Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Flaifel A, Ward N. Nodal T follicular helper cell lymphoma, follicular type. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaFPTCL.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- A rare subtype of nodal lymphomas of T follicular helper (Tfh) cell origin with a follicular or perifollicular growth pattern exhibiting strong and consistent expression of T follicular helper markers
- These cases distinctly lack histologic features commonly associated with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL), such as interfollicular polymorphous infiltrate, proliferation of high endothelial venules or expanded follicular dendritic cell meshworks
Essential features
- Clinical and laboratory findings similar to AITL
- Histologically characterized by a follicular or perifollicular growth pattern with consistent expression of Tfh markers (2, preferably 3 markers)
- Lacks histologic features commonly associated with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL), including proliferation of interfollicular high endothelial venules or expanded follicular dendritic cell meshworks
- t(5;9)(q33;q22) ITK-SYK rearrangement seen in about 20% of cases
Terminology
- Follicular peripheral T cell lymphoma (F-PTCL)
- Follicular T cell lymphoma (FTCL)
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma with a nodular, follicular or perifollicular pattern
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma with follicular involvement
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9702/3 - mature T cell lymphoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare
- 1 - 2% of all T cell lymphomas
- Slightly M > F
- Middle aged and elderly
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:682
Sites
- Most commonly presents as disseminated / advanced stage nodal disease
- Less commonly at extranodal sites: skin, bone marrow, liver and spleen
Pathophysiology
- F-PTCL shares with AITL not only morphologic features but also similar clinical features, genetic landscape and molecular signatures, which may suggest a common pathophysiology (Haematologica 2017;102:e148)
Etiology
- Association with EBV may suggest a role for the virus (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1636)
- AITL and F-PTCL have been reported to share molecular abnormalities related to the same origin of TFH cells, including RHOA, TET2, IDH2 and DNMT3A aberrations (Exp Hematol Oncol 2021;10:33)
Clinical features
- Generalized lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly
- B symptoms
- Skin rash
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:682
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis by a constellation of morphologic and immunophenotypic profiles on tissue biopsy (i.e. lymph node)
