Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Shestakova A, Perry AM. High grade B cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaburkittlike11q.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare B cell lymphoma that resembles Burkitt lymphoma morphologically, phenotypically and by gene expression profiling
- Negative for MYC rearrangement
Essential features
- Rare, germinal center-derived mature B-cell lymphoma characterized by proximal gains and telomeric losses of chromosome 11q (including 11q-gain/loss, telomeric loss or telomeric LOH pattern)
- Features overlapping with Burkitt lymphoma, but lacks MYC rearrangement
- Most patients are children and young adults presenting with lymphadenopathy
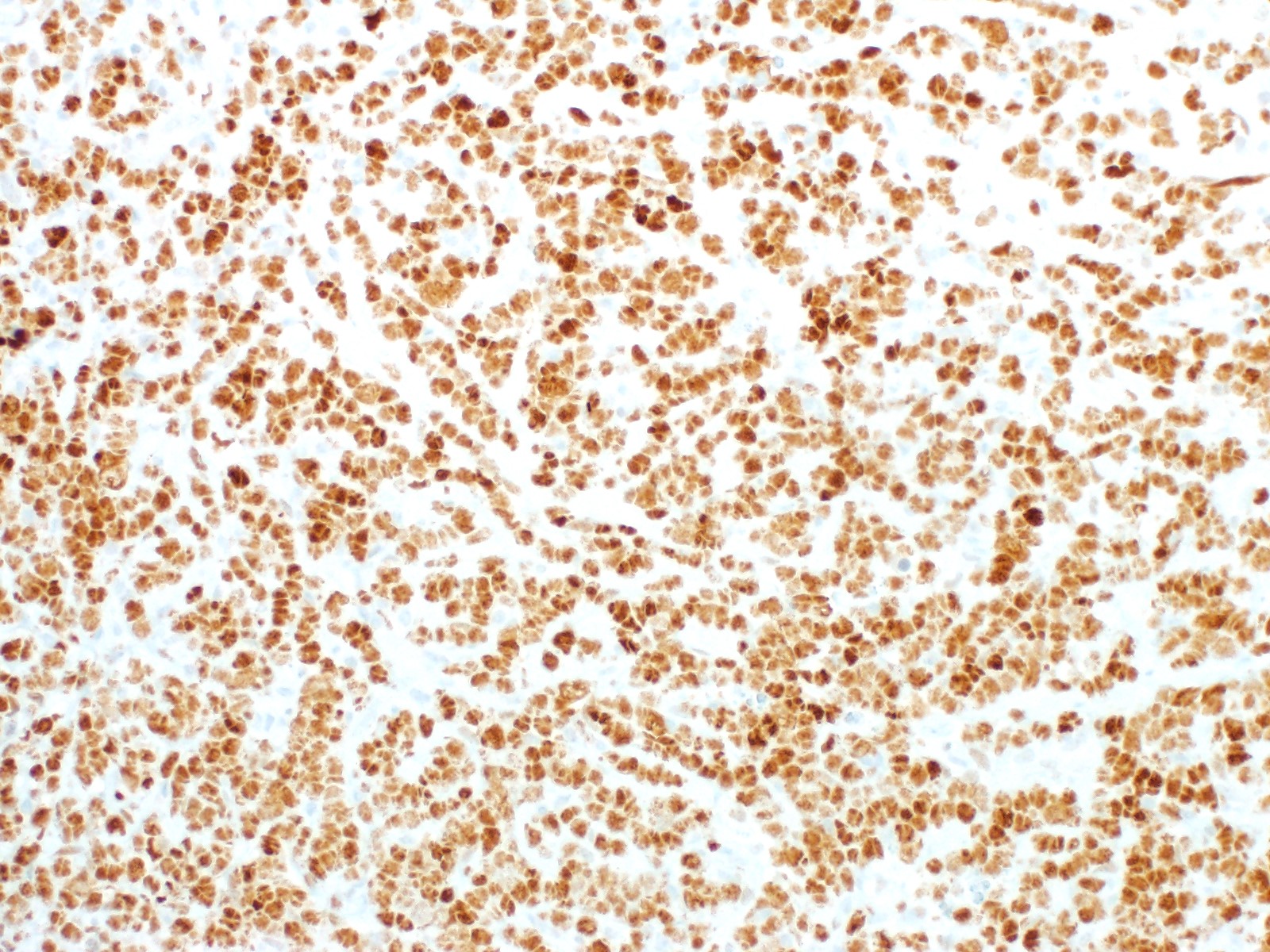
- Diffuse infiltrate of medium sized to large cells, frequently with interspersed tingible body macrophages and apoptotic debris
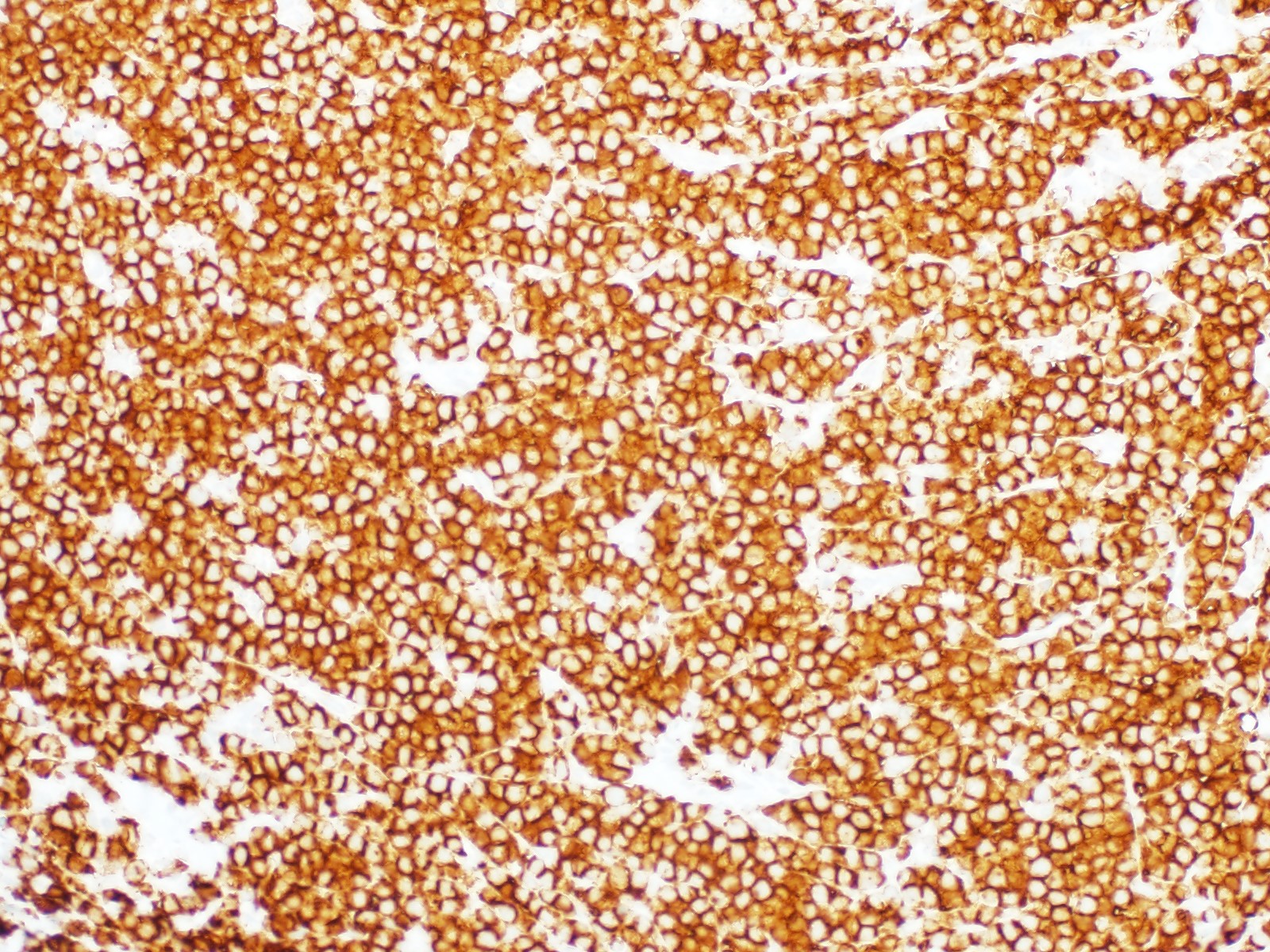
- Lymphoma cells positive for CD20, CD10, and BCL6, and negative for BCL2, with Ki67 > 95%
