Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Crane G. POEMS syndrome (osteosclerotic myeloma). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaPOEMS.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Paraneoplastic syndrome due to an underlying plasma cell neoplasm
- POEMS = polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, M protein spike and skin changes
- But the acronym does not include several of the common clinical manifestations
Essential features
- Major criteria for diagnosis are:
- Polyradiculopathy
- Clonal plasma cell disorder
- Sclerotic bone lesions
- Elevated vascular endothelial growth factor
- Castleman disease (also known as angiofollicular hyperplasia, 11 - 30% of cases, most commonly multicentric Castleman disease)
Terminology
- POEMS acronym coined in 1980 by Bardwick et al. (Medicine (Baltimore) 1980;59:311)
- Other names: osteosclerotic myeloma, Takatsuki syndrome, Crow-Fukase syndrome
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D47.7 - other neoplasms of uncertain behavior of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue
- See also WHO coding
Epidemiology
- Prevalence of approximately 0.3 per 100,000 reported in Japan but occurs worldwide
Pathophysiology
- VEGF levels are high and correlate with disease activity but may not drive the process
- IL12 also correlates with disease activity; IL6 produced by plasma cells may play a role
Clinical features
- In addition to essential features above, other clinical features include:
- Organomegaly
- Endocrinopathy
- Characteristic skin changes
- Papilledema
- Extravascular volume overload / anasarca
- Thrombocytosis, with propensity for thrombosis