- Demonstrates a mature T follicular helper phenotype and does not meet criteria for AITL in the WHO classification (Blood 2016;127:2375)
- Staging: bone marrow biopsy
Laboratory
- Positive Coombs test or hypergammaglobulinemia, findings typically associated with AITL, can occasionally be seen in FTCL
- Increased LDH
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:682
Prognostic factors
- Typically aggressive course with reported 50% mortality within 24 months of diagnosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:682)
- Occasional indolent / protracted with localized presentation
Case reports
- 27 year old man with flu-like illness, jaundice, widespread lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly (Br J Haematol 2008;143:439)
- 47 year old man with FTCL mimicking lymphocyte rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) (J Clin Exp Hematop 2021;61:97)
- 50 - 70 year old men with generalized lymphadenopathy (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:395)
- 81 year old Japanese woman with malaise, fever and generalized lymph node swelling (Pathol Int 2002;52:400)
- 85 year old man with mediastinal lymphadenopathy, fever and night sweats (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;123:448)
- 90 and 91 year old women with skin lesions (Histopathology 2010;56:548)
Treatment
- Distinction between F-PTCL and PTCL, NOS has currently no impact on clinical management
- New therapeutic approaches and targeted interventions, such as hypomethylating agents, are promising (Br J Haematol 2015;168:913)
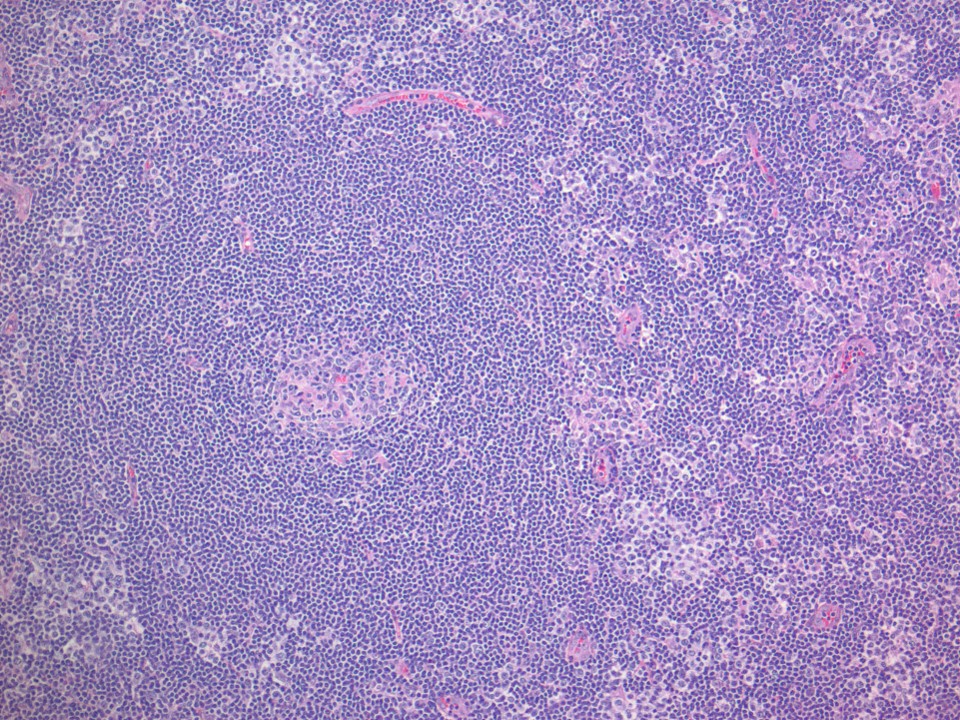
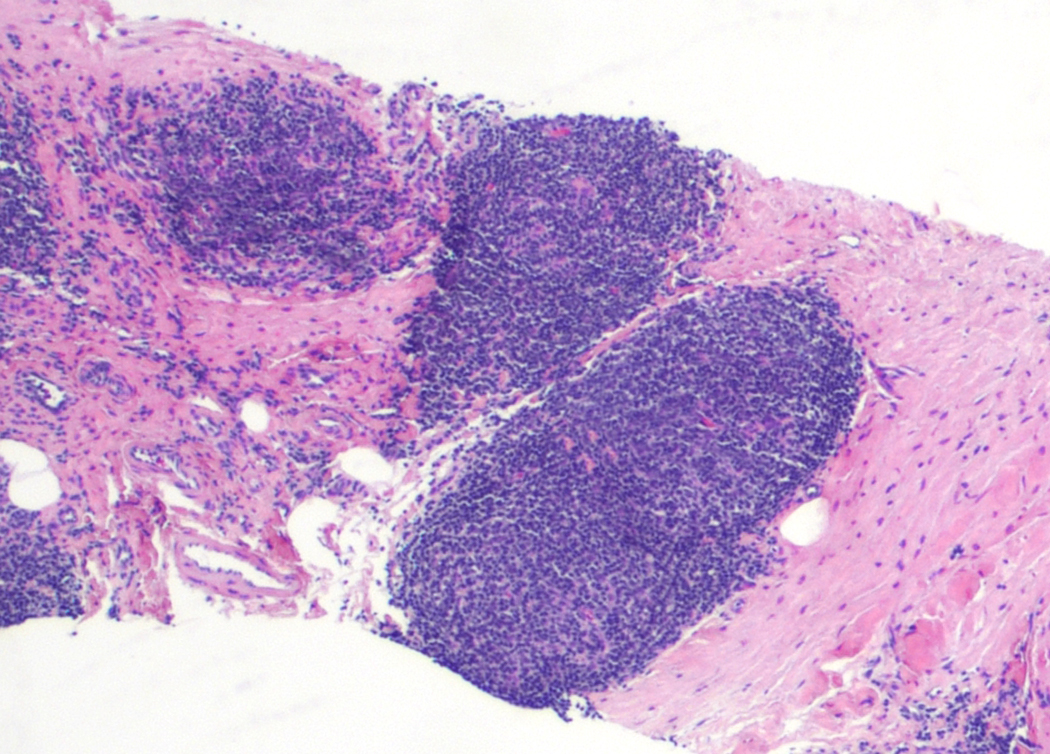
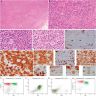
Microscopic (histologic) description
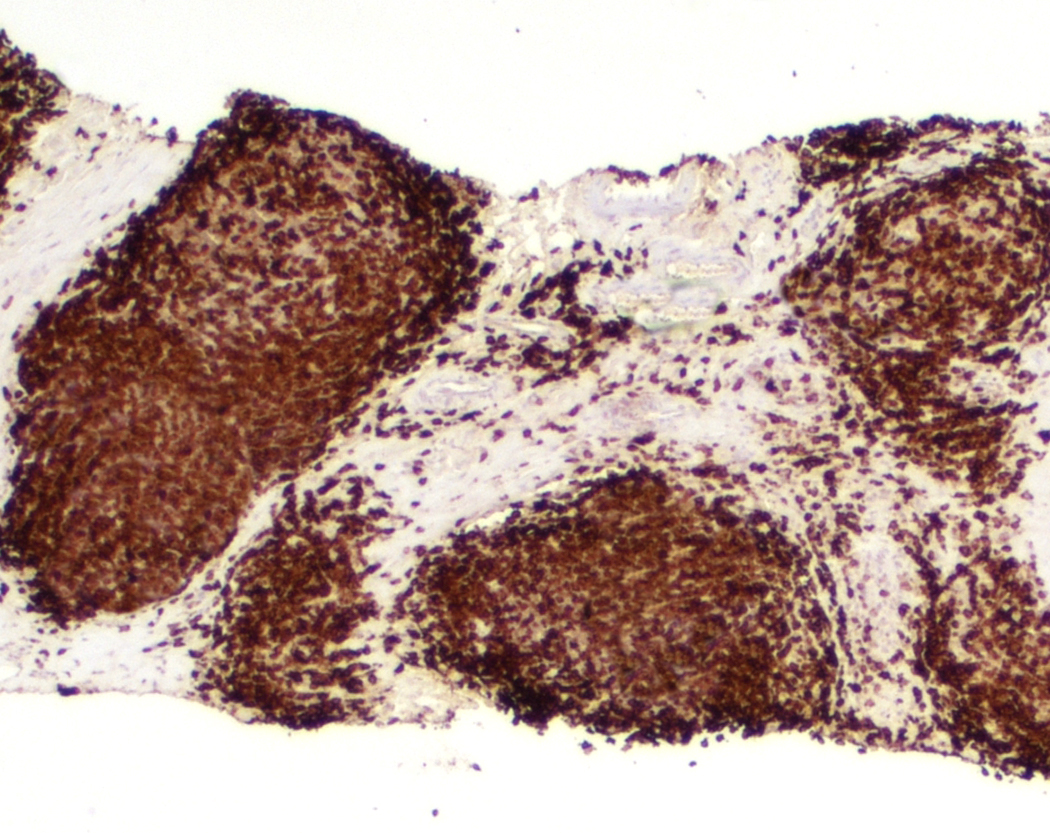
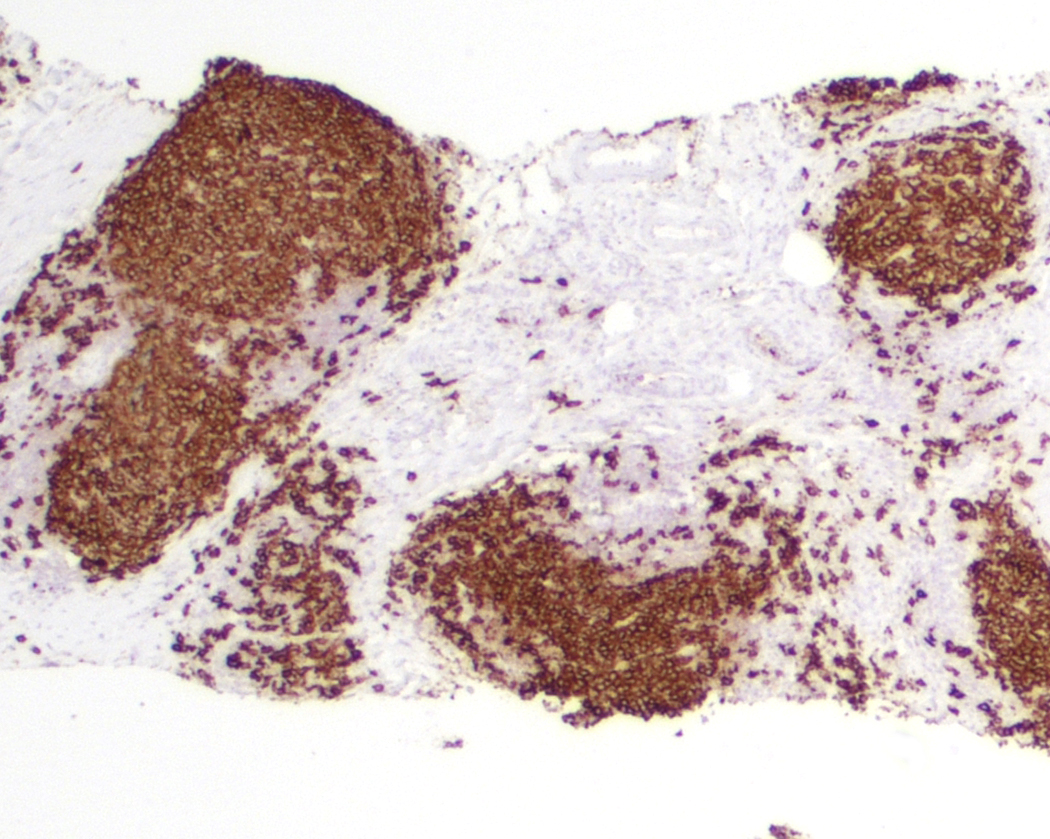
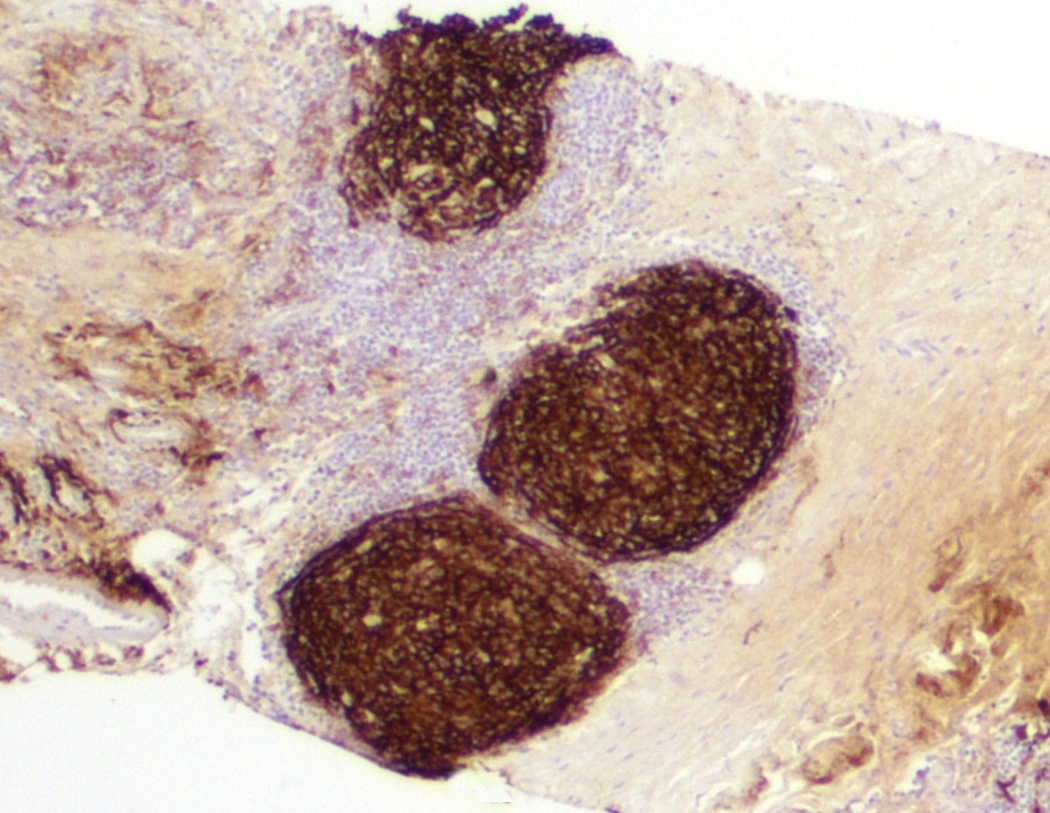
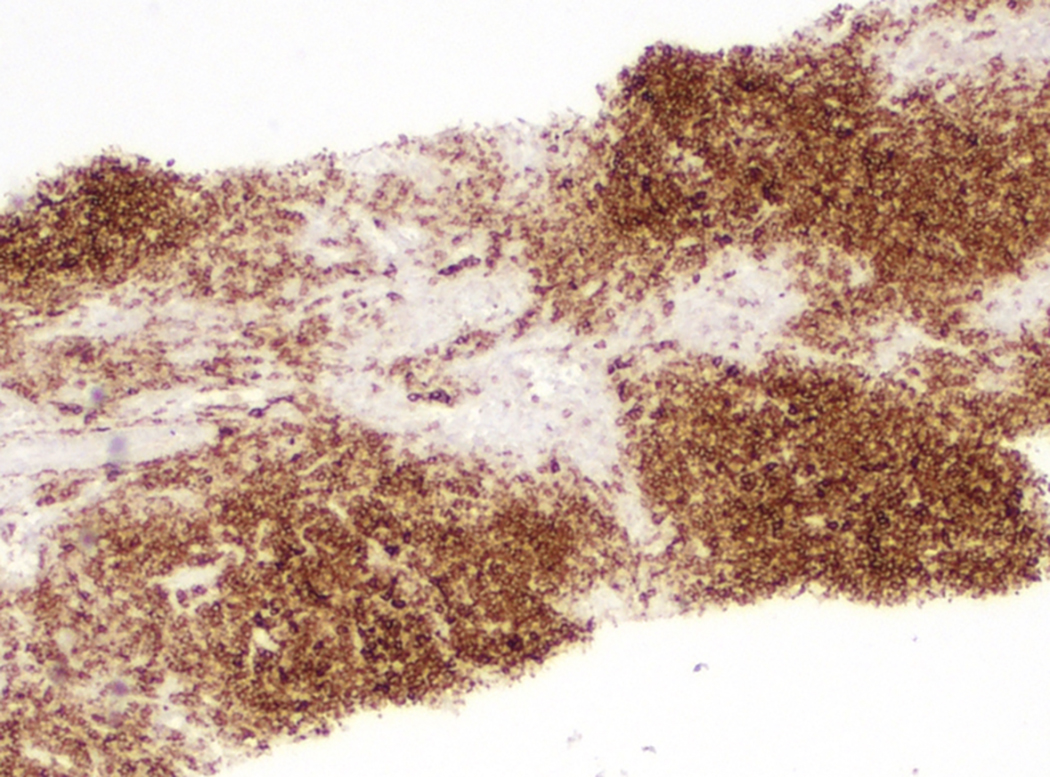
- 2 main architectural patterns in lymph nodes:
- Progressive transformation of germinal center (PTGC)-like pattern
- Well defined aggregates of T cell lymphoma cells immersed by numerous IgD positive B lymphocytes appearing as PTGC with H&E stain
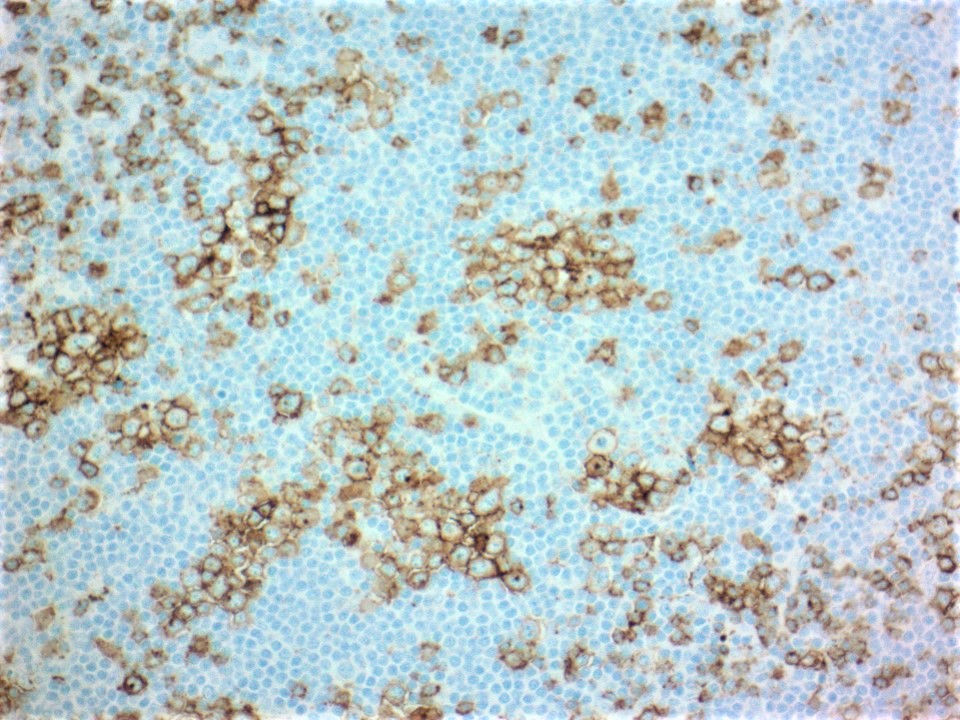
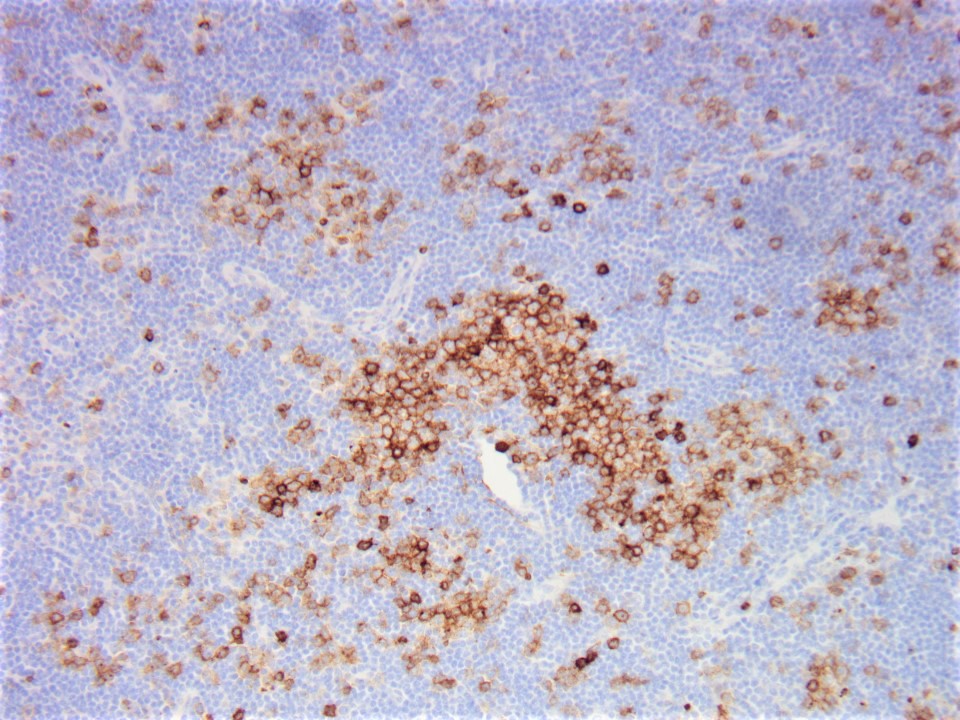
- Follicular lymphoma-like pattern: most common
- Tumor cells form intrafollicular aggregates or nodules confined within lymphoid follicles often with attenuated / absent mantle zones
- Follicular lymphoma-like and PTGC-like patterns are frequently together
- Progressive transformation of germinal center (PTGC)-like pattern
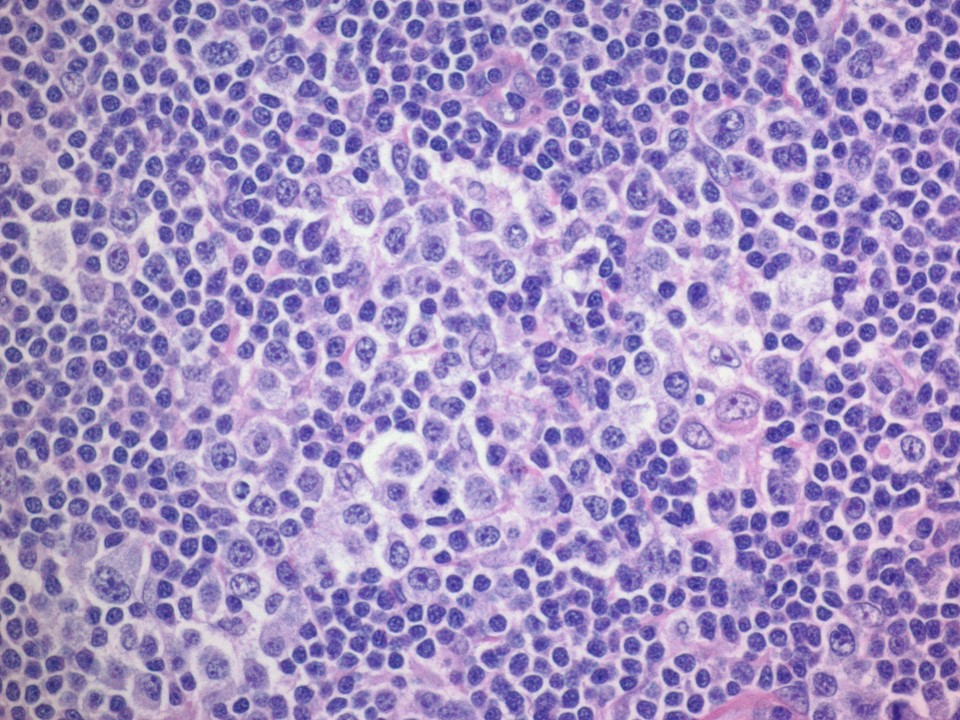
- Neoplastic cells are intermediate in size, monotonous with vesicular to coarsely granular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, moderate or abundant, clear or pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and only mild atypia