- Lymphoma cells show LMO2 and sometimes CD56 expression (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- Favorable prognosis with intensive chemoimmunotherapy
Terminology
- Large B cell lymphoma with 11q aberration (Blood 2022;140:1200)
- High grade B cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- Not recommended: Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration
- Burkitt-like lymphoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9687/3 - Burkitt lymphoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Most common in children and young adults, median in third decade (Mod Pathol 2018;31:732, Haematologica 2019;104:1822, Blood 2014;123:1187)
- Male predominance
- Seen in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients (such as posttransplantation) (Haematologica 2015;100:e275)
Sites
- Lymph nodes are most commonly affected
- Occasionally involves extranodal sites (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
Diagnosis
- Tissue biopsy of lymph node or extranodal site
Prognostic factors
- Overall good prognosis, comparable to Burkitt lymphoma; 5 year overall survival of 80% (Mod Pathol 2018;31:732, Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
Case reports
- 17 year old girl with a neck mass (Case Rep Hematol 2020;2020:8896322)
- 37 year old immunocompetent woman and 56 year old man with HIV, both with cervical lymph node involvement (Open Med (Wars) 2021;16:428)
- 65 year old man with abdominal mass (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:1823)
Treatment
- Intense chemoimmunotherapy with central nervous system prophylaxis (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
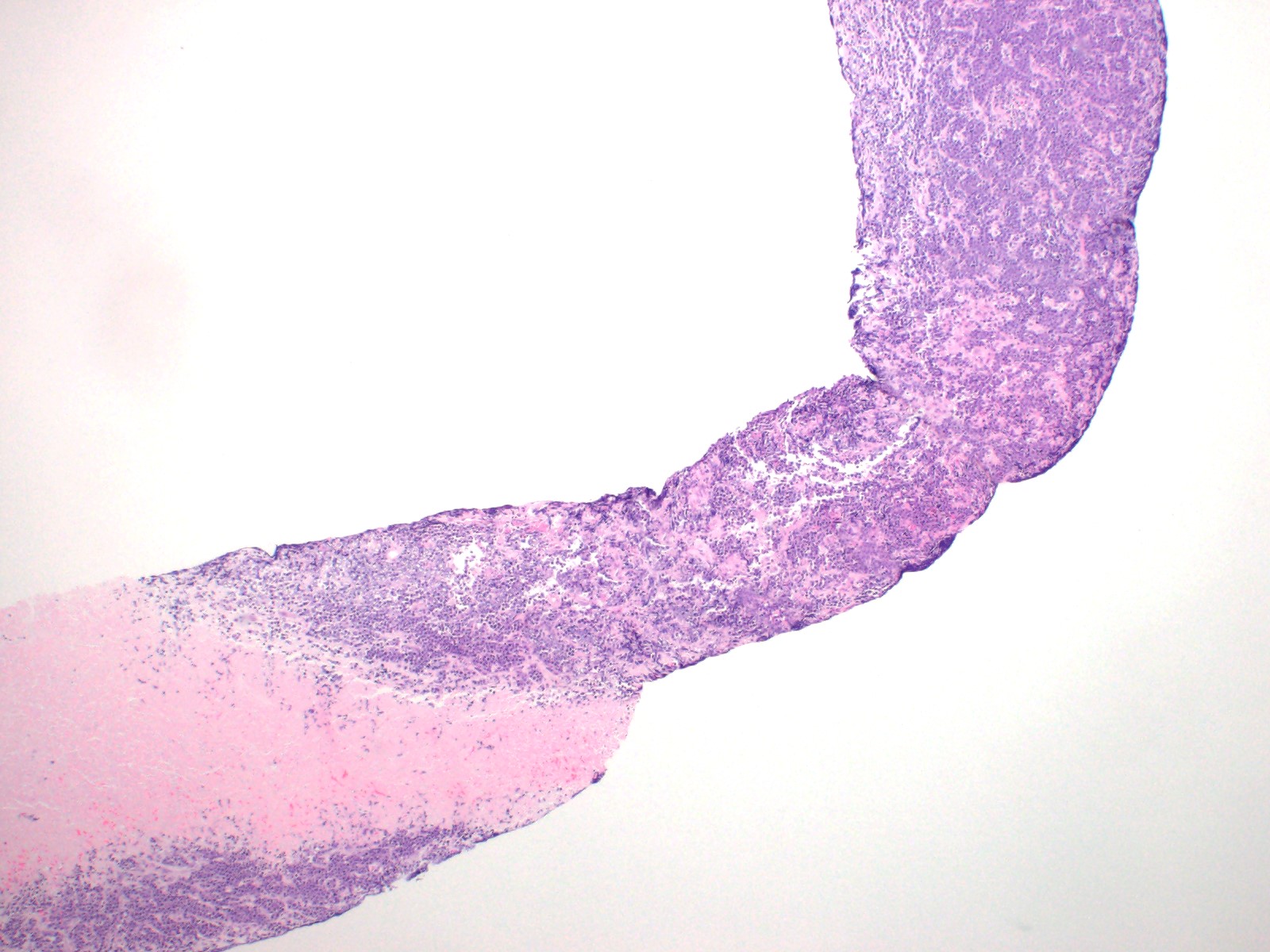
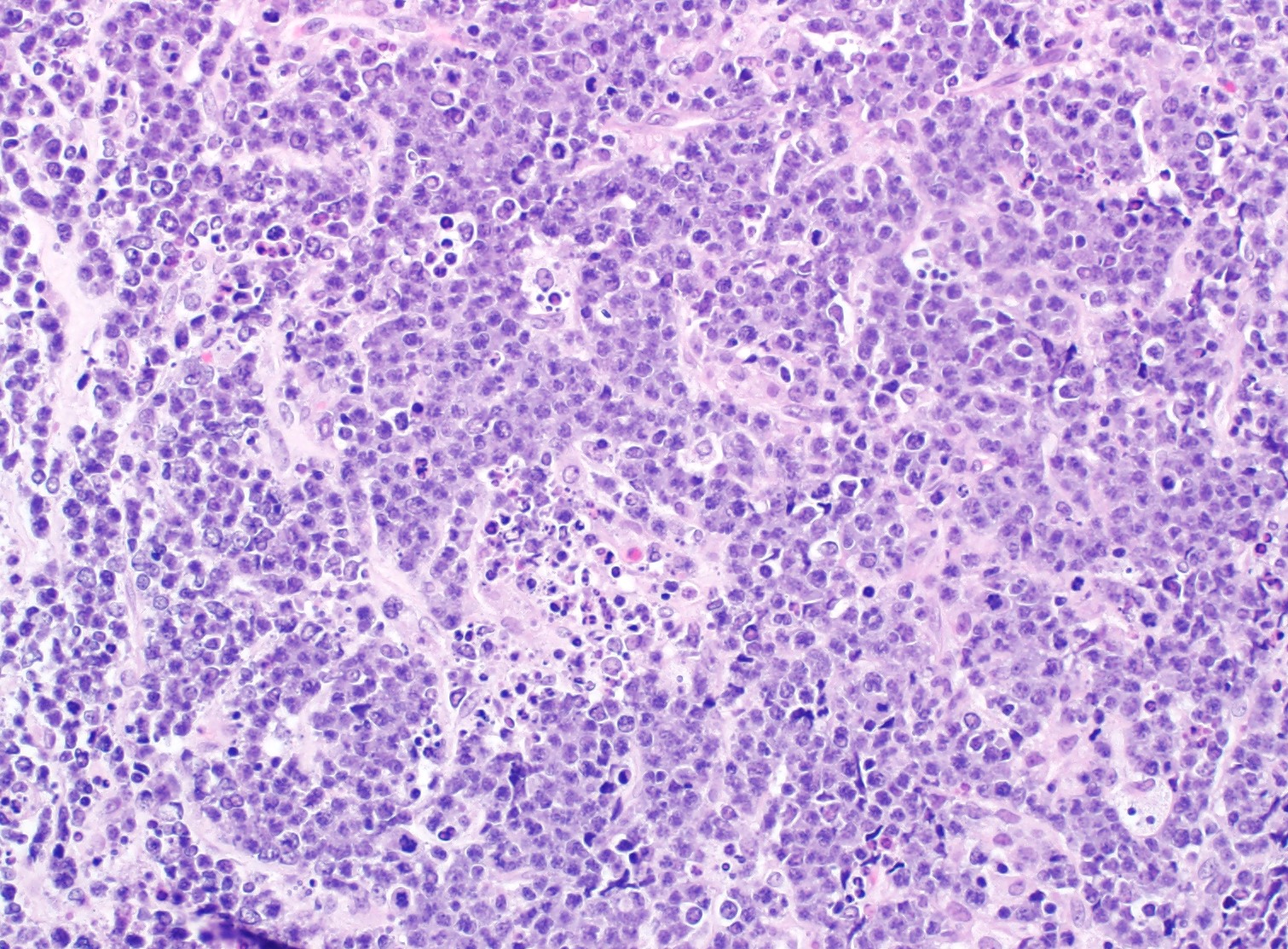
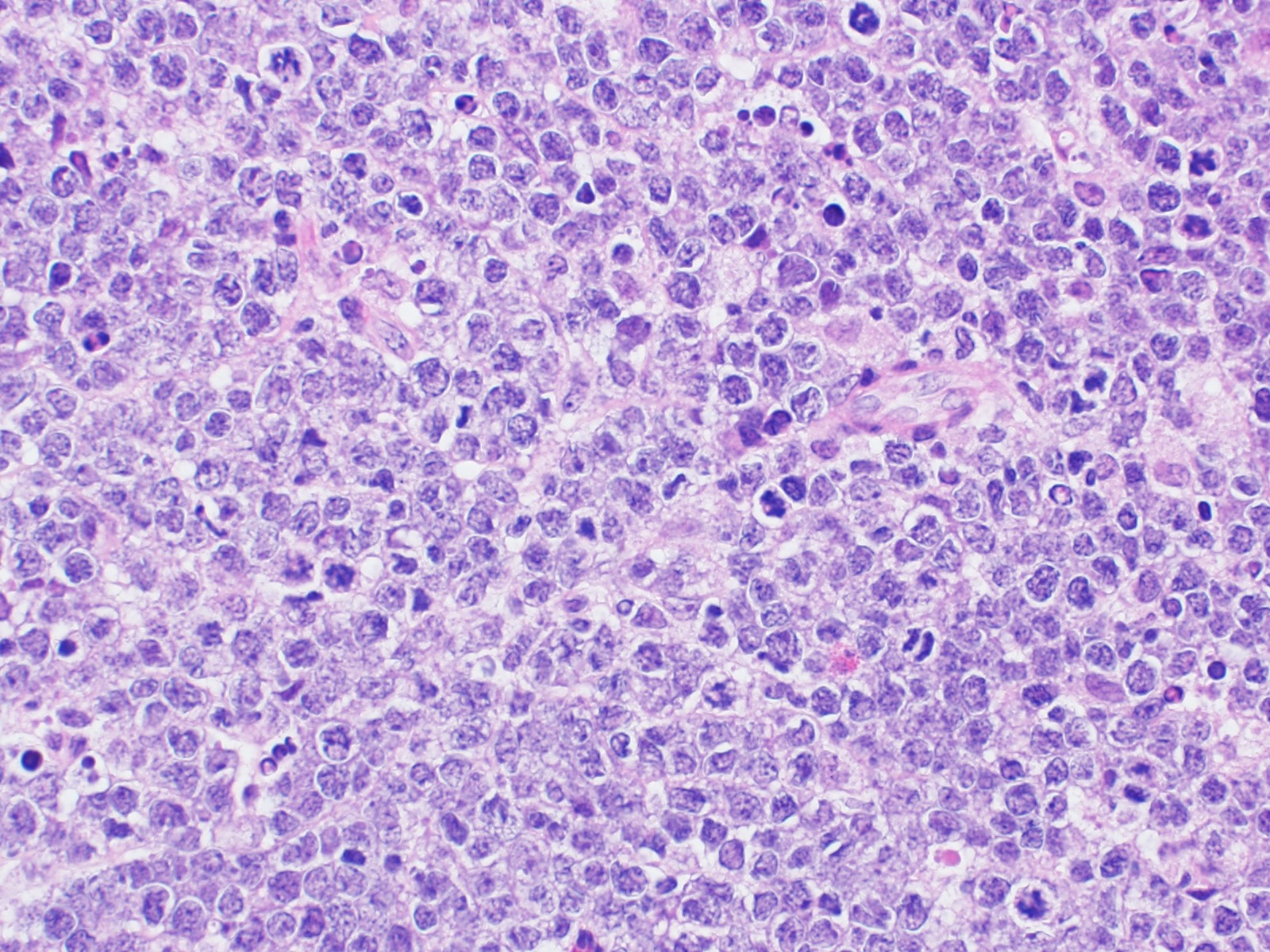
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Diffuse involvement by sheets of lymphoma cells
- Occasional cases show a vaguely nodular pattern (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
- Some cases are similar to Burkitt lymphoma, with tingible body macrophages, exhibiting starry sky pattern
