Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Wright MF, Mason E. Classic Hodgkin lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonBclassic.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL): B cell derived lymphoma characterized by distinctive immunophenotype and relatively few malignant cells in a nonneoplastic inflammatory background
- 4 subgroups (nodular sclerosis, mixed cellularity, lymphocyte rich, lymphocyte depleted) with distinct clinical, morphologic and epidemiologic characteristics
Essential features
- B cell derived lymphoma characterized by distinctive immunophenotype and relatively few malignant cells in a nonneoplastic inflammatory background
- 4 subgroups (nodular sclerosis, mixed cellularity, lymphocyte rich, lymphocyte depleted) with distinct clinical, morphologic and epidemiologic characteristics
- Involves lymph nodes (cervical > axillary, mediastinal, para-aortic)
- Bimodal age distribution: peaks at 15 - 35 years and 50 - 70 years
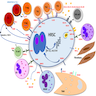
- Multiple mechanisms to evade immunosurveillance, including upregulation of programmed death ligand 1 / programmed death ligand 2 (PDL1 / PDL2)
Terminology
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
- Hodgkin disease
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- CHL: ~90 - 95% of Hodgkin lymphomas
- Bimodal age distribution: peaks at 15 - 35 years and 50 - 70 years
- Epidemiology varies by subgroup (Br J Haematol 2019;184:45)
- Nodular sclerosis (~70% of CHL in Western countries)
- F > M
- Age: 15 - 35 years
- Most common in urban areas, wealthier nations and individuals with high socioeconomic status
- Minority (10 - 25%) are Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+
- Mixed cellularity (~20% of CHL)
- M > F
- Children and adults > 60 years
- More common in developing countries and rural areas
- Majority (70 - 80%) are EBV+
- Lymphocyte rich (~5% of CHL)
- M > F
- Age: 30 - 50 years
- Lymphocyte depleted (< 1% of CHL in Western countries)
- M > F
- Age: 30 - 70 years
- Nodular sclerosis (~70% of CHL in Western countries)
Sites
- Lymph nodes (cervical > axillary, mediastinal, para-aortic)
- Mediastinal involvement in 80% of nodular sclerosis CHL
- Extranodal sites: spleen (20%), liver, lungs, bone marrow (5%)
- Typical anatomic distribution varies by subgroup (Br J Haematol 2019;184:45)