- Interfollicular areas lack the polymorphic infiltrate and vascular proliferation characteristic of AITL
- However, the presence of enlarged B cells, Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg (HRS)-like cells or epithelioid histiocytes is common in interfollicular areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1636)
- Diagnosis of FTCL at extranodal sites can be highly challenging unless the diagnosis already has been established
- Skin lesions typically manifest with an extensive pandermal nodular lymphocytic infiltrate with admixed histiocytes; variable extension into the subcutaneous fat is noted (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39(5):374)
- Bone marrow pattern of involvement by FTCL has been reported to be paratrabecular or interstitial (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1789)
- FTCL at extranodal mucosal sites show association with lymphoepithelial lesions, similar to those of extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma) (Mod Pathol 2002;15:420)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Broad spectrum of cytologic features (cannot diagnose based on cytology alone)
- Neoplastic infiltrate typically features a monotonous lymphoid infiltrate exhibiting vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, abundant pale / clear cytoplasm and only mild atypia; Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg (HRS)-like cells or epithelioid histiocytes are both seen in most cases (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1789)
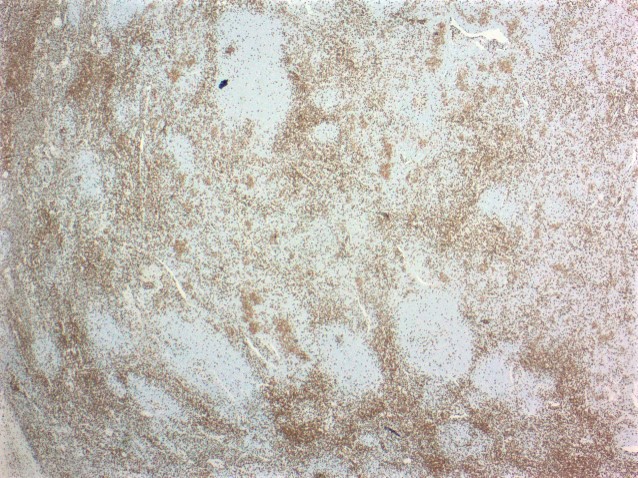
Positive stains
- Pan T cell antigens CD2, CD3 and CD5 (with frequent loss of CD7)
- Helper T cell phenotype CD4+ and CD8- (rare CD4 / CD8 double negative cases)
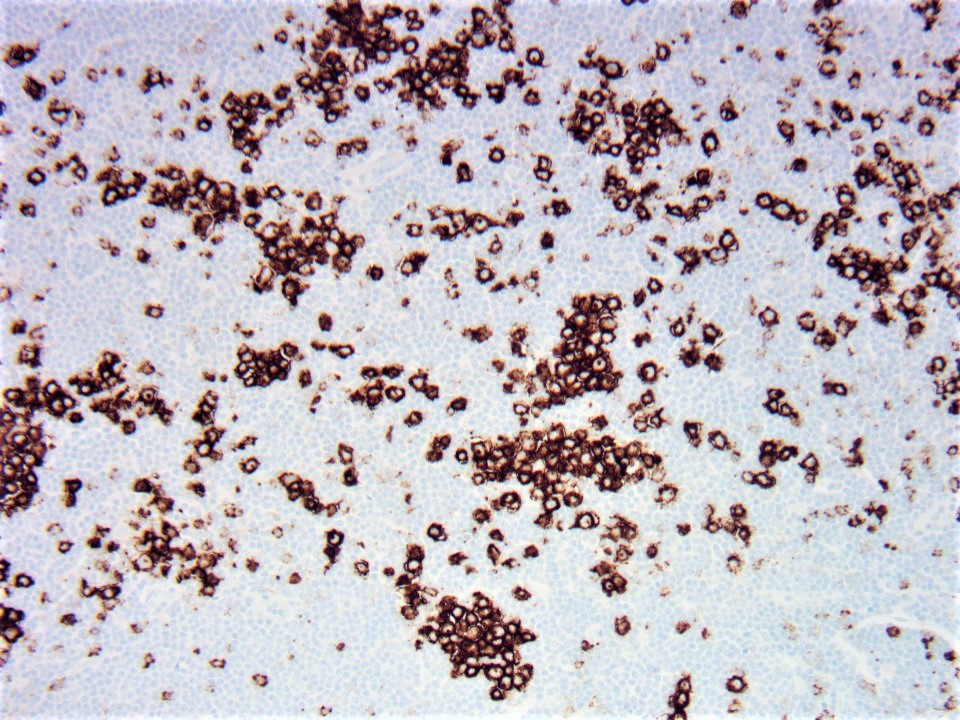
- At least 2 (preferably 3) TFH cell markers (e.g. PD-1, CXCL13, BCL6, CD10 and ICOS)
- Largely intact follicular dendritic cell meshwork structure: CD21, CD23 and CD35 staining within remnant follicles, without evidence for expansion or arborization
- Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg-like large cells: CD30, CD15, PAX5 (weakly) and frequently EBV (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:816)
- Ki67 immunoreactivity variable, ranging from 5 - 70%; median and mean values of approximately 45% (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1789)
Negative stains
- CD56
- Cytotoxic antigens, such as TIA1 and granzyme B
Flow cytometry description
- Flow cytometry may be helpful in identifying aberrant T cell population
- CD3- / dim CD4+ T cell population is commonly identified in cases of peripheral T cell lymphomas of follicular type (Mod Pathol 2016;29:1173)
