Table of Contents
Definition / general | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Negative stainsCite this page: DePond WD. Rheumatoid arthritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesrheumatoidarthritis.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Associated with lymphadenopathy during course of disease in 82%, usually axillary (J Int Med Res 2003;31:345)
- Lymphadenopathy usually disappears during disease remission
- May also have fever, weight loss, anemia
- Modestly increased risk of lymphoma, may be due to methotrexate treatment
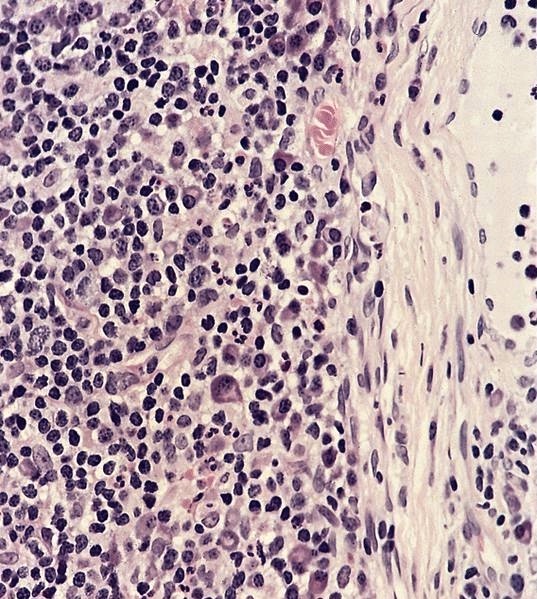
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Follicular hyperplasia with sparse (J Clin Pathol 1990;43:106) vs. active (Acta Pathol Jpn 1990;40:249) proliferative activity, interfollicular plasma cells with Russell bodies, vascular proliferation
- Capsular lymphocytic infiltrate
- May resemble plasma cell variant of Castleman disease
- Often PAS+ extracellular hyaline material
- Occasionally focal necrosis and microabscesses
- May have sarcoid-like granulomas
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
- Polyclonal plasma cells (no light chain restriction)