- Other cases have fewer macrophages but frequently show apoptotic bodies
- Lymphoma cells are medium-sized to large and usually have more cytological pleomorphism than typical Burkitt lymphoma with more irregular nuclei
- Some cases morphologically resemble diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Haematologica 2019;104:1822, Am J Clin Pathol 2017;149:17)
Microscopic (histologic) images
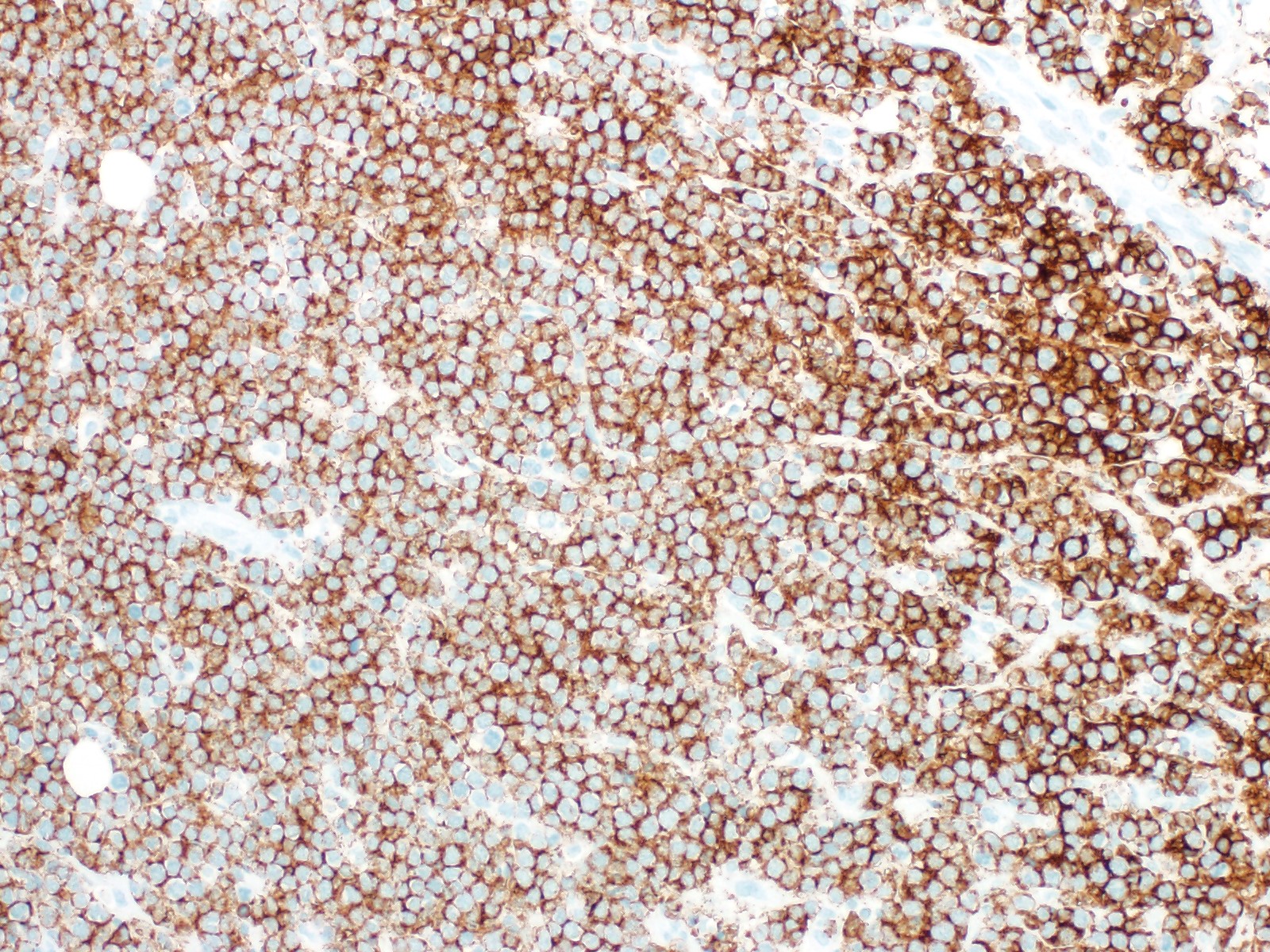
Positive stains
- Pan B cell markers: CD19, CD20, CD79a, PAX5
- CD10, BCL6, LMO2
- MYC (positive in majority of cases) (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;149:17, Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
- Ki67 shows high proliferative index (> 95%) (Mod Pathol 2018;31:732)
Negative stains
- BCL2 (vast majority of cases), MUM1, TdT, CD30 (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;149:17, Case Rep Hematol 2020;2020:8896322)
- EBV (Haematologica 2015;100:e275)
Flow cytometry description