- Nodular sclerosis: mediastinal, cervical, supraclavicular lymph nodes
- Mixed cellularity: peripheral lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow
- Lymphocyte rich: peripheral lymph nodes
- Lymphocyte depleted: retroperitoneal lymph nodes, abdomen, bone marrow
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology is not completely understood
- Malignant Reed-Sternberg cells derived from preapoptotic germinal center B cells with a disrupted B cell program (Blood 2000;95:1443)
- In a subset of cases, IgVH mutations lead to dysfunctional / absent B cell receptor, prohibiting antigenic selection; incompatible with survival of normal B cells (J Exp Med 1996;184:1495)
- Postulated to circumvent apoptosis by differentiating toward distinct subset of CD30+ post germinal center memory B cells (J Clin Invest 2018;128:2996)
- Cell proliferation and survival promoted by alterations in signaling pathways, including JAK / STAT, NFkB, PI3K / AKT and MAPK / ERK (Leukemia 2021;35:968, Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:682)
- EBV infection thought to drive aberrant signaling in EBV+ cases (Histopathology 2021;79:451)
- Reed-Sternberg cell cytokine secretion recruits nonneoplastic inflammatory infiltrate; reciprocal cytokine / chemokine secretion by immune cells supports Reed-Sternberg cell survival and proliferation
- Reed-Sternberg cell evasion of immunosurveillance
- Increased programmed death ligand 1 / programmed death ligand 2 (PDL1 / PDL2) expression (J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2690, Blood 2017;130:2420)
- Downregulation of MHC I / MHC II expression (Cancer Immunol Res 2016;4:910)
- Secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines
- Infection (EBV, human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]) is thought to facilitate in a subset of cases
Etiology
- Cause incompletely understood
- Factors associated with increased risk of developing CHL
- EBV positive CHL: prior infectious mononucleosis, HLA-A*01 allele (Blood 2019;134:591)
- HIV infection (Blood 2006;108:3786)
- Family history of CHL, particularly siblings
Clinical features
- Peripheral lymphadenopathy
- 30 - 40% of patients present with B symptoms (fever, night sweats, weight loss), pruritis
- Stage at presentation (Blood Rev 2002;16:111)
- Nodular sclerosis, lymphocyte rich usually present with early stage disease