- Abnormal pulmonary function tests, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension
- Diarrhea, calciphylaxis (rare)
- Generally no bone pain
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is made by fulfilling at least 3 major criteria, 2 of which must include polyradiculoneuropathy and a clonal plasma cell disorder, along with at least 1 minor criterion (Am J Hematol 2017;92:814)
- Mandatory criteria (must have both): polyneuropathy and monoclonal plasma cell disorder
- Other major criteria (at least 1 present): Castleman disease, sclerotic bone lesions, increased VEGF levels
- Minor criteria (at least 1 present):
- Organomegaly
- Extravascular volume overload (edema, pleural effusion, ascites),
- Endocrinopathy (adrenal, thyroid, pituitary, gonadal, parathyroid, pancreatic); hypogonadism most common
- Skin changes (hyperpigmentation, hypertrichosis, glomeruloid angiomata, plethora, acrocyanosis, white nails, sclerodermoid changes, clubbing)
- Papilledema
- Thrombocytosis / polycythemia
Laboratory
- Monoclonal light chain (especially lambda)
- VEGF levels are high
- Thrombocytosis or erythrocytosis, absence of cytopenias
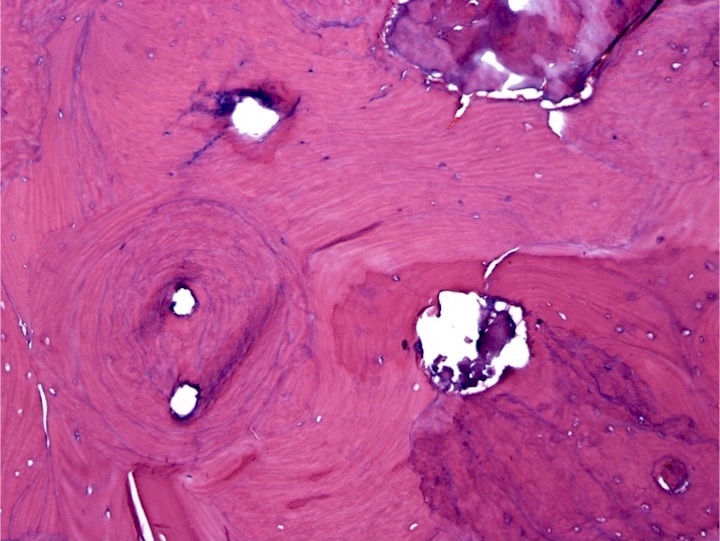
Radiology description
- Bone lesions
- Signs of volume overload (e.g. pleural effusion, ascites)
Prognostic factors
- Risk associated with the extent of the plasma cell disorder
- Bone marrow plasmacytosis increases risk of cerebrovascular event
- Number of clinical criteria met is not prognostic
- Generally better overall survival than myeloma, older data shows median survival of 14 years
Case reports