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- t(5;9)(q33;q22) translocation, leading to ITK-SYK fusion in 20% of cases (Haematologica . 2021 Feb 11eukemia 2006;20:313)
- Monoclonal rearrangement of the T cell receptor genes is seen in 85 - 100% of cases (Mod Pathol 2019;32:37)
- Frequency of a clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) gene rearrangement is variable (Mod Pathol 2019;32:37)
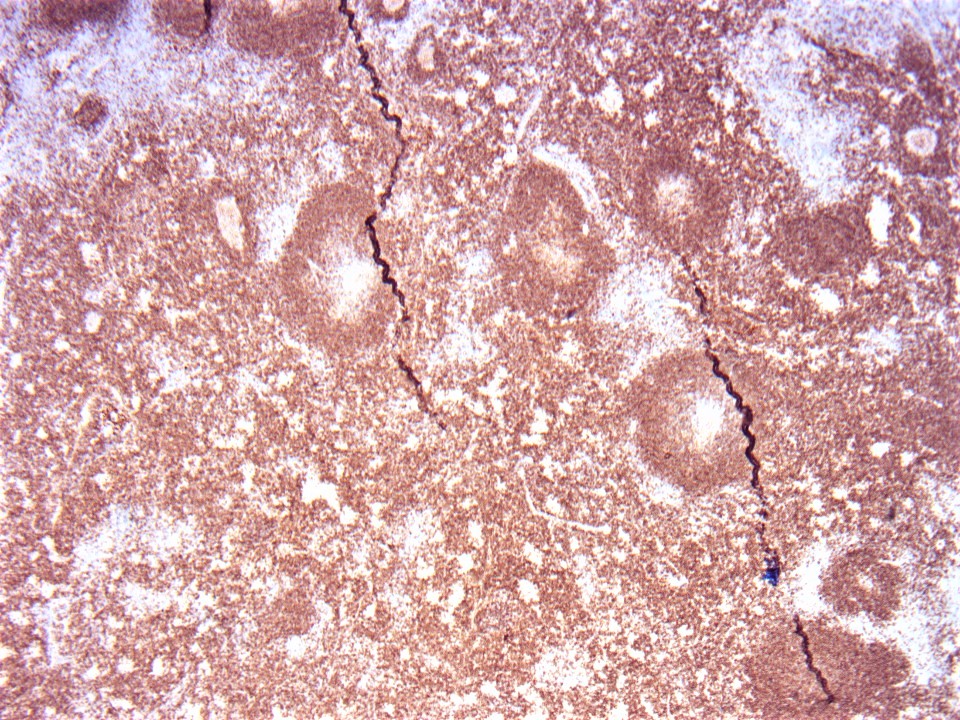
- Targeted next generation sequencing analysis identified frequent mutations, including TET2, RHOA, DNMT3A and IDH2 (Haematologica 2017;102:e148, Virchows Arch 2021;479:355)
- RHOA Gly17Val mutation was detected in cases of AITL and PTCL-TFH (Haematologica 2021 Feb 11 [Epub ahead of print])
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, neck, right, excision:
- Follicular T cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show an enlarged lymph node featuring numerous follicles associated with a perifollicular expansion of neoplastic T cells that, by immunohistochemical staining, are consistent with that of T follicular helper cell derivation. No significant polymorphous infiltrate, proliferation of high endothelial venules or expanded follicular dendritic cell meshworks are noted. Overall, findings are consistent with that of a follicular T cell lymphoma.