- Mixed cellularity and lymphocyte depleted associated with HIV infection and EBV often present with advanced stage disease
- Immunosuppression (including HIV infection) associated with advanced stage disease
Diagnosis
- Excisional lymph node biopsy or tissue biopsy
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) and core needle biopsy may be insufficient given importance of tissue architecture for diagnosis and potential rarity of Reed-Sternberg cells
Laboratory
- Nonspecific
- Elevated C reactive protein
- Eosinophilia (20%)
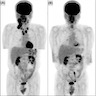
Radiology description
- Lower cervical, supraclavicular and mediastinal lymphadenopathy
- Bulky mediastinal disease in 50% of nodular sclerosis subtype
- Positron emission tomography / computed tomography (PET / CT) recommended for staging (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:3059)
- PET / CT has high sensitivity for detecting bone marrow involvement
Prognostic factors
- Differences in prognosis between different subgroups largely diminished with modern therapy
- Immunosuppression and HIV infection are associated with worse prognosis
- Staging critical for accurate prognostication and treatment
- Early stage disease includes favorable and unfavorable groups
- Unfavorable prognosis associated with B symptoms, bulky mediastinal disease, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), involvement of multiple lymph node groups, extranodal disease, older age (> 40 - 50 years)
- Advanced stage disease: prognosis associated with International Prognostic Score, based on 7 variables that independently predict outcome (N Engl J Med 1998;339:1506)
- Early stage disease includes favorable and unfavorable groups
- 80 - 90% cure rates with stage adapted therapy
- 10 - 25% of patients have primary refractory disease or relapse
- Increased percentage of CD68 positive macrophages in a diagnostic lymph node biopsy associated with shorter progression free and disease specific survival and increased failure rate after secondary treatment, including autologous stem cell transplant (N Engl J Med 2010;362:875)
Case reports
- 11 year old boy with initial extranodal osseous presentation of CHL (AME Case Rep 2019;3:22)
- 52 year old man with bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy (Clin Case Rep 2020;8:466)