- 47 year old man with POEMS syndrome with a plasmacytoma causing craniocervical instability (J Clin Neurosci 2017 Oct 31 [Epub ahead of print])
- 48 year old woman with 2 week history of peripheral neuropathy (Blood 2013;122:159)
- 2 patients with plasma cell dyscrasias, original description by Bardwick et al. (Medicine (Baltimore) 1980;59:311)
Treatment
- If no bone marrow involvement by plasma cell clone, local radiation therapy may be adequate (e.g. sclerotic plasmacytoma)
- If disseminated disease or progression following local radiation, systemic therapy advised
- Corticosterioids as a temporizing measure
- Alkylating agents a mainstay, including high dose with stem cell transplant
- Thalidomide, bortezomib can be considered but may worsen peripheral neuropathy
- Prompt treatment recommended
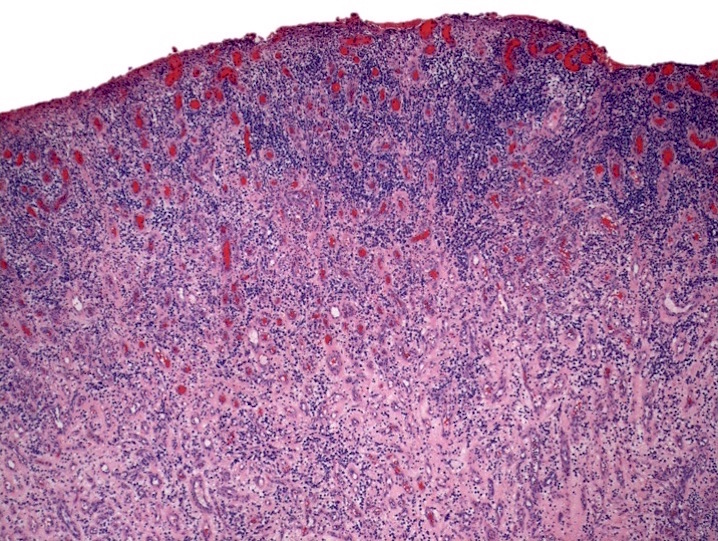
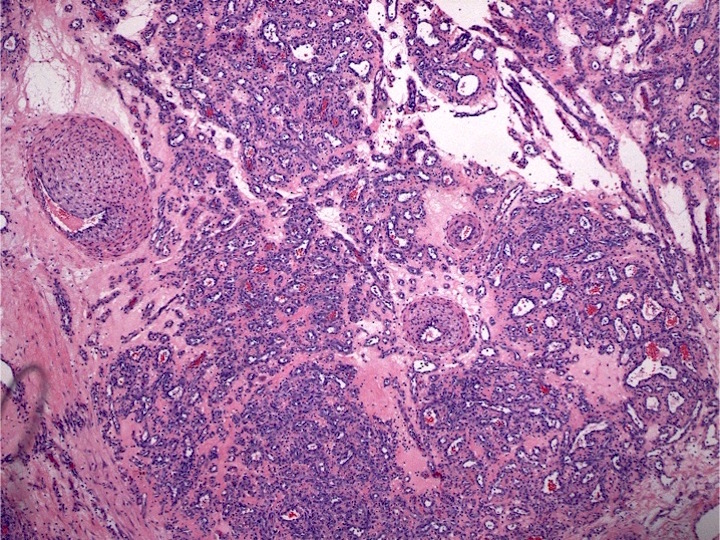
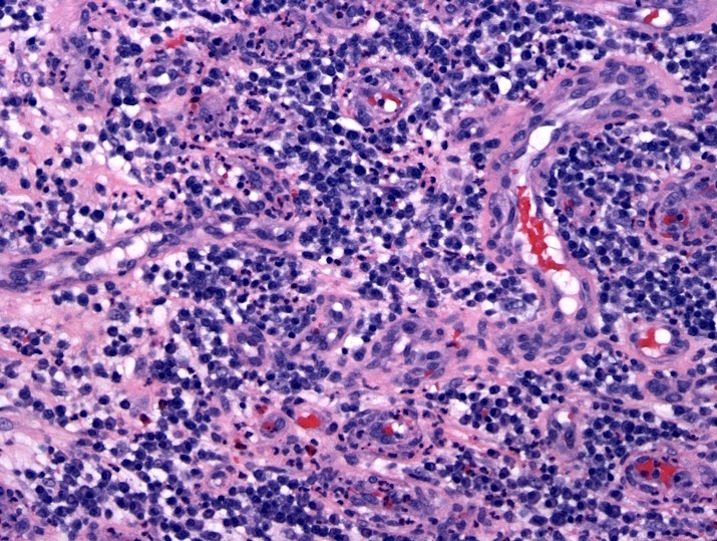
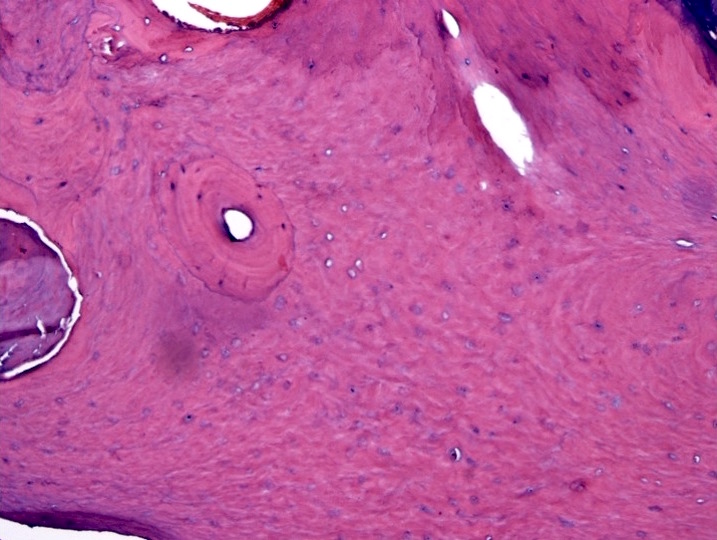
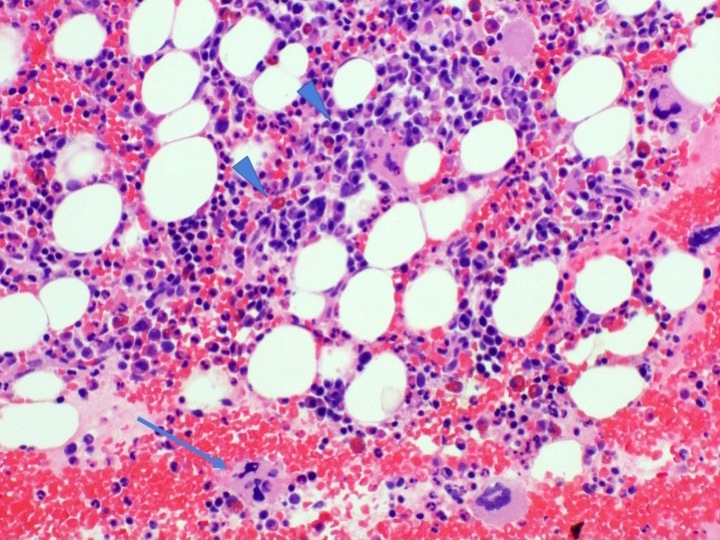
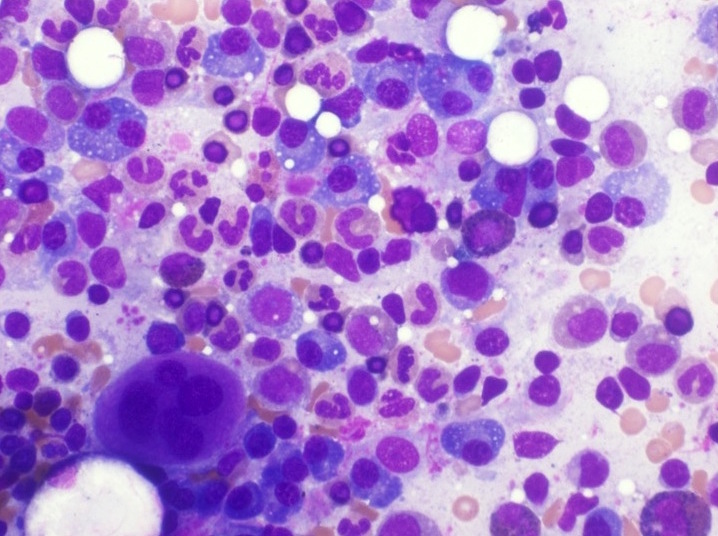
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Bone marrow biopsy may show megakaryocyte hyperplasia and clustering (no JAK2 mutation)
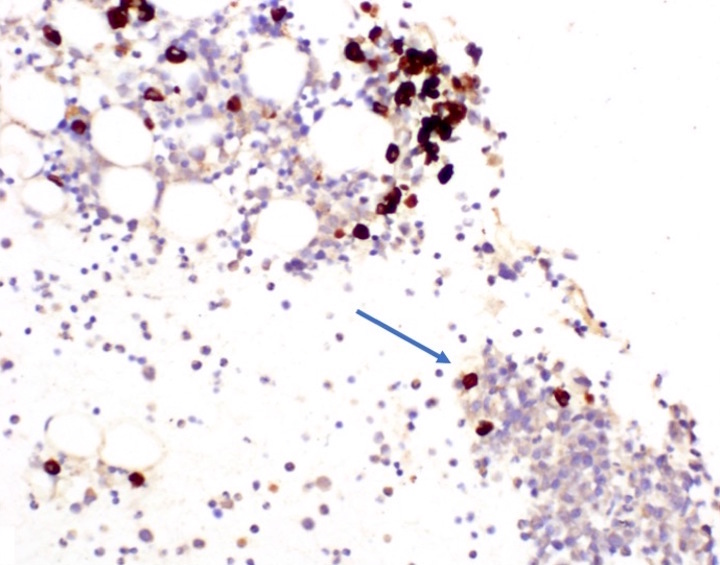
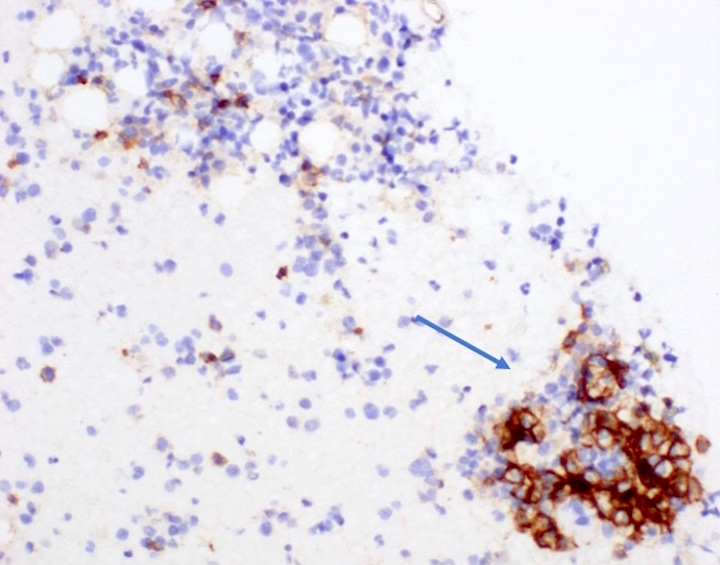
- Lymphoid aggregates (50% of cases) with clonal plasma cell rimming
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Genevieve M. Crane, M.D., Ph.D. and Sarah Elsoukkary, M.D.
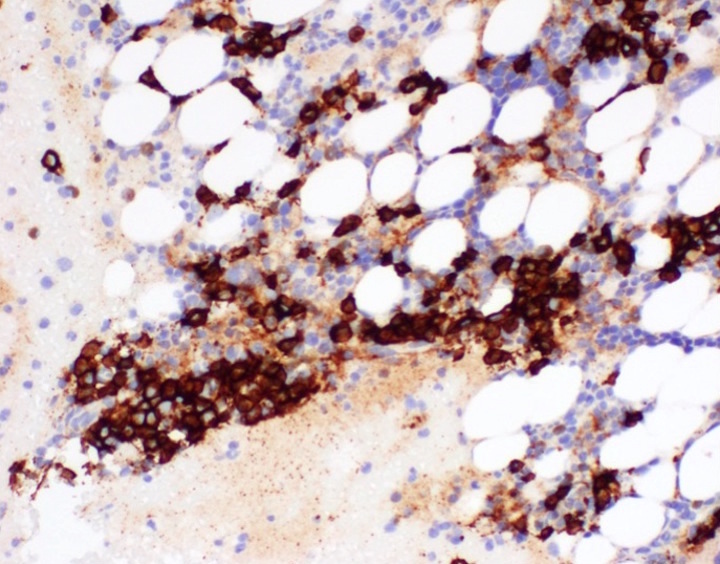
Positive stains
- Lambda clones predominate (95% of cases)
- Other features are as for clonal plasma cell populations
Electron microscopy description
- No features of macrophage associated demyelination in contrast to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculopathy
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Tend to have restricted immunoglobulin variable chain usage (IGLV1)
- Translocations and deletion of chromosome 13 have been described
Differential diagnosis
- POEMS disease is rare and can be mistaken for other processes:
- Castleman disease variant of POEMS syndrome: no associated clonal plasma cell process and little to no peripheral neuropathy
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculopathy: a predominantly neurologic disorder (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2016;4:116)
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), solitary plasmacytoma
- Osteosclerotic lesion differential by radiology: aneurysmal bone cysts, nonossifying fibromas, fibrous dysplasia
- Plasma cell myeloma: POEMS symptoms of neuropathy, endocrine dysfunction, volume overload not associated with myeloma; myeloma symptoms of bone pain, renal failure less common in POEMS
Board review style question #1
Which 2 of the following clinical features are more commonly associated with POEMS syndrome than multiple myeloma?
- Bone pain
- Demonstration of clonal plasma cells
- Neuropathy
- Pleural effusion
- Renal failure
Board review style answer #1
C and D. Neuropathy and pleural effusion; volume overload and neuropathy are characteristic features of POEMS syndrome. POEMS syndrome is less frequently associated with bone pain and renal failure as compared to multiple myeloma. Both require demonstration of clonal plasma cells.
Comment Here
Reference: POEMS syndrome (osteosclerotic myeloma)
Comment Here
Reference: POEMS syndrome (osteosclerotic myeloma)