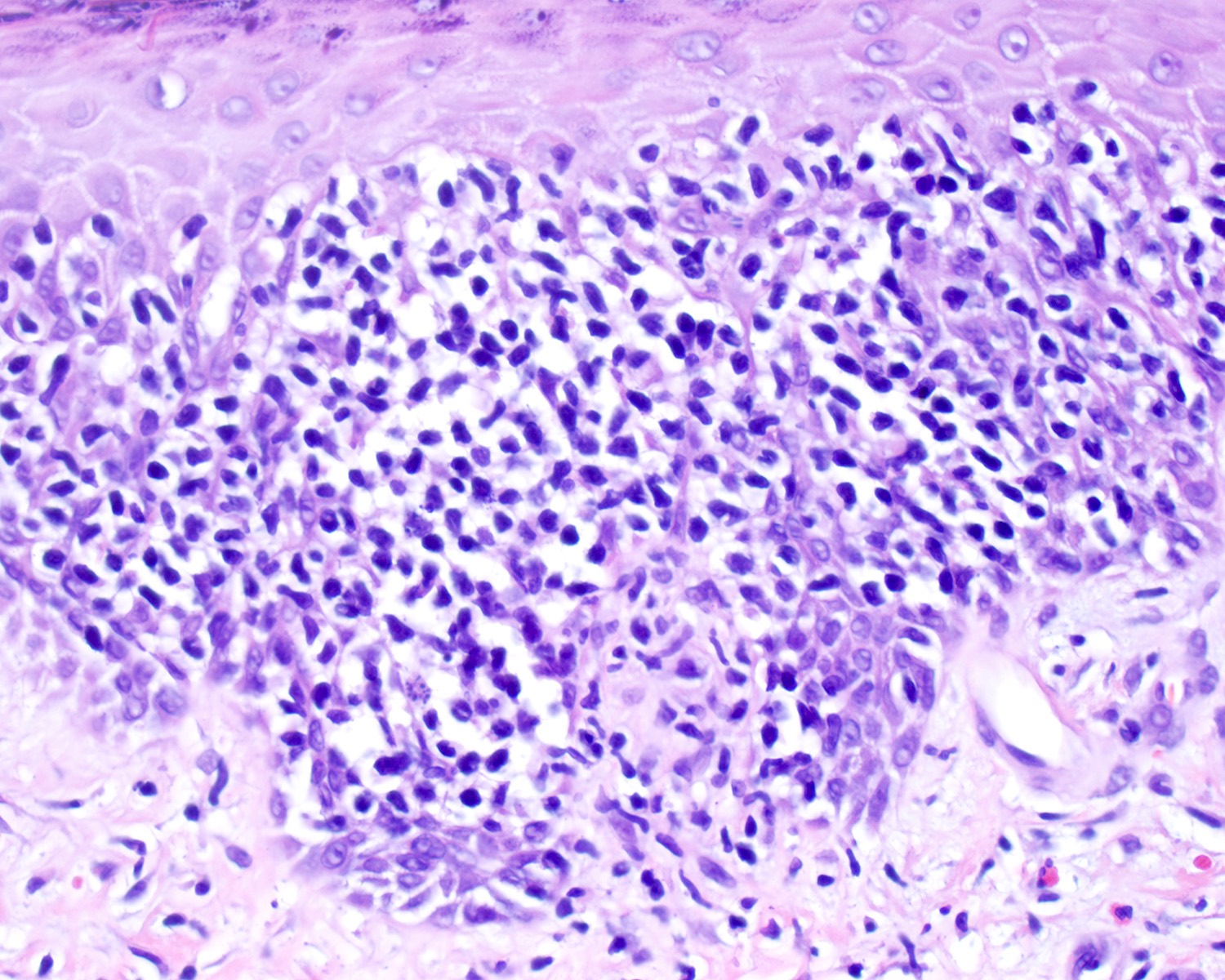
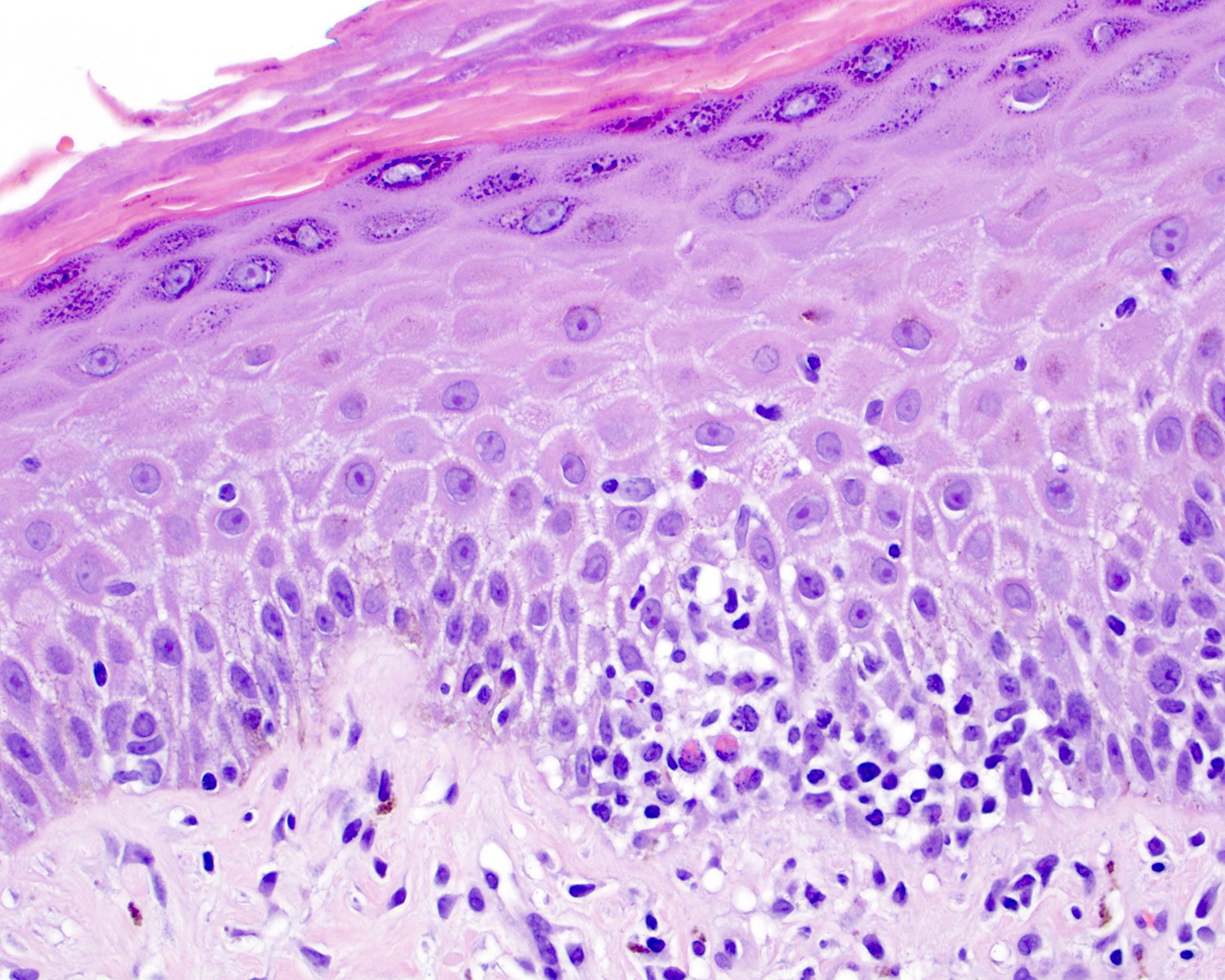
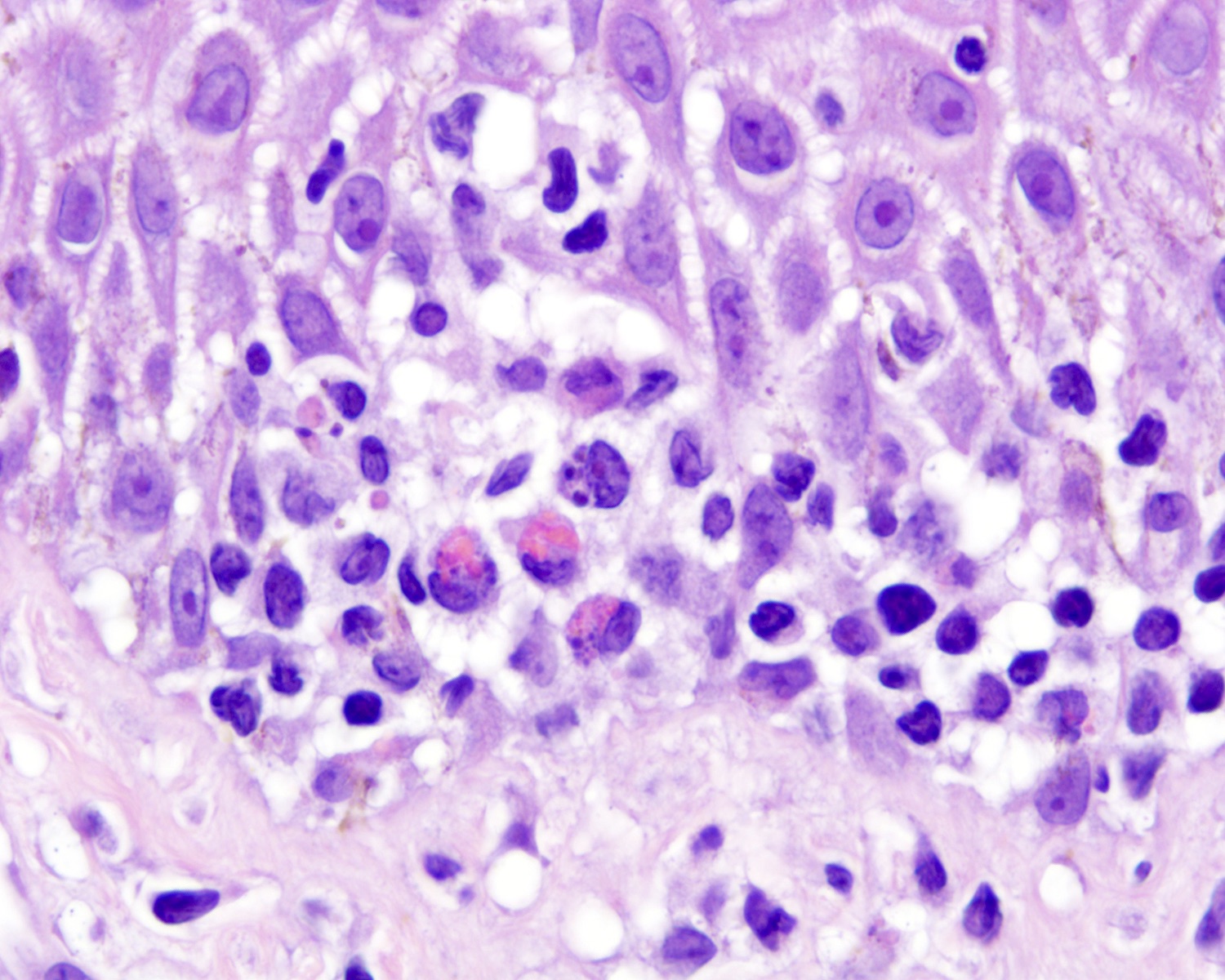
Microscopic (histologic) description
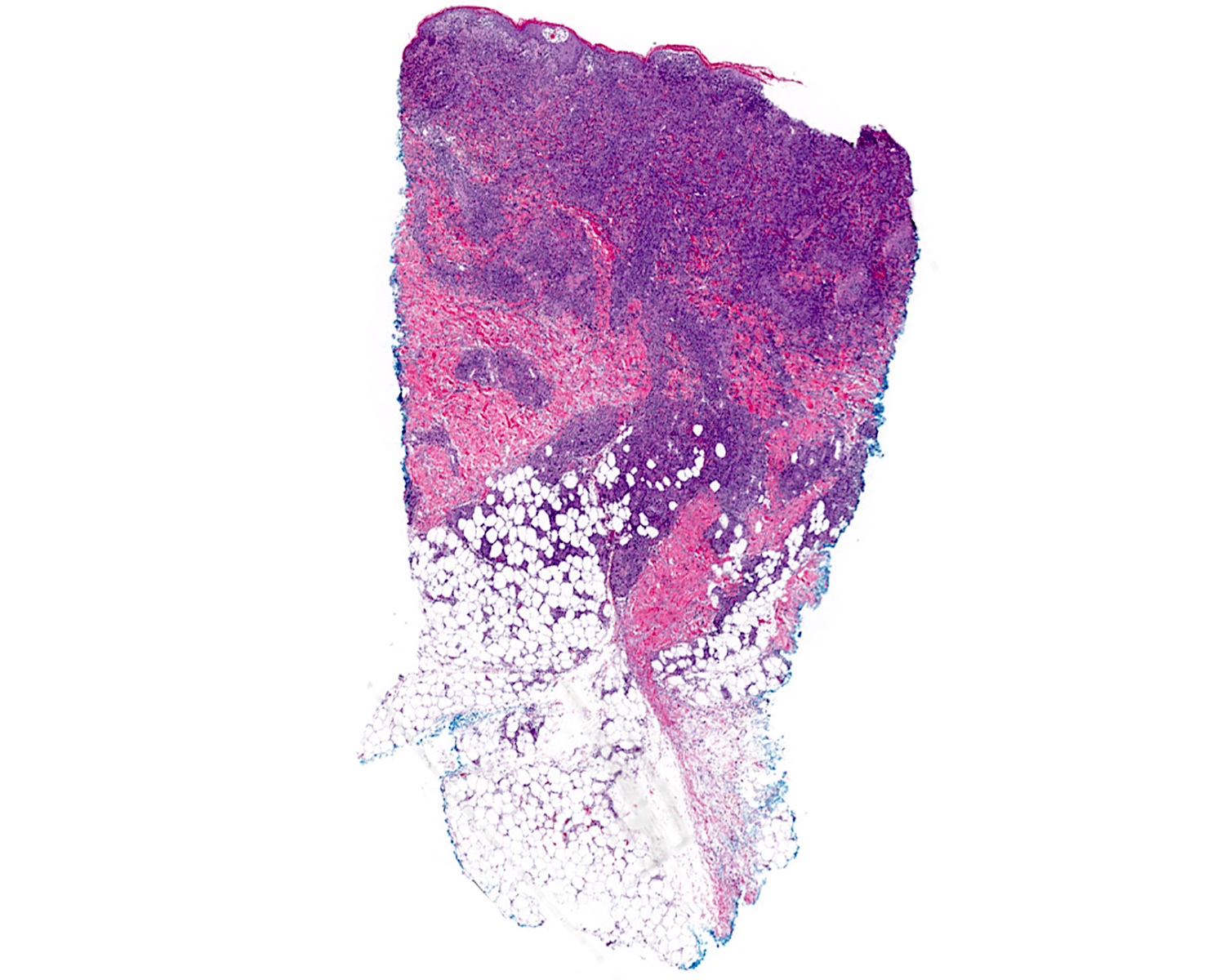
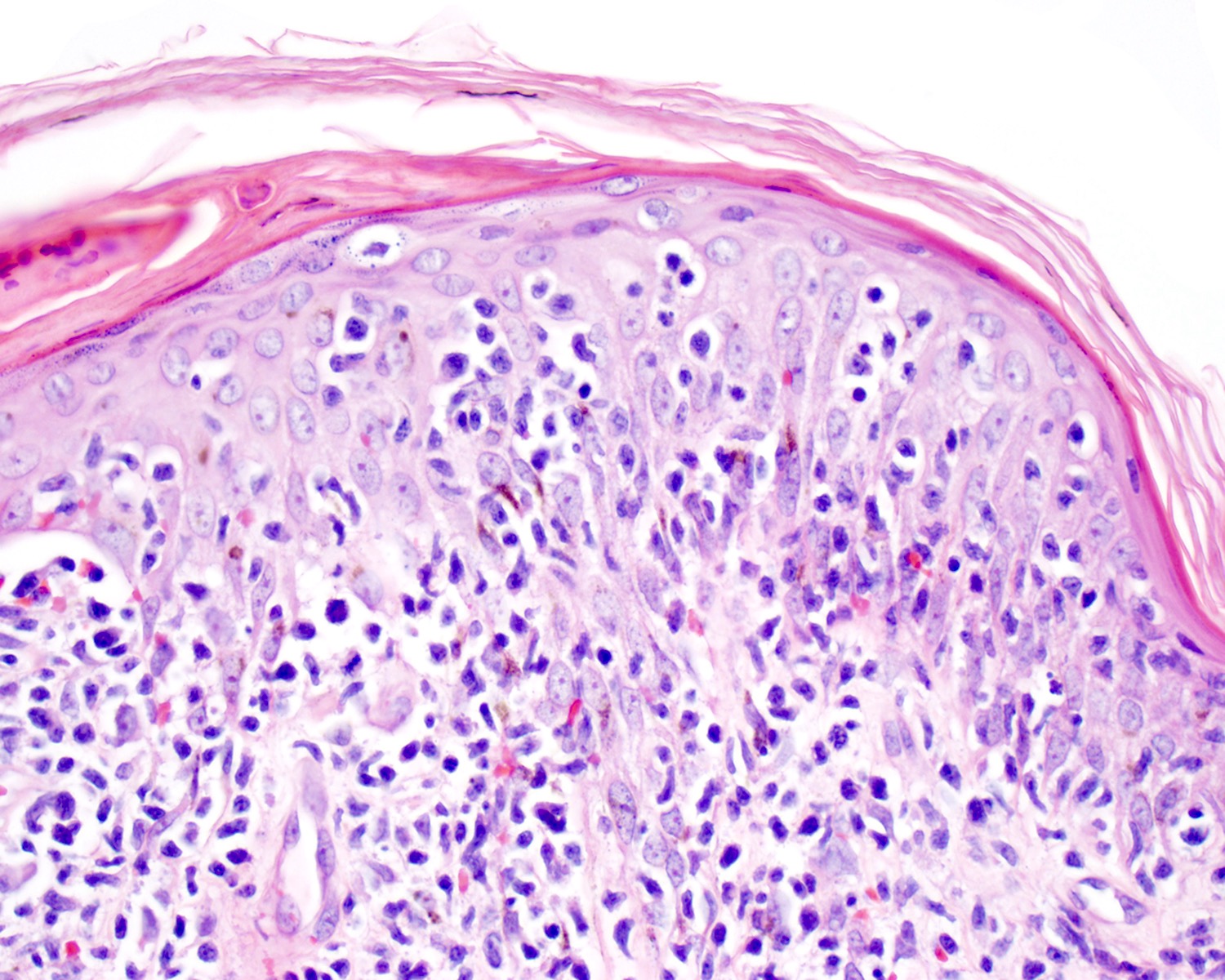
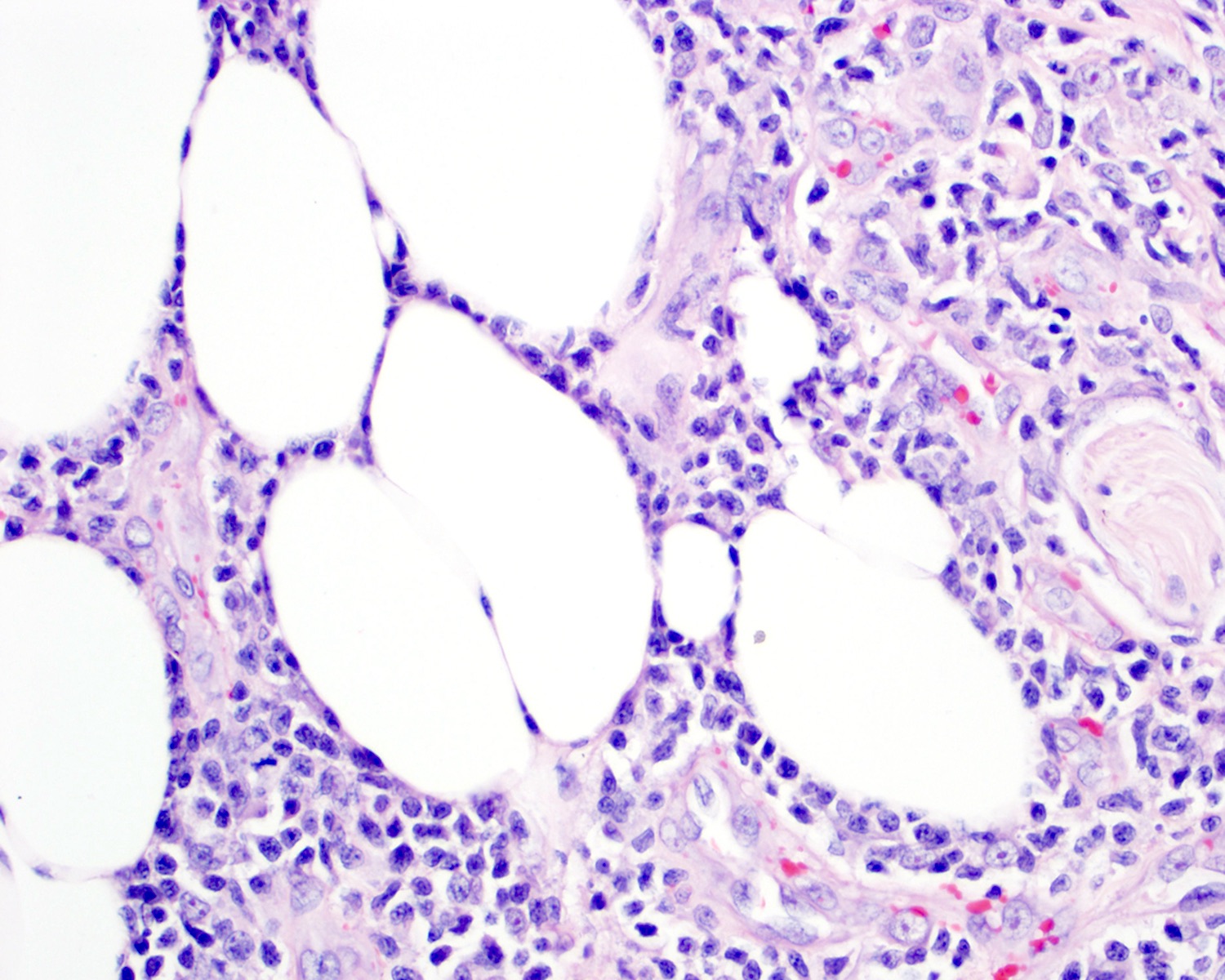
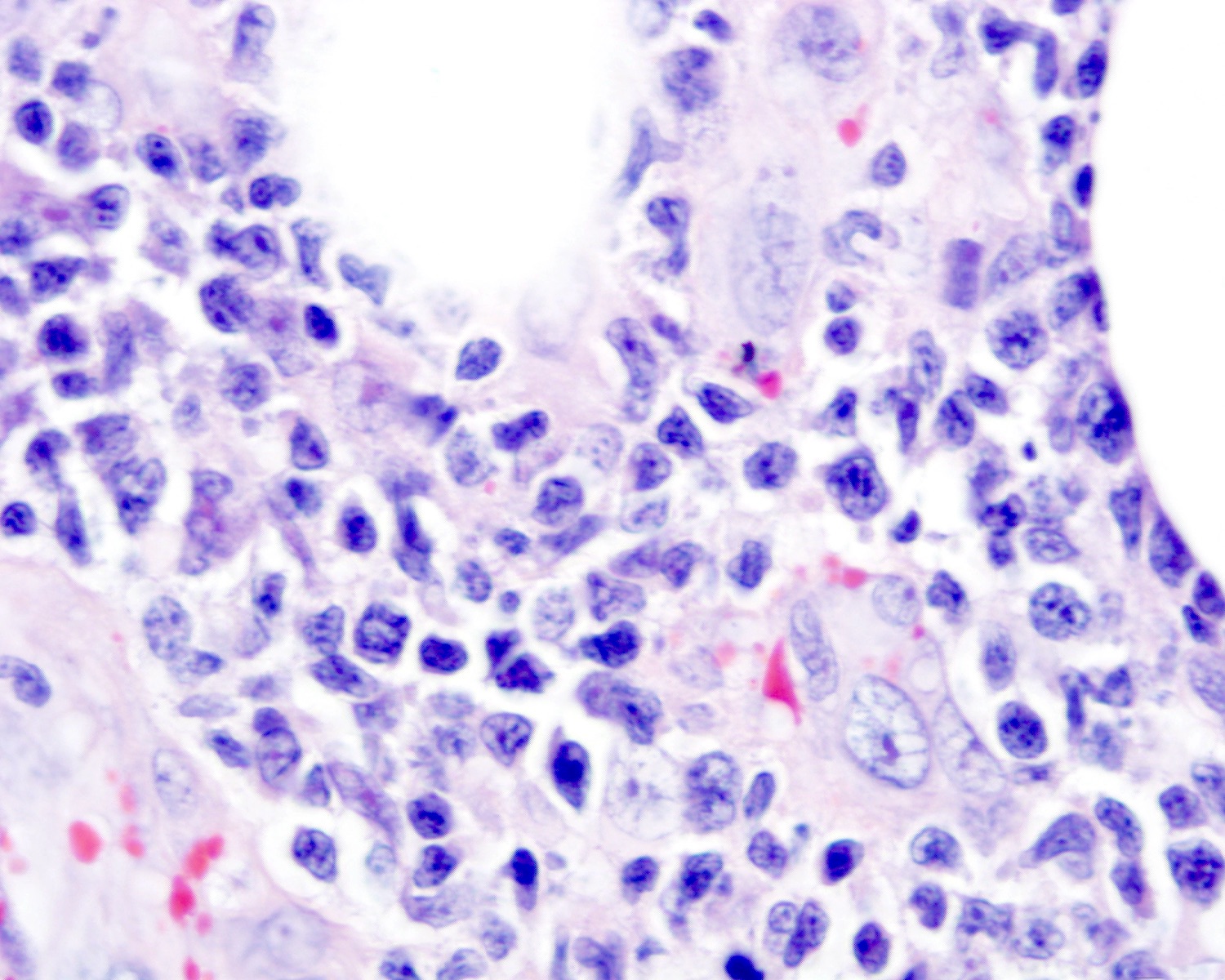
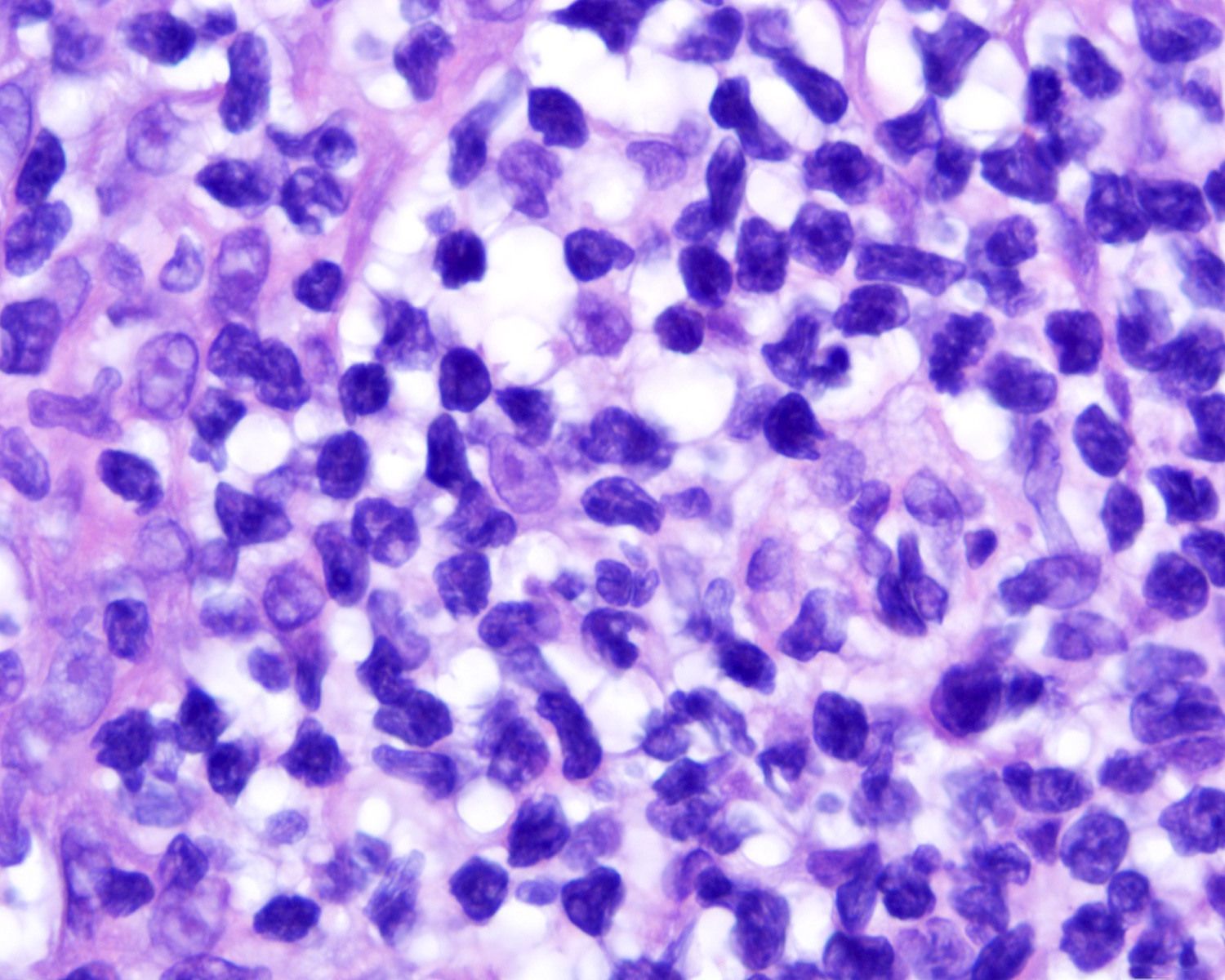
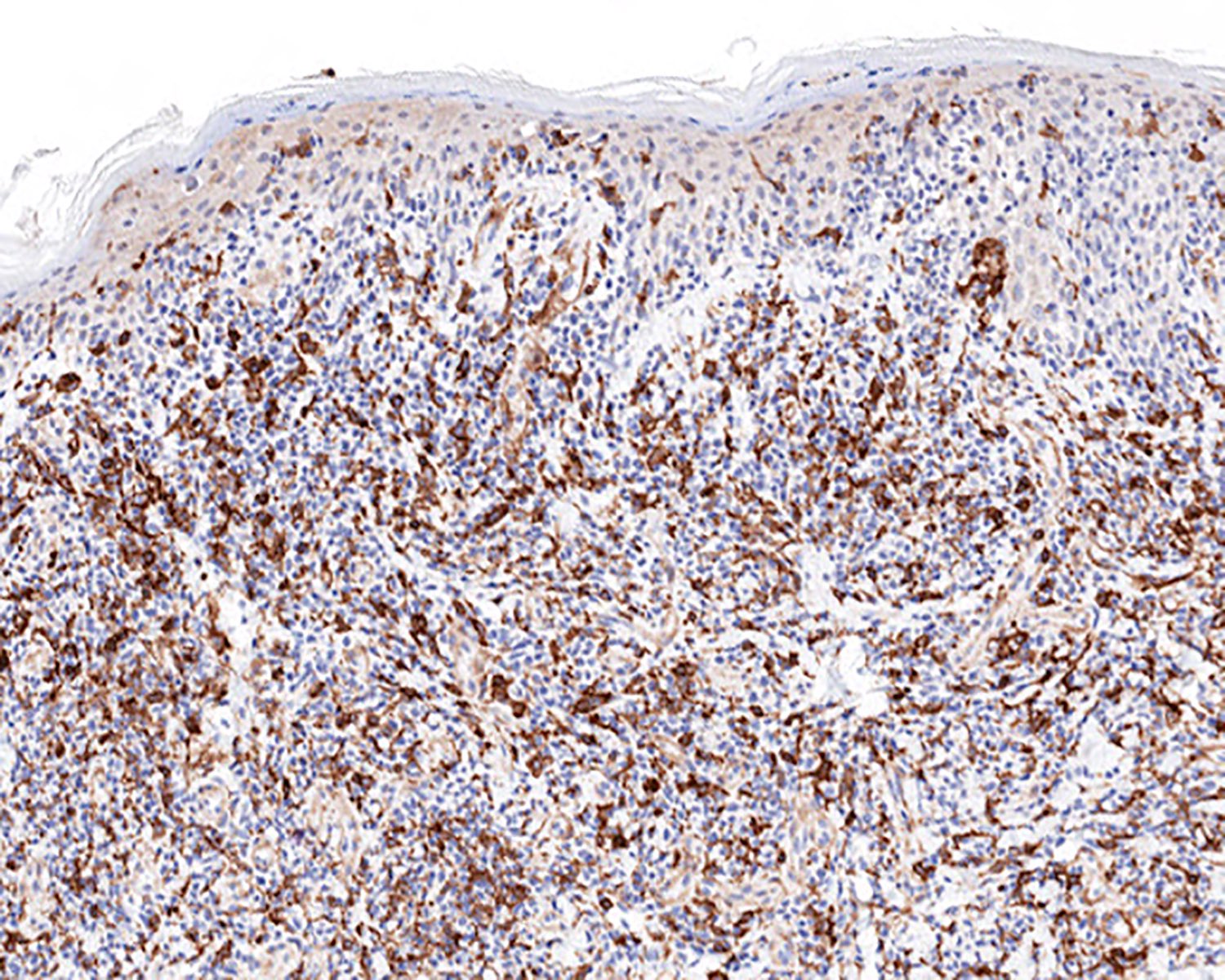
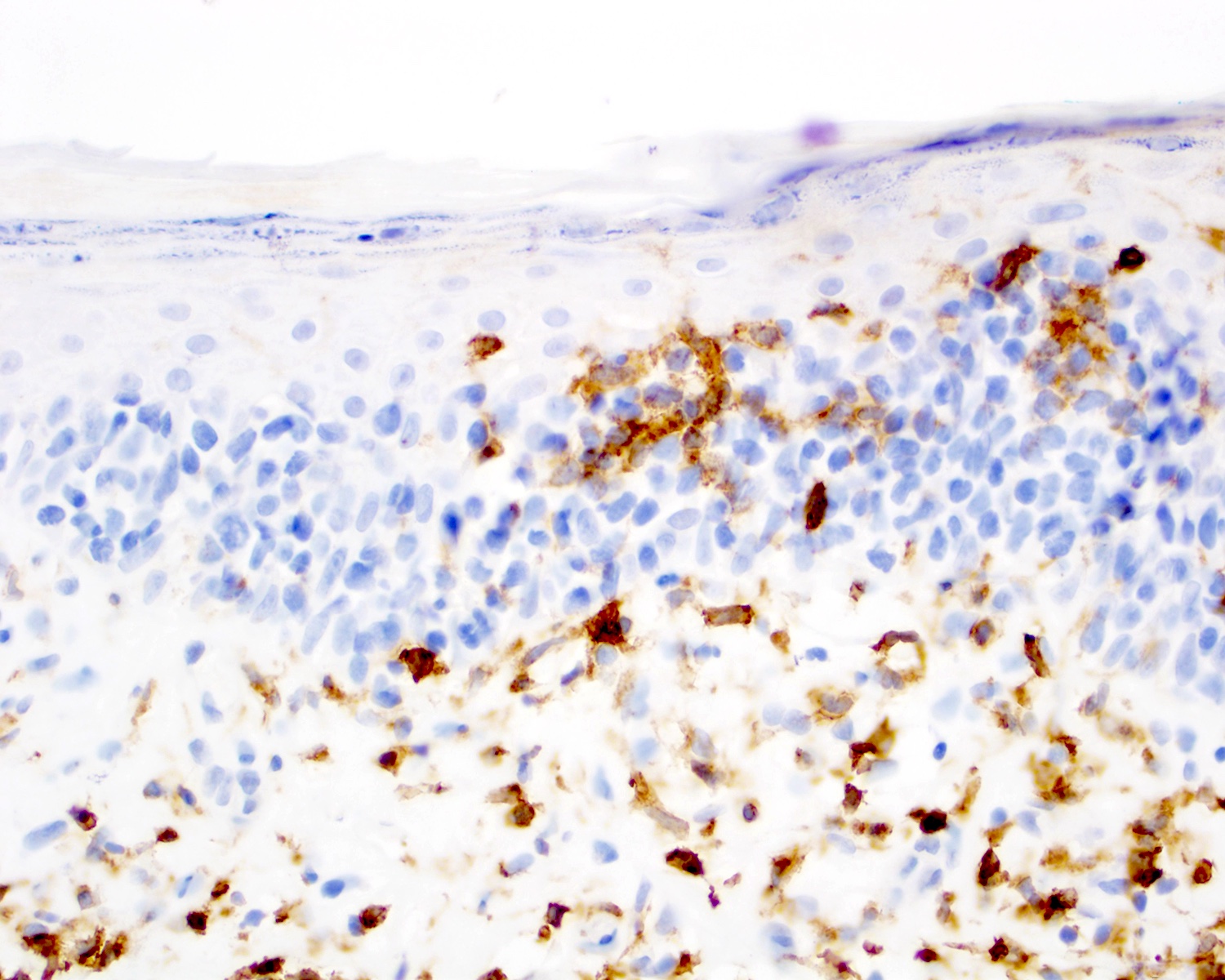
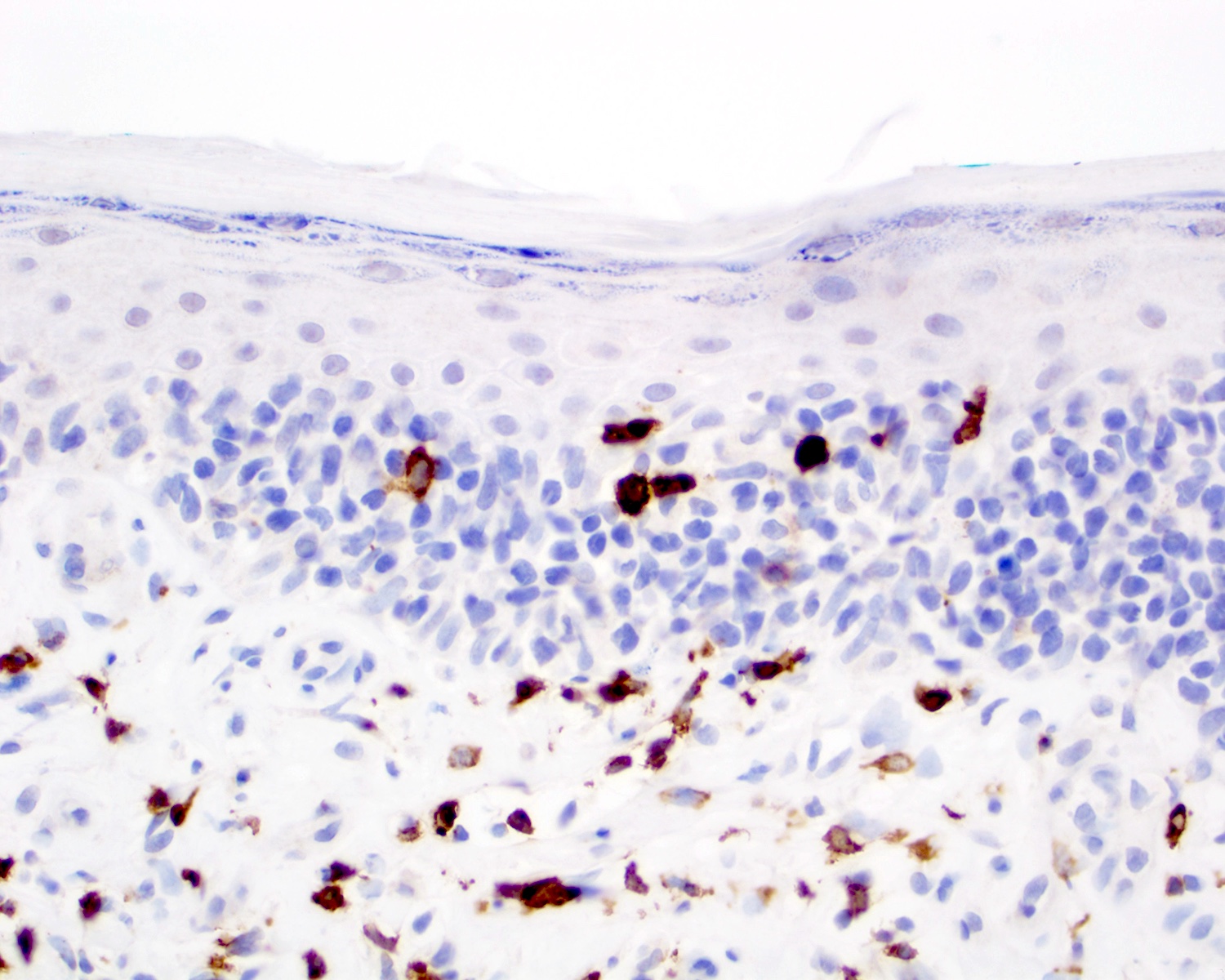
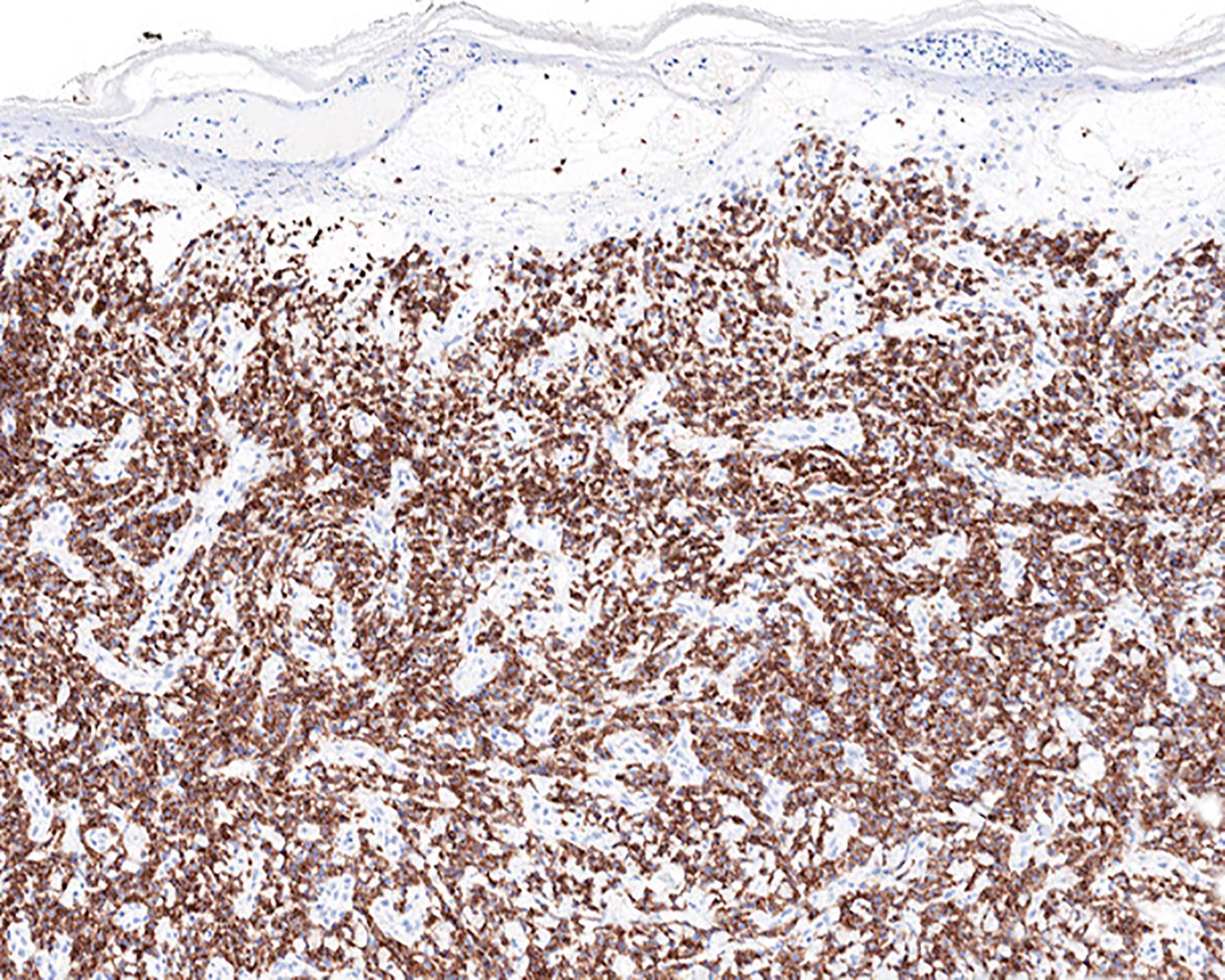
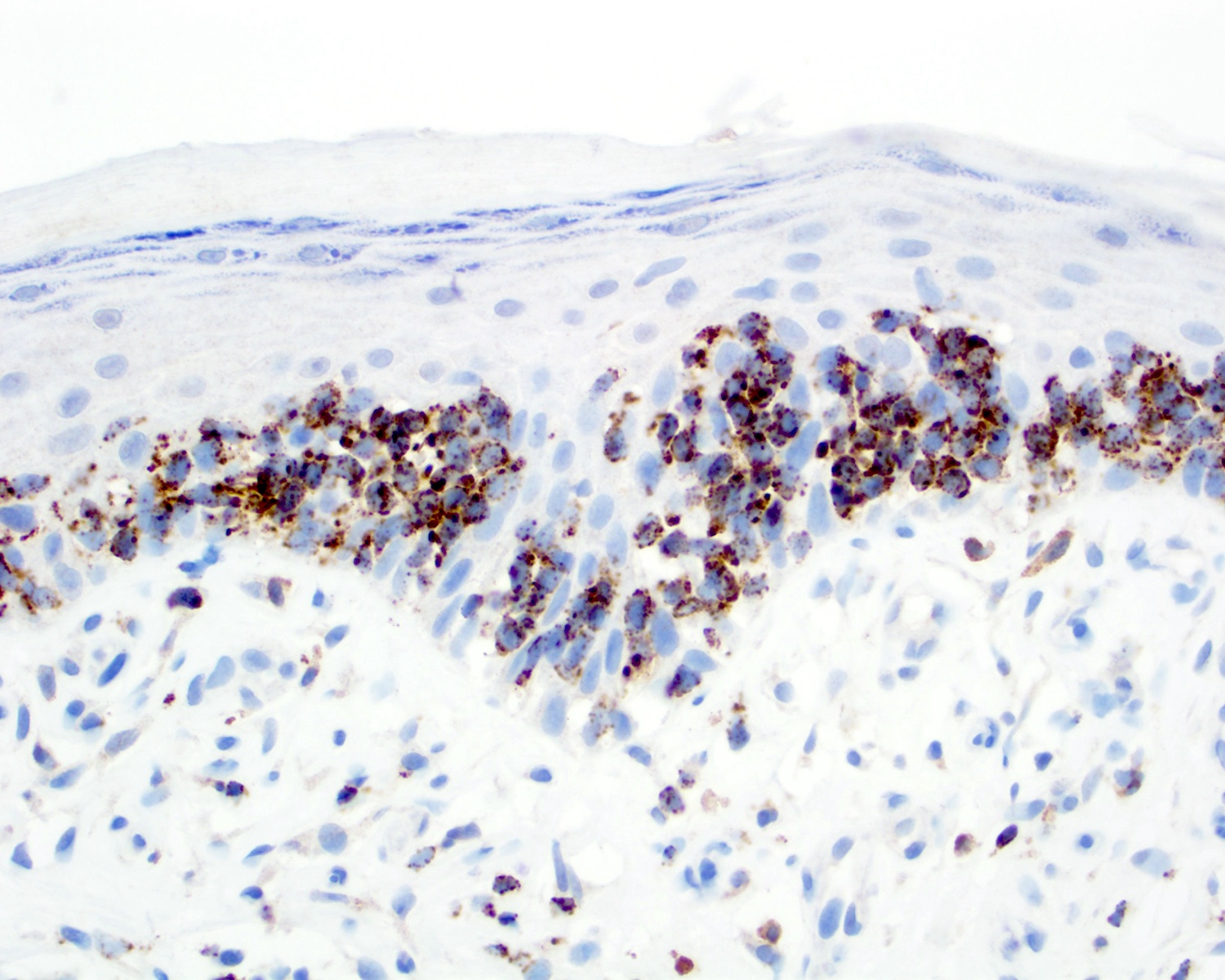
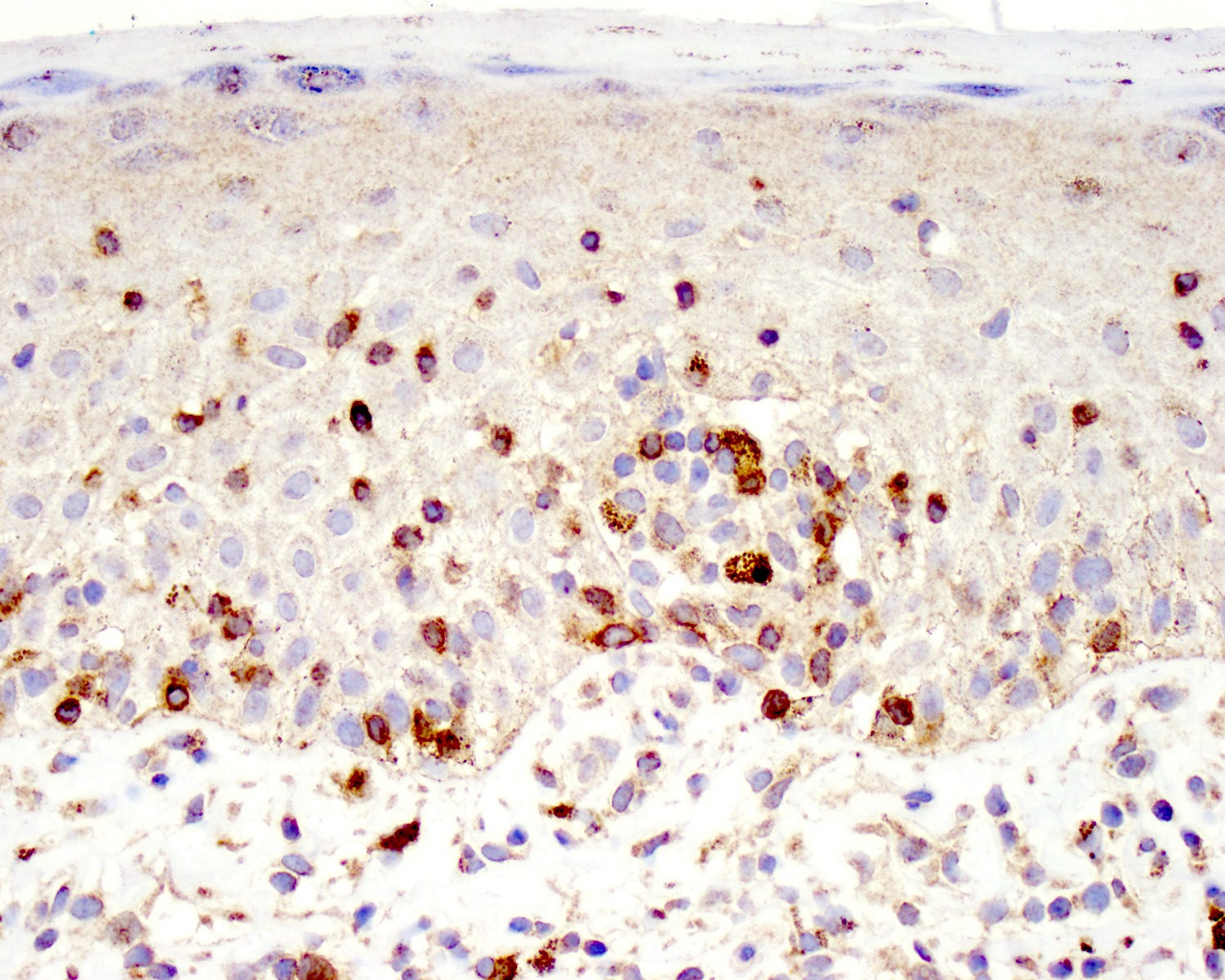
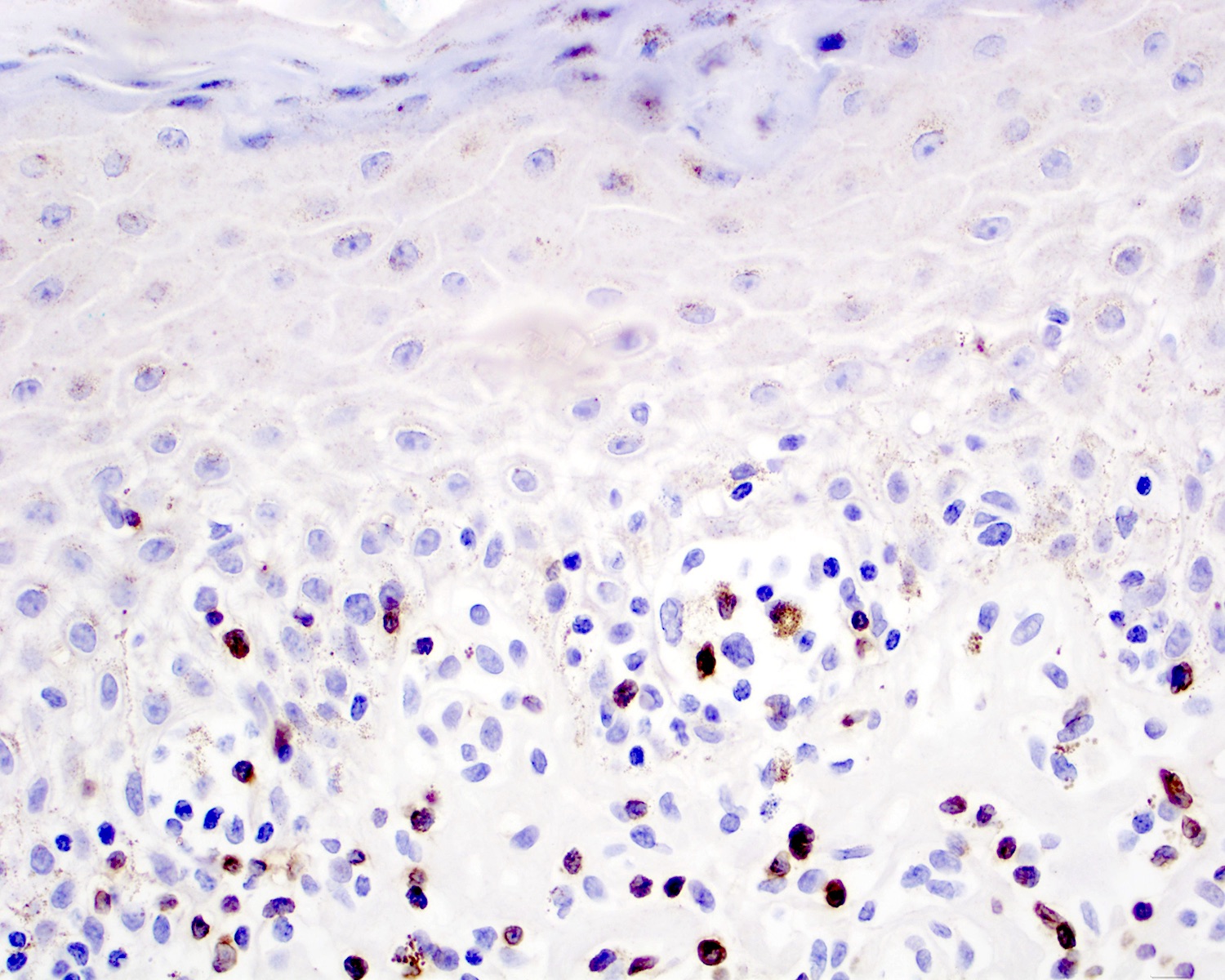
- Medium to large sized lymphocytes with irregular nuclei contours, clumped chromatin and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- Rare forms with blastoid morphology: fine chromatin and prominent nucleoli
- Distributed in 3 major histologic patterns (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36, Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206):
- Epidermal
- More common
- Spongiosis, parakeratosis, necrotic keratinocytes and acanthosis