- 53 year old man with CHL associated superior vena cava syndrome (Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e929437)
- 56 year old man with cutaneous involvement by CHL (World J Clin Cases 2019;7:2513)
- 85 year old woman with a 10 year history of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Case Rep Oncol 2020;13:120)
Treatment
- ABVD (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine) with or without IFRT (involved field radiation therapy)
- BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone), AVD with brentuximab vedotin (anti-CD30 antibody drug conjugate) or AVD with immune checkpoint inhibitor may be used in advanced disease
- Options for relapsed / refractory disease include brentuximab vedotin, chemotherapy, checkpoint inhibitors, high dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant, allogeneic stem cell transplant
- Risks of treatment related morbidity, including therapy related malignancy (> 4x risk of cancer compared with the general population), cardiovascular complications from mediastinal IFRT (Br J Haematol 2019;184:9)
- Interim PET scan after 2 cycles of chemotherapy may be used to guide treatment (PET adapted therapy) (Br J Haematol 2019;184:9)
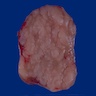
Gross description
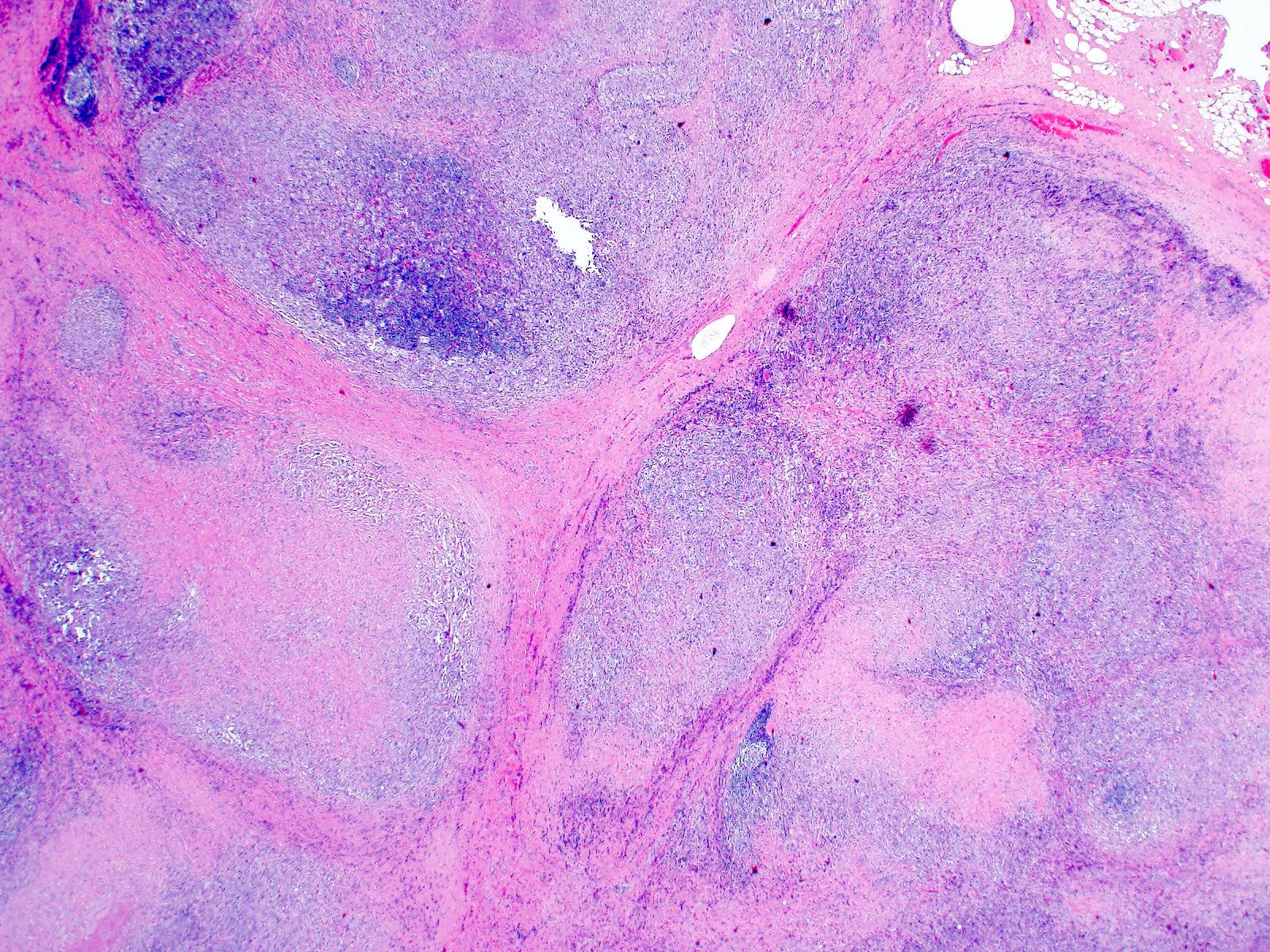
- Nodular sclerosis subtype: enlarged lymph node, thickened capsule, fibrotic bands with prominent nodularity
- Nodular involvement of spleen
Frozen section description
- Effacement of nodal architecture
- Nodularity
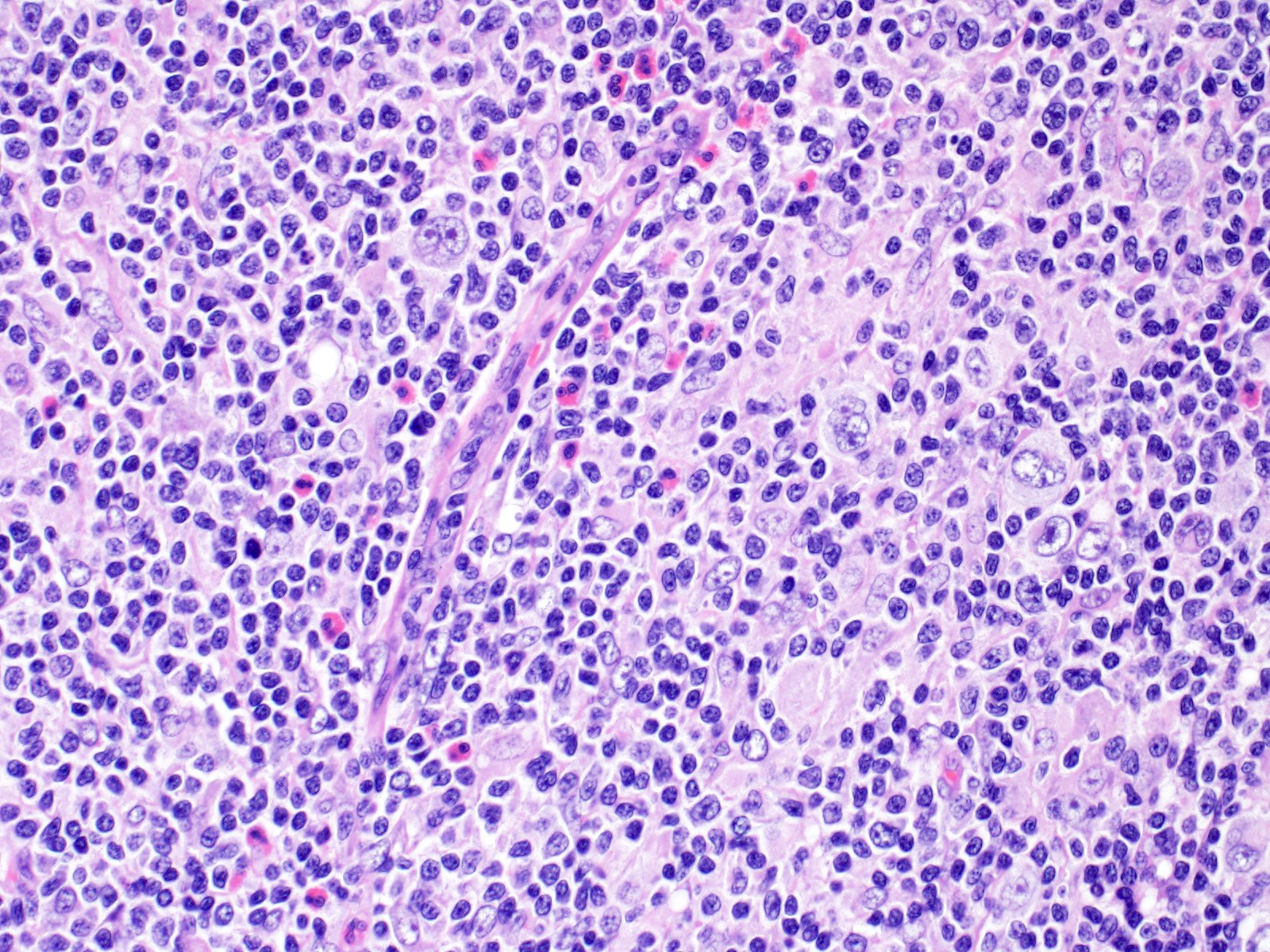
- Mixed inflammatory background (small lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes)
- May see scattered large Reed-Sternberg cells with multilobated nuclei and prominent nucleoli
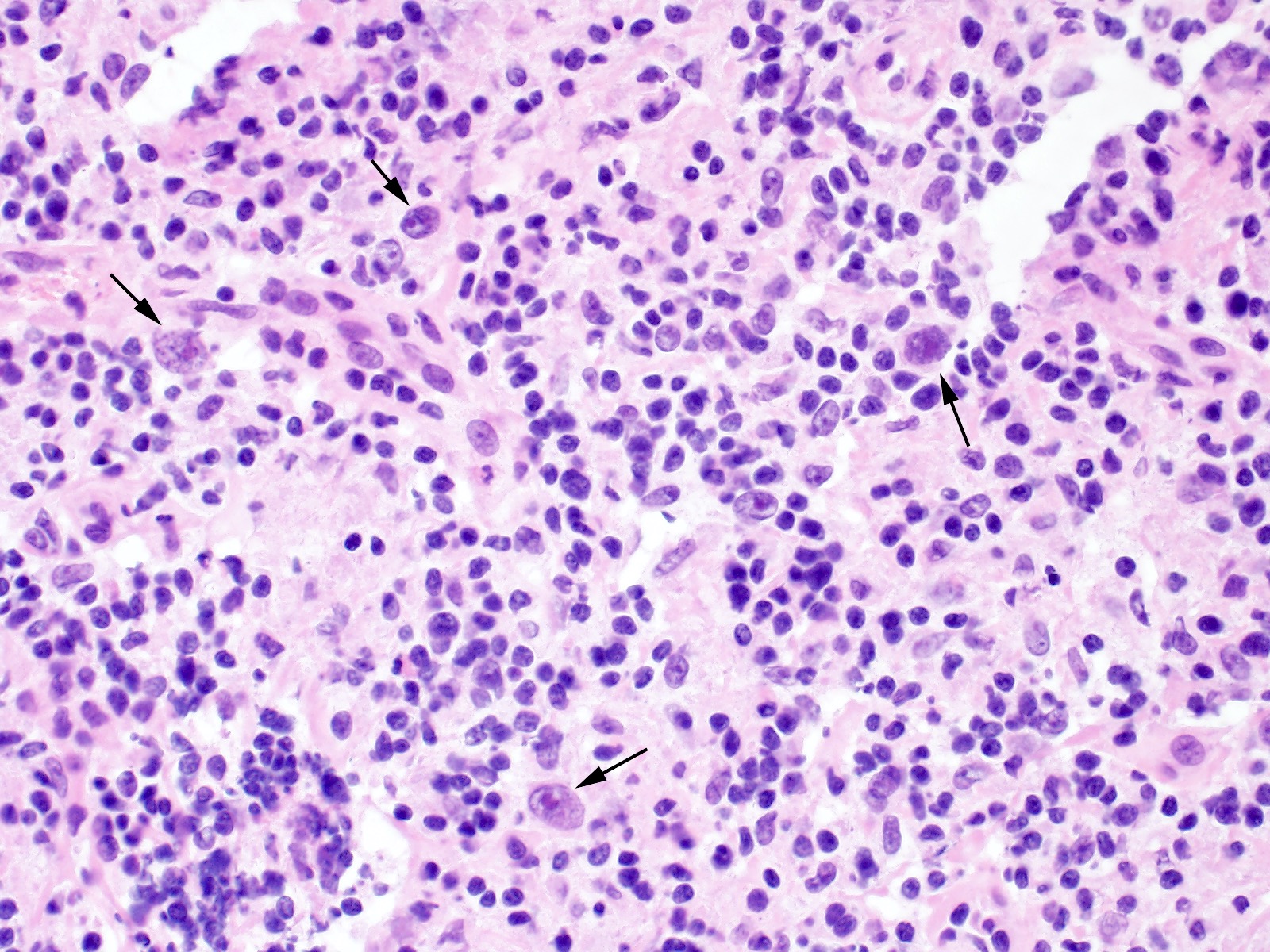
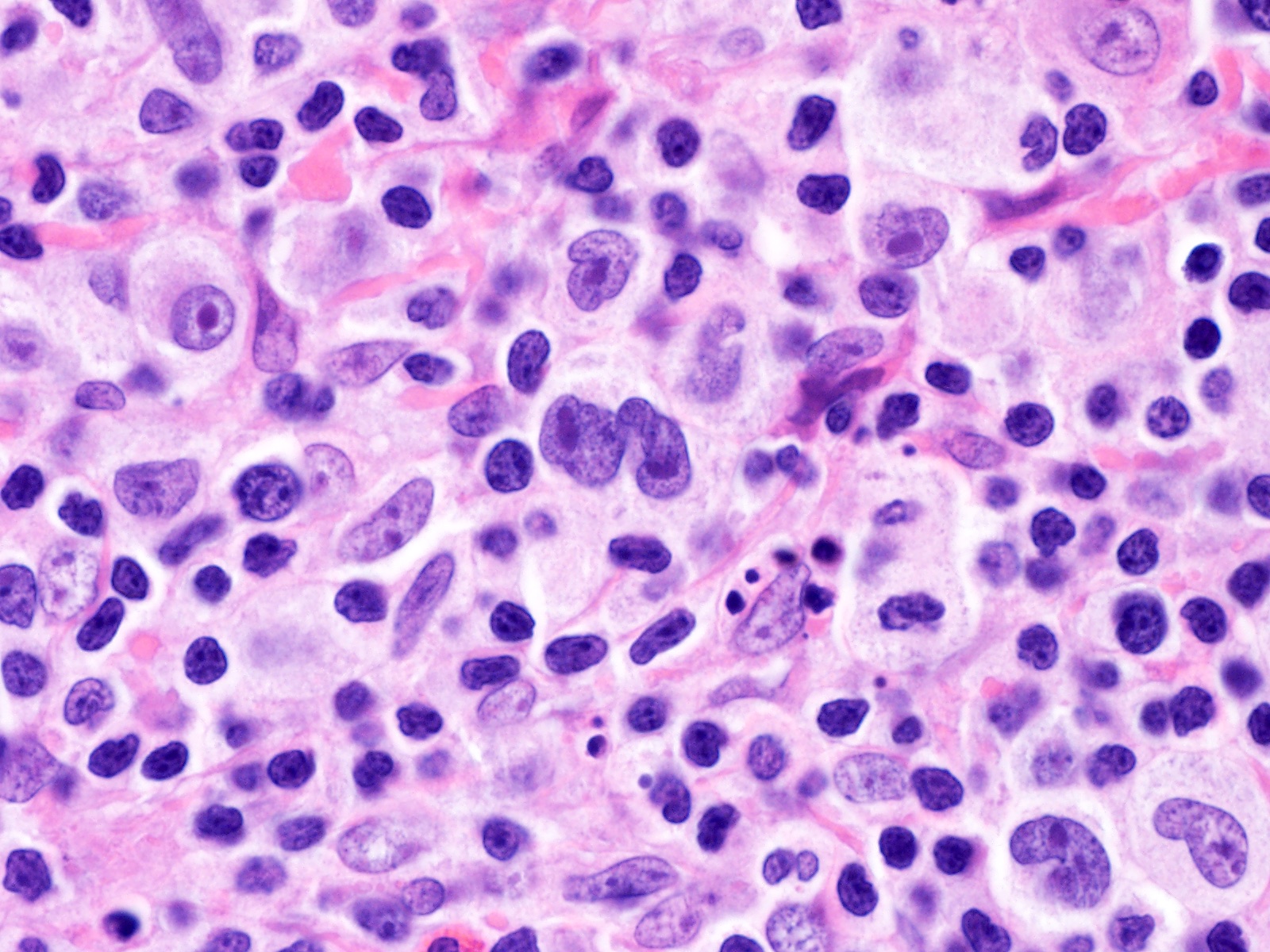
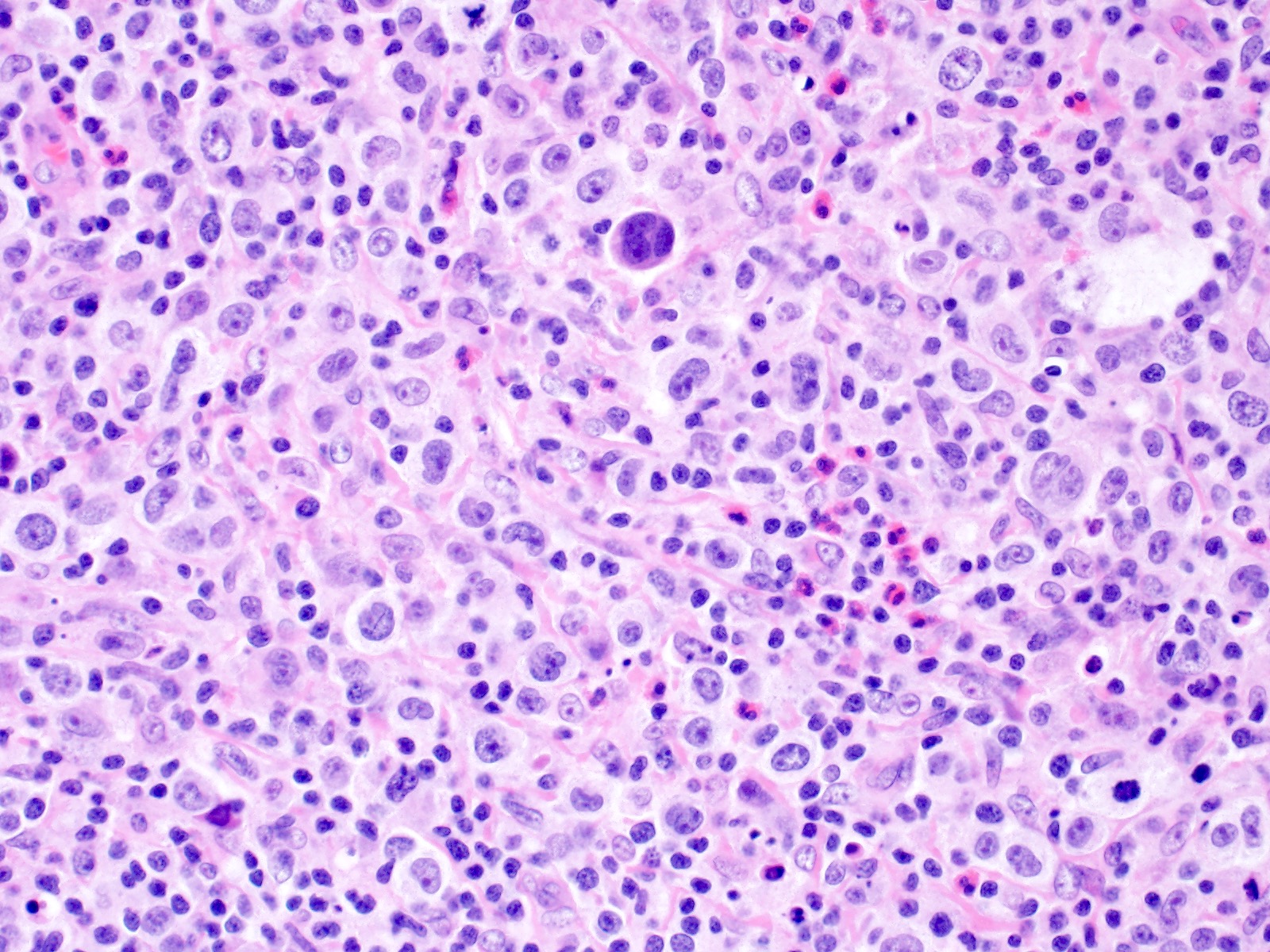
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Total or partial effacement of nodal architecture
- Nodular sclerosis subtype: nodularity, dense collagen bands, thickened capsule
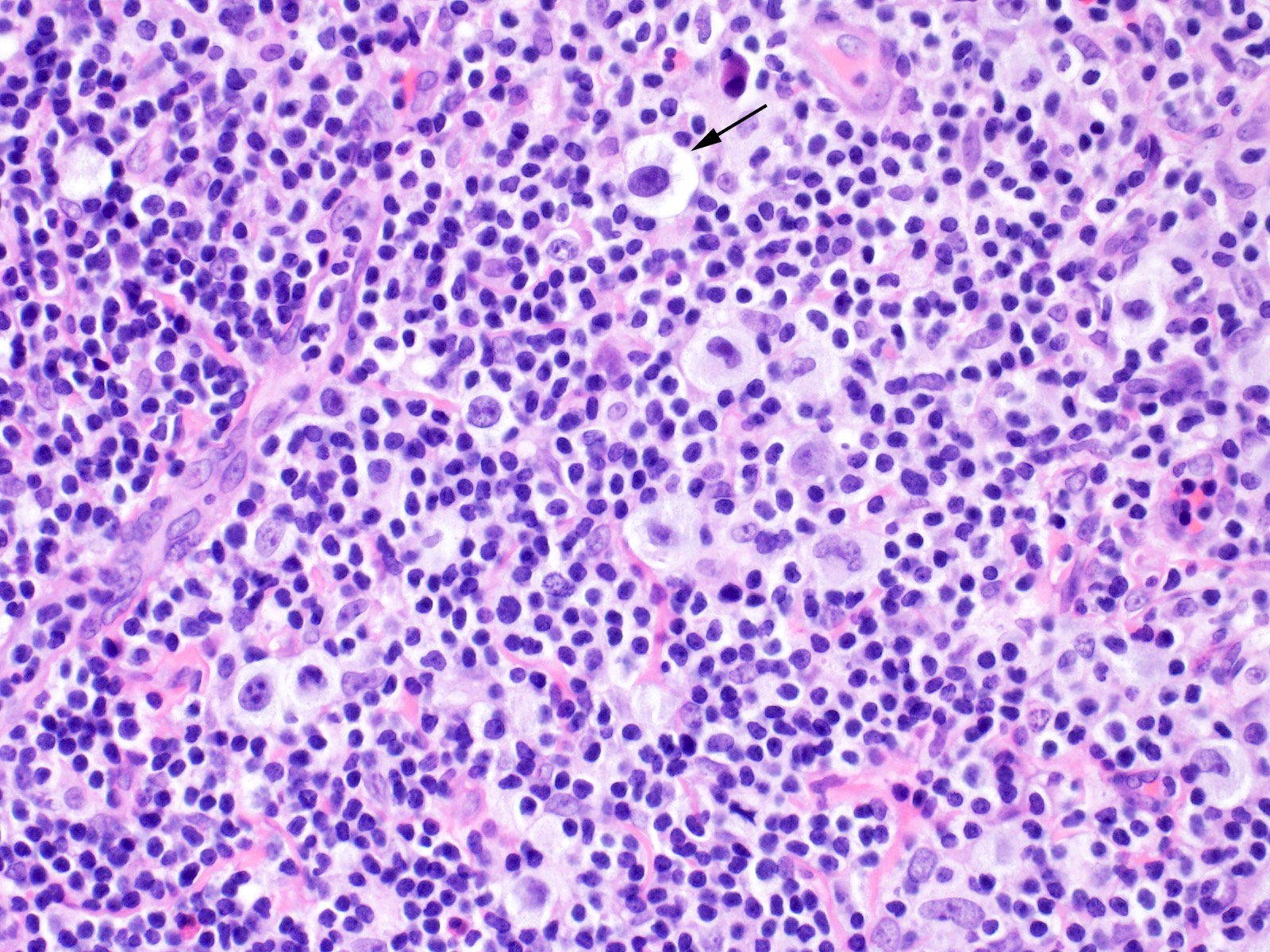
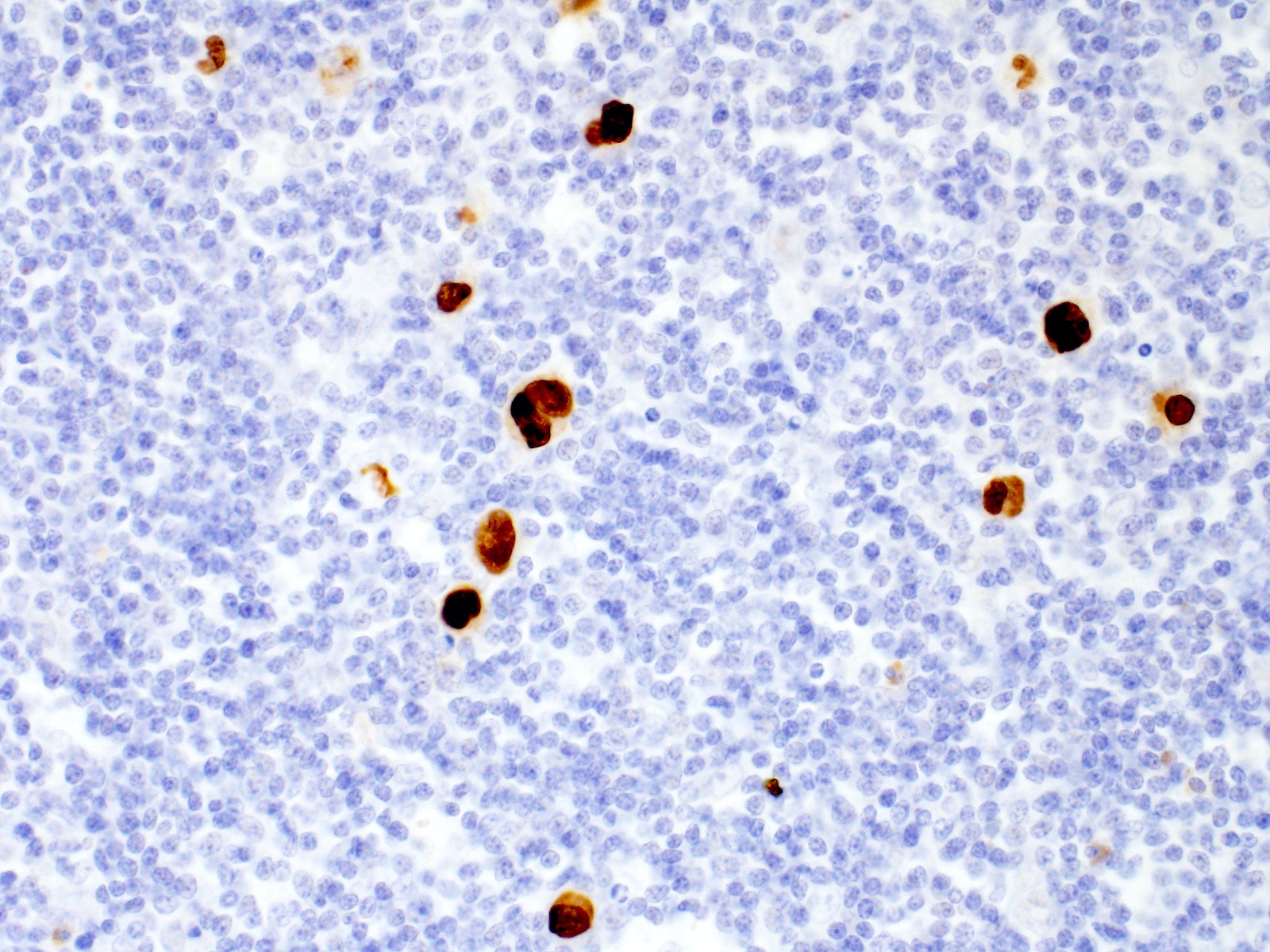
- Diagnostic cell = Reed-Sternberg cell: large size (up to 100 microns), bilobated to multilobated nucleus, prominent eosinophilic nucleolus, ample amphophilic cytoplasm
- Mononuclear variants = Hodgkin cells: single round to oval nucleus with prominent eosinophilic nucleolus
