Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Tsang P, Pernick N. Plasmacytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesplasmacytoma.html. Accessed March 28th, 2025.
Definition / general
- This topic only discusses features of plasmacytoma in lymph nodes different from plasmacytoma and myeloma
- Very rare (< 50 reported cases)
- Diagnosis of primary plasmacytoma of lymph node requires exclusion of extramedullary plasmacytoma (15% of upper respiratory tract plasmacytomas metastasize to cervical nodes) and myeloma (40% of high stage myelomas metastasize to nodes)
- 2/3 male; median age 59 years (range 39 - 76 years)
- Often involves cervical nodes
- Similar survival to other extramedullary plasmacytomas, although does not progress to myeloma (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:119, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1083)
Case reports
- 65 year old man with cervical and submandibular node involvement (Korean J Intern Med 2005;20:183)
- 71 year old man with diffuse hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy of chest, abdomen and pelvis (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:153)
- 81 year old man with Sjögren syndrome (Pathol Int 1999;49:577)
- Patient with Castleman disease (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:157, Am J Clin Pathol 1982;78:541)
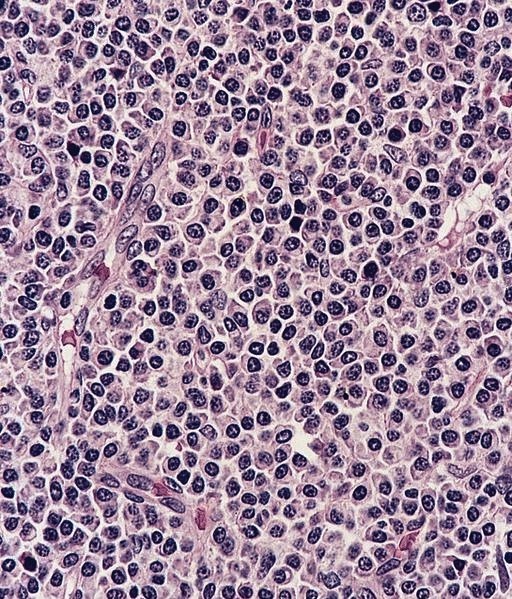
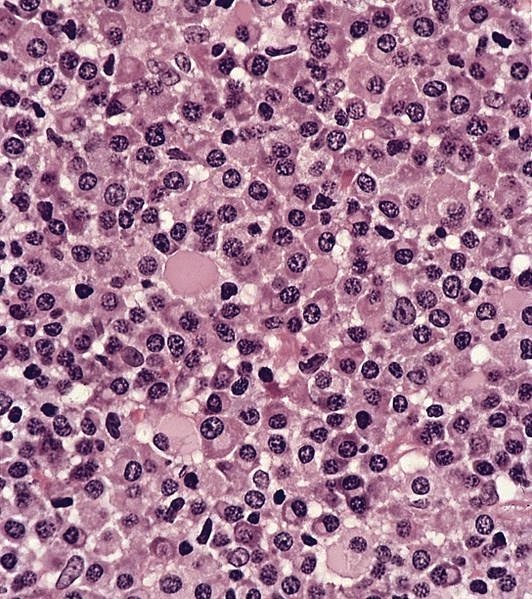
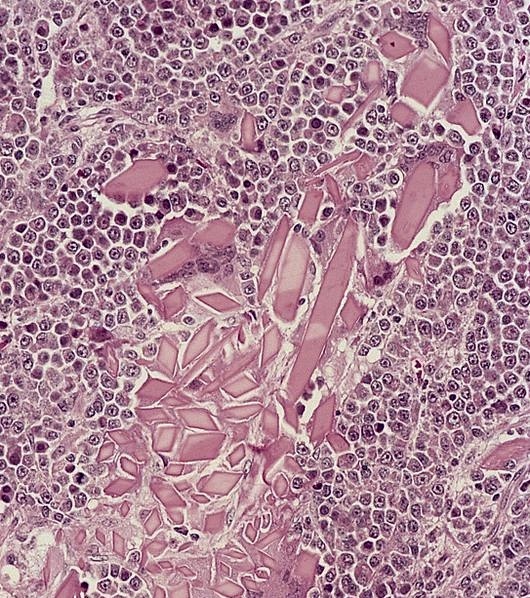
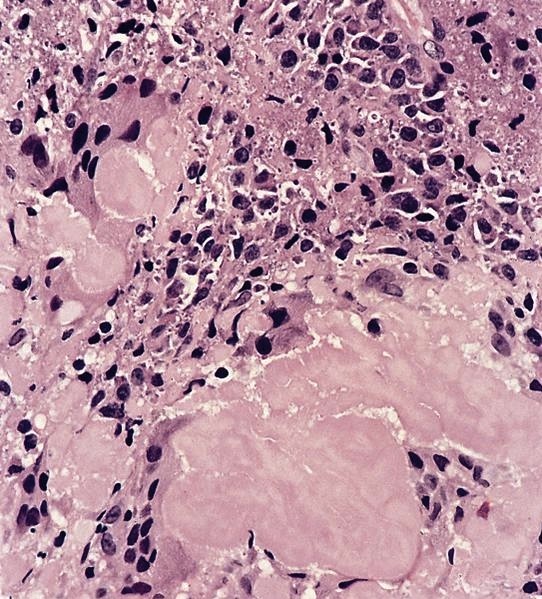
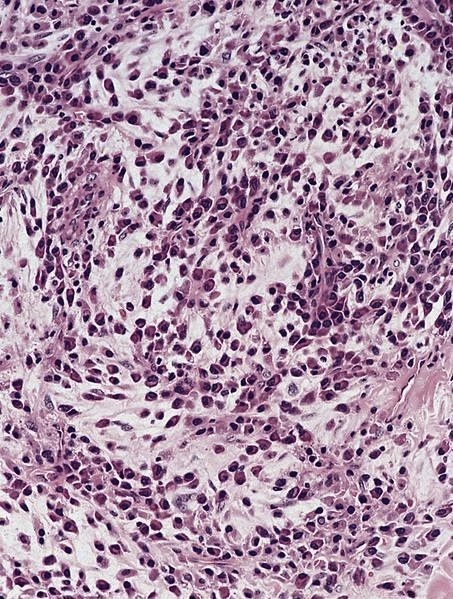
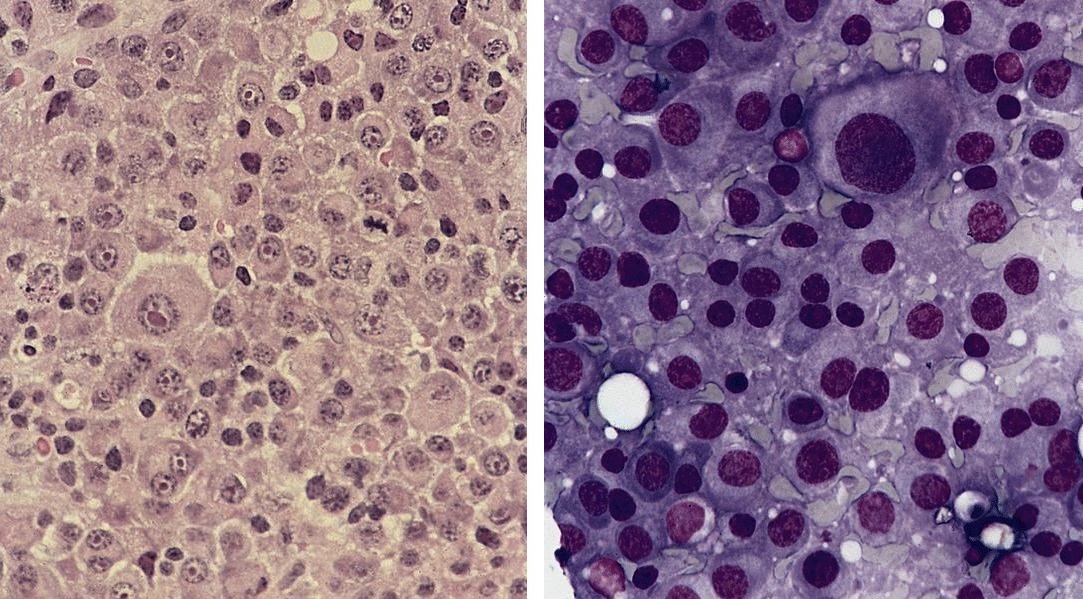
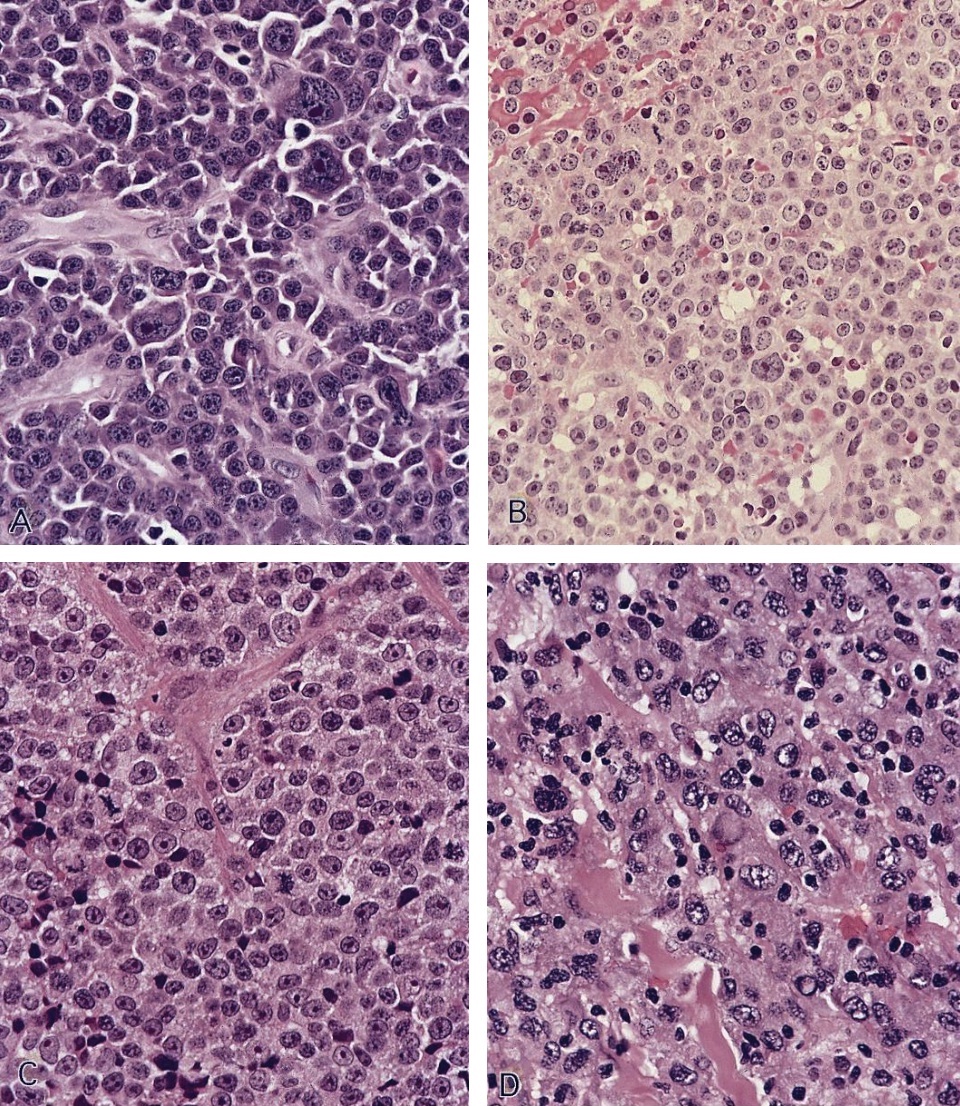
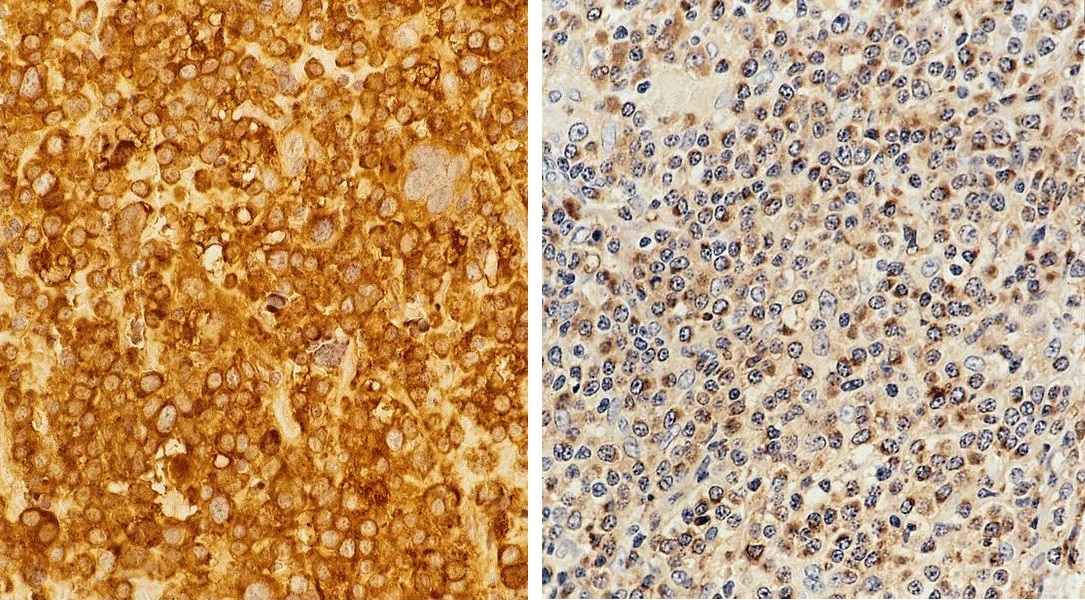
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Castleman disease, plasma cell variant
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma:
- Also has neoplastic small lymphocytes
- Often shows IgM restriction and MYD88 gene mutation
- Marginal zone lymphoma:
- May have plasmacytoid features but more extensive sampling may reveal B cell component
- CD20 expression by neoplastic B cells and plasmacytoid cells
- Clonal B cell population by flow; molecular or cytogenetic features of marginal zone lymphoma
- Large cell lymphoma:
- May have immunoblastic or plasmablastic features
- Plasma cell myeloma with nodal involvement:
- Must be excluded by radiographs, bone marrow biopsy
- Plasmablastic lymphoma:
- Mostly extranodal; less frequent nodal involvement
- Associated with HIV or other immunosuppressive states and EBV
- Reactive plasmacytosis:
- Often follicular hyperplasia
- No light chain restriction