- Variable (minimal to marked) epidermotropism
- Can mimic pagetoid reticulosis or Pautrier microabscesses
- Interface changes and hemorrhage
- Dermal
- Nodular or diffuse involvement
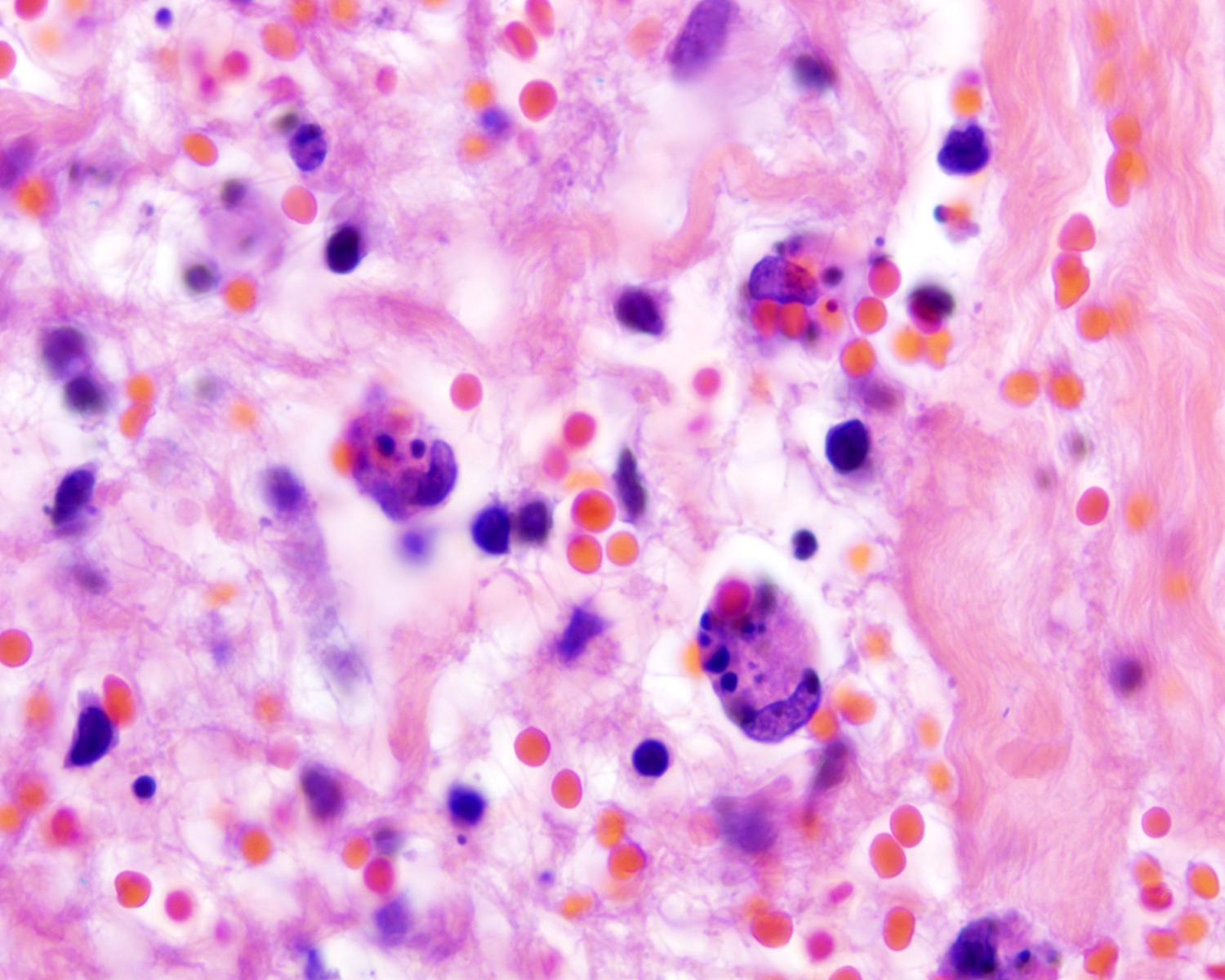
- Necrosis, apoptotic figures, hemophagocytosis, angiocentrism and adnexotropism may occur
- Subcutaneous (panniculitis)
- Rimming intralobular adipocytes
- Epidermal
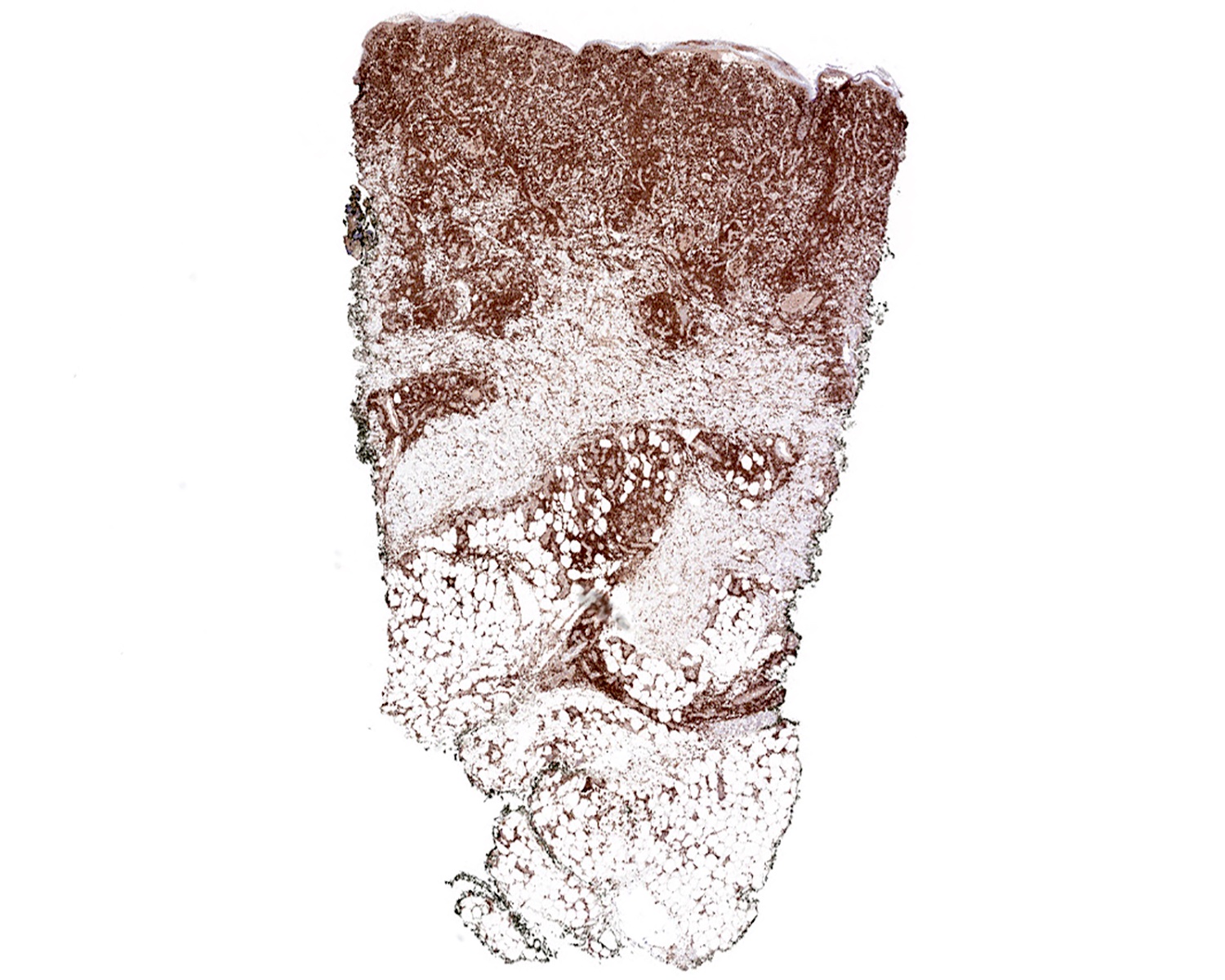
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Positive stains
- CD2 (60 - 80%), CD3 (~95%), CD56 (40 - 80%) (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707)
- Cytotoxic granules: granzyme B, perforin, TIA1 (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
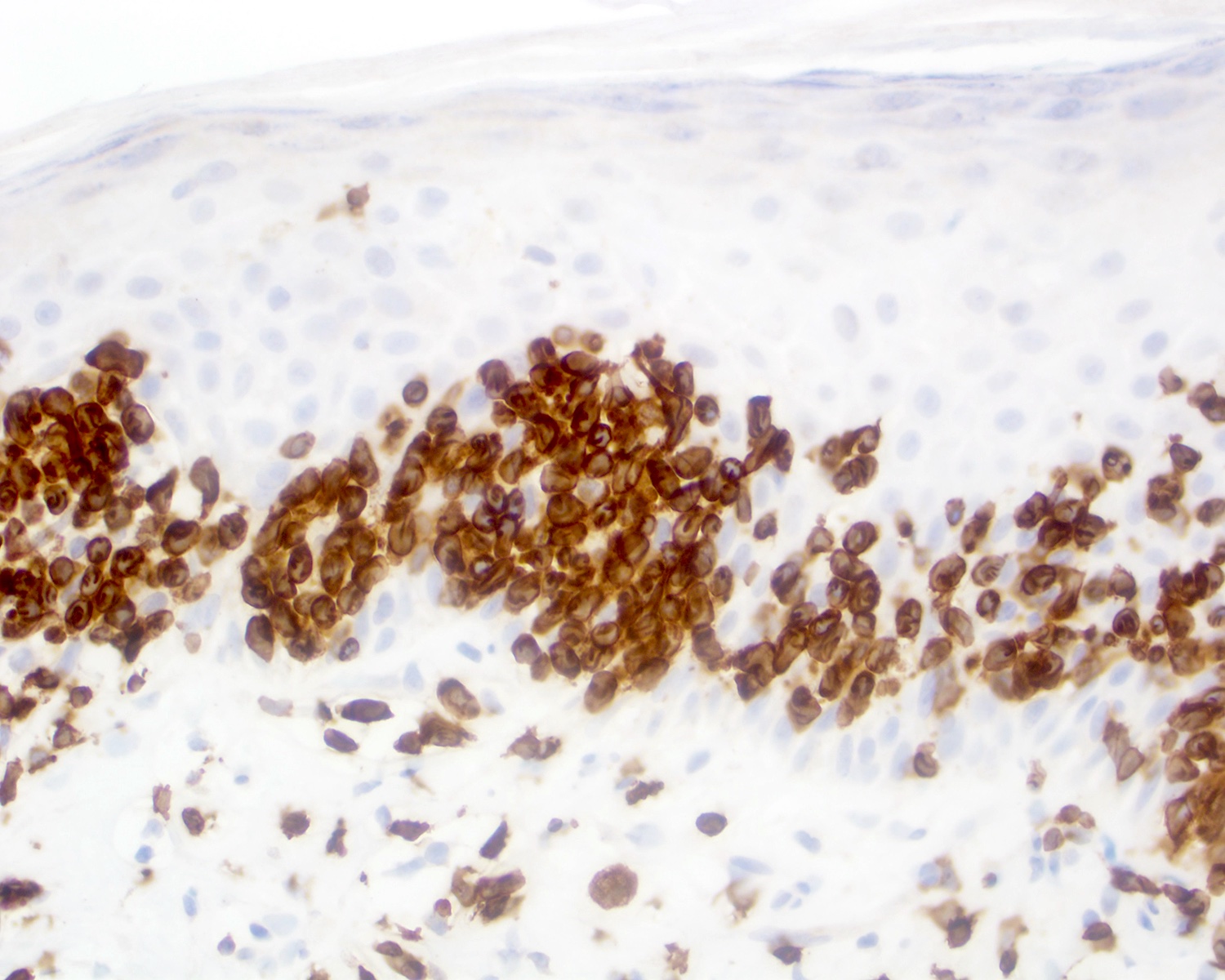
- TCR delta, TCR gamma (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707, Blood 2003;101:3407)
Negative stains
- CD4, CD8 (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- Up to 40% are positive for CD8
- Variable loss: CD5, CD7 (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1449, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:431)