- Mummified forms: degenerated Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells, condensed hyperchromatic nuclei
- Lacunar cells: characteristic of nodular sclerosis subtype, lobulated nuclei, pale retracted cytoplasm (artifact of formalin fixation), creating lacunae-like spaces
- Mixed inflammatory background (Br J Haematol 2019;184:45)
- Nodular sclerosis: small lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes, plasma cells, necrosis and microabscesses common, with banding fibrosis
- Mixed cellularity: small lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes, plasma cells, epithelioid granulomas common
- Lymphocyte depleted: reduced background infiltrate
- Lymphocyte rich: nodules of small B cells, epithelioid histiocytes
- Diagnostic Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells may be rare to frequent depending on the subtype
- Syncytial variant: variant of nodular sclerosis subtype; Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells present in aggregates and sheets, with typical inflammatory background and immunophenotype of nodular sclerosis subtype
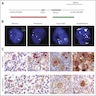
Microscopic (histologic) images
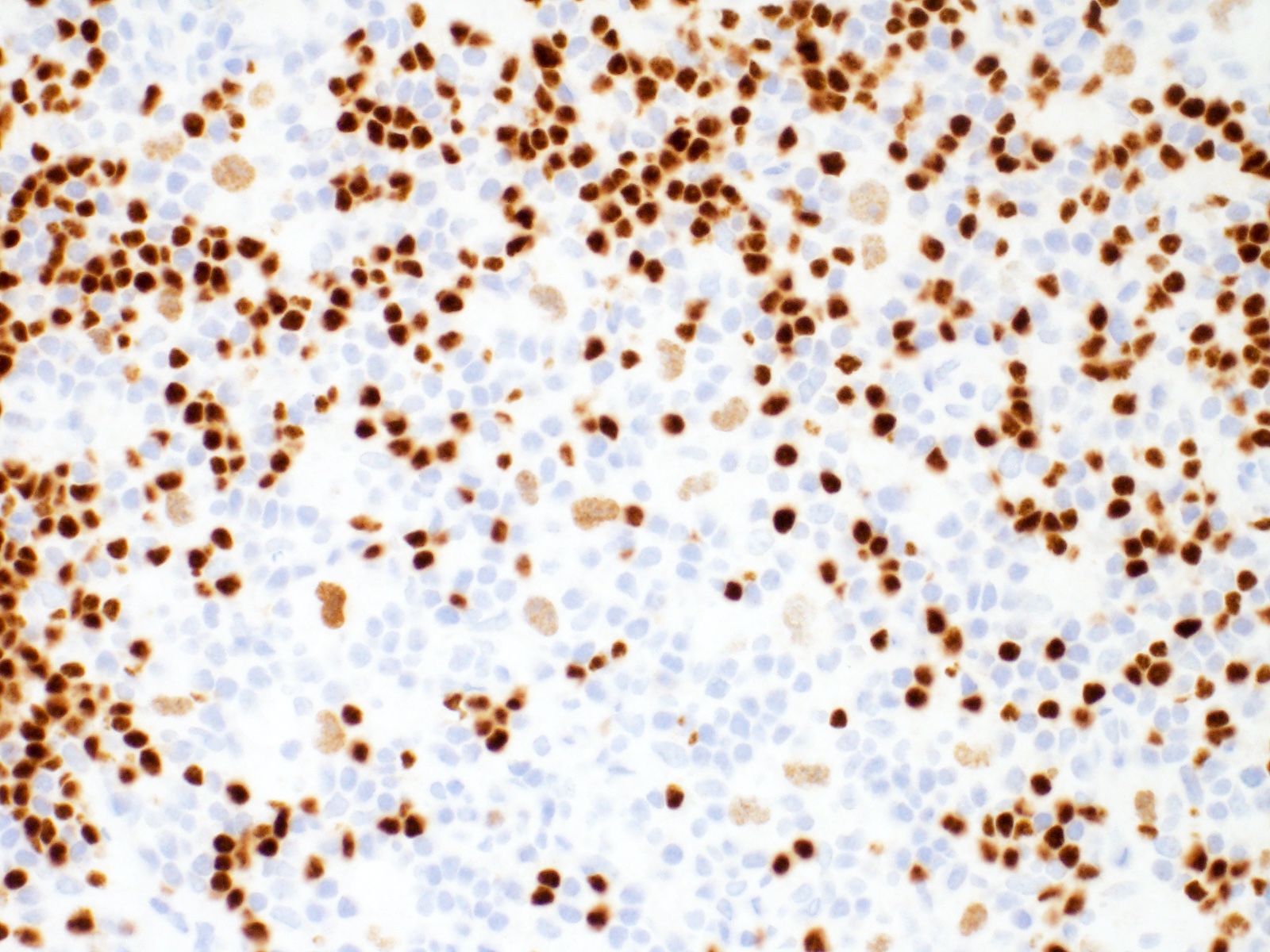
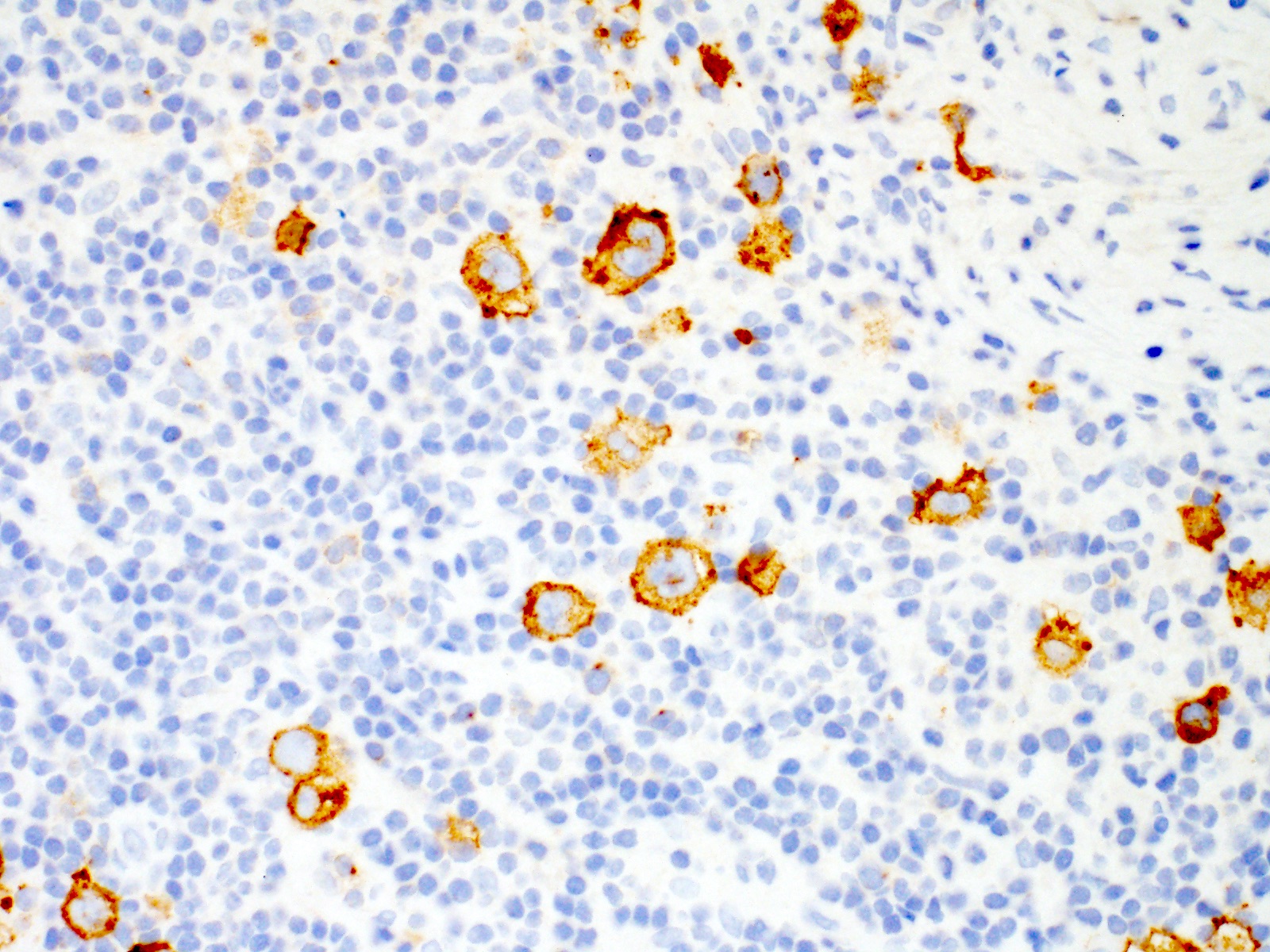
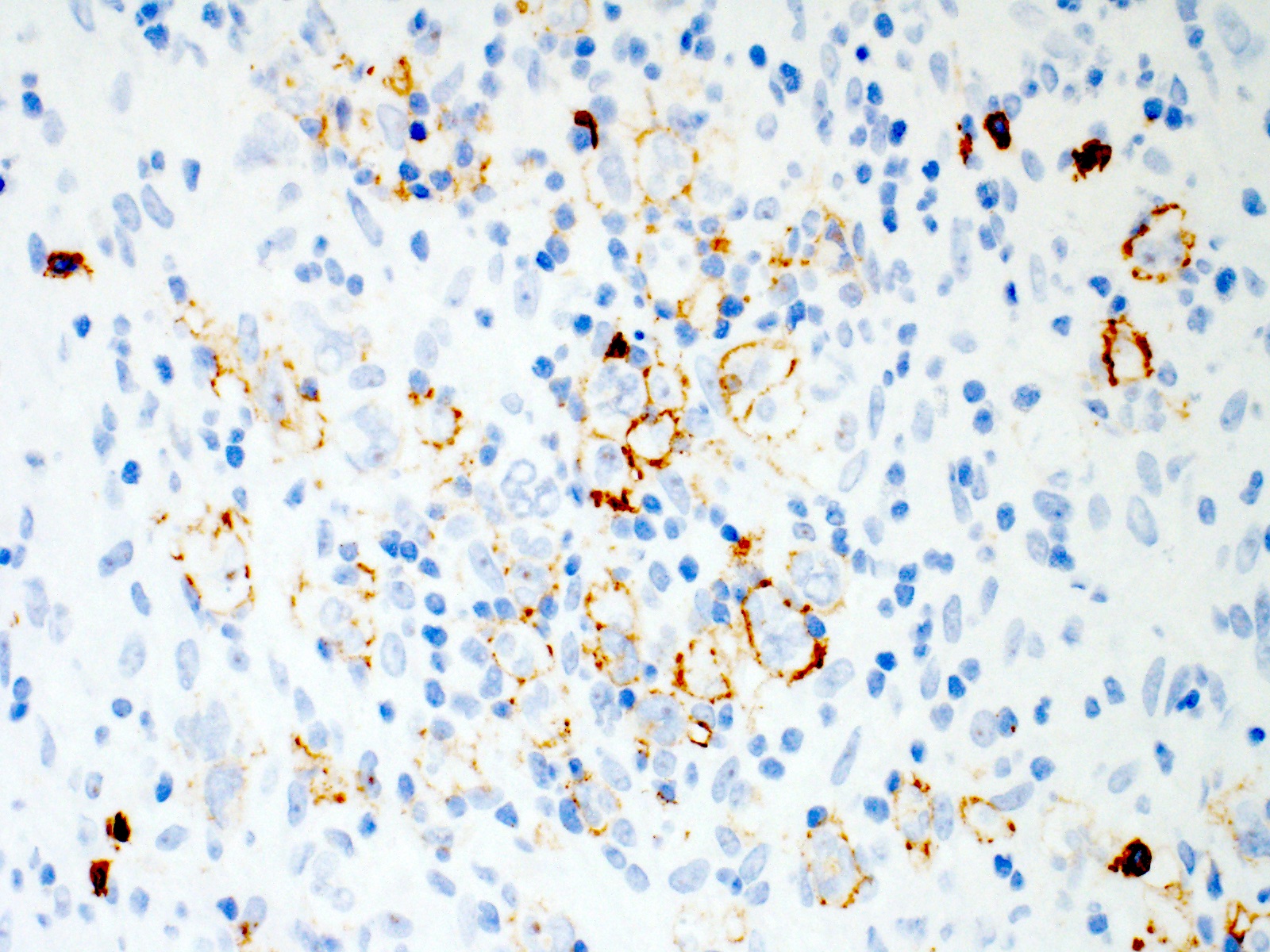
Contributed by Emily Mason, M.D., Ph.D.
Cytology description
- Mixed inflammatory background (small lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes)
- May see scattered large Reed-Sternberg cells with multilobated nuclei and prominent nucleoli
Positive stains
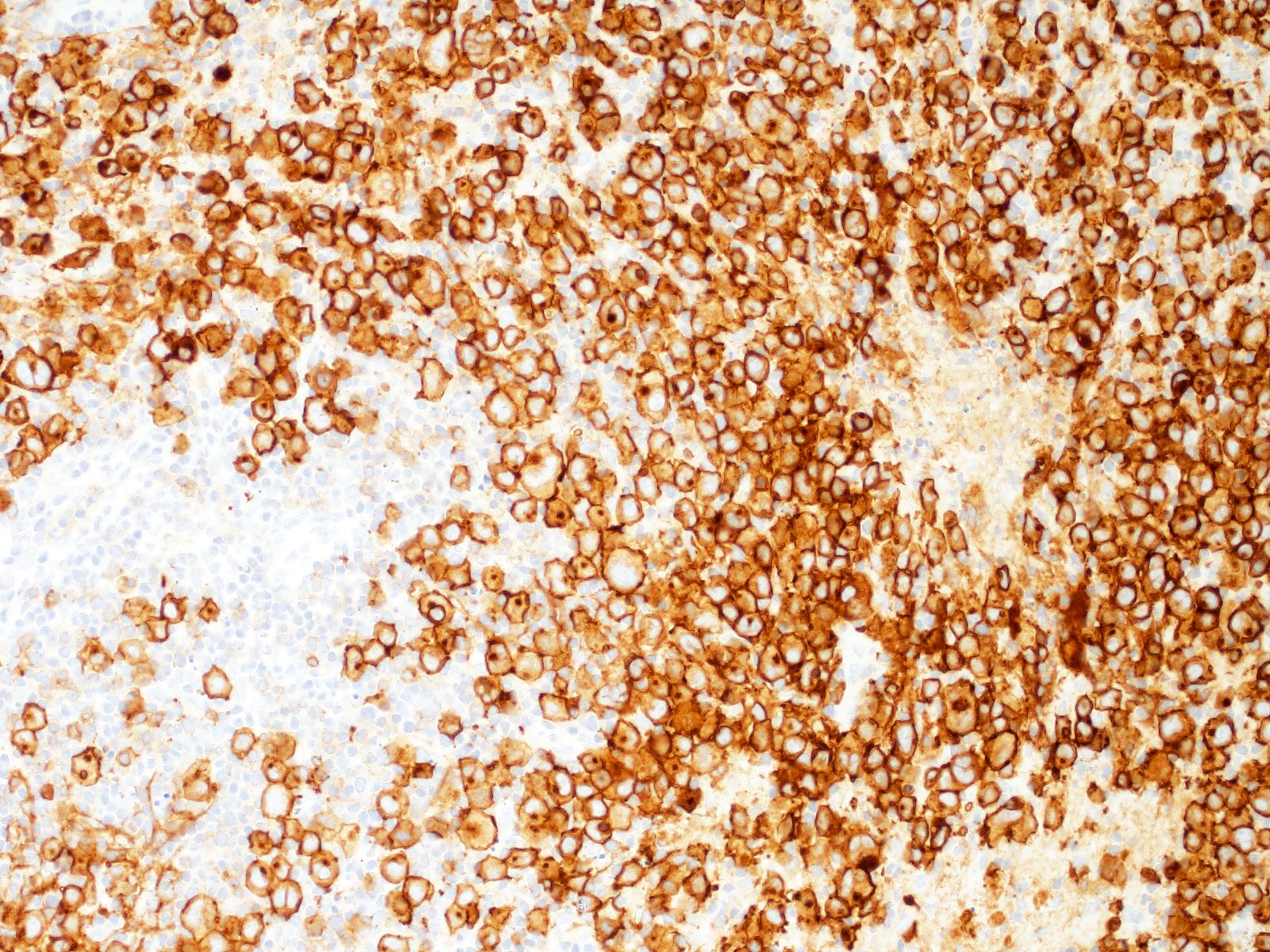
- Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells are positive for
- PAX5 (weak)
- CD30
- CD15 (75 - 80% of cases)
- MUM1 / IRF4
- Fascin (EBV positive and negative cases; EBV LMP1 induces fascin expression) (Cell Commun Signal 2014;12:46)
- EBER and EBV LMP1 positive in EBV positive cases (more common in mixed cellularity)
- PDL1 / PDL2
- CD200 (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;134:726)
- STAT6 (~80% of cases) and pSTAT6 (Mod Pathol 2020;33:834, Blood 2002;99:618)
- GATA3 (66 - 100% of cases) (Am J Pathol 2005;166:127, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:180)
Negative stains
- Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells are negative for
Flow cytometry description
- Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells typically not identified by flow cytometry (Br J Haematol 2019;184:45)
- Flow cytometry shows background infiltrate
- Typically, mixed T cells with increased CD4:CD8 ratio
Electron microscopy description
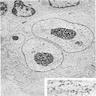
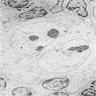
- Large rounded or oblong nuclei with folding, indentation and lobulation (Am J Pathol 1976;85:195)
- Occasional multinucleation
- Very large nucleoli
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells = B cells with clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangements (microdissection of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells is required for detection) (Blood 2000;95:1443)
- Immunoglobulin gene expression silenced in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells (Blood 2000;95:1443)
- Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells show numerical chromosome abnormalities in almost all cases (Blood 1995;86:1464)
- 90% of CHL shows copy number gain or amplification at 9p24.1; causes increased expression of PDL1 and PDL2 (J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2690)
- Gene mutations in components of the JAK / STAT and NFkB signaling pathways promote cell proliferation and survival (Leukemia 2021;35:968, Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:682)
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, left neck, excision:
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular sclerosis subtype (see comment)
- Comment: H&E stained sections show an enlarged lymph node with near total architectural effacement by a nodular mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of small lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils and numerous eosinophils, with scattered admixed large abnormal cells. The large abnormal cells have oval to occasionally multilobated nuclei, vesicular chromatin, prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm, consistent with Reed-Sternberg cells and mononuclear variants. Lacunar cells are present. The lymph node capsule is thickened and banding fibrosis is present
- Immunostains show that the large abnormal cells are positive for PAX5 (weak), CD30 and CD15 (subset) and are negative for CD20, CD45 and CD3. In situ hybridization for EBV encoded RNA (EBER) is negative. CD3 highlights background small T cells.