- Microscopic description: H&E stained sections show lymph node tissue featuring a PTGC-like pattern with well defined aggregates associated with dispersed interfollicular lymphoid aggregates of neoplastic cells. The neoplastic cells are medium sized with clear cytoplasm and irregular nuclei. A CD3 stain highlights interfollicular aggregates of neoplastic T cells with coexpression of Tfh markers: PD-1, ICOS and CXCL13. CD20 immunostain reveals numerous follicles as well as interfollicular IgD positive B cells, which surround neoplastic T cells. CD21 demonstrates intact follicular dendritic cell meshworks as well as staining interfollicular B cells.
Differential diagnosis
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma:
- Associated with polymorphous infiltrate, florid proliferation of high endothelial venules and enlarged follicular dendritic cell meshworks
- Subset of cases may recur as FTCL and vice versa, cases of FTCL can recur as AITL, supporting the notion that AITL and FTCL are part of the same spectrum
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma with a T follicular helper phenotype:
- Diffuse neoplastic proliferation (BMC Public Health 2021;21:432, Virchows Arch 2021;479:355)
- Evidence of positivity for a minimum of at least 2 (preferably 3) Tfh associated immunohistochemical markers is recommended
- Th1-like (TBX21 expression) and Th2-like (GATA3 expression) (Br J Haematol 2020;189:54)
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (J Clin Exp Hematop 2021;61:97):
- HRS-like cells have been reported in interfollicular areas of FTCL cases
- Immunophenotype of the HRS-like cells in F-PTCL may overlap with the phenotype of classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Assessment of the neoplastic T cell population for expression of CD10 and CD30 or the presence of a T cell clone favor a diagnosis of F-PTCL rather than classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Follicular lymphoma:
- Monotonous lymphoid infiltrate with abundant pale / clear cytoplasm and only mild atypia with notable absence of centrocytic / centroblastic morphology suggest the diagnosis of F-PTCL rather than follicular lymphoma
- IHC, flow cytometry and FISH for IGH-BCL2 translocation may limit confusion with FTCL
- Methotrexate associated LPD with features of FTCL (Pathol Int 2021 Sep 2 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Histopathology and immunophenotype similar to FTCL
- No apparent loss of T cell antigens; no monoclonality demonstrated
- Lesion may regress upon removal of methotrexate
- Reactive changes / paracortical hyperplasia:
- Staining for CD4 and CD8 populations would reveal an admixture as opposed to a typically CD4 predominating infiltrate in F-PTCL
- Lacks the occasional cytologic T cell atypia seen in FTCL
- May express Tfh markers (Am J Clin Pathol 2021;156:409)
Board review style question #1
A 54 year old woman presented with cervical lymphadenopathy. Lymph node biopsy showed tumor cells predominantly confined within lymphoid follicles. The cells are medium sized with clear cytoplasm and irregular nuclei. Immunohistochemical stains showed that the tumor cells are positive for CD3, CD5, CD4, CD10, ICOS and PD-1 while negative for CD7, CD8 and CD20. Which of the following features would favor a diagnosis of follicular T cell (FTCL) lymphoma over angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL)?
- Absence of interfollicular high endothelial venules or expanded follicular dendritic cell meshworks
- Interfollicular polymorphous infiltrate
- Ki67 proliferation index of 40%
- Neoplastic cells with a centrocytic / centroblastic morphology
- Large Hodgkin-like cells positive for CD15 and CD30
Board review style answer #1
A. Absence of interfollicular high endothelial venules or expanded follicular dendritic cell meshworks. The main differential of follicular T cell lymphoma is AITL. FTCL is usually confined to lymphoid follicles, while most cells in AITL are extrafollicular and associated with a polymorphous infiltrate, proliferation of high endothelial venules and expanded and distorted follicular dendritic cell meshworks. Centrocytes and centroblasts are features of follicular (B cell) lymphoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular peripheral T cell lymphoma (F-PTCL)
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular peripheral T cell lymphoma (F-PTCL)
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2