- GATA3, CXCR3, CCR4 (J Dermatol Sci 2018;89:88, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515)
- CD30 (Ann Hematol 2021;100:2653, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021;8:515)
- Expressed in 40% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:431)
- Epstein-Barr virus encoded small RNAs (EBER) in situ hybridization (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Blood 2003;101:3407, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:204)
- TCR alpha / beta or TCR βF1 (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Blood 2003;101:3407, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
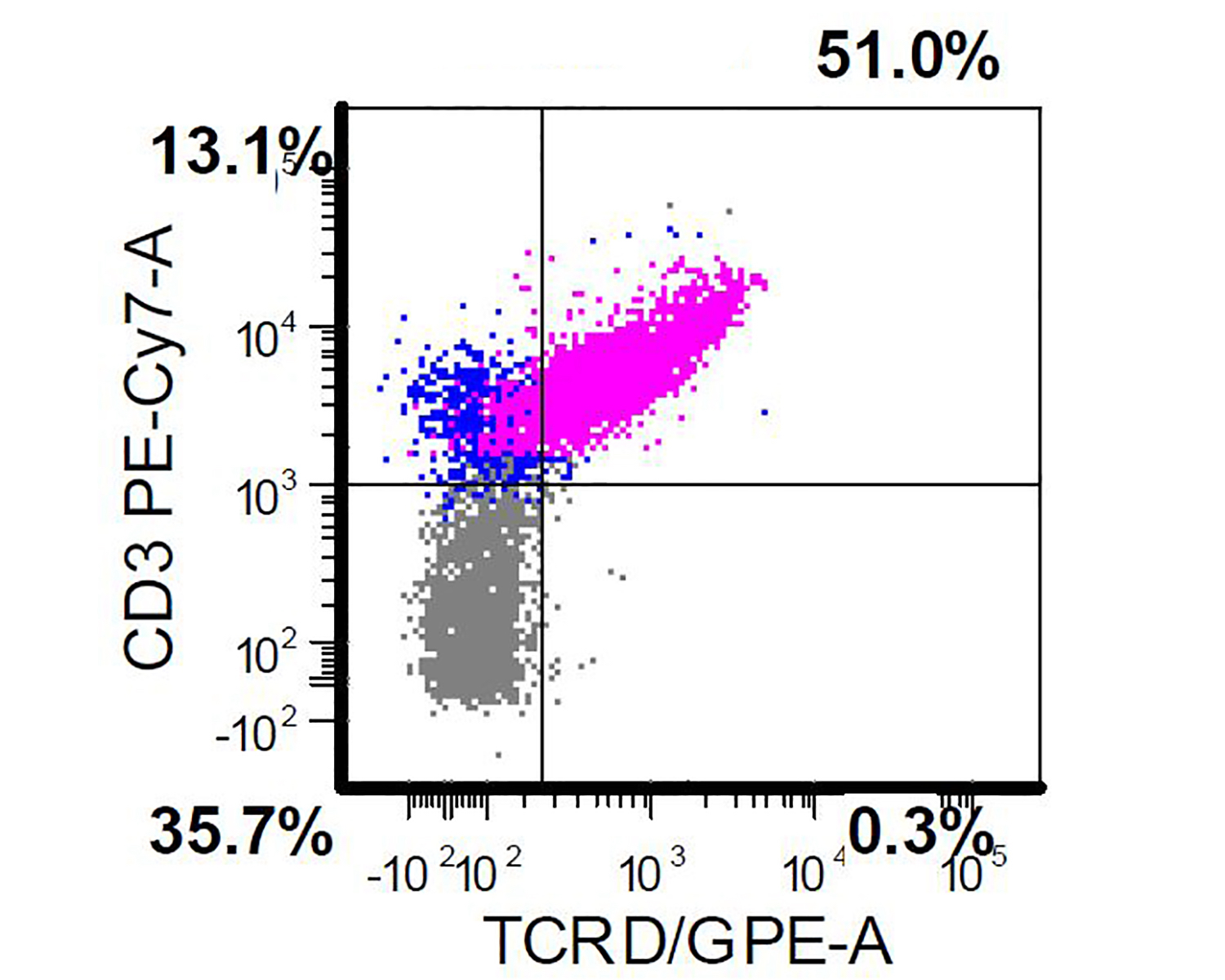
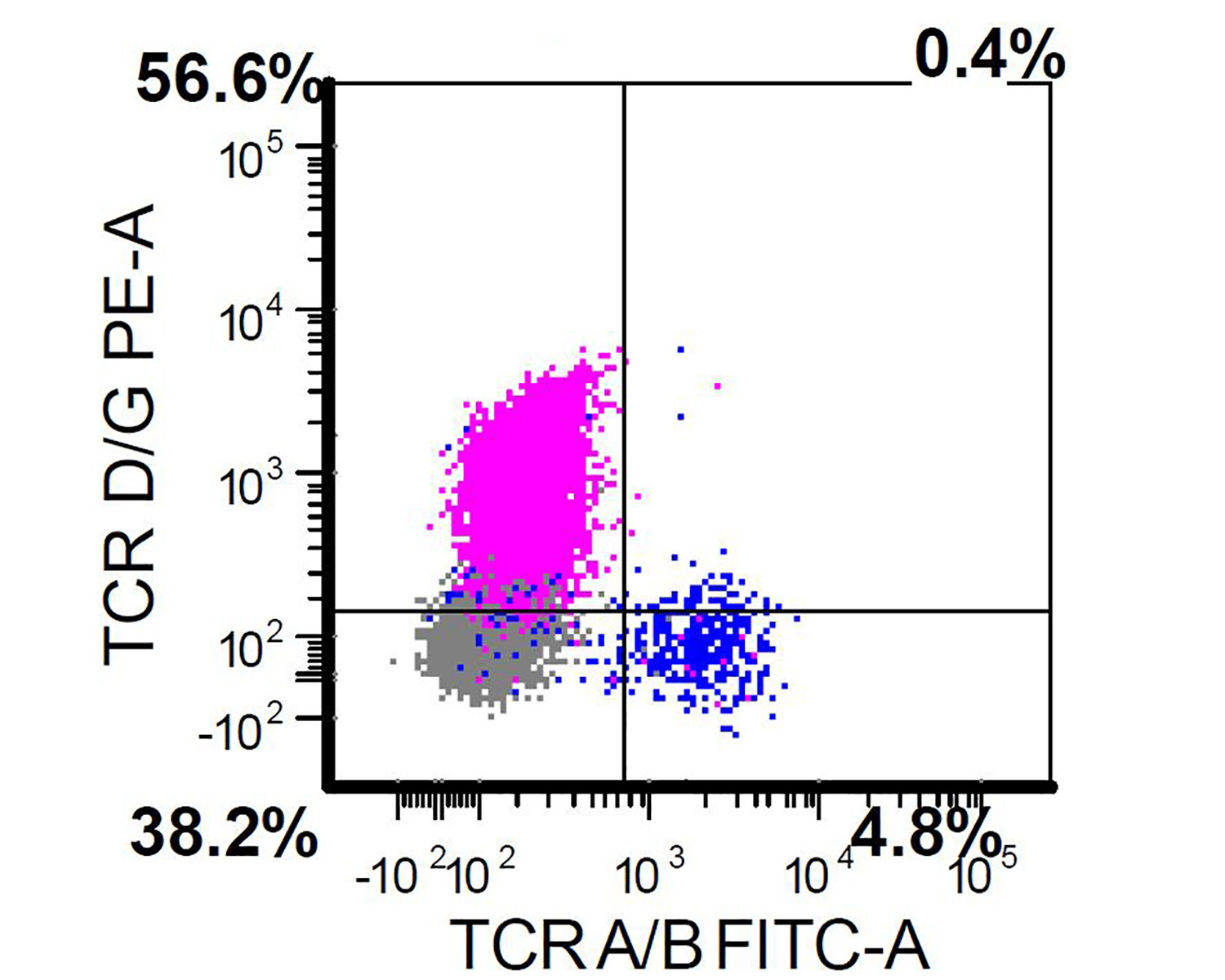
Flow cytometry description
- Usually performed on bone marrow or peripheral blood of patients with a suspected diagnosis of primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177)
- Positive for CD2, CD3, CD56 and TCR gamma delta
- Negative for CD4, CD8, TCR alpha beta
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No specific cytogenetic abnormality (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009;6:707)