- Flow cytometry showed polytypic B cells and mixed T cell subsets.
Differential diagnosis
- Reactive immunoblastic reaction:
- Lymph node architecture is maintained
- Infectious mononucleosis:
- Particularly in children and young adults
- Although potentially distorted, the overall lymph node architecture is maintained
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL):
- T cell lymphoma
- Hallmark cells with bean or horseshoe shaped nuclei
- Involvement of lymph node sinuses
- May show loss of some T cell markers but typically positive for CD43, CD4 and cytotoxic markers (TIA1, granzyme B)
- ALK1 typically positive in children and young adults
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma:
- Typically low stage at presentation
- Large neoplastic cells are positive for CD20, CD45 and EMA
- Neoplastic cells typically negative for CD15 and CD30, although rare cases may be positive
- Nonneoplastic CD30 positive immunoblasts may be present
- Neoplastic B cells typically negative for CD200; neoplastic cells may be rosetted by CD200 positive follicular helper T cells (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;134:726)
- Neoplastic B cells typically negative for STAT6 and GATA3 (Mod Pathol 2020;33:834)
- Primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma:
- Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma:
- Sparse inflammatory infiltrate with high cell density
- Disconnect between morphology and immunophenotype: Reed-Sternberg cell morphology with strong homogenous expression of multiple B cell markers or diffuse proliferation of large cells with strong, homogenous expression of CD30 and often CD15 and loss of B cell markers (Blood Adv 2017;1:2600)
- Uniform CD20 expression in a tumor that is otherwise typical for nodular sclerosis CHL should not lead to a diagnosis of gray zone lymphoma (Br J Haematol 2019;184:45)
- T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma:
- EBV positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma:
- EBV positive mucocutaneous ulcer:
- Localized involvement of cutaneous or mucosal sites (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:405)
- Occurs in the setting of iatrogenic or age related immunosuppression
- Sharply circumscribed ulcerative lesion
- Most cases CD30 positive but typically CD15 negative