- Mature B cell lymphoma with germinal center immunophenotype, positive for CD19, CD20, CD10 and CD38 with surface light chain restriction (Mod Pathol 2018;31:732)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Defined by 11q aberrations, including proximal gains and telomeric losses
- Negative for MYC rearrangement (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
- More complex karyotypes than seen in Burkitt lymphoma
- Gains of 12q12-q21.1 and losses of 6q12.1-q21 (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
- Negative for 1q gain, seen in Burkitt lymphoma
- Detected mutations include BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300 and GNA13 (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
- Negative for ID3, TCF3 or CCND3 mutations that are typical for Burkitt lymphoma (Haematologica 2019;104:1822)
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, cervical, core needle biopsy:
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration
Differential diagnosis
- Burkitt lymphoma (BL):
- Morphology and immunophenotype do not reliably distinguish between the 2 entities
- BL shows MYC rearrangement and usually has a less complex karyotype
- Subset of Burkitt lymphomas are EBV+
- Rare cases with concomitant MYC rearrangement and 11q aberration exist (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;149:17)
- High grade B cell lymphoma, NOS:
- Morphology and immunophenotype do not reliably distinguish between the 2 entities
- 11q aberrations usually absent but can have MYC rearrangement without concomitant BCL2 or BCL6
- Diagnosis reserved for cases that cannot be confidently classified as Burkitt lymphoma or diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Insights Imaging 2019;10:56, Pathology 2018;50:74)
- High grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 rearrangements:
- Rearranged MYC and BCL2 or BCL6 genes (Blood 2018;131:2060)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL):
- Lymphoma cells are usually large and more pleomorphic
- Immunophenotypes can overlap
- Rare cases with 11q aberrations have DLBCL morphology
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 20 year old man presents with abdominal pain and recent 20 pound weight loss. He was found to have a 10 cm peripancreatic mass, which was biopsied and shown in the figure above. Cytogenetic studies are negative for MYC gene rearrangement. Chromosomal genetic microarray shows 11q aberration with proximal gain and telomeric loss. Which of the following is the typical immunophenotype seen in this entity?
- CD20+, CD10+, BCL6+, MUM1-, BCL2-, Ki67 > 95%
- CD20+, CD10+, BCL6+, MUM1+, BCL2+, Ki67 > 95%
- CD20+, CD10-, BCL6-, MUM1+, BCL2+, Ki67 > 95%
- CD20+, CD10-, BCL6-, MUM1+, BCL2-, Ki67 > 95%
Board review style answer #1
A. Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration usually shows the following immunophenotype: CD20+, CD10+, BCL6+, MUM1-, BCL2-, Ki67 > 95%
Comment Here
Reference: Large B cell lymphoma with 11q aberration
Comment Here
Reference: Large B cell lymphoma with 11q aberration