- Amplifications, deletions and breakpoints: 1q, 15q, 7q, 14q, 18q
- Targetable mutations in JAK::STAT pathway (Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36)
- STAT3 and STAT5B mutations in up to 30% of cases (Clin Hematol Int 2022;4:1)
- Mutations in MAPK, MYC, chromatin modification and other pathways (Nat Commun 2020;11:1806, Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206)
- KRAS, CDKN2A, ARID1A, KMT2D and TP53
- Cell of origin differs between superficial (Vδ1) and deep (Vδ2) variants (Nat Commun 2020;11:1806)
Sample pathology report
- Right thigh, proximal, skin punch:
- Primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: According to clinical notes, this is a 64 year old man with a history of multiple ulcerated nodules, plaques and tumors in the extremities of a very recent onset (past 2 months). The patient has a previous history of diabetes mellitus in regular treatment with metformin.
- The histologic sections of the punch biopsy show an ulcerated lesion infiltrated by intense lymphoid infiltrate located in the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue. This infiltrate is composed predominantly of medium sized lymphocytes with irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Mitotic figures, necrosis and hemophagocytosis are noted.
- Immunohistochemical studies reveal the neoplastic cells are positive for CD2, CD3, CD56, granzyme B, perforin, TIA1 and TCR delta and negative for CD4, CD7, CD8, CD30, CCR4, EBER, TdT and TCR alpha beta. CD5 and CD7 present a partial loss in the neoplastic infiltrate.
- Concurrent flow cytometry immunophenotype of the bone marrow and peripheral blood shows absent monoclonal T cell population. Clinical correlation and follow up is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma (Hematol Oncol 2021;39:46, Semin Diagn Pathol 2017;34:36):
- Lupus panniculitis (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:24):
- F > M
- Multiple or single lipoatrophy, erythema or subcutaneous nodules
- More common in extremities (upper arms), followed by face and trunk
- Lymphocytic lobular / septal panniculitis with mild or no cytological atypia