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified:
- Follicular helper T cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic type:
- T cell lymphoma with expression of T cell markers
- Mixed inflammatory infiltrate
- May show scattered large B cells that are often EBV positive
- T cell clonality studies usually positive for T cell clone
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. CD45. The image shows Reed-Sternberg cells, which are typically negative for CD45. Answers A, B, D and E are incorrect because these markers are all typically positive in Reed-Sternberg cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is most consistent with the immunophenotype of Reed-Sternberg cells?
- Positive: CD3, CD30, CD45, ALK1 / negative: CD15, CD20, EBER, MUM1
- Positive: CD15, CD20, MUM1, ALK1 / negative: CD3, CD15, CD45, EBER
- Positive: CD15, CD30, MUM1 / negative: CD3, CD20, CD45
- Positive: CD15, CD45, EBER / negative: CD20, CD30, MUM1
- Positive: CD20, CD30, CD45, ALK1 / negative: CD15, CD3, EBER
Board review style answer #2
C. Positive: CD15, CD30, MUM1 / negative: CD3, CD20, CD45. Answer A is incorrect because Reed-Sternberg cells are negative for ALK1. Answer B is incorrect because Reed-Sternberg cells are most commonly negative for CD20 and ALK1 and positive for CD15. Answer E is incorrect because Reed-Sternberg cells are negative for ALK1 and are typically positive for CD15. Answer D is incorrect because Reed-Sternberg cells are negative for CD45 and positive for CD30 and MUM1.
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Board review style question #3
Which of the following subtypes of classic Hodgkin lymphoma is most commonly associated with EBV?
- Lymphocyte depleted
- Lymphocyte rich
- Mixed cellularity
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant
- Nodular sclerosis
Board review style answer #3
C. Mixed cellularity. EBV is most commonly positive in mixed cellularity classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Answers A, B and E are incorrect because EBV is less commonly positive in these entities. Answer D is incorrect because nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma / B cell lymphoma is not a subtype of classic Hodgkin lymphoma and is negative for EBV.
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Comment Here
Reference: Classic Hodgkin lymphoma