- Mucin deposits and mild vasculitis
- Mixed cell infiltrate shows CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD20+
- Aggregates of CD123+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- Polyclonal TCRγ gene rearrangement
- Primary cutaneous aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177, Mod Pathol 2017;30:761):
- Rapidly progressive necrotic tumors
- Predominantly epidermotropic pattern
- Positive for CD3, CD8, TIA1, TCR alpha beta / TCR βF1, granzyme B, perforin
- Negative for CD4, TCR gamma, TCR delta
- Poor prognosis
- Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) (Hematol Oncol 2021;39:46, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1, Eur J Haematol 2015;94:206):
- Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Hematol Oncol 2021;39:46):
- Primary cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021;35:658):
- Solitary or disseminated papulonodular or tumor lesions with rapid growth and necrosis
- Nodular or diffuse infiltrate in dermis and subcutaneous tissue
- Variable morphology, usually large, pleomorphic cells
- Epidermotropism absent or focal
- CD3+ / CD4- / CD8- or CD3+ / CD4+ / CD8-
- CD8+ may also occur
- Poor prognosis
- 3 year overall survival is ~60%
- 5 year overall survival is ~50%
- Gamma delta mycosis fungoides (J Am Acad Dermatol 2021;85:1352):
- Classical presentation with patches and plaques
- Early stage
- Epidermotropic atypical infiltrate
- Positive for CD3, granzyme B, TIA1, TCR gamma+ or TCR delta+
- Negative for CD4, CD8, TCR alpha beta / TCR βF1
- Controversial whether this represents a variant of primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma
- Hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177):
- Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma involving skin (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:177):
- Dermatitis with gamma delta infiltrate (Immunol Rev 2020;298:61; Front Immunol 2021;12:627139):
- May be associated with inflammatory (e.g., psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis) or infectious diseases (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection)
- Mild or no cytologic atypia
- Mixed cell infiltrate with loss of 1 or 2 T cell antigens but polyclonal TCR gene rearrangement
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Lymph node and bone marrow involvement are uncommon. Primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma usually presents as rapidly progressing disseminated and ulcerated nodules, plaques and tumors. The predominantly epidermotropic form conveys a better prognosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Primary cutaneous gamma delta
Comment Here
Reference: Primary cutaneous gamma delta
Board review style question #2
Which of the following immunophenotypic patterns corresponds to primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma?
- CD2+, CD3-, CD4+, CD8+, TIA1-, granzyme B-, TCRγδ+
- CD2+, CD3+, CD4+, CD8-, TIA1+, granzyme B-, TCRɑβ+
- CD2+, CD3-, CD4-, CD8+, TIA1-, granzyme B+, TCRγδ+
- CD2+, CD3+, CD4-, CD8-, TIA1+, granzyme B+, TCRγδ+
Board review style answer #2
D. CD2+, CD3+, CD4-, CD8-, TIA1+, granzyme B+, TCRγδ+. This is the most typical immunophenotype.
Comment Here
Reference: Primary cutaneous gamma delta
Comment Here
Reference: Primary cutaneous